Dizziness is a distorted perception of the position of one’s body in space, in which there is an imaginary sensation of movement of either the body or space. This symptom occurs in many diseases and has no specificity. Dizziness can accompany somatic, neurological and mental illnesses. This disorder is sometimes called "vertigo", but this is a somewhat outdated expression.
Dizziness is almost always detected with VSD or neurocirculatory dystonia.
Types of dizziness
Depending on the cause and characteristics of its occurrence, there are 5 main types of dizziness:
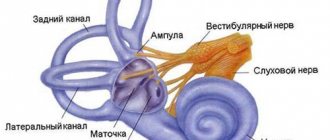
- Vestibular - associated with irritation of the vestibulocochlear nerve or semicircular canals of the middle ear. It manifests itself in a rotational form (right - left) and linear (forward - backward).
- Lipotymic is a condition that develops before fainting and with a sharp decrease in glucose levels. It manifests itself as a feeling of lightheadedness, fog, and often ends in a fall.
- Postural - occurs in older people, is accompanied by instability when walking, occurs against the background of insufficiency of many analyzers - visual, auditory and others.
- Cervicogenic – with lesions of the cervical spine, when there is pain and limited mobility in the neck.
- Psychogenic or psychophysiological – occurs with neuroses and borderline personality disorders. This type of dizziness is a characteristic sign of VSD.
Psychogenic dizziness has its own characteristic distinctive features. It occurs at the peak of anxiety and fear, becoming a component of a panic attack. This is facilitated by hyperventilation syndrome, when a person begins to breathe deeply and frequently, which leads to a lack of oxygen.
Quite often, dizziness becomes a physical expression of fear, occurring only in certain situations - when traveling on public transport, in specific stores, crossing a bridge, being in a large crowd of people (at an exhibition or concert) or in an empty room.
What other diseases cause numbness in hands, feet and tongue?
Lesions of the cervical, cranial, and lumbar nerves can cause numbness. But in addition to this, other symptoms are usually present: pain, tingling, dysfunction (claudication, arm weakness, slowness and blurred speech).
Metabolic diseases can also cause changes in sensitivity, including numbness of body parts. If you often limit yourself to meat, fish, eggs, and do not supplement your diet with synthetic vitamin B12, then this can cause metabolic disorders and cause weakness in your arms and legs.
Loss of sensation in the left hand may be one of the classic symptoms of myocardial infarction. At the same time, the general condition worsens, the person looks very pale or, on the contrary, turns red, dizziness or headache, a feeling of heaviness in the chest or a burning sensation appears.
A hernia in one part of the spine can put pressure on a nerve, causing pain or loss of sensation.
Decreased sensation in the feet can be a complication of diabetes. This is one of the first signs of diabetic foot and should be reported to your doctor as soon as possible.
Symptoms of psychogenic dizziness
This species can be distinguished from others by certain characteristics.
For dizziness due to VSD:
- there is never a feeling of rotation;
- associated with a feeling of instability;
- almost always worsens when walking.
It is difficult for a person experiencing dizziness due to neurocirculatory dystonia to describe their sensations, since there is little certainty in them. Patients are bothered by heaviness in the head, swaying, as if intoxicated, and lightheadedness.
An objective sign of dizziness is nystagmus or involuntary rhythmic vibrations of the eyeballs. Nystagmus is determined by tracking the hammer with the eyes. Depending on the location of the lesion, nystagmus can be directed in different directions. This symptom occurs with all types of dizziness, except psychogenic. No matter how disturbing the painful sensations in the form of walking disturbances, nausea and lightheadedness are, nystagmus is never detected in psychophysiological dizziness with VSD.
It must be recalled that vegetative-vascular dystonia is a mismatch between the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts of the autonomic nervous system. The disorder is functional or reversible; researchers associate it with a congenital defect in adaptive systems.
Psychogenic dizziness does not occur in all people, but only in those who are prone to depression and the formation of compulsions or obsessions. The presence of these personality disorders aggravates the situation, since an episode of dizziness becomes the cause and occasion for new experiences.
Familiar story
Some patients do not believe that the digestive organs are so closely related to VSD. Poor appetite can be explained by daily stress and apathy that follows a panic attack. But what does nausea have to do with all its manifestations: nagging sensations, restless stomach, vomiting?
Often, along with these symptoms, the following occur:
- Tachycardia;
- Trembling throughout the body;
- Weakness;
- Increase in temperature (37-38 degrees);
- Severe aversion to food;
This picture can be mistaken for poisoning or an allergic reaction. A person begins to chaotically change his diet, check the expiration date on each package, and re-read the instructions for medications.
But these measures do not bring relief, but only drive us deeper into a dead end. This is the story of a typical VSD person: inventing a lot of diseases for yourself and trying to save yourself from them.
Nausea with VSD cannot be treated with Smecta, mint tea and gentle diets. But it is within the power of every person to understand the nature of this unpleasant symptom and remove it forever.
Diagnostics
An experienced doctor already in the process of talking with a patient understands the main reason for his suffering. The conversation may reveal the specific reason that became the trigger for the development of dizziness during VSD. In the classic version, this is an event that affects a vital aspect of the patient’s life - wounded pride, unrequited love, betrayal of a spouse, career failure, problems with children or relatives, property disputes.
In this case, it can be difficult to convince the patient that his suffering is of a psychogenic nature. In unexamined patients, neuroimaging methods are always used, since there is always the possibility that there may be developmental anomalies - the craniovertebral junction, blood vessels or cerebral sinuses.
In any case, the diagnosis of VSD includes standard clinical examination methods to exclude organic lesions of the nervous system and ENT organs.
Psychotherapy is the leading method of treating neurocirculatory dystonia, but it can only be started after the examination is completed and there are no organic causes.
Treatment
Treatment of psychogenic dizziness with neurocirculatory dystonia includes the following mandatory items:
- psychotherapy;
- vestibular gymnastics;
- SSRI drugs and other antidepressants;
- benzodiazepines.
It is possible to improve the condition and get rid of dizziness due to VSD, as well as mitigate other manifestations of VSD only with a complex effect, when all methods are used simultaneously. Medicines help to quickly relieve disturbing symptoms, but systematic improvement requires the efforts of both the doctor and the patient.
Illusions - eliminate them!
VSD doctors are very well-read and sometimes know more than trainee doctors. But the interns are distinguished by the fact that they do not suffer from hypochondria and are not inclined to make a melanoma out of a pimple. The same cannot be said about people suffering from VSD. Any rare or strange symptom automatically falls into the category of “deadly warnings”. If your hands go numb during VSD, this is definitely a stroke or a brain tumor, since “your hands just can’t give up.”
But my hands didn’t give up! No matter what symptoms the patient’s panicked state has acquired, first of all, it is necessary to include logic and use the existing store of medical knowledge wisely.
The following symptoms are usually observed with VSD:
- Both hands go numb, sometimes alternately or with varying degrees of intensity.
- The patient feels goosebumps, slight alienation of the hands, lack of smoothness and confidence of movements, poor tactility, trembling in the fingertips.
- Your hands may be cold and your body may feel trembling, especially in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Periodically, chills or heat are felt in the limbs and face area.
- Blood pressure is most often low, lethargy is felt, muscle tone is weak, and apathy is present.
- In certain body positions, the patient feels pain or spasms in different parts of the skeleton.
In case of a stroke or tumor, the patient is in a much worse situation: in addition to a numb limb (and only one of the two arms is numb), the patient has a number of other complications, usually not comparable to normal life activities.
And if a person with VSD is limited by phobias and depression, then a person with a stroke (tumor) is sometimes simply physically unable to perform a basic task. If a VSD student is still fixated on his beliefs, he has the right to undergo a full examination in order to officially rule out fatal diseases.
Drug treatment
At the initial stage, drugs that compensate for vestibular dysfunction are used, primarily Betahistine or Betaserc. The medicine acts on the inner ear and vestibular nuclei of the nervous system. In the labyrinth and cochlea of the inner ear, as well as in the brain stem, capillary blood flow and transmission of nerve impulses improve. In these same structures, lymph pressure is normalized, and blood circulation in the main or basilar artery is optimized. While taking it, your hearing becomes slightly stronger, but this is only beneficial.
According to indications, selective (selective) serotonin reuptake inhibitors or SSRI drugs are used. These are Paroxetine, Paxil, Plizir, Adepress, Asentra, Zoloft, Stimuloton, Prozac, Fluoxetine, Lenuxin, Citalopram and others.
Medicines in this group quickly lift your mood, reduce internal tension, and relieve fears. Their huge advantage is that they do not have a sedative component, and their use does not disrupt the usual rhythm of life. The exception is driving vehicles and high-precision machinery; these types of activities should be avoided while taking them. The medications have virtually no effect on the internal organs, and with a gradual reduction in doses they do not cause addiction or withdrawal symptoms.
The group of benzodiazepines has a pronounced hypnotic and anxiolytic (mood-leveling) effect. Medicines in this group are numerous and well known: Phenazepam, Gidazepam, Diazepam and the like.
In some cases, mild antipsychotics, in particular Sulpiride (Betamax, Eglonil), have a quick effect. It is an atypical antipsychotic that modulates dopamine or neurotransmitter transmission. Depending on the dose, it can either activate or mildly sedate. At the same time, it protects the mucous membrane of the digestive canal, which is valuable in itself.
Selecting a drug and adjusting doses is a purely medical matter. All psychotropic drugs (except those intended to relieve psychomotor agitation) have one feature - their effect does not unfold immediately, but gradually. Therefore, when prescribing such drugs, interaction with a doctor is required, who will explain the specific features of taking the drugs.
Vestibular gymnastics
There are many variations of this gymnastics; the goal of all exercises is to train the vestibular apparatus, which ensures balance. In general, the complex of vestibular gymnastics includes exercises for the eyes, head and body.
For the eyes: sitting on a chair, look up and down and left and right. At first the pace is slow, then you can speed up without getting too dizzy. It is convenient to fix your gaze on some object.
For the head: in a sitting position, tilt your head back and forth, then left and right. Accelerate the pace gradually, focusing on how you feel. When the dizziness subsides, you can close your eyes.
For the body: from a sitting position, stand up, bend down and pick up any object from the floor. Then, from a sitting position on a chair, stand up and sit down again. After mastering these movements, throw the ball from one hand to the other. The frequency of repetition of each movement is at least 20 times.
Danger of pathology
It is important to treat numbness of the limbs in a timely manner to avoid negative consequences.
If the patient's tongue, arms or legs go numb, this indicates serious disorders in the body that can lead to complications if left untreated. If the decrease in sensitivity occurs due to compression of the nerve endings, then over time the situation will worsen with severe pain. When a blood vessel is squeezed, tissues whose sensitivity is reduced will gradually begin to die.
In addition to deteriorating physical health, numbness of the face or limbs makes the patient worry about his condition, often nervous, which only aggravates the situation. VSD is often diagnosed in people prone to exaggeration. Concern about their own health in such people leads to a disturbance in their emotional and psychological state. At the same time, VSD worsens, additional symptoms of the disease appear, such as dizziness, disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract, heart pain, and sleep problems.