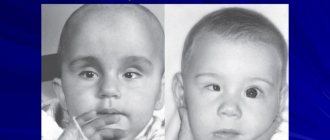
Hyperpigmentation affects everyone. For some, these are moles or nevi, for others, pigment spots located on various parts of the body. Such “marks” appear in children at birth or in the first year of life, have varying degrees of intensity, and require at least a consultation with a dermatologist. Any coffee stains on the baby’s skin are a signal to the mother about the need to observe them, monitor deformation and color changes. How dangerous is excess pigmentation?
Causes of appearance on the skin of a child
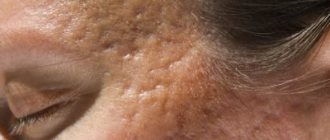
Coffee pigmentation occurs in 20% of the world's inhabitants. The formation is benign, has a pronounced uniform color and structure, a smooth surface, the boundaries are not blurred, increases in size in accordance with the growth of the child, and occurs with equal frequency in children of both sexes. In the dark-skinned population, pigment metabolism disorders are diagnosed more often than in people with fair skin.
Histological examination of the material shows an increased content of melanocytes in the skin, which produce more melanin compared to non-pigmented skin. The color of the spots varies from pale brown to tan. The darker the area, the greater the accumulation of cells in this place, responsible for the production of pigment that colors the skin in its usual shade.
Spots can be visualized on all parts of the body, but are absent on the mucous membranes. The formation does not pose any danger even if the skin is damaged, has a low risk of malignancy, and is purely a cosmetic defect. The tendency to form age spots is transmitted genetically.
Classification
The division of neoplasms depending on the presence of a clearly limited tumor border divides the pathology into:
- encapsulated neurofibroma - characterized by the fact that it is formed in large neural trunks, and the capsule of formation is the membrane of the nerve bundle. Against the background of disorderly growth of neurofibers, a transformation of the nerve is observed - it becomes spindle-shaped. The most common location is the mediastinum, retroperitoneal cavity and soft tissues. In appearance, it is a dense knot with clear outlines, a uniform structure and a grayish-white tint. The volume of such a tumor can reach 4 centimeters;
- diffuse or plexiform neurofibroma - formation occurs in small nerves in the form of many small nodules that do not have a clear boundary. It can be localized both subcutaneously and subcutaneously; it is extremely rare in the axillary space.
According to its histological structure, neurofibroma can be:
- myxoid - the tumor contains a large amount of mucin;
- tactile - based on structures similar to tactile bodies;
- plexiform - based on many nerve bundles consisting of matrix, collagen fibers, basophils and mucin;
- pigmentary - expressed externally and has the appearance of dermatofibrosarcoma.
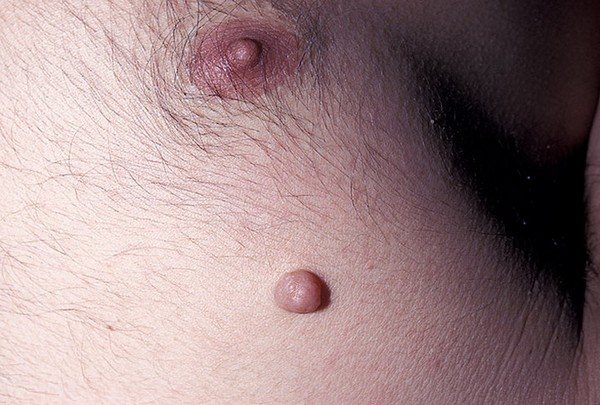
Neurofibroma on the skin
In addition, there are several options for the course of such a pathology:
- Type 1 - has the appearance of pigment spots. It can be either congenital or acquired. They often form in the armpits and inguinal folds. As a rule, it is multiple in nature;
- Type 2 - characterized by minimal clinical manifestations. Neurofibromas are formed in only 19% of patients; in other cases, the presence of pigmented neoplasms is noted;
- Type 3 - expressed in the presence of tumors in the central nervous system and is most often diagnosed in the age category from 20 to 30 years;
- Type 4 - characterized by the presence of a large number of skin neurofibromas;
- Type 5 is a segmental lesion of the skin or soft tissues;
- type 6 - there is a complete absence of tumors, only pigment spots are detected;
- Type 7 - in such cases, neurofibromas appear in the age category over 20 years.
Is it dangerous to appear
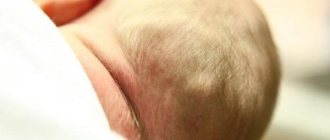
Cafe au lait stains on a child do not cause discomfort to a newborn baby. Pigmentation sizes range from a few millimeters to 20 centimeters. Single cases do not require a biopsy; laboratory diagnosis is recommended when there is a possibility of a systemic hereditary disease.
Treatment of coffee stains in a child is carried out if it is necessary to eliminate pigment in the baby on visible areas of the body. Several round-shaped neoplasms up to 4 cm in diameter are not a pathology and are factors that require the attention of a doctor. When visiting a medical facility for the first time, the doctor collects an anamnesis:
- age of appearance of pigmentation in a child;
- whether there is a delay in physical and intellectual development;
- whether the child has photosensitivity, whether he has taken medications that promote photosensitivity;
- whether the patient has had multiple fractures or tumors;
- presence of disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system;
- curvature of the spine, lower leg bones;
- eye pathologies.
The main method of treating coffee stain birthmarks is laser therapy; laser treatment of infants is not advisable unless there are complaints from the patient. In some cases, cryodestruction (liquid nitrogen) or surgical intervention is allowed; such methods are traumatic and can leave scars. Before laser exposure, the patient is tested on a limited area of the body to check the effectiveness of the effect and prevent hyperpigmentation. Despite the achievements of modern medicine, coffee stains after laser removal can recur; defects in half of the patients respond to treatment.
Relapses are observed 6-12 months after laser therapy; in certain cases, slight lightening of the spot is the maximum achievable therapeutic result. Local treatment with lightening creams does not give the desired effect, despite the fact that the phenomenon is superficial. The laser is contraindicated for dark-skinned and tanned patients.

What diseases may this indicate?
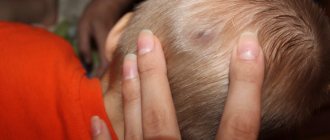
Cafe-au-lait spots on a child’s body, if there are more than 6 of them, require consultation with a dermatologist and geneticist. The presence of coffee stain birthmarks may be a sign of neurofibromatosis - a genetic disease characterized by the appearance on the body of multiple spherical flesh-colored tumors - neurofibromas, protruding above the skin level, having a diameter of up to 1 cm. The disease occurs in one case in 3300, the type of inheritance is autosomal dominant.
There are several types of the disease, united under the general name - neurofibramatosis, which give a reaction from the nervous system and skin. A common type in children is neurofibramatosis type I, another name for which is Recklinghausen's disease, described in 1882.
If neurofibromatosis is suspected, a child is prescribed a genetic test to identify mutations in the NF1 gene on 17q, the chromosome responsible for the development of the disease. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, the patient requires constant monitoring. The appearance of the first nodules occurs before the age of 10 years; if the disease has not manifested itself before this age, then there is no need to worry about neurofibromas in the future. The course of the disease is individual for everyone and may be accompanied by:
- Stunted growth.
- Macrocephaly, seizures.
- Difficulty in mastering new information, delayed speech development.
- Problems in neurology: behavioral deviations, hyperactivity.
- Freckles in the armpits and genitals.
- Lisch nodules on the iris.
- Tumors of the optic nerve, spinal cord, and brain.
To make a diagnosis, the presence of several signs is required, since each of them separately does not signal the disease. The presence of coffee stains on a child’s body does not mean neurofibramatosis, just as their absence does not indicate the impossibility of this diagnosis. Treatment is symptomatic, aimed at relieving pain in the late stages of the disease when multiple tumor nodules form before removing the tumors using hardware techniques or surgery. Early diagnosis and prescribed therapy guarantee that the disease will not reach the stage of formation of skin tumors - neurofibromas. The risk of tumors degenerating into a malignant formation is low, amounting to no more than 5% of precedents. There is no connection between the number, size of spots and the severity of the disease. The disease worsens during pregnancy and increases the risk of developing arterial hypertension and spontaneous abortion.
Multiple coffee spots on the skin may be manifestations of other systemic genetic abnormalities:
- tuberous (lumpy) sclerosis;
- Bloom's syndrome;
- McCune-Albright syndrome;
- Russell-Silver syndrome;
- Watson's syndrome;
- Westerhof syndrome.
The disease is differentiated visually by the type of neoplasm and accompanying symptoms.

Treatment
Given that neurofibroma often has a benign course, treatment is based on symptom relief with the help of appropriate medications prescribed individually for each patient.
However, in some situations, a tumor can transform into a malignant one, as indicated by the following signs:
- progression of nervous system disorders;
- the addition of severe pain;
- merging of adjacent formations or age spots;
- gigantic size of neurofibroma.
Cosmetic discomfort may also be an indication for surgery.
Surgical treatment is aimed at:
- performing an open operation, i.e. excision of large tumors;
- the use of minimally invasive techniques, namely enucleation, diathermoregulation, cryodestruction or exfoliation of single neurofibromas.
To consolidate the positive effect of medical intervention, a course of chemotherapy is necessary.
Komarovsky’s opinion on removing coffee stains from a child’s skin
The World Health Organization does not consider coffee pigmentation on the skin to be a basis for making any diagnosis. The International Classification of Diseases ICD-10 assigned code L81.3 to this type of stain. The presence of moles, warts or coffee stains on a child’s skin, according to Dr. Komarovsky and other pediatricians, does not require removal if the defects do not cause discomfort to the little patient. If they are located on the face, hands and other open areas of the body, cause complexes, and are constantly exposed to sunlight, they should be removed. From childhood, the child should be observed by a dermatologist, ophthalmologist, and neurologist in order to notice the development of pathology in time and prescribe the necessary examination. Consultation with a geneticist is required if there are more than 6 spots on the body with a diameter of 1.5 cm or more. The main recommendation of doctors if there is pigmentation on the body is to protect the skin from ultraviolet radiation.
Other types of pigmentation
- mastocytosis;
- poikiloderma;
- acanthosis nigricans.
Mastocytosis (urticaria pigmentosa) mainly occurs in children and appears as red-pink patches on the body. Over time, these formations turn into blisters with clear liquid or blood inside. When they open, brownish-brown marks remain on the surface of the skin. Urticaria pigmentosa in adults occurs in a more severe form and can be complicated by systemic mastocytosis.
Poikiloderma is accompanied by the appearance of dark spots and atrophy of the skin. It can be congenital or acquired and occurs on the upper and lower extremities, in the face or neck. The disease causes increased sensitivity to ultraviolet rays and occurs with redness and swelling of the tissues.
The cause of this pathology is:
- endocrine disorder;
- skin irradiation;
- muscle tissue diseases;
- oncological tumors.
Acanthosis nigricans leads to the formation of black or brown spots on the surface of the epidermis and occurs in a malignant or benign form. Pigmentation usually occurs in skin folds or elbow areas. Hormonal drugs, hereditary factors, and endocrine disorders contribute to the development of acanthosis.
Acanthosis nigricans in adolescents or young adults usually occurs against the background of endocrine pathology, and for older people such a disease can become a sign of the formation of a malignant process.
When to see a doctor
Since coffee stains on the body are noticeable from birth, the pediatrician’s attention is drawn to them during the first examination. During routine examinations with a neurologist or ophthalmologist, the mother needs to draw the specialists’ attention to excessive coloration of the skin. For additional consultation, you should contact a dermatologist and undergo an examination with a geneticist. If neurofibromatosis is suspected, diagnostic measures include studies:
- Blood vessels for stenosis of the renal or cephalic artery.
- Musculoskeletal system for curvature of the leg bones or scoliosis.
- The endocrine system for hormonal imbalances due to tumor pressure on the optic nerve.
- CT scan or MRI of the brain for further monitoring.
Coffee-colored spots on the body do not pose a health hazard, are benign formations and do not cause pain to the patient. But you need to carefully monitor your skin. Experts recommend regularly measuring the size of pigmentation, photographing it, and recording the dynamics of their development. When exposed to the sun, it is not recommended to cover the pigmentation with patches, so as not to increase the body temperature under it. It is enough to wear light, loose clothing made from natural fabrics.
If a birthmark begins to pigment, inclusions of a different color appear on it, its borders become blurry, jagged, and rapid dynamics in its increase are observed; such a formation requires consultation with an oncodermatologist.