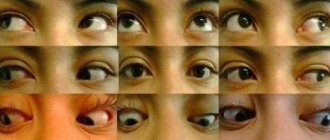
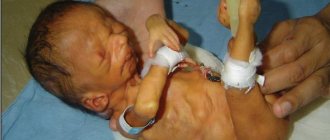
Why does the symptom of the setting sun have such a poetic name? Because the white of the eye is like the sky - especially if the eyes are blue-rimmed, while its center is the cornea and iris with a flat well of the pupil, in this small-scale sky they are very reminiscent of the sun.
And this “sun” is almost always in, with the exception of a rare “glancing” to the side or a mannered rolling of the eyes upward at the moment of particularly “juicy” sensations.
But sometimes there come moments when the “sun” noticeably leans toward the “horizon” of the lower eyelid, moving downward and partly inward, leaving above it an unnaturally wide strip of sclera usually covered by the upper eyelid.
However, the “sun” cannot completely set behind the lower eyelid, because this is impossible for purely biological reasons - the muscles that rotate the eyeball in different directions have a length and limit of contractility, so none of them will “pull” their “counter” ” – a muscle with opposite intentions.
But the “eye-turning” muscles do not work on their own; they are executors of someone else’s “higher will”, emanating from the nuclei of the oculomotor and trochlear nerves (III and IV pairs of cranial nerves), located in the bottom of the III ventricle of the brain.
Pathogenesis of the symptom
And the processes in the third ventricle, which is part of the liquor-conducting system, sometimes occur strange and unnatural, and it can become unusable for a variety of reasons.
Take, for example, hydrocephalus - dropsy of the brain. More precisely, a case caused by the causes of increased intracranial pressure. Yes, not abstract, but concrete, associated with the area of the aqueduct in the midbrain and its bridge, because it is near its bottom that the nuclei of the oculomotor nerves are located, and it is compression of the brain stem that leads to a disorder of their function.
This same area becomes problematic when:
- hemorrhage in the intraventricular area;
- hydrocephalus of posthemorrhagic origin;
- nuclear jaundice.
There are other nervous pathologies, including both functional and organic disorders, developing both in the area of exits and the routes of the III and IV pairs of cranial nerves - both in the form of isolated and combined lesions.
But it is precisely with hydrocephalus that the setting sun syndrome manifests itself most often and most clearly, which allows it to be used as a diagnostic criterion of a neurological nature.
This pathological sign can also arise from a man-made, surgical intervention - the creation of a ventriculoperitoneal shunt, which should eliminate the consequences of hydrocephalus of post-hemorrhagic etiology. In this case, if there are no other organic lesions of the brain stem, the symptom gradually disappears over time.
Symptoms of Graefe's condition
Graefe syndrome can manifest itself in a significant set of symptoms confirming the presence of this condition:
- The most important factor indicating this disease is considered to be nystagmus - involuntary motor activity of the child’s eyes. It can occur involuntarily, be characterized by large amplitude, constancy, and high repeatability of movements. Movements can occur both during active interaction with the child, and at a time when the baby is at rest. When the eyes move, a strip of the eye white located above the iris may be visible; the movements themselves begin spontaneously and can last quite a long time or almost constantly.
- Blueness of the baby's fingers and toes and skin near the baby's nose and lips. This symptom requires immediate intervention from the attending physician, since in most cases it indicates serious diseases of the baby’s heart and blood vessels.
- Marbling of the skin. The occurrence of this symptom also indicates a disruption in the blood supply and the presence of problems with the vegetative-vascular system.
- The natural process of heat exchange in the baby’s body is disrupted.
- There is increased breathing, and breathing may also be shallow.
- Contractions of the heart muscle occur with excessively high repeatability, and it can be very difficult to listen to the beating of a child’s heart.
- Oblique position of the child's body. Sometimes children with Grethe syndrome may also experience incorrect positioning of the torso. In this case, the baby’s head may turn clearly in the opposite direction from the hemisphere of the brain in which there are any disorders.
- A general decrease in muscle tone or convulsive phenomena.
If the child’s condition is complicated by impaired respiratory or cardiac activity, or convulsive phenomena, contacting a doctor should be done as an emergency.
"Setting Sun" of newborns
Being a frightening phenomenon for parents, Graefe's symptom (the second name for the setting sun symptom, not to be confused with Graefe's syndrome), which appears in the first months in newborns, can go away completely without consequences when the child's nervous system reaches the proper level of maturity.
The symptom of “surprisedly swollen” eyes can be not only a consequence of intrauterine growth retardation or prematurity, but also a feature of the child’s constitution, and therefore persist into adulthood.
The need for especially careful observation and, if necessary, treatment arises with diagnostically confirmed hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome, although cases of its diagnosis in pediatric medical practice are not uncommon.
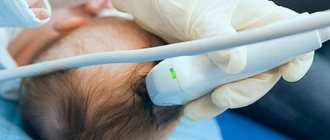
Modern methods of diagnosis can help in difficult cases in the form of:
- neurosonography;
- MRI of the brain.
Reasons for the development of the disease
The condition we are considering in some cases can occur in infants who are in quite good health. This is due to the fact that the first time after birth, the baby’s nervous system actively adapts to the changed conditions. In the absence of any disease, this symptom will most likely disappear within a few weeks or months after birth. In babies born prematurely, Grete's symptom may persist for a longer time. It also happens that this condition is caused by a congenital feature of the baby’s eyes.
Grethe syndrome, in most cases, is congenital. If the disease is acquired, it can manifest itself at any age. Acquired Grete syndrome can be caused by traumatic brain injury, dehormonization of metabolism, infection of the body with infectious pathogens and some other reasons.
In newborns, this syndrome most often appears for the following reasons:
- difficult childbirth;
- prolonged pregnancy or premature birth of a baby;
- infectious diseases suffered by the expectant mother during pregnancy;
- chronic diseases of the mother;
- heredity.
In these cases, immediately after identifying the syndrome, the baby will be registered with a pediatric neurologist for further monitoring of the development of the disease.
It is worth clarifying that if an uncharacteristic position of the eyes is noted during active interaction with the baby, then most likely, over time, the disease may go away on its own. However, if the condition persists long after birth, the syndrome is most likely due to high intracranial pressure. In this case, leaving the child without treatment is highly not recommended.
How to Test a Patient for a Symptom
If in a pronounced case the symptom is easily observed in a calm state, then in a doubtful case, “sunset” is especially indicative when rotating the head with the eyes following an attractive object.
The gaze cannot fixate on an object slowly moving downwards, and the eyes periodically “float” down and partly inward, exposing a strip of sclera of inadequate width.
The combination of a positive test with nystagmus and convergent strobism should be the reason for a more in-depth neurological study.
Which doctor treats Grette syndrome?
Even if the baby was diagnosed with this syndrome, in most cases, this should not cause unnecessary worry. After all, if the syndrome is expressed only in the incorrect position of the eyes and is noted soon after the birth of the baby, in most cases, this condition goes away on its own without medical intervention. However, if this illness does not go away for a long time and additional painful symptoms are added to it, you will have to start treatment with a pediatric neurologist. The attending physician may undergo a comprehensive examination of the child, which may also include an ultrasound of the baby’s brain. After receiving the results of the examination, the doctor will be able to draw conclusions about the severity of the disease and prescribe treatment appropriate to the child’s condition.
It is extremely important for parents to ensure that the recommendations received from the doctor for treating the baby are carried out in full. You should not interrupt the course of treatment immediately after the child’s condition improves, because the removal or weakening of symptoms does not mean recovery.
Depending on the general condition of the baby, the severity of existing symptoms and the effectiveness of the prescribed treatment, the doctor can decide whether to admit the child to the hospital, or whether treatment can be continued at home. Of course, disturbances in cardiac and respiratory activity, as well as increased intracranial pressure, are very dangerous conditions that threaten the life of a child. However, it must be remembered that Graefe syndrome does not always indicate the presence of any serious illnesses. Therefore, when treating this disease, it is extremely important to strictly follow the recommendations of the attending neurologist, without underestimating or exaggerating the severity of your child’s condition.
Graefe's sign in infants
In this part, I want to tell you a little about the so-called hypertension syndrome - a syndrome of increased intracranial pressure. This is a rather painful topic. Because in Russia with this diagnosis in children under 1 year of age there is a complete bacchanalia. After consultation, pediatric neurologists very often make this diagnosis for children under 1 year of age with various manifestations, especially when some changes are detected during a neurosonographic (NSG) study.

I want to say right away that regurgitation, trembling of the chin (tremor), standing up of the child while leaning on his tiptoes, restlessness and screaming are not signs of hypertension syndrome in a child under 1 year of age. Very often, when Graefe’s symptom is detected (a lag of the upper eyelid from the iris when fixating the gaze on an object slowly moving downwards, while a white strip of sclera remains between the upper eyelid and the iris - it looks as if the child is “surprised”), a diagnosis of hypertension syndrome is made . It is not right.
Graefe's symptom can be observed in children as a sign of immaturity of the central nervous system. And maybe even in adults due to the peculiarity of facial expressions. I saw a ten-year-old boy who had been diagnosed with Graefe's symptom since birth. And his pediatric neurologist treated him for intracranial pressure. Just awful. By the way, this syndrome can occur in children and adults with a disorder of the thyroid gland - hyperthyroidism. Also, Graefe's symptom can be observed with increased intracranial pressure, but there must be other clinical and instrumental evidence.

Often, after performing an NSG on a child, pediatric neurologists note that there is enlargement of the ventricles (cavities in the brain) and make a diagnosis of hypertension syndrome. Not every expansion of the ventricles of the brain can be a sign of increased intracranial pressure. Or it may be that the child’s blood pressure test is normal, but there are signs of hypertension syndrome. Once again, I want to say that such a syndrome occurs, but much less frequently than it is diagnosed by pediatric neurologists in children under 1 year of age in Moscow in particular, and Russia in general.
Answering questions from people on various websites, they often write to me about neurosonography data (NSG - ultrasound of the brain) and ask me to comment and prescribe treatment from a pediatric neurologist in the office or at home. NSG data must always be correlated with a specific child. And treat a specific child, and not NSG data. Neurosonography is an auxiliary examination in diagnosis to clarify the disease.
The article uses photographs of Anna Geddes.
Author: Voronov Igor Anatolyevich, pediatric neurologist of the PreAmbula network, candidate of medical sciences
Cost of seeing a neurologist:
Primary 1750 rubles, Repeated 1550 rubles.
How to reduce the cost?
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT PRICES
Treatment
Treatment methods for Graefe syndrome depend on diagnostic results; neurosurgeons, neurologists and ophthalmologists are involved in eliminating the disease
If Graefe's symptom in a newborn does not have accompanying pathologies, then it does not require specialized treatment. The problem goes away as the child grows up if the following recommendations are followed:
- correct daily routine;
- careful personal hygiene;
- the child should be fed upon request;
- professional massage.
All this helps to quickly strengthen the baby’s nervous system.
If a baby is diagnosed with Graefe syndrome (and not just a symptom), the pathology will be treated by the following specialists:
- neurosurgeon;
- neurologist;
- ophthalmologist.
The disease can only be overcome with an integrated approach. As a rule, Graefe syndrome in newborns is treated in specialized neurological centers.
Drugs
Drug therapy is based on the use of the following drugs:
- Diuretics. The action of these medications is based on removing excess fluid from the body. The most famous representative of drugs in this group is Furosemide.
- Nootropics. They optimize the activity of the central nervous system, normalize neurometabolic processes occurring in the brain.
- Multivitamin complexes that provide support for the body. The most famous representatives of the group are drugs such as Milgamma and Combilipen.
- Drugs to improve vascular tone and normalize cerebral circulation - Curantil, Actovegin.
- Sedatives – Diazepam, Tazepam.
- Antiviral drugs and antibiotics (if necessary).
Medicines are selected by a doctor who focuses on the patient’s age and the causes of the pathology
Not only health depends on the results of therapy, but the possibility of a full life for the patient is selected by the doctor, who focuses on the patient’s age and the causes of the pathology
If a patient experiences a severe attack of the syndrome, he needs emergency treatment. As a rule, it involves a dehydration procedure. To do this, intramuscular injections of the drug Lasix or its analogues are performed.
Physiotherapy
The following procedures help stabilize the patient's condition:
- acupuncture;
- exercise therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- magnetotherapy.
Surgery
If conservative treatment of Graefe syndrome is ineffective, surgical intervention is used to improve the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid from the skull. Surgical treatment options:
- bypass;
- ventricular or lumbar puncture;
- endoscopic surgery.
ethnoscience
Folk remedies can significantly improve the patient's condition. However, these prescriptions should not be considered as full-fledged treatment - they only improve the effectiveness of official medicine.
The most popular treatments for Graefe syndrome are:
- Tincture of mint leaves with the addition of eucalyptus essential oil and hawthorn fruit.
- Infusion of nettle and string.
- Mulberry decoction.
- A decoction of dry or fresh plantain leaves.
Eating foods such as garlic and lemon can significantly alleviate the patient's condition.
The above means help normalize intracranial pressure. They effectively combat the manifestation of pathological symptoms. However, before taking traditional medicines, it is necessary to consult a specialist. He will certainly be able to offer the most effective and safe methods.
Causes of the disease
There are two types of Graefe syndrome:
- symptoms appear when the child’s body position changes;
- symptoms appear systematically, regardless of the child’s movement and position.
In the first case, the disease should go away on its own within two to three months. Its occurrence is associated with defective development of the nervous system.
In the second case, it is necessary to urgently contact a specialist to conduct several tests, studies and further prescribe treatment.
Good to know: the development of the syndrome is caused by the difficult course of labor in which the baby was injured. Its manifestation may indicate the presence of intracranial birth injury, cerebral edema, intracranial hypertension and intracranial hemorrhage.

Also, the causes of the disease may be:
- untimely birth;
- infectious and chronic diseases of the mother during pregnancy;
- hereditary predisposition.