One of the most common reasons people go to the doctor is pain in their hands. They usually do not cause such serious discomfort as leg or back pain, but they also greatly reduce the quality of life. After all, it is with the help of hands that a person performs many actions and serves himself. And painful sensations often prevent this, making it difficult to perform the usual work.
If a person’s arm hurts, it not only causes suffering, but also reduces performance. Therefore, many people try to quickly get rid of discomfort with the help of ointments or painkillers. But the fact is that pain is not always localized exactly where its cause is. It happens that they are caused by pathologies of the spine, blood vessels or internal organs. Therefore, treatment with painkillers alone can lead to serious complications.
Symptoms and treatment of brachial neuralgia
A rather painful disease, the main symptom of which is severe pain in the arm, is called brachial neuralgia; its symptoms and treatment depend on the cause.
Most often, the background for sharp pain in the shoulder and arm is prolonged physical activity, past infections, and osteochondrosis.
The immediate cause of neuralgia is compression (squeezing) of the nerve by spastically compressed and inflamed muscles, tendons or deformed intervertebral discs.
Clinical manifestations
In most cases, it is difficult to raise your hand up or move it to the side.
Factors that trigger the pathological process are:
- strenuous physical activity;
- trauma - severe bruise, sprain, dislocation;
- severe intoxication - poisoning or alcoholism;
- a sharp decrease in immunity, for example, due to acute respiratory viral infections or severe stress;
- systemic health disorders due to endocrine disorders - diabetes, thyroid disease, pituitary gland;
- pathologies of the vascular system.
In most cases, the working hand is affected - the right, and the left in left-handed people. The nature of neuralgia depends on which roots of the nerve segments are pinched.
There may be sudden paroxysmal burning or piercing pains, radiating to the back, side, chest, periodically increasing and temporarily disappearing, or constant painful aching sensations with almost no light intervals.
With deep localization of the lesion, the symptoms can be so alarming that they suggest a developing heart attack or gastric ulcer.
Often the pain is accompanied by local tissue swelling, increased sweating, stiffness in the shoulder area, impaired mobility, involuntary twitching or tremors. It is difficult to raise your arm up or move it to the side. The skin on the affected area turns red. Any, even the lightest touch to a sore spot causes severe discomfort.
During periods of calm attacks, paresthesia is possible - a feeling of crawling, trembling, tingling, slight numbness, weakness in the affected arm and other neuralgic symptoms.
There is sharp pain when pressing with a finger in the armpit or on the border of the biceps and triceps in the middle of the shoulder - at the so-called Valle points.
There are primary and secondary neuralgia of the shoulder joint.
In the first case, the pathology is limited to pain, local inflammation, may be accompanied by fever, increased temperature, is not complicated by edema and is quite easily reversible, its cause is often simple hypothermia. In itself, this condition causes more physical pain than serious health hazard.
Secondary brachial plexus neuralgia is a symptom of other, more serious disorders in the body, for example, osteochondrosis, and cannot be completely cured without treating the underlying disease.
Diagnosis and treatment
Treatment of brachial neuralgia should be carried out at the first signs of the disease, and not only because it causes severe discomfort. Long-term lack of therapy aggravates the condition of the pinched nerve, intensifying pain attacks, provoking the further development of polyarthritis or neuritis - a serious lesion with impaired function of the shoulder joint, including paralysis.
Diagnosis is complicated by the similarity of symptoms with a number of other diseases and requires differentiation from manifestations of cervical osteochondrosis and neuritis.
In addition to collecting anamnesis, instrumental methods are used:
- ultrasonography;
- radiography;
- magnetic resonance and computed tomography.
Treatment of brachial neuralgia has several goals: to relieve a person from physical suffering, to restore normal mobility to the limbs, and to eliminate the root causes that caused the disease.
Complex therapy is used:
- The pain syndrome is relieved by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Drugs containing ibuprofen and analgesics are used: Ibuklin, Nurofen, Diclofenac, Ketanov, Next, Solpadeine. Tablet analgesics are effective for pain of mild and moderate intensity, but for severe acute attacks they may not be effective enough. In addition, long-term use of painkillers negatively affects the condition of the liver and kidneys, causing disruption of their functions.
- To ensure a lasting therapeutic effect, oral administration of analgesics is combined with local treatment with anti-inflammatory and warming ointments and gels - Finalgon, Viprosal, Capsicam. In cases of persistent unbearable pain, novocaine blockade is used.
- Since neuralgia of the shoulder joint causes prolonged severe physical suffering to the patient, which inevitably affects the psycho-emotional background and mood, treatment is accompanied by the use of mild antidepressants.
- As part of complex therapy, injections of B vitamins are prescribed, which are necessary to stimulate intracellular metabolism in tissues.
- Physiotherapy plays an important role in the treatment of shoulder neuralgia. Acupuncture, ultrasound treatment, electrophoresis, laser therapy have an analgesic and targeted restorative effect, help eliminate congestion in the affected area, relieve swelling, which allows you to reduce the use of analgesics. Primary neuralgia can be completely cured after undergoing a course of physiotherapy.
- Therapeutic exercise is necessary to strengthen the muscular and ligamentous apparatus and restore joint mobility. Exercise therapy exercises are prescribed by doctors; after several training sessions on an outpatient basis, they can be performed at home. In order to ease the load on the sore joint, bandages and bandages that fix the arm can be used.
- With the approval of a doctor, you can supplement treatment with traditional medicine: rubbings based on hot pepper, mustard, bee venom, and medicinal herbs.
The most thorough treatment of secondary neuralgia of the shoulder joint will not have the desired effect if the underlying disease that caused it is not treated. Self-diagnosis based on symptoms alone is also unacceptable: it is easy to cause severe nerve damage. All therapeutic measures must be prescribed by doctors and carried out under medical supervision.
Symptoms and treatment of brachial neuralgia Link to main publication
Source: //hondrozz.ru/oslozhneniya/nevralgiya/plechevogo-nerva-simptomy-lechenie.html
Treatment for arm pain
Photo: Shutterstock
It is impossible to determine the causes of pain without a thorough examination. If you try to drown out the pain with home remedies or medications, you can waste time and develop a serious illness - the real cause of the pain.
It’s better not to wait for the weather by the sea, but to go to the doctor. You may need to do a series of tests, including a computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging scan, an x-ray, or a myelogram. After determining the cause of the unpleasant symptoms, the doctor will prescribe treatment. As a rule, therapy is complex, including drug treatment, physiotherapeutic procedures, and special exercises. Many diseases require a special therapeutic diet.
Ulnar neuralgia: symptoms and treatment methods. How to treat neuralgia of the hands
Neuritis is a disease in which part of the nervous system is affected and inflammatory processes begin. The disease can affect one or several nerves. In this case, the extent depends on the pathology.
Regardless of which nerve is affected, there are basic signs such as:
- sensation of pain near the nerve endings;
- impaired sensitivity;
- muscle weakness and pain under the shoulder blade.
One way or another, many people know about ulnar nerve neuritis, and not by hearsay, since this ailment is considered very common among such diseases.
About the anatomy and causes of the disease
The reasons that cause this condition are varied, since there are places on the arm along the ulnar nerve that are often compressed.
It is known that the ulnar nerve is a nerve of the brachial plexus.
It enters the arm directly from under the muscle fossa, then passes through the intermuscular septum somewhere in the middle of the shoulder, and passes into the osteofibrous canal.
In addition, it is located close to the bone formations, which causes compression of the nerve fibers in this place. This can be felt simply by hitting some part of the elbows.
After the nerve exits the canal, it is directed to the side between the muscles of the forearm, and then divides into the dorsal branch of the hand and the palmar branch, where it also lends itself to compression.
In what cases can this nerve be damaged:
- in the presence of a fracture or dislocation of the shoulder, hand or forearm;
- if there is compression of the fibro-osseous canals, including the cubital canal.
Most often, injury occurs through compression, which may not necessarily be sudden or acute. As a rule, the development process occurs at a slow pace, as a result of prolonged exposure to a traumatic nature. For example, this could be frequent bending at a given joint or working on a machine, at a desk or workbench, and other similar situations.
In addition to the above reasons, this disease can appear if the nerve is compressed by a tumor or enlarged lymph nodes, or with arthrosis of the elbow joint, as well as joints on the wrist.
Other reasons include any infection or hypothermia, diabetes, damage to nerve tissue by toxins, as well as chronic alcohol consumption.
Treatment of neuralgia in the acute stage
Pain in the shoulder joint in the acute stage cannot be eliminated with medications alone. Treatment in this case should be comprehensive.
Painkillers
Among the huge range of analgesics, preference for shoulder joint neuralgia is given to traditional ones - analgin, spasmalgon, baralgin. If these drugs are not enough to relieve pain, non-steroids may be additionally prescribed, but for a short course. Neuralgic pain is well relieved by local distractions - mustard plasters, plasters, compresses.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
In combination with analgesics, NSAIDs are used, which perform a dual role - they relieve pain and eliminate the inflammatory process. Neuralgia of the arm and shoulder joint is treated with drugs such as Ibuprofen, Sulindac, Indomethacin, Ketorolac.
Important! All drugs related to NSAIDs are strong chemical reagents, they can treat one thing, but harm another. For example, side effects of NSAIDs include kidney problems and irritation of the stomach lining.
In order not to harm the body and cure neuralgia, the option of using a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug should be prescribed by a doctor.
Ointment
Ointment is used to treat neuralgia.
The main task of this tool is to:
- a warming effect that acts on the ligaments and relaxes them;
- stimulating blood circulation;
- increasing the elasticity of damaged ligaments;
- activation of the metabolic process.
Throbbing pain in the back of the head is a symptom that cannot be ignored
The composition of the medicinal ointment includes painkillers and anti-inflammatory components. Ointments prepared using bee or snake venom or capsicum have a good effect. Doctors recommend using ointments such as Myoton, Finalgon, Viprosal, Apizartron.
Before using any of the variations of medicinal ointment, you must carefully read the instructions for use. Most warming and anti-inflammatory ointments cannot be used by women during pregnancy or lactation.
Injections
If tablets, ointments or gels do not bring the desired effect and do not relieve the patient from the unpleasant symptoms of the disease, then treatment of neuralgia continues with injections. Injections are most often used in cases where the patient is suffering from severe and unbearable pain. Injections such as Baralgin, Ketorolac, Voltaren have a therapeutic effect.
Source: //pro-acne.ru/pro-sustavy/nevralgiya-ruki-simptomy-loktevogo-nerva-i-ego-lechenie.html
Symptoms of nerve damage
Nerve fibers located in various parts of the human body allow all organs and systems to function normally. The nervous system signals any problems with pain or numbness. Therefore, when a chemical or physical effect occurs on the nervous structure, a person immediately feels it.
Neuropathies manifest themselves with several symptoms.
- Most often, the hand begins to hurt suddenly, after waking up.
- The pain intensifies when you try to move your arm.
- Pain is felt in individual areas or along the entire arm.
Sometimes, due to pathology, any movements can be blocked. This occurs when severe pain occurs or impulse transmission along the radial nerve is disrupted. Complete or partial paralysis in various parts of the arm is characterized by loss of motor function of the elbow joint, as well as in the phalanges of the fingers or the wrist area.
Neuralgia of the brachial nerve (plexus, joint) of the hand: symptoms and treatment
Neuralgia caused by muscle tension is a frequent and quite common phenomenon, especially in older and elderly people.
The disease is insidious, develops quickly, becomes chronic, and there is a risk of serious damage to the nerves themselves, which ultimately affects the functioning of the joints.
The causes and main manifestations of the pathology, stages of development, modern methods of differential diagnosis and treatment of neuralgia of the brachial nerve, or as it is also called - the shoulder joint of the arm or plexus, will be discussed in the article.
What it is? ICD-10 code
Anatomically, the nervous system is the most important component of the human body ; it is responsible for the coherence and consistency of the work of other organs and vital systems.
There are some pathologies that are directly related to damage to the nerve trunks - these are various neuralgia (occipital, trigeminal, external femoral nerve).
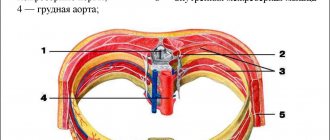
Brachial neuralgia - spasms of the shoulder muscles , pinching and damage (in clinical cases) to the peripheral nerve processes or roots of the brachial plexus.
The plexus of nerves emerges from the cervical spine and is located at the level of the joint (at the junction of the clavicle, the process of the scapula and the head of the humerus). This plexus then branches throughout the arm.
The essence of the interaction between the nervous and muscular systems is simple - the branches of the brachial plexus send electrical signals to the muscle, which contracts under the influence of this signal. Any movement is a muscle contraction.
With neuralgia, the inflammatory process only compresses, but does not damage the nerve fibers.
According to the international classification of diseases (1999) - ICD-10 - the disease is assigned the code: G54.0, denoting diseases of the nervous system, class No. 6. This pathology can also be classified as class M, No. 13 (diseases of the musculoskeletal system), depending on the root cause of its origin. If the diagnosis is “blurred”, specialists use coding M79.2 (subsection of unspecified neuralgia).
Causes
By origin, brachial neuralgia can be:
- primary (essential) - clinical examination did not reveal any associated diseases affecting the inflammatory process;
- secondary (symptomatic) - tumors and inflammations are detected that negatively affect the structure of nerve fibers.
Main reasons:
- age-related changes in the body (according to statistics, pathology is more common in elderly patients);
- birth injuries (during pathological childbirth, damage to the nerve trunk in a newborn is possible);
- severe and systematic hypothermia (sharp fluctuations in temperature critically reduce immunity and cause inflammation);
- various viral, fungal, bacterial infections, complications of colds and flu - the cause of primary neuralgia;
- poisoning of the body (toxins and chemicals can be causative agents of the disease);
- tumors, including cancer - any neoplasm causes severe compression of nerve branches (oxygen deficiency in tissues provokes cell death, impulses become weak or disappear altogether);
- shoulder injuries - dislocations, fractures, bruises, micro tears of the tendon, damage to muscles and ligaments (with the rapid expansion of blood vessels, inflammation and swelling occur);
- improperly applied tourniquet, plaster, long-term use of crutches;
- diseases of the vascular bed (poor patency, blood clots, plaques) - a violation of the exchange between tissue fluid and blood causes excess (accumulation) of fluid, causing edema;
- heavy physical activity (athletes, hard work) causes swelling, spasms of muscles and ligaments;
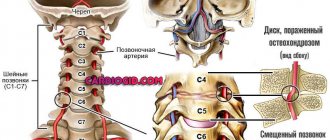
- cervical and thoracic osteochondrosis, vertebral hernia (bone tissue, disc deformation damages brain vessels, disrupts blood flow, pinches nerves);
- diabetes mellitus, chronic diseases of the stomach and duodenum (ulcers, colitis), hormonal imbalance (metabolic disorder) causes tissue inflammation, which becomes an indirect cause of neuralgia;
- against the background of stress, pathology may appear;
- weakened immunity.
Clinical picture: manifestations and symptoms
Most often, brachial neuralgia develops unilaterally, on the right side.
If the disease is caused by hypothermia or is a consequence of influenza, ARVI, acute respiratory infections and other infections , it manifests itself in an acute form:
- pain in the shoulder and neck appears immediately;
- accompanied by general weakness and fever;
- temperature rise is possible.
For injuries:
- pain increases gradually;
- the pain subsides over time;
- slight stiffness when moving the arm and shoulder;
- partial numbness.
The duration of attacks varies - from 2-3 seconds (shooting pain) to several hours (dull, aching, obsessive).
In the advanced stage:
- constant pain (discomfort both during the day and at night);
- sweating;
- redness and severe burning of the skin;
- tearfulness;
- convulsions are possible.
General symptoms:
- muscle spasms (periodic involuntary twitching, sometimes lasting 1-2 minutes);
- as the disease develops, swelling of muscle tissue is observed;
- aching constant pain of an exhausting nature occurs;
- attacks of unbearable, burning pain occur spontaneously, periodically.
It is difficult to independently determine the original source, since it can hurt and radiate in different areas.
Possible patient complaints, depending on the affected area:
- Bottom form – severe pain is concentrated in the inner surface of the shoulder and forearm area, manifests itself when moving.
Partial loss of sensitivity is possible (the nerve fibers of the plexus are responsible for tactile and temperature sensitivity).Impairment of fine motor skills and decreased muscle tone (difficulty forming fingers into a fist or holding small objects) are also possible.
- Upper form – pain above the collarbone, radiating to the forearm area. Sensation is lost in the outer part of the forearm. The mobility of the arm is limited, a sharp cutting pain occurs when moving, it is difficult to bend the arm at the elbow and straighten the shoulders.
- The total form is the most dangerous; the general symptoms include fever, drowsiness, weakness, possible nausea and lack of appetite. This type of neuralgia often occurs against the background of poisoning and weakened immunity.
In an advanced state, the pain syndrome becomes excruciating, spreads to the area of the shoulder blade and chest, and radiates to the back.
Diagnostics
The first thing the patient needs to do is contact a neurologist or kinesiologist . Only a specialist can make a presumptive diagnosis and find the cause of inflammation based on:
- initial examination taking into account complaints and characteristic manifestations of the disease;
- medical history (lifestyle, activity, concomitant diseases, etc.).
A biochemical blood test is required, revealing:
- leukocyte count;
- erythrocyte sedimentation rate;
- blood protein ratio;
- exclusion of anemic condition.
To exclude other diseases and pathological neoplasms (stomach ulcer, renal pathologies, heart failure, vertebral hernia, etc.), the patient is prescribed additional differential diagnostics:
- MRI is a modern method that studies the structure of the vertebrae and tissues and detects neoplasms.
- Electroneuromyography - using myographs, the condition of the muscles and peripheral nervous system is studied (conductivity of the electrical impulse, the exact location of the affected area).
- X-rays monitor the displacement of the vertebrae, the presence of bone growths that clamp the nerve endings.
- Ultrasound allows you to assess the condition of blood vessels, and examines the movement of blood (to exclude vascular pathologies).
- In clinical cases, a spinal cord puncture is performed (the presence of harmful microorganisms causing pathology).
Features of therapy
The choice of treatment methods and techniques is directly related to the cause of the disease.
At the first stage, brachial neuralgia can be treated conservatively:
- analgesics (Ibuprofen, Tempalgin, Ketoprofen) are prescribed to relieve pain and inflammation;
- for severe pain, injection blockade with Novocaine is used;
- to reduce swelling, diuretics (Veroshpiron) are prescribed;
- anti-inflammatory ointments are used (Fastum-gel, Viprosal);
- only after the swelling has been removed can you use warming gels (Capsicam, Finalgon), they restore the functioning of muscle tissue;
- antibiotics are prescribed according to indications;
- to fix the arm, special splints and bandages are used;
- support of the body is required (B vitamins).
The therapy lasts 2 weeks; with proper treatment, the patient returns to a full life quite quickly.
In the absence of positive dynamics, surgical methods are recommended:
- neuroexeresis;
- neurotomy;
- tractotomy.
Application of acupuncture
After general treatment, the specialist recommends undergoing a recovery course (electropheresis, massage, mud baths, etc.)
Acupuncture – a combination of reflexology and acupuncture – impact on biologically active points (a complex of acupuncture, massage and warming).
The peculiarity of the method is that tissue restoration occurs faster, the risk of complications and recurrence of the disease is reduced.
Traditional methods
It should be noted that any alternative medicine recipes for neuralgia can only be used as an additional treatment:
- Tincture of black elderberry flowers not only relieves inflammation and pain, but normalizes metabolic processes. The preparation method is simple: 2 tbsp. l. crushed raw materials are steamed with boiling water (1 l), infused for 2-3 hours. Take 100 g 3 times. per day after meals for 2 weeks. You can add honey to the decoction.
- with a tincture of crushed raspberry stems and leaves . Recipe: pour 250 g of boiling water 1 tbsp. l. raspberries, simmer in the oven or over low heat for 40 minutes, cool. Take 3 tbsp. l. infusion 3 r. a day before meals (half an hour). The course of treatment is at least 2 – 3 months.
- A decoction of fireweed leaves is a natural analgesic that relieves pain and inflammation. The tincture can be prepared in a thermos - 2 tbsp. l. pour 0.5 liters of boiling water over the raw material and leave for a day. Take 50 g 3 times. per day before meals for a month.
- A heat compress from flax seeds is applied topically: boil the seeds in a gauze or fabric bag for 2 minutes, cool to a comfortable temperature so as not to cause a burn. A warm compress is applied to the sore spot and covered with an insulating cloth or towel. It is better to use before bedtime.
- For systemic pain, a decoction of the centaury herb . Pour 1 cup boiling water over 3 tbsp. l. chopped grass. Leave for 2 - 3 hours. Take 3 tbsp. l. infusion 3 r. per day before meals for 10-14 days.
Possible complications, prognosis and prevention
If you consult a doctor in a timely manner, the prognosis is always positive.
Self-medication or ignoring the first symptoms can lead to complications:
- neuralgia of the brachial nerve takes on a chronic form and becomes fixed;
- the disease degenerates into plexitis (the nerve fibers of the brachial plexus are damaged);
- risk of developing Horner's syndrome (affects the eyeball);
- significant damage to the nerve plexuses leads to loss of sensitivity and decreased mobility;
- in critical cases, paralysis of the arm and complete muscle atrophy are possible.
It is known that preventing a disease is easier than completely eradicating it.
Prevention:
- prevent hypothermia of the body;
- exclude situations of injury (ice, moderate sports activities);
- timely treatment of viral infections;
- balanced diet (vitamins, meat, dairy products);
- Hardening, sports and a healthy lifestyle strengthen the immune system and resist any viruses and infections.
In conclusion, brachial neuralgia should be treated immediately . Only in this case is a complete recovery guaranteed without complications or relapses.
Source: //nerv.guru/zabolevaniya/nevralgiya/vidy-n/plechevogo-nerva.html
Pain and numbness in fingers is a sign of disease
26.10.2015
www.coalcreekpt.com
Many people complain of numbness in their fingers and pain that wakes them up at night and interferes with full-time work.
However, not everyone goes to the doctor when the disease has not yet progressed so far, and irreversible changes can be avoided.
We talk with orthopedist-traumatologist at the Medical Center for Diagnostics and Treatment, Simonas SAREIKA, about which symptoms should cause concern and in which cases surgical intervention is necessary.
– What hand and wrist diseases do patients most often present with?
– These are mainly diseases caused by pinched nerves - carpal and ulnar tunnel syndromes, as well as diseases caused by inflammation of the tendons - the so-called “snapping” finger and tenosyvitis of the radius. Joint diseases, pain in the hand, and disorders of the subcutaneous structure are common.
The most common and well-known tunnel syndrome is carpal tunnel syndrome (from English - “carpal tunnel syndrome”), i.e. compression of the median nerve under the transverse carpal ligament, which occurs between the three bony walls and the tight ligament that hold the tendons of the muscles that flex the fingers and hand.
Carpal tunnel syndrome and diseases caused by inflammation of the tendons are more often diagnosed in women over 50 years of age or in young people burdened with heavy physical work. They cannot sleep at night due to numbness and pain in their fingers. During the holidays, these symptoms most often subside.
Wrist pain sometimes appears after an injury, gradually intensifies and begins to interfere with everyday life. Cubital tunnel syndrome affects both men and women over 30 years of age.
Dupuytren's contracture (palmar fibromatosis) - painless scar degeneration and shortening of the palmar tendons - is inherited, more often observed in smoking, physically working men over 60 years of age.
– How do the symptoms of these diseases differ?
– With carpal tunnel syndrome, the fingers go numb at night, pain appears in fingers 1-4, and they are stiff in the morning. At the initial stage, the numbness goes away after waking up, but as the disease progresses, it remains, and objects begin to fall out of the hands, and it becomes difficult for the patient to fasten buttons, although at night there may be no pain at all.
Elbow joint syndrome most often manifests itself only in numbness of the fingers, less often in pain at night. 4-5 fingers are damaged. As the disease progresses, the muscles of the palm weaken and strength disappears.
The main cause of stenosing tenosynovitis (“snapping” finger) is pain in the hand. The palm begins to hurt when you move your fingers. The pain spreads to the forearm.
As the disease progresses, it becomes more difficult to straighten the finger, it “gets stuck”, and a characteristic sound appears - a click, which gave the popular name to this disease. Sometimes the finger does not straighten at all, then you have to return it to its place with the other hand.
Snapping finger syndrome is caused by a nodule in the extensor tendon. Most often, patients have damaged fingers 1, 3, and 4.
Dupuytren's contracture is manifested by the inability to straighten the fingers and nodular thickening of the skin on the palms. At first it may be painful, then changes occur in the fingers - it is impossible to straighten them.
Wrist hygroma (hernia) is a small, rounded protrusion under the skin. Occurs as a result of a sharp turn with a load or after heavy physical exertion. Because of this formation, patients most often turn to a hand surgeon. A “bump” seems to grow on the hand, this really scares people.
Diseases of the joints of the hand and wrist are very complex, which is why a thorough examination is necessary.
– What is the cause of this or that disease?
– The most common cause is excessive physical activity or injury, as a result of which the tendons become inflamed, enlarged, begin to injure other tissues, and pinch nerves. After an injury, joints begin to wear out faster.
Hormonal changes and, oddly enough, everyday habits also have an impact, for example, while sleeping, take a position with strongly bent arms, while working, constantly resting your elbows on the table, and for drivers, on the edge of the car door.
The causes of some diseases are not completely clear.
– What symptoms should lead a person to see a doctor?
– You should always contact a specialist if your fingers gradually or suddenly become numb - this is a sign of a pinched nerve, also if a tumor has appeared and begins to grow.
When a person does not consult a doctor due to diseases manifested by numbness of the fingers, night pain, the nerve is damaged more and more - the fingers lose sensitivity, the muscles of the hand begin to atrophy, the hands weaken, it becomes difficult to grasp small objects, the hands are afraid of the cold.
In this case, even after surgery, hand function may not be fully restored. If the finger gets stuck and the disease progresses, even after surgery, movement may remain limited.
Very often, it is difficult for patients to name clear symptoms, so conditions in which the nerve is pinched may remain undiagnosed for a long time. By applying on time, the patient can receive qualified help. A very informative diagnostic test in these cases is electroneuromyography, which helps to determine the extent and amount of damaged tissue.
– What are the tactics for treating these diseases?
– At the initial stage, these diseases are treated conservatively. If this does not help, the doctor decides whether surgery is required. It is important that the patient comes in on time. Operations carried out in a timely manner are simple and very effective. When the disease is advanced, the effectiveness of operations is not so high.
Conservative treatment of carpal and ulnar tunnel syndromes boils down to reducing physical stress on the arm, prescribing non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, B vitamins that improve blood flow and nerve nutrition, vasodilator drugs, and splinting. Electroneuromyography helps diagnose these diseases and determine treatment tactics.
I most often begin treatment for trigger finger with hormonal blockade with Kenalog. When treating tenosynovitis, a splint and hormonal blockade are prescribed. The neoplasm - in the case of hernias of the wrist, finger joints, tendons - is punctured. Changes in the wrist joints are treated with splints, anti-inflammatory drugs, physiotherapeutic procedures, and injections into the joint.
– When is surgery necessary?
– Always with Dupuytren’s contracture, in other cases – if conservative treatment methods do not help, and the symptoms persist or progress.
The operations are reimbursed by the Health Insurance Fund, so the patient does not have to wait in line and goes to any clinic that can perform such an operation, for example, to our Center. After all operations, the patient is discharged home on the same or the next day. The main thing is not to hesitate at the first symptoms in order to prevent serious illnesses.
For any questions, please contact your personal manager Beata Putrameneta by phone 2 (Russia, Viber, WhatsApp) or by email. by mail, as well as by the general number of the department for receiving foreign patients: +370 5 247 63 69
Source: //www.medcentras.lt/ru/stati/bol-i-onemenie-paltsev-ryki-mogyt-svidetelstvovat-o-sereznix-zabolevanijax,nid.626
Neuralgia. The best treatment is prevention
More and more people today are diagnosed with neuralgia. This medical term literally means “nerve pain” when translated from Greek. When peripheral nerves are damaged, a person is accompanied by excruciating pain attacks in certain areas. More often this diagnosis is made to women; as a person ages, the risk of getting this disease increases.
It should be noted that neuralgia should not be confused with neuritis. The latter is accompanied by disturbances in movement activity and loss of sensitivity.
An attack of pain can affect any part of the body, but most often with neuralgia the trigeminal nerve (the main and most “problematic” nerve of the face) is affected, but there are cases of damage to other nerves (for example, intercostal ones).
If a person is diagnosed with neuralgia, it is possible that it was the result of some disease. Therefore, treatment will most likely be prescribed as part of eliminating the causes that provoked the attack of neuralgia.
Where does the pain of neuralgia come from?
The occurrence of an attack of acute pain in this disease is difficult to predict. The pain does not have a seasonal framework, and can also appear both during the day and late at night.
Very often, acute burning pain is not relieved even with effective painkillers. People sometimes fall out of the schedule of their usual life for several days and lose their ability to work.
Possible causes (provocations) of exacerbation of neuralgia may be:
- Hypothermia. Long stay in the cold accompanied by severe physical activity contributes especially actively to the disease.
- Intoxication. In these cases, neuralgia may be a consequence of previous infectious diseases, the use of certain medications, contact with heavy metals, or alcohol abuse.
- Problems with the musculoskeletal system. For example, old injuries of the spine, joints, and congenital anomalies of the skeletal system may make themselves felt.
- Tumors of various types.
- Frequent stress, fatigue, regular overexertion.
There are also a number of diseases that increase the risk of neuralgia. These are atherosclerosis, diabetes mellitus, and other problems with blood supply.
In addition to very severe pain that appears in attacks, a person may be tormented by convulsive muscle contractions (pain tics), redness of certain areas of the skin, painful skin sensations (paresthesia and hyperesthesia) even after the end of the attack.
Neuralgia – everyone has their own.
The disease can develop in different ways. Here are a few main ones:
- Damage to the trigeminal nerve. It can occur as a consequence of facial injuries, severe toothache, and even malocclusion. Pain can be caused by external factors such as cold, loudness, sound, careless touch. Pain may be preceded by itching or paresthesia.
- Intercostal. It is often a consequence of osteochondrosis, scoliosis and can be accompanied by intense pain in the area of the ribs. It is especially aggravated by coughing and can limit the depth of breathing movements.
- Neuralgia of the occipital nerve. It hurts not only the back of the head, but even the area of the eyes and temples.
- Neuralgia of the external cutaneous nerve of the thigh. Any movement increases pain in the outer thigh. There may even be a burning sensation, or less often, numbness.
- Neuralgia of the pterygopalatine ganglion. These are attacks with pain in the neck, palate, eyes, temples. In severe cases, the pain may radiate (give) to the hands.
- Neuralgia of the glossopharyngeal nerve. In this rarest form, the throat, lower jaw, and ear hurt.
How can you help with neuralgia?
If attacks of the disease worsen, you should contact a neurologist to prescribe treatment. It is important that treatment can be prescribed only after determining the type and cause of neuralgia.
After exacerbations are relieved and in the absence of contraindications (such as a tumor, early postoperative period, and others), it is advisable to carry out a number of preventive measures.
A healthy lifestyle, physical activity, and taking complex vitamin preparations (especially group B) will help prevent an attack of the disease.
Hypothermia and traumatic situations should also be avoided.
All of the above can be optimally achieved with the help of a set of sanatorium-resort procedures, selected taking into account the factors that provoked the attacks, as well as providing treatment for concomitant diseases.
Today, many sanatoriums have modern medical facilities in combination with natural healing factors designed to treat diseases of the peripheral nervous system, including neuralgia.
It must be remembered that people suffering from neuralgia with rare attacks and only in remission are allowed to undergo sanatorium-resort treatment.
Possibilities of sanatorium-resort treatment of neuralgia.
In the sanatoriums of Belarus and Caucasian Mineralnye Vody, a set of procedures has been developed to help people with diseases of the peripheral nervous system, including neuralgia. All of them are aimed at improving the general condition of the body and preventing attacks of this disease. The following procedures are carried out:
- Physiotherapeutic treatment (exposure to electromagnetic fields, low-voltage pulse currents, ultrasound, infrared radiation, electrophoresis of medicinal substances);
- Balneological procedures:
- Heat therapy (ozokerite therapy);
- Acupressure;
- Laser therapy;
- Acupuncture;
- Complexes of exercises of therapeutic gymnastics and health path.
A number of other procedures are also used, necessarily in accordance with the prescriptions of a neurologist. When treating in a sanatorium, you should not act on the principle that more is better. All procedures must be taken strictly according to the recommendation and under the supervision of a doctor.