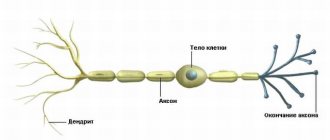
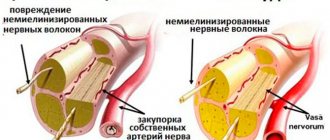
Diabetic polyneuropathy is one of the most serious complications of diabetes mellitus. The nervous system is easily involved in the pathological process, which is why the peripheral part suffers mainly, because the brain is affected at a secondary level when the disease is caused by vascular insufficiency. The pathology also affects the autonomic nervous system. Typically, diabetic polyneuropathy appears in those patients who have been suffering from diabetes for a long time and are of advanced age.
Manifestations of polyneuropathy occur in more than half of patients suffering from diabetes. The disease progresses and occurs in a cumulative manner - the longer the patient suffers from endocrine disorders, the more severe manifestations of neuropathy are diagnosed. According to the results of surveys of patients with diabetes mellitus, the first signs of polyneuropathy are detected five to ten years after the onset of endocrine disorders.
The earlier appearance of neuropathy is due to the fact that patients take little care of their health when diagnosed with diabetes. If you do not control your sugar level, have increased body weight and unsatisfactory blood test results, then you can encounter the first signs of polyneuropathy much earlier.
Cardiovascular pathologies, which do not combine well with polyneuropathy, are especially dangerous for patients. In the presence of vascular diseases and polyneuropathy, healing of trophic ulcers occurs much more slowly, and in severe situations, diabetic distal polyneuropathy covers the foot so much that it has to be amputated. At the same time, mortality rates from diabetes complicated by polyneuropathy remain high.
Causes
If we consider the causes of the appearance of polyneuropathy against the background of existing diabetes, then doctors are currently considering three groups of causes and studying the influence of each group on the appearance of pathology. Today there are:
- metabolic;
- vascular;
- autoimmune causes.
Metabolic reasons, according to researchers, are the accumulation of sorbitol in the nerve endings, insufficient concentrations of myoinositol, non-enzymatic glycation of proteins and oxidative stress that the nerve endings of a patient suffering from diabetes receive.
IMPORTANT! The negative impact of smoking in diabetics has also been proven, since in smoking patients the oxidative reactions of lipids in the body are accelerated.
A study by an international organization dedicated to diabetes and disease control shows the key role that persistently high blood sugar levels play in the development of polyneuropathy. According to scientists, due to increased sugar, progressive demyelination of nerve fibers and axonal degeneration occurs, which inhibits the normal conduction of nerve impulses along the fibers. And with prolonged metabolic disorders and electrolyte imbalance, diabetic polyneuropathy only gets worse.
A group of Russian scientists studying the problem of diabetes indicates that such high sugar levels are not decisive in the causes of polyneuropathy, since data on hyperglycemia and the incidence of polyneuropathy are not correlated, i.e. there is no direct relationship between high sugar levels and damage to nerve endings. According to scientists, the polyol pathway and oxidative stress are becoming more important.
Research shows that it is the increased presence of sorbitol in nerve fibers that is a marker of the appearance or non-appearance of neuropathy, and a certain level of sorbitol can be considered a threshold, beyond which the damage to the nervous system develops. And it is also noted that patients with polyneuropathy have a higher level of aldose reductase in the blood, which is associated with gene polymorphism.
The autoimmune theory is also confirmed by the fact that in a study of type 2 diabetics, autoimmune immunoglobulin was found in patients, which provokes neuronal apoptosis. Moreover, the level of cytotoxic influence is directly related to the severity of neuropathy in patients - both autonomic and sensory neurons are affected.
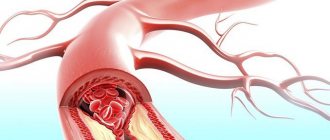
As for the vascular factors in the appearance of polyneuropathy, doctors identify the most threatening microangiopathies that directly affect the damage to the peripheral nervous system. In type 2 diabetes mellitus, vascular disorders are often aggravated by coronary heart disease and cerebral circulatory disorders. Disturbances in protein and lipid metabolism in the vascular endothelium play a certain role in aggravating the pathology, which accelerates the development of atherosclerosis.
The natural development of such disorders is damage to the nervous system. Patients experience ischemia of nerve endings at the cellular level, which ultimately leads to problems in the functioning of the nervous system and metabolic disorders.
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy
Distal symmetric sensorimotor polyneuropathy
Distal symmetric sensorimotor polyneuropathy (commonly referred to in the literature as diabetic polyneuropathy) is the most common clinical manifestation of diabetic damage to the nervous system.
Diabetic autonomic neuropathy
The incidence of damage to the autonomic nervous system in diabetes mellitus ranges from 13.8 to 71% (on average, observed in 20-40% of people with diabetes mellitus)[9]. It is more often observed in people with IDDM and is often accompanied by diabetic polyneuropathy[1]. Studies prove that diabetic autonomic neuropathy is an important independent prognostic factor for mortality in people with diabetes, which clearly reduces the survival rate of patients [10].
Any system or organ that has autonomic innervation can be affected by diabetes mellitus, but clinical significance is currently given to the following manifestations of autonomic neuropathy[1]:
Anomaly of pupillary function
Patients are concerned about the slow adaptation of vision when moving from a well-lit to a poorly lit space, deterioration of vision at dusk and in the dark - the result of dysfunction of the sympathetic nervous system, as a result of which there is a violation of pupil dilatation in poor lighting conditions. In addition, people with diabetes have a decrease in rhodopsin production, which exacerbates the slowdown in the process of vision adaptation[1].
Sweating dysfunction
Almost half of people with diabetes have impaired sweating function as a result of damage to postganglionic sympathetic fibers[1].
Gastrointestinal autonomic neuropathy
Diabetic enteropathy
Diabetic enteropathy (diabetic diarrhea) is the most common intestinal lesion - most patients are concerned about constipation (one of the reasons: a violation of the extramural innervation of the colon). However, the most typical manifestation of gastrointestinal autonomic neuropathy is considered to be diabetic diarrhea, the clear and characteristic symptoms of which are observed in only 1% of patients (A. S. Efimov et al., 1985).
Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy
Hypoglycemia failure syndrome
Diabetic neuropathic cachexia
One of the forms of diabetic neuropathy. The syndrome includes diabetic distal symmetric sensorimotor polyneuropathy, autonomic neuropathy and severe weight loss[1] (up to 50-60% of the original).
The main pathogenetic factor
(as with polyneuropathy in general) is the presence of prolonged hyperglycemia. It most often develops in men over 50 years of age who have had diabetes for a long time.
This syndrome is characterized
severe pain, especially in the legs, a symptom of “restless legs.” Pain in the legs worsens at night, combined with paresthesia and a feeling of stiffness. Patients sleep poorly, become depressed, lose appetite, and progressively lose weight. Disorders of trophic innervation develop, accompanied by degenerative changes in the skin and tendons. Sick men suffer from impotence[11].
Treatment
carried out according to the rules for the treatment of diabetic neuropathy.
Forecast
, as a rule, favorable - within 6-18 months, patients regain weight, manifestations of sensorimotor neuropathy are stopped[1].
Classification
In the medical literature, attempts to classify diabetic polyneuropathy have been made for a long time. Various characteristics were taken as a basis - depending on the cause of occurrence, severity, pathogenetic mechanisms.
The main problem with polyneuropathy is associated with damage to the myelin sheath of nerve endings.
Currently, Thomas's 1997 classification is considered one of the most adapted classifications. According to this division, neuropathy occurs:
Why do the soles of my feet hurt?
- hyperglycemic;
- generalized, or also called diffuse (among such neuropathy there are sensorimotor, acute painful sensory, autonomic, acute motor);
- focal or multifocal (sometimes thoracolumbar, radiculoneuropathy, proximal);
- hypoglycemic;
- chronic inflammatory demyelination.
Each of these types of pathology has its own characteristics of development in patients and features of symptoms.
Other scientists now identify two broad categories of diabetic polyneuropathy. This classification is based on the prevalence of damage to the peripheral nervous system. According to the classification, polyneuropathy is:
- diffuse, or symmetrical - this includes sensory, autonomic and motor polyneuropathy;
- focal, or asymmetrical – this is mononeuropathy, radiculopathy, plexopathy, cranial neuropathy.
Diagnostic measures
Knowing what diabetic polyneuropathy is, it is necessary to become more familiar with the features of diagnosis. First of all, the specialist will need to carefully study the patient’s medical history and complaints. A number of tests will be required: levels of glucose, insulin, C-peptide and other components.
The pathology is diagnosed not only by an endocrinologist or diabetologist, but also, depending on the symptoms, by a cardiologist, gastroenterologist, neurologist and other specialists. The primary study of the cardiac and vascular system involves performing an ECG, echocardiography, as well as identifying cholesterol and lipoproteins.
It is strongly recommended to pay attention to the fact that the diagnosis and treatment of polyneuropathy may include:
- electrophysiological studies - electromyography, electroneurography and others;
- assessing reflexes and various types of sensory sensitivity;
- performing a biopsy of the sural nerve and skin. However, this is resorted to in atypical forms of the disease;
- a number of gastroenterological examinations: ultrasound of the peritoneal organs, endoscopy, radiography of the stomach.
If a patient has complaints about the urinary system, we are talking about conducting a general urine test, ultrasound of the kidneys, bladder, internal urography and a number of other checks. Only after this will it be possible to talk about the beginning of a rehabilitation course.
Liver cirrhosis due to diabetes mellitus
Symptoms
The most common type is the distal symmetrical sensory form of polyneuropathy. The disease develops several years after the patient is diagnosed with the underlying pathology – diabetes. Typically, symmetrical sensorimotor polyneuropathy develops at a slow pace and is represented by a chronic type of disease according to the classification according to the course of the pathology.
The first symptoms of diabetic polyneuropathy are paresthesia and numbness. These sensations occur in the lower extremities, usually symmetrically, but can affect only one foot. In 15% of patients, the disease manifests itself as a chronic neuropathic pain syndrome due to a neurological deficit. Damage occurs to unmyelinated fibers and those with a weak myelin sheath. These are mainly thin nerve endings.
Damage to the fibers is accompanied by severe discomfort. Patients experience unbearable shooting and burning pain. It feels like your legs are tingling and you have goosebumps crawling over them. Hyperalgesia develops, in which the body has increased susceptibility to pain.
IMPORTANT! Temperature sensitivity is impaired, and ulcers of various sizes appear on the feet.
Patients complain of pain caused by both irritants and spontaneous pain that appears against the background of absolute calm and the absence of external stimuli. This pain is called allodynia. With damage to thick nerve fibers that have a myelin sheath, deeper sensory disturbances occur and tendon reflexes decrease.
Along with such disorders, autonomic abnormalities also develop; not all of them are recognized during the diagnostic process. Autonomic diabetic polyneuropathy is considered the most dangerous for the patient. According to the leading pathology syndrome, there are:
- cardiac;
- urogenital;
- gastrointestinal;
- trophic neuropathy.
Frequent manifestations of the disease in patients are bladder dysfunction associated with sphincter insufficiency and atony of the bladder itself. Patients have frequent diarrhea, especially diarrhea at night. Men suffer from impotence.
Patients develop orthostatic hypotension, and tachycardia is observed in cardiac function. The feet and joints swell, the skin suffers from lack of moisture and becomes dry. Typically, such signs indicate the development of cardiac neuropathy - the most life-threatening. Once diagnosed with cardiac neuropathy, statistically, from 25 to 50 percent of patients die within the first ten years of the development of the pathology.
Patients with diabetic polyneuropathy experience a fixed pulse phenomenon.
Impaired heart function and failures of sympathetic and parasympathetic control of the organ’s activity lead to the phenomenon of a fixed pulse in diabetics. As studies show, during physical activity: running, squatting, fast walking, patients’ heart rate does not change, as happens in a healthy person in response to physical activity.
Orthostatic hypotension also causes problems for patients. The problem is a violation of vascular tone due to improper functioning of the nervous system. Patients have reduced blood pressure, sometimes to critical levels, especially when standing for a long time or when getting out of bed. This is associated with frequent patient complaints of dizziness.
A complication of cardiac neuropathy in diabetes is a denervated heart. This symptom, characteristic by name, clearly reflects problems in the functioning of the organ. Because of this, patients often have painless “silent” heart attacks and arrhythmias, causing sudden death.
Stages
The disease occurs in stages, of which there are four. At stage zero, the patient has no symptoms or signs of polyneuropathy, tests show negative results, and electroneuromyography of peripheral nerves does not reveal any abnormalities.
IMPORTANT! Although stage zero is not characterized by obvious manifestations of polyneuropathy, it is already the first, hidden stage in the development of pathology in patients with polyneuropathy.
The first stage of the disease is called subclinical. At this stage, two variants of the course of the disease are distinguished. In the first case, patients may not express complaints and neurological changes are not diagnosed in them, however, electroneuromyography or autonomic tests may be positive. The second variant of the course of this stage also passes without complaints from the patient, but there are already two or more neurological signs of pathology.
The second stage of the disease is clinical. Patients express typical complaints, including numbness and burning in the limb, paresthesia and pain. Neurological abnormalities are present, but not necessarily present. In the second variant of development, which is more progressive, patients can no longer stand on their feet or rest on their heels, since motor fibers are involved in the pathological process.
The third stage of the disease is characterized by the most severe symptoms that worsen the patient’s situation. Patients with diabetes mellitus already develop diabetic foot, there is orthostatic hypotension, and severe pain.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of diabetic polyneuropathy of the lower extremities begins with collecting anamnesis and visual examination of the lower extremity. Patients are given special questionnaires, where patients evaluate their sensations using a scale and describe the signs of polyneuropathy.
Typically, patients find it difficult to correctly describe their sensations, so doctors ask leading questions. Paresthesia and allodynia are already present among the complaints of patients. Symptoms manifest themselves symmetrically.
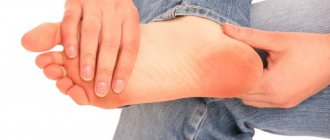
When visually examining the foot, it is important to determine the characteristic signs inherent in polyneuropathy. In patients, the skin on the feet becomes dry and thin, and the disease affects the upper extremities indirectly. Areas of hyperkeratosis, calluses and corns are noticeable. Ulcers may be visible on the soles, sides, and toes. The toes are deformed and there is muscle atrophy.
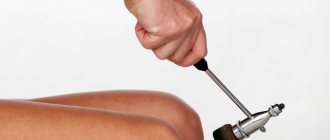
Among all diagnostic methods, neurological examination gives good results. Its purpose is to determine the sensitivity threshold of various surfaces. Reflexes are assessed and the strength of different muscle groups in the legs and arms is assessed. The indicator of vibration sensitivity is very important, since in some cases it may be the only sign indicating the early development of polyneuropathy.
The sensitivity threshold is assessed using a tuning fork. Tactile sensitivity is determined by monofilament. And the patient’s reaction to pain, temperature stimulus and tendon reflexes is also examined.
Electrophysiological examination methods are effective in diagnosis. These are non-invasive and fairly objective research methods, in which you can assess the severity of the pathology, the progression of the disease, form an idea of the structure of the nerve fibers and assess the nature of the damage to the nerve endings. Electrophysiological examination allows one to differentiate diabetic polyneuropathy from other types.
And skin biopsy and detection of damage to unmyelinated fibers are also used. At the same time, a nerve biopsy is performed. Based on research results, comprehensive diagnostics makes it possible to identify signs and determine the distal type of the disease.
Diabetic distal polyneuropathy
The longest nerve fibers in the human body are located in the legs. Damage to them in any area means loss of nerve function, so polyneuropathy is most often distal, localized in the lower extremities. The most serious changes are observed in the so-called “toe area” - on the feet and ankles. First of all, tactile, temperature, and then pain sensitivity are impaired.
Additionally : Swelling of the legs due to diabetes - how to get rid of them?
Subsequently, changes begin in the muscles, as a result of which the appearance of the foot changes - the toes bend and overlap each other, the arch flattens. Skin that is deprived of sensitivity becomes an excellent target for various injuries, which, due to concomitant nutritional disorders and the outflow of metabolic products, gradually cease to heal, forming trophic ulcers. Constant local inflammation destroys bone tissue. As a result, distal polyneuropathy can turn into gangrene and osteomyelitis with loss of the ability to move independently.
Diabetic polyneuropathy of the lower extremities at the initial stage has symptoms such as numbness, tingling, heaviness in the feet at night, the inability to feel a light touch, a constant feeling of coldness in the toes, decreased sweating on the feet or, conversely, constantly moist skin, peeling and redness in places friction.
Treatment
Treatment of diabetic polyneuropathy is extremely complex, since it is necessary to influence not only the manifestations of the disease, but also the pathogenetic mechanism of the appearance of polyneuropathy itself. The disease cannot be eliminated with folk remedies, so it is definitely necessary to contact the clinic for professional help. Doctors select the most effective treatment methods for patients, but not all of them are equally effective in patients.
Diabetic foot is a major problem faced by doctors and patients.
Not the least attention is paid to eliminating pain, because pain significantly worsens the quality of life of a patient already suffering from symptoms of diabetes. For the treatment of neuropathic pain, patients are prescribed anticonvulsants - these are Pregabalin, Gabapentin, Carbamazepine, drugs with valproic acid, as well as antidepressants - Venlafaxine and Duloxetine. At the same time, these drugs only affect the clinical manifestations of the pathology and are not able to influence the pathogenetic mechanism.
Patients are prescribed vitamin preparations, especially with vitamin B. Preparations with benfotiamine Milgamma, Thiogamma have a good effect. With the development of diabetic foot, it is necessary to treat the patient with rheological drugs, anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents.
It is important to properly treat wounds on the legs, constantly clean the wound from accumulated discharge and carry out open treatment. The surface must be cleaned with special solutions; after washing, antibacterial ointments are used. The prognosis in most cases is unfavorable, however, much depends on the time of treatment of the patient and the severity of the underlying disease - diabetes, which cannot be cured, but its manifestations can be minimized as much as possible.
Treatment methods for diabetic polyneuropathy
Treatment of diabetic polyneuropathy must be gradual and consistent. First of all, this will be impossible without compensation for diabetes itself. Thus, diabetic polyneuropathy begins to be cured precisely by normalizing blood sugar levels. Endocrinologists point out that pathology can be cured using various medications, physical therapy methods and other types of interventions.
Experts point out that figuring out how to heal legs is much easier at the initial stage of the disease. That is why it is advisable to start drug and other types of therapy at the first symptoms for everyone who is at risk.
Medications
If a patient is diagnosed with type 1 diabetes, the sugar level is adjusted by selecting insulin therapy. For the second type, you should use sugar-lowering drugs available in tablet form. In the future, treatment of diabetic polyneuropathy of the lower extremities can be carried out using the following medications:
- lipoic, or thioctic, acid - Berlition, Dialipon and others;
- Trental, or Pentoxifylline, which helps reduce platelet sedimentation. Another effect should be considered improvement of microcirculation;
- Vazaprostan - ensures expansion of peripheral vessels, minimizes the likelihood of blood clots settling on the walls of blood vessels;
- various antibiotics and antiseptics that are used in the presence of ulcers.
Drug therapy is far from the only means of treating diabetic polyneuropathy. However, in the vast majority of cases, it is this technique that is the basis of the recovery course. It is also recommended to take neurotropic vitamins (category B), antioxidant components (alpha-lipoic acid, vitamin E) and microelements (Mg and Zn preparations). In case of pain, it makes sense to use analgesics and special anticonvulsants.
Physiotherapy
Diabetic neuropathy can be treated through physical therapy techniques. Most often we are talking about warming up the feet with a gentle massage and the most common warm socks. It should be noted that the use of heating pads, open flames or, for example, hot baths is contraindicated. In addition, the patient is advised to wear specialized orthopedic insoles to provide unloading of the foot.
Symptoms, classification, treatment of diabetic nephropathy
When wounds form, it is mandatory to treat them with an antiseptic followed by the use of certain materials. We are talking about moisture-absorbing and dressing materials. Another method is exercise therapy, which involves performing exercises for at least 10 minutes throughout the day. It is very important that the elements are previously discussed with a specialist. It is in this case that physical therapy will be most beneficial and will not be associated with complications.
Non-drug therapy
Treatment of diabetic polyneuropathy will be complete through the introduction of a special diet and determination of a physical activity regimen for the purpose of weight loss. It is very important for patients to daily monitor the current condition of their feet and how comfortable and “correct” their shoes are. It is important to exclude the possibility of developing calluses and corns, because this is fraught with complications.
Treatment with folk remedies can only be carried out after consultation with a specialist.
It is also important that such therapy is perceived as an addition to treatment, and not the main rehabilitation course. It is permissible to periodically perform foot baths and prepare creams yourself from proven ingredients. This will improve the condition of the skin and normalize the process of blood flow.
The most important
Diabetic polyneuropathy is a complex metabolic disorder that develops against the background of diabetes mellitus and affects nerve fibers. Due to the destruction of the myelin sheath in patients, nerve conduction suffers, which seriously disrupts tissue trophism.
The result of this is various disorders, primarily in the distal sections. Diabetic foot is the main complication that diabetics have to deal with. It is difficult to make predictions, since much depends on the underlying disease. At the same time, treatment of the disease is extremely complex and does not always bring the expected results, and sometimes leads to disability and even death.
Causes of polyneuropathy
Diabetic polyneuropathy develops during a long course of diabetes mellitus, when vascular disorders occur due to a constant deficiency of insulin and elevated levels of glucose in the blood. The mechanism of metabolic processes in cells and tissues also changes, which leads to disruption of the peripheral nerves.
As a result of oxygen starvation of nerve fibers and a decrease in the concentration of nitric oxide, blood supply deteriorates and the function of nerve fibers is disrupted.