Primary characteristics of the disease
Vascular psychoses include psychoses that develop as a result of atherosclerosis, stroke, hypotension, hypertension, thrombosis or other cerebral vascular diseases.
Vascular psychosis can develop in several forms:
- Acute form . Characterized by a state of “confusion” of consciousness. The psychotic state occurs periodically and lasts several hours. Most often, the attack occurs at night, and during the daytime the patient has a clear consciousness.
- Subacute forms a. A complicated type in which psychosis lasts longer. It may be accompanied by confusion, or, with the patient clearly conscious, it may be characterized by intermediate syndromes. This form is characterized by disorders that are complicated by so-called “small-scale” delusions and verbal hallucinatory experiences.
From the point of view of the origin of mental disorders caused by vascular dysfunction, there are:
- syndromes at the inception stage, in a pseudoneurotic form - such disorders usually appear if vascular disease is at the initial stage of development;
- vascular dementia : neurological and mental disorder associated with a certain stage of development of vascular disease;
- other syndromes caused by external factors (exogenous): delusional disorders, hallucinations and others.
Vascular psychoses
Psychopathological manifestations in the form of acute psychoses can occur at any stage of the vascular process, even in a state of dementia.
F. Stern (1930) described “arteriosclerotic states of confusion.” Such psychoses are characterized by a number of common clinical properties. First of all, the syndromes of stupefaction that arise in the structure of these psychoses as reactions of an exogenous type are distinguished by their atypicality, lack of expression of all their components, and syndromic incompleteness.
Manifestations of acute vascular psychoses do not always correspond to the most typical pictures of delirium, amentia, twilight state, oneiroid and others, which makes it possible to quite reasonably qualify them as states of “confusion” (M. Bleuler, 1966).
Another property of vascular psychoses is that acute psychotic episodes are quite often short-lived, occur sporadically, and last no more than a few hours. As a rule, such an episode unfolds at night, and during the day patients can be in clear consciousness, without psychotic disorders.
A common property of vascular psychoses is also their recurrence, sometimes more than once. This primarily applies to nocturnal states of confusion. The course of acute vascular psychoses differs from the course of symptomatic psychoses of other etiologies - such as alcoholic delirium, acute traumatic psychosis.
Thus, in the dynamics of delirium tremens, the increase in the severity of the disease is most often expressed by the deepening of the delirious syndrome itself (the transition of “occupational delirium” to delirium), and in acute vascular psychoses, various syndromes of altered consciousness can replace each other (delirious syndrome may be followed by amentive, etc. .).
In the subacute course of vascular psychoses with a more protracted course, in addition to stupefaction syndromes, reversible syndromes not accompanied by a disorder of consciousness, but also reversible syndromes, which X. Vick called “transitional” or “intermediate”, may occur.
Compared to symptomatic psychoses, such protracted and more complex forms of vascular psychoses are much more common. E.Ya.
Sternberg emphasizes that in vascular psychoses, almost all types of intermediate syndromes can occur, preceding the syndromes of clouded consciousness: neurotic, affective (asthenic, depressive, anxiety-depressive), hallucinatory-delusional (schizoform), as well as organic circle syndromes (adynamic, apathetic). -abulic, euphoric, expansive-confabulatory, amnesic, Korsak-like).
Depressive states occur, taking into account various data, in 5 - 20% of all cases. At the same time, along with the symptoms of melancholy and grumpiness, pronounced tearfulness and hypochondriasis are almost always observed (“tearful depression”, “aching depression”).
With each new recurring episode of depression, an organic defect with the formation of dementia becomes more and more obvious.
Depressive episodes are just as often accompanied by anxiety, unaccountable fear, and they often precede an acute cerebrovascular accident.
Paranoid (schizoform) psychoses are characterized by acute sensory delusions with ideas of relationship, persecution, poisoning, influence.
Such psychoses are usually short-term and usually occur in the initial stages of cerebral atherosclerosis with signs of arterial hypertension. The later stages of cerebral atherosclerosis are characterized by acute hallucinatory-paranoid states.
Hallucinations in such cases are of a scenic nature, and visual illusions (both illusions and hallucinations) often occur.
Protracted endoform psychoses of vascular origin are the most difficult to recognize. In addition to constitutional genetic predisposition, special properties of the organic process play an important role in the development of prolonged vascular psychoses.
As a rule, protracted endoform psychoses develop with vascular processes that manifest themselves quite late (at the age of 60–70 years), occurring with slow progression and without severe focal disorders.
Such patients with a picture of delusional psychosis are not characterized by the usual initial asthenic manifestations of the vascular process; sharpening of personality characteristics is more common.
Clinically, the most justified is the identification of protracted paranoid psychoses in men, mainly in the form of delusions of jealousy. It is characterized by little development of the topic and poorly systematized. At the same time, the predominance of sexual details with great nudity of this plot can be considered a distinctive feature.
Typical topics in the descriptions of patients are his wife’s infidelity with young people, young members of the patient’s family, including his son and son-in-law. Delusions of jealousy are usually combined with ideas of damage (the wife feeds her rival lovers better, gives them the patient’s favorite things, etc.). The mood is tearful and depressed with outbreaks of irritability, anger and aggressiveness.
Such organic stigmatization is more pronounced with deep psychoorganic changes.
Chronic verbal hallucinosis as part of vascular psychosis is also diagnosed quite often.
It is revealed as a polyvocal (many “”) true verbal hallucinosis, flows in waves, sometimes at the height of development it becomes scenic, usually intensifies in the evening and at night, its content is predominantly threatening. The intensity of hallucinosis is subject to fluctuations.
Its vascular nature is often proven in parallel by a registered increase in blood pressure, an increase in other vascular stigmata (headache, increased tinnitus, dizziness, etc.)
Source: https://www.psyportal.net/476/sosudistyie-psihozyi/
Causes and mechanisms of the disorder
The main reason for the development of this form of psychosis is diseases associated with disruption of the vascular system of the human body.
Among the diseases that most often provoke psychosis of vascular origin are:
- atherosclerosis;
- stroke;
- hypertension;
- thromboangiitis;
- endarteritis.
What leads to mental disorders in the case of these deviations and diseases? What is the sequence of processes that determines the mechanisms of the appearance and progression of the disease? To date, there is no exact answer to this question. There is no clear understanding of why only some vascular diseases and brain injuries lead to the appearance of mental disorders.
We can only talk about the following cause-and-effect relationships:
- Sudden changes in blood pressure can lead to changes in the structures of the brain, which leads to the appearance of acute or subacute psychosis. Its main features are confusion and hallucinations.
- The progress of psychotic deviations of vascular origin is influenced by the individual characteristics of the body , which have developed on the basis of hereditary and acquired properties, as well as general somatic factors.
- An acute form of the disorder may occur due to a decrease in blood pressure at night , which, in turn, provokes a deficiency in the blood supply to the brain. The development of deviations is promoted by atherosclerotic damage to the heart vessels and various types of infectious diseases.
- Mental disorder often occurs during a period of severe disruption of blood circulation in the brain , so vascular psychosis is a common occurrence after a stroke.
Article on the topic: Eye stroke - causes and signs of the disease, diagnosis, treatment methods, possible complications
Mental disorders in cerebral vascular pathology
They arise as a result of cerebral circulation disorders in diseases such as atherosclerosis, hypertension, intracranial aneurysms, vasculitis, and cerebral vascular amyloidosis. Significantly more frequent in the second half of life. They account for about a third of all cases of mental pathology in people over 60 years of age. There is no direct relationship between mental disorders and the nature and severity of vascular pathology. Other reasons also take an active part in the development of mental disorders: heredity, constitution, somatic diseases, age-related changes in the brain, trauma, etc., and often endogenous mental diseases. There are three groups of mental disorders of vascular origin: exogenous-organic, endoform and vascular dementia.
Features of the clinical picture
With this type of disorder, non-psychotic symptoms, intertwined with disorders of an organic nature, are combined with symptoms of a psychopathological type. The latter have mildly expressed neurological features.
Symptoms that make it possible to diagnose vascular psychosis at the initial stage of development:
- sudden onset and then quickly disappearing tinnitus;
- in the morning there may be pain in the back of the head;
- numbness of the lower part of the face (cheeks, chin), voluntary contraction of the facial muscles;
- non-recurrent dizziness, uncoordination of movements when walking;
- sleep disorder: the patient is able to sleep for only 3 hours, and upon waking up, cannot fall asleep again;
- unstable emotional background: constant desire to cry, forgetfulness, increased fatigue, inattention;
- reaction and speech slow down;
- The appearance of hypochondria cannot be ruled out.
Symptoms characteristic of mental disorders arise much later and manifest themselves as delusions, hallucinations, and a schizophrenic picture.
Diagnosis of the disease
At an early stage, when there are symptoms of a neurotic nature, vascular psychosis is diagnosed based on signs of hypertension, arteriosclerotic stigmas, changes in the fundus, and mild neurotic abnormalities.
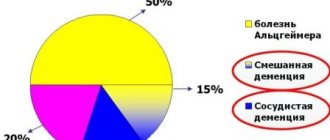
It is more difficult to diagnose vascular dementia. It is not easy to distinguish from senile dementia. Characteristic features of dementia are random deviations and flickering of the main signs in vascular disorders.
With age-related dementia, symptoms will only increase and no periods of stabilization can be expected. In addition, the onset of vascular psychosis is more acute and may be accompanied by increased confusion.
Treatment options
Treatment is best started with treatment of the underlying vascular disease that caused the psychosis.
Psychotropic medications will definitely be prescribed. Their choice is determined by the type of mental disorder. At the first stage of treatment, tranquilizers are prescribed: Atarax, Phenazepam, Rudotel and others. Antipsychotics are usually prescribed Propazine (the dose of this drug varies 25-75 mg/day), Rispolept in the form of drops.
If the patient has anxiety-depressive syndrome, then atypical antidepressants are prescribed, such as Remeron, Cipramil and others.
Treatment is not limited to the use of specialized products. The patient should take vitamins, general health-improving medications, and medications intended to affect the higher mental functions of the brain (Mexidol, Piracetam).
The patient will have to give up smoking, alcohol, avoid overwork and emotional outbursts.
It is impossible to cure vascular psychosis or dementia. There is no chance for a person to recover completely, but you can try to raise your standard of living to the highest possible level.
Preventive measures
The prevention of mental disorders associated with dysfunction of the vascular system will be facilitated by:
- timely diagnosed vascular disease;
- establishing a constant and orderly daily routine;
- preventing excessive loads;
- giving up smoking, alcohol and other bad habits;
- proper, balanced, dietary nutrition;
- giving up a sedentary lifestyle;
- physical therapy classes;
- constant monitoring of blood pressure and taking measures to normalize it even with minor deviations from the norm.
Article on the topic: Which long-acting and instant-acting pills for increasing potency in men are better and more effective?
The disorder never goes away without a trace. Modern medicine is not able to completely cure it; you can only take drugs that improve the blood supply to the brain, drugs that help strengthen memory, but in any case it will not be possible to completely get rid of all the symptoms. They will appear again at one time or another.
Treatment of psychosis
So, as mentioned above, you cannot cope with the disease at home. You need to contact specialists who will develop treatment methods. They will depend on what kind of disease the person is facing.
Treatment of alcoholic psychosis
Alcoholic psychosis is a severe mental disorder that is caused by drinking alcohol for a long time. To save a loved one, you need to pay attention to the following symptoms:
- sadness;
- unreasonable fears;
- hallucinations;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- depression.
To promptly help a person return to normal life, contact professionals. They will carry out treatment according to all established rules.
Treatment of alcoholic psychosis involves cleansing the body of toxic substances. After detoxification, the person is placed in a rehabilitation clinic, where psychologists regularly work with him. They eliminate the underlying causes of the disease and also cope with its symptoms. Under the supervision of specialists, the risk of relapse is completely eliminated.
Treatment of disintegrative psychosis
This name is given to a heterogeneous group of conditions that occurs in most situations in children aged three to four years. With the onset of the disease in a short time, prodromal symptoms are lost in a not so long ago completely healthy baby. He loses his speech and understanding skills. Treatment of disintegrative psychosis improves the quality of life of a young patient.
Development of pathology
The onset of disintegrative psychosis can be almost invisible. The child's motor behavior gradually begins to decline. Hyperactivity develops. As it develops in a short time, the symptoms increase. Gradually all acquired skills and abilities disappear. In medical practice, this pathology often occurs when a child is diagnosed with autism.
When diagnosed, the loss of at least two of the skills acquired in the first years of life is highlighted. These include:
- speech skills;
- ability and desire to support the game;
- performing social skills;
- control of bladder and bowel movements.
In some cases, young patients lose all 4 previously acquired skills. In such a situation, doctors will diagnose, according to the international classification, “basic loss of interest in objects and the surrounding world.” This pathology is also often called childhood dementia. This syndrome was first described in 1909 by a doctor from Germany, Geller.
Childhood dementia is irreversible and progresses rapidly. Despite research, today the causes of the disease have not been established. The possibility of the presence of an organic nature of the onset of pathology is considered. At the same time, doctors talk about identifying severe stressful situations in children with childhood dementia.
Treatment options
Childhood dementia, which is disintegrative psychosis, cannot be cured or at least stopped with modern methods. Contacting specialized clinics helps develop a course of therapy that maintains a high quality of life for a small patient suffering from infantile dementia. The development forecast is negative. Within a period of one to several years, the stage of deep dementia is diagnosed. Most patients remain with severe mental retardation for the remaining years of their lives.
The course of therapeutic therapy includes the treatment of neurological and mental disorders, and the activities of social services that provide support. A big role is given to the social adaptation of family members of a small patient suffering from an incurable disease.
Treatment of affective psychosis
Affective psychosis is a mental illness that manifests itself by alternating periods of excitement and hyperactivity (mania), and decreased mood, apathy (depression). This condition is also called bipolar disorder or manic depression.
The patient's phases of mania and depression change unpredictably and can last from several hours to months or years. In this case, long periods of remission are possible when the patient does not have any symptoms.
To treat affective psychosis, medications are used - atypical neuroleptics, lithium drugs, antiepileptic drugs (valproate and carbamazepine). In addition, psychotherapy (mainly cognitive behavioral therapy, interpersonal therapy) and the method of deep cranial stimulation are used.
Treatment of amphetamine psychosis
Amphetamine psychosis occurs when a person uses the drug amphetamine for a long time. Symptoms of this disease vary widely, but usually consist of hallucinations and confusion. If a person continues to use the drug, the symptoms will develop into a chronic form, so it will be impossible to detect them.
Amphetamine psychosis, the treatment of which is trusted to specialists, is similar to other types of mental disorders. You can treat a person in a psychiatric clinic. But if we are talking about a mild form of psychosis, then outpatient treatment will be sufficient.
Treatment of manic psychosis
Manic psychosis is a serious personality disorder that is accompanied by sudden changes in mood, excessive physical activity, and increased activity. But, at the same time, a person is prone to depression. He suddenly withdraws into himself, refusing to make contact.
Treatment of manic psychosis is a complex process consisting of many steps. The patient needs special medications, which are prescribed by the attending physician. In addition, he must regularly visit a psychologist to restore his psychological health. Classes can be either individual or group.
Treatment of depressive psychosis
Depressive psychosis occurs due to a prolonged stressful situation that causes negative emotions. This condition is dangerous because a person can behave aggressively and unpredictably. You need to contact specialists in a timely manner to avoid problems.
Treatment of depressive psychosis is carried out in a hospital setting. The patient is regularly looked after by professionals who monitor his condition. Work with a psychologist is carried out every day, because you need to eliminate the trouble and the causes of its occurrence.
Treatment of acute psychosis
Acute psychosis is a mental disorder that is accompanied by disturbances in social adaptation. A person suffers from sudden mood changes, unexpected attacks of aggression, and other problems.
Treatment of acute psychosis is mandatory with hospitalization of the patient. This is due to the fact that he is not able to control his own actions, so he can harm the people around him. Medicines are selected only on an individual basis by a specialist, because self-medication is strictly prohibited. In addition, a psychologist should regularly work with a person to convince him that only the best is wished for him. Remember that a sudden change in environment can cause a psychological breakdown.
Acute infectious psychosis
Deviations can occur at different stages of infectious diseases. The following symptoms are observed:
- physical activity;
- disorientation in space;
- visual/audio hallucinations;
- affective arousal;
- sense of anxiety;
- accelerated thinking and speech;
- decreased appetite;
- increased attraction to the opposite sex;
- feverish delirium;
- sleep disturbance;
- increased irritability.
Relief of symptoms is observed after treatment of the underlying disease.
Where to go for help
Specialists at the private clinic “Salvation” treat acute infectious psychosis using proven pharmacotherapy. Experienced doctors will do everything possible to alleviate the patient’s condition and eliminate the source of the problem. We have good diagnostic capabilities and highly qualified personnel; we can make a correct diagnosis and establish the exact cause that led to the disorder. Other arguments to contact us for help:
- complete confidentiality;
- on-site consulting;
- decent conditions for keeping patients;
- availability of services of psychotherapists and psychiatrists;
- proven treatment methods;
- 24-hour operation of the center;
- convenient location of the clinic.
Near the health resort there is a landscaped park area. A change of environment benefits all of our patients. We provide productive treatment and a comfortable stay within the walls of the center, maximum care for each patient. We are recommended for responsibility, professionalism, and effectiveness. Contacting our center is a good opportunity to return a loved one to normal life. Call us, we are ready to help even in the most advanced cases!
Paranoid psychosis
The disease is characterized by the appearance of delusional ideas. The patient claims that he is being pursued by fantastic creatures, intelligence agencies, and law enforcement agencies, that they want to kill, kidnap, and rob him. A person is convinced that someone wants to harm him. Auditory pseudohallucinations are observed. Paranoid psychosis is also characterized by:
- suspicion of betrayal of a partner;
- suspicion of deceiving colleagues;
- inappropriate behavior;
- strong feelings about the slightest comments;
- belief in the biased attitude of others;
- rancor.
A deviation may occur due to metabolic disorders, damage to the mucous membranes of the brain by Treponema pallidum, head trauma, or diseases of the internal organs. Treatment of paranoid is carried out in parallel with the underlying disease.
Where to go for help
The Salvation Clinic provides treatment for mental disorders using modern drug therapy, individual and group psychotherapeutic training. We will be able to reliably make a diagnosis, alleviate the symptoms and general well-being of the patient. Other reasons to contact us for help:
- highly qualified psychiatrists and psychotherapists;
- many years of experience in successful treatment of paranoid psychosis, depression and other mental illnesses;
- keeping patients in comfortable conditions;
- the presence of a landscaped park area near the clinic;
- courteous junior medical staff;
- anonymous consultation;
- reasonable prices for doctors' services.
You can contact us at any time. The hotline operates 24 hours a day. We are ready to provide support to anyone who needs quality psychotherapeutic assistance. Call, many mental disorders today can be successfully treated if you consult a doctor in a timely manner!
Childhood atypical psychosis
With this deviation, there is a violation of social connections. However, the behavior of children with such a diagnosis can be completely opposite. Some are closed, prefer loneliness, avoid communication with people, others want to be in society, but cannot establish relationships with others.
Parents often complain that the child does not respond to any requests; they suspect that he has hearing problems. But this is not true at all. A person is so immersed in his own world that he does not notice what is happening. Sometimes such behavior is perceived as indifference. It is worth considering that patients with childhood atypical psychosis have a limited vocabulary, and they cannot always express their feelings and emotions through speech.
Where to go for help
The Salvation Clinic diagnoses and treats atypical forms of autism. We are ready to provide complete isolation from the external environment, long-term observation of the child’s behavior, and the reliability of the diagnosis. Advantages of visiting the clinic:
- maximum individualization of treatment;
- the ability to establish an individual nursing station;
- advanced treatment techniques;
- highly qualified specialists;
- quick response to all requests from parents;
- anonymous counseling at home;
- reasonable prices for treatment, food, rent of a separate room;
- the location of the center in one of the most picturesque corners of Moscow Region;
- European health care service.
The clinic staff will do everything possible to alleviate the child’s health condition and provide him with a normal life within the walls of the clinic and beyond. Contact us, we are ready to help today, we work seven days a week and are always in touch!
Treatment of schizophrenic psychosis
Dangerous schizophrenic psychosis is accompanied by extremely unpleasant symptoms. Often a person withdraws into himself, refusing to communicate with people around him. He also experiences sudden mood changes. He can laugh and then burst into tears a minute later.
Treatment of schizophrenic psychosis is determined individually for each patient. The technique depends on how acute the problem is. Usually this means medications and work with a psychologist. Thanks to regular monitoring by specialists, relapses are excluded, and the patient gradually restores his mental health.
Treatment of schizotypal psychosis
Schizotypal psychosis is a disorder characterized by strange reasoning and beliefs, a lack of emotion, and unclear reactions to events. Experienced specialists are engaged in diagnosing such problems and eliminating them. The occurrence of such diseases is influenced by hereditary factors and biochemistry. It is impossible to protect yourself from them if you are prone to developing them.
Treatment of schizotypal psychosis is carried out in a hospital setting. In case of trouble, you need to use special medications. In addition, regular work with a psychologist is necessary. A professional will definitely select those treatment methods that are suitable for a person in a particular situation.
Treatment of schizophreniform psychosis
A similar problem is also often encountered among the population of our country. Every fifth person encounters it. The disease is characterized by sudden changes in mood and an unstable emotional state. The person needs immediate help as he or she may experience prolonged depression.
Treatment of schizophreniform psychosis is a complex and responsible process that requires the intervention of a specialist. Professionals prescribe appropriate medications and regularly work with patients to restore their mental health. It is important to eliminate the cause of the development of mental health problems, because otherwise relapses in the future are not excluded.
Treatment of reactive psychosis
Reactive psychosis is a mental disorder that can occur after mental trauma and severe shock. The symptoms and course of the disorder depend on the individual and the specific characteristics of the injury.
Treatment of this problem is carried out in a hospital. The patient is prescribed special remedies that make it possible to eliminate the problem. It is also necessary to involve psychotherapy.
It is imperative to eliminate the psychogenic situation in order to cope with a mental disorder. If this is not done, the situation will worsen. The disease will become more acute, which will lead to problems and unpleasant consequences. Therapeutic tactics are selected depending on the characteristics of the current situation.
Treatment of vascular psychosis
Vascular psychosis is a problem that is extremely common in our time. It manifests itself in constant headaches, sudden jumps in blood pressure and changes in health for the worse. Such a disorder causes a lot of discomfort to a person.
The main part of therapeutic measures is the elimination of the disease, which is somatic in nature. A professional should prescribe psychotropic medications based on the specific characteristics of the mental disorder. It is also necessary to use tranquilizers, which have a complex effect on the body.
Neuroleptics are prescribed to patients in minimal dosages. To cope with anxiety and fears, you should use antidepressants. Only in this case, confusion of consciousness is completely excluded.
Treatment of senile psychoses
Senile psychosis is a disease that manifests itself after sixty years of age. It manifests itself in disorders of various types, so its symptoms are similar to endogenous mental illnesses. It should be noted that such a diagnosis is characterized by senile dementia.
Old people suffer from memory loss because their concentration is impaired. They may not remember exactly what they did a few minutes ago. The relative needs to be patient, because sometimes old people show sudden aggression and behave incomprehensibly. Do not be nervous, because this condition is transmitted to the elderly person, who also begins to worry.
An individual type of treatment is selected for each patient. The characteristics of the psychosomatic state play an important role. The course of therapy is carried out under regular supervision of a specialist. The acute form of the disease is considered more favorable for cure. If the course of the disease is long-term, then you will be able to simply cope with the symptoms, but you will not be able to get rid of them completely. The patient’s relatives must learn to behave with a sick person, putting up with his attacks, since no one is immune from such problems.
Treatment of childhood psychosis
Childhood psychosis is a phenomenon that is quite rare. Usually its causes are problems in the family, which negatively affect the mental state of the baby. Children who grow up in dysfunctional families are especially susceptible to such problems. Their psyche is regularly exposed to negative influences that destroy moral health.
Episodic attacks of psychosis subside when the underlying illness disappears. If a child has suffered a severe episode of psychosis, he will need professional help. In the most difficult situations, children need to be sent to a clinic for rehabilitation. Typically, therapy is selected taking into account the main features of the disease.
If a child has experienced a psychotic breakdown due to a stressful situation, then he will definitely need short or long-term help from a psychotherapist. In complex and advanced situations, it is necessary to treat the child using special medications. If the child's behavior is very aggressive, then he is prescribed tranquilizers.
Treating psychosis at home
Only qualified specialists can determine by what rules psychosis is treated at home. However, there are general tips that should be followed if your relative suffers from such a problem. As soon as you notice the symptoms described above, start taking action:
- if a person begins to mention that he will commit suicide, or begins to show aggression towards you, immediately call an ambulance to prevent negative consequences;
- never try to argue with a patient, because he does not understand what he is saying, and opposition on your part can lead to unpredictable results;
- always silently listen to crazy ideas without entering into dialogue with the person, as this will not end in anything good.
Do not forget that psychosis is expressed in different moments. Most often it is depressive or manic in nature. That is why the treatment regimen is selected depending on the specific situation. For example, in the first case, you cannot give a person antidepressants. But if he is faced with manic psychosis, then it is simply impossible to do without such drugs. If you do not want to expose your loved one to risks, then it is better to seek help from qualified professionals who better understand such mental health problems.
Post-traumatic organic psychosis
Post-traumatic organic psychosis is a consequence of brain injury. In adult life, childhood trauma can trigger the disease. Symptoms:
- confusion;
- incorrect perception of reality;
- disorientation of behavior.
The Salvation Clinic treats post-traumatic organic psychosis. We have modern diagnostic capabilities, a staff of highly qualified specialists, and many years of experience in the successful treatment of mental illnesses. We offer real help for various disorders in a relative. We are ready to assist with hospitalization in a hospital and provide medical support.
Patients are accommodated in single, double and triple wards. The rooms are equipped with modern furniture, private bathroom, TV, air conditioning. Our patients are under constant supervision of responsible staff and do not need anything.
Features of treatment in our clinic
The treatment regimen for patients with post-traumatic organic psychosis is developed collectively. Other features of our treatment:
- long-term monitoring of the patient’s condition;
- individual approach;
- use of proven drug therapy;
- emphasis on psychotherapy.
We are ready to make the lives of our patients better and provide them with proper care. Walks in the fresh air are carried out daily. The clinic is located in a forested area. Active activity in the fresh air improves blood supply to the brain, normalizes sleep and wakefulness, and strengthens the immune system. Contact us, the Salvation clinic is an excellent opportunity to improve the patient’s quality of life and provide him with a chance for a full existence in this world!
Drugs to treat psychosis
The main medications for treating psychosis are neuroleptics or antipsychotics. The first type of medicine was developed many years ago. They stop psychosis, preventing the problem from developing further. But patients noted the occurrence of a variety of unpleasant side effects. That is why the drugs began to be used less and less in practice.
Atypical antipsychotics are a real breakthrough in the world of treating people with psychosis. The drugs act only on certain nerve receptors, so a negative effect on the body is excluded. With their help, you can cope with psychoses of various types, regardless of the degree of complexity of the disease.
Only a specialist who develops an individual treatment regimen for each patient can prescribe atypical antipsychotics. You need to immediately contact a professional if your loved one or you yourself are faced with similar troubles. Usually the course of treatment lasts for several months, but in some situations it can last for several years.