Ways of inheritance of pathology
Hereditary cerebellar ataxia Pierre-Marie is passed on to children from an affected parent. In this case, the probability of having a child with a pathology is 50%. Both girls and boys are equally susceptible to the disease.
If a child is born into a family with such a disease, then in the future he can pass the disease on to his children. The danger of the pathology lies in the fact that at the time of childbirth a person may not even suspect that he is sick. The first signs of Pierre-Marie's cerebellar ataxia appear at a fairly mature age. Healthy children are not carriers of the defective gene and do not pass the disease on to their offspring. This type of inheritance is called autosomal dominant by geneticists.
Diagnosis of Pierre-Marie ataxia
The symptom complex of cerebellar ataxia is identical to the clinical picture of Friedreich's hereditary ataxia. Therefore, difficulties arise when making a diagnosis.
The main difference is the type of inheritance. Dominant inheritance is characteristic of cerebellar Pierre-Marie disease. The recessive form is characteristic of Friedreich's ataxia. The age at which symptoms of the disease appeared is taken into account. Earlier manifestation is characteristic of the autosomal recessive nature of the disease.
The neurologist examines changes in tendon reflexes, which are increased in the cerebellar form of ataxia and decreased in Friedreich's disease. In addition, Pierre-Marie ataxia is not characterized by bone deformities and loss of sensation.
It is very difficult to differentiate multiple sclerosis and cerebellar ataxia. Both diseases are characterized by pyramidal defects of the feet, oculomotor disorders, and neuromuscular motor disorders. However, with multiple sclerosis, as opposed to ataxia, periods of remission are possible. In addition, deep paraparesis and more pronounced pelvic disorders are hallmarks of sclerosis.
Causes of the disease
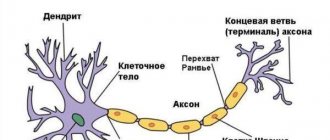
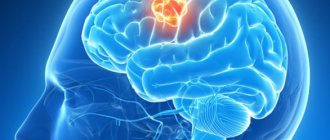
The immediate causes of Pierre-Marie's cerebellar ataxia are pathological changes in the cerebellar cortex and nuclei. This organ in the human body is responsible for the balance of the body and ensures coordination of movements when moving.
In a sick person, the cells of the cerebellum undergo degeneration. As a result, the organ decreases in volume. Other parts of the central nervous system undergo the same changes, for example, the pons, which is responsible for the transmission of spinal impulses. Degenerative processes occur in the medulla oblongata and in the spinal cord pathways. The disease affects almost all body systems responsible for balance and movement of the body.
In the later stages of the disease, the optic nerves are affected, leading to blurred vision.
Differential diagnosis of Pierre-Marie ataxia
Of no small importance in diagnosis is the scrupulous collection of information about the genetic morbidity of immediate relatives and the characteristics of the clinical picture.
Diagnostics involves laboratory and instrumental studies:
- Electroencephalography (EEG). Detects diffuse delta/theta activity and attenuation of alpha rhythm;
- Electromyography. Detects axonal demyelinating disorder of peripheral nerve fibers;
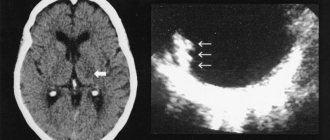
- Magnetic resonance imaging. Records morphological changes in the structures of the spinal cord and brain;
- DNA test. Determines the genetic nature of ataxia;
- Lab tests. Allows you to recognize disorders of amino acid metabolism.
An isolated case in a family of cerebellar ataxia requires a more in-depth examination and differential diagnosis. In addition to the above diseases that have the symptom complex of ataxia, an examination is carried out to exclude a cerebellar neoplasm, abscess or hematoma of the brain, cerebellitis and hydrocephalus.
In case of ophthalmological disorders, examination by an appropriate specialist is required.
To confirm a preliminary diagnosis of familial ataxia, genetic consultation is necessary.
How does the disease manifest itself?
Symptoms of Pierre-Marie cerebellar ataxia usually appear after the age of 30. The following signs of pathology can be identified:
- The disease always begins with a gait disorder. A person is forced to spread his legs wide to maintain body balance. There is noticeable strong staggering when walking; it is especially difficult for the patient to make turns. The patient walks unsteadily and sometimes falls. This is the result of not only a balance disorder, but also poor coordination of movements. In the future, coordination problems are observed not only when walking, but also in a standing position.
- Then hand movements are disrupted. It becomes difficult for the patient to reach the object. The patient often misses the target with his hand. Fine motor skills are difficult. For this reason, handwriting deteriorates, it becomes sweeping and unclear. Tremors of the upper extremities are observed when moving.
- The patient's speech changes. The patient speaks slowly, dividing words into syllables and emphasizing them with stress or special intonation. Neurologists call this kind of speech scanned.
- Facial expressions become poor. The facial expression is frozen, mask-like.
- Very often there is trembling of the eyeballs - nystagmus. Other visual disturbances also occur: drooping of the upper eyelid (ptosis), paralysis of the eye muscles, strabismus, and binocularity disorders. Because of this, a person feels double vision. When the optic nerves are damaged, there is a narrowing of the fields of perception. The patient is not able to see all the objects that are in front of him. Cataracts occur quite often.
- Muscle tone decreases, limbs become weak. Over time, pain occurs in the legs and lower back. Muscle twitching occurs periodically.
- With Pierre-Marie's disease, the human psyche often suffers. At first, difficulties arise in remembering information. Depression often appears. In the future, this leads to a decrease in intelligence. Such signs are not observed in all patients. But in about half of the cases there is a decrease in mental abilities.
This characteristic of Pierre-Marie's cerebellar ataxia suggests that this is a very serious and severe disease. It is steadily progressing. The course of the pathology is aggravated by infectious diseases, mental or physical stress.
Symptoms of Pierre-Marie ataxia
The main symptom of a hereditary disease will be neuromuscular motor disorders that are not limited to a single muscle group or specific movements.
Cerebellar ataxia is characterized by characteristic symptoms:
- gait disturbance;
- static disorder;
- tremor of the limbs and body;
- muscle twitching;
- involuntary frequent oscillatory eye movements;
- slow speech;
- change in handwriting towards a significant increase in letters;
- decreased muscle tone.
Diagnosis of the disease
If signs of ataxia appear, you should consult a neurologist. An external examination of the patient reveals nystagmus and other oculomotor abnormalities. Speech disturbances are noticeable. The doctor performs a finger-nose test: the patient is asked to touch the tip of his nose with his eyes closed. A patient with ataxia usually cannot hit the target. When tapping the tendon with a neurological hammer, increased reflexes are detected.
The doctor may prescribe additional types of examinations to identify the origin of ataxia:
- MRI and CT of the brain;
- Ultrasound of the brain.
The research results show cerebellar atrophy. In addition, the doctor collects anamnesis. It is necessary to clarify whether family members have had similar diseases. This will help to draw a conclusion about the hereditary nature of ataxia.
It is not difficult to identify violations of motor coordination. It is more difficult to separate Pierre-Marie's cerebellar ataxia from other similar diseases.
Ataxia: types, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of pathological condition
Ataxia is a neuromuscular motor disorder characterized by impaired coordination of movements, as well as loss of balance both at rest and when walking.
Inconsistency in the actions of various muscles can arise as a result of damage to certain parts of the brain or vestibular apparatus, which is sometimes due to genetic predisposition.
Treatment of ataxia and the prognosis of its development depend on the cause of the disease.
Types of ataxia
In clinical practice, the following types of ataxia are distinguished:
- Sensitive;
- Vestibular;
- Cortical or frontal;
- Cerebellar.
With sensitive ataxia, deep sensitivity fibers are damaged, which carry information about the features of the surrounding space and the position of the body in it. The cause may be damage to the posterior columns of the spinal cord, thalamus or spinal nerves, as well as polyneuropathy and vitamin B12 deficiency.
Upon examination, the following symptoms of sensitive ataxia are revealed:
- Dependence of coordination on visual control;
- Violation of vibration and joint-muscular sensitivity;
- Losing balance with eyes closed in Romberg pose;
- Loss or decrease in tendon reflexes;
- Unsteady gait.
A characteristic sign of sensory ataxia is the sensation of walking on carpet or cotton wool. In order to compensate for movement disorders, patients constantly look at their feet, and also lift their legs high and strongly bend their legs at the knee and hip joints, and then forcefully lower them to the floor with the entire sole.
In vestibular ataxia, dysfunction of the vestibular apparatus leads to specific gait disturbances, systemic dizziness, nausea and vomiting.
All symptoms intensify with sudden turns of the head and changes in body position. Possible hearing impairment and horizontal nystagmus - involuntary movements of the eyeballs.
This type of disease can be caused by brainstem encephalitis, ear diseases, tumors of the brain ventricles and Meniere's syndrome.
Cortical ataxia is caused by dysfunction of the frontal lobe of the brain as a result of dysfunction of the fronto-pontine-cerebellar system. The cause may be improper cerebral circulation, tumors or abscesses.
Frontal ataxia occurs on the side of the body opposite the affected hemisphere. Instability, bending or falling over begin at turns, and with severe injuries, patients are not able to stand or walk at all. This coordination disorder is also characterized by disturbances in the sense of smell, mental changes and a pronounced grasping reflex.
Features of cerebellar ataxia are loss of fluency of speech, tremors of various types, muscle hypotonia and oculomotor dysfunction. The gait also has characteristic features: patients spread their legs widely and sway from side to side.
In the Romberg position there is extreme instability, often falling backward. A severe lack of coordination of movements occurs during tandem walking, when the heel of one leg is placed against the toe of the other.
Cerebellar ataxia can be caused by a wide range of diseases - from vitamin deficiency and drug intoxication to a malignant tumor.
Hereditary degenerative changes in the cerebellum cause spinocerebellar ataxia - chronic diseases of a progressive nature, which can be of a dominant or recessive type.
The autosomal dominant cerebellar form of the disease is often accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Tremor;
- Hyperreflexia;
- Amyotrophy;
- Ophthalmoplegia;
- Pelvic disorders.
The pathological sign of Pierre Marie's ataxia is cerebellar hypoplasia, less often - atrophy of the inferior olives and pons. The first gait disturbances begin, on average, at 35 years of age. Subsequently, disturbances in facial expressions and speech are added. Mental disorders manifest themselves in the form of depression and decreased intelligence.
Autosomal recessive spinocerebellar ataxia is associated with the following symptoms:
- Areflexia;
- Dysarthria;
- Hypertonicity of muscles;
- Scoliosis;
- Cardiomyopathy;
- Diabetes mellitus.
Friedreich's familial ataxia occurs due to damage to the spinal systems, most often as a result of consanguineous marriage. The main pathological symptom is increasing degeneration of the posterior and lateral columns of the spinal cord.
At about 15 years of age, unsteadiness when walking and frequent falls appear. Over time, skeletal changes cause a tendency to frequent joint dislocations and kyphoscoliosis. The heart suffers - the atrial waves are deformed, the heart rhythm is disturbed.
After any physical exertion, shortness of breath and paroxysmal pain in the heart begin.
Diagnosis and treatment of ataxia
For cerebellar ataxia, the following studies are performed:
- EEG. Reveals reduction of alpha rhythm and diffuse delta and theta activity;
- MRI. Carry out to detect atrophy of the brain stems and spinal cord;
- Electromyography. Shows axonal demyelinating damage to peripheral nerve fibers;
- Lab tests. Allows observation of amino acid metabolism disorders;
- DNA test. Establishes a genetic predisposition to ataxia.
Treatment of ataxia is aimed at eliminating symptoms. It is carried out by a neurologist and includes:
- General restorative therapy - anticholinesterase drugs, cerebrolysin, ATP, B vitamins;
- Exercise therapy complex – strengthens muscles and reduces incoordination.
When treating spinocerebellar ataxia, a course of immunoglobulin may be required to correct immunodeficiency, and any radiation is contraindicated. Sometimes succinic acid, riboflavin, vitamin E and other drugs are prescribed to maintain mitochondrial function.
The prognosis for hereditary ataxia is unfavorable. Working capacity, as a rule, decreases, and mental disorders progress.
Ataxia
Ataxia is a lack of coordination of movements that is not caused by muscle weakness. In this case, the patient is able to perform movements, but there is a lack of coordination.
The result is a violation of most body functions - movement, speech, walking, swallowing, fine motor skills.
Ataxia is not considered an independent disease, but rather a secondary one, since it develops against the background of diseases of the nervous system.
Doctors classify ataxia depending on which area of the brain is affected. There are four forms of the disease in total.
- If the vestibular apparatus is damaged, vestibular ataxia is diagnosed.
- Patients with damage to the frontal or high-occipital region are diagnosed with cortical ataxia.
- Cerebellar ataxia is detected in patients with cerebellar lesions.
- Sensitive - when there is a violation of the conductors of deep muscle sensitivity.
Sensitive ataxia
In most cases, this pathology occurs due to damage to the posterior columns, posterior nerves, peripheral nodes, thalamus opticus, and parietal cortex. Signs of sensitive ataxia can be observed in all limbs at once, or in only one of them. Doctors often diagnose signs of ataxia, which occurs due to a disorder of the joint-muscular sensation in the legs.
Characteristic signs of ataxia will be the patient's instability, excessive bending of his legs at the knee and hip joints.
Many patients often feel as if they are walking on cotton wool or a carpet. Patients try to compensate for walking impairments with the help of vision, as they begin to constantly look at their feet.
Due to severe damage to the posterior columns, patients almost completely stop walking.
Cerebellar ataxia
It occurs due to serious damage to the cerebellar vermis, as well as its legs and hemispheres.
However, it is worth noting that cerebellar ataxia can be a symptom of diseases such as multiple sclerosis, encephalitis, or a malignant neoplasm in the cerebellum or brain stem.
Patients with this pathology usually fall toward the damaged cerebellar hemisphere when walking. During such episodes, even falls are possible.
The patient usually staggers greatly when walking, and also places his legs too wide, his movements are slow, sweeping and awkward. Impaired coordination remains virtually unchanged even with vision control.
Patients may experience serious speech disturbances, which gradually slow down, become scanned and drawn out. There are also problems with handwriting, which becomes uneven and splayed.
Vestibular ataxia
This pathology occurs due to damage to the vestibular nerve, labyrinth, cortical center and nuclei in the brain stem.
This type of ataxia is observed in various ear diseases, brainstem encephalitis, Meniere's syndrome, and tumors of the fourth ventricle of the brain.
The main sign of the pathology is considered to be regular severe dizziness, as a result of which the patient begins to feel as if all objects are moving in the same direction. Turning his head, the patient feels increased dizziness.
Severe dizziness leads to unsteady gait and falls. It is also noticeable that the patient tries to make very careful head movements. Vestibular ataxia is also characterized by symptoms such as vomiting, nausea and horizontal nystagmus.
Cortical ataxia
Cortical ataxia in most cases occurs due to damage to the frontal lobe of the brain. Its most common causes include tumors, circulatory disorders in the brain, and abscesses. In the case of this type of ataxia, symptoms such as unsteadiness when walking, falling over, or bending to the side appear.
Due to severe damage to the frontal lobe, patients may lose the ability to walk and stand. Cortical ataxia is also characterized by other symptoms: mental changes, grasping reflex, impaired sense of smell. In many ways, the clinical picture of cortical ataxia is similar to the symptoms of cerebellar pathology.
Cerebellar Pierre-Marie ataxia
The main manifestation of the disease is cerebellar ataxia. The disease occurs due to hypoplasia of the cerebellum, atrophy of the pons and inferior olives. Typically, the first signs of pathology appear in a patient at the age of 35 years.
The most characteristic symptoms of the disease are considered to be disturbances in gait, speech and facial expressions. In addition, patients usually experience dysmetria, static ataxia, adiadochokinesis, increased tendon reflexes, and decreased strength in the muscles of the limbs. Patients are often diagnosed with oculomotor disorders:
- lack of convergence;
- ptosis;
- paresis of the abducens nerve;
- Argyll-Robertson sign;
- decreased visual acuity;
- narrowing of visual fields;
- atrophy of the optic nerves.
Ataxia-telangiectasia
This type of ataxia is also hereditary and is transmitted in an autosomal recessive manner. Often the first symptoms of pathology appear at a very early age.
The disease progresses very quickly, so at the age of 10 years the child almost completely loses the ability to walk independently.
The pathology may be accompanied by damage to the cranial nerves and mental fatigue.
Familial Friedreich's ataxia
This disease is hereditary and occurs due to damage to the spinal systems. As a result of research, it was found that many patients with this type of ataxia often have consanguineous marriages in their pedigree. The main symptom of ataxia is an unsteady and clumsy gait.
The gradual development of the disease leads to impaired hand movements, problems with facial expressions, slowed speech, and hearing loss. Further development of ataxia leads to changes in the skeleton, heart rhythm disturbances, endocrine disorders, frequent dislocations, and kyphoscoliosis.
Diagnosis of ataxia
- Diagnosis of the disease begins with the collection of complaints and anamnesis.
Namely, the doctor must ask the patient how long ago he began to have complaints about unsteadiness of gait and poor coordination of movements, and how often and regularly these symptoms appear. It is definitely worth checking with the patient whether his relatives have had this disease. It is also necessary to find out whether the patient has taken any medications such as benzodiazepines and barbiturates. - Patients suspected of having ataxia require a neurological examination. This examination involves assessing coordination of movements and gait, assessing strength in the limbs and muscle tone, the presence of nystagmus, and strength in the limbs.
- A correct assessment of hearing will also require an examination by an otolaryngologist.
Laboratory research
Laboratory tests are of great importance in the diagnosis of ataxia.
- Namely, to study signs of poisoning, which could cause a lack of coordination, a toxicological analysis is prescribed.
- A blood test is required, since ataxia may cause signs of inflammation in the blood and an increase in the level of leukocytes.
- The concentration of vitamin B12 in the blood is also determined.
Additional tests
For a more detailed study of the disease, a consultation with a neurosurgeon will be required, as well as a number of instrumental studies.
- In particular, a lot of information about the disease can be obtained using electroencephalography. This technique evaluates the electrical activity of various parts of the brain, which tends to change in various diseases.
- No less effective techniques are also CT and MRI of the brain. They allow you to study the structure of the brain layer by layer, detect violations of the structure of its tissues, identify ulcers, tumors, and hemorrhages.
- Magnetic resonance angiography will help detect tumors in the brain and assess the integrity of the arteries in the skull.
Source: https://storm24.media/news/93954
Differential diagnosis
There are many cerebellar ataxias and other diseases accompanied by disorders of coordination of movements, speech and vision. The doctor needs to make a differential diagnosis of these conditions.
Similar manifestations occur with another hereditary disease - Friedreich's ataxia. But this pathology manifests itself at a younger age. With Pierre-Marie's disease, tendon reflexes are increased, and with Friedreich's ataxia, they are decreased. The type of inheritance of the disease also differs. Friedreich's disease can be transmitted to offspring from completely healthy parents who are carriers of defective genes.
Another similar disease is multiple sclerosis. But this pathology also manifests itself at a younger age. An MRI examination will help distinguish these two diseases. In multiple sclerosis, areas of demyelination of brain neurons will be visible. This is not observed in Pierre-Marie ataxia.
What results can you get by studying F. Belgau's program?
- improved concentration and attention;
- increasing endurance and performance in classes;
- improved hand-eye coordination;
- development of spatial perception and imagination;
- development of motor abilities: reaction speed, dexterity;
- development of all types of memory: visual, visuospatial, sound, figurative, and especially motor and others;
- development of perception of oral and written speech, their automation, which in turn is the basis for the formation and development of one’s own speech and writing skills;
- optimization of rote reading skills;
- development of intellectual abilities;
- development of mathematical and logical abilities;
- development of abilities to plan and control one’s activities;
- harmonization of the emotional-volitional sphere;
- normalization of behavior;
- personal changes.
The most effective is cerebellar stimulation in combination with classes of a speech therapist, psychologist, speech pathologist, or neuropsychologist. Exercises on a balancing board allow you to speed up the solution of correctional problems in speech therapy and psychology.
Is the disease curable?
Today this disease is incurable. It is impossible to select a therapy that would stop the process of degeneration of cerebellar cells. The doctor can only offer symptomatic treatment. The following types of drugs are used:
- Nootropic drugs (“Piracetam”, “Cinnarizine”, “Cavinton”). They improve memory and reduce dizziness.
- Antidepressants are prescribed for mental disorders.
- B vitamins normalize brain function.
These medications are not able to completely cure Pierre-Marie's cerebellar ataxia. They will only help alleviate symptoms and slow down the progression of the disease.
Forecasts and possible consequences
The loss of the ability to coordinate one's actions often results in injuries to the paws and fingers. Head tremors that interfere with chewing food can lead to life-threatening exhaustion. In case of complete paralysis and stable deterioration of health, euthanasia is recommended.
A favorable prognosis is typical for acquired vestibular and sensitive pathologies detected at an early stage. If all neurological signs disappear during treatment, the animal is able to live a normal life again.
Physiotherapy
Patients are prescribed therapeutic exercises to strengthen muscles and improve coordination of movements.
Patients with Pierre-Marie ataxia benefit from balance exercises. First, tasks are performed in a sitting position. This could be training precision movements, turning the body, lifting and moving objects. Gradually, the exercises become more difficult, reducing the plane of the seat support.
Then the person makes movements with his legs, holding onto the bars with his hands. When the patient manages to maintain balance in this position, you can move on to walking. The patient tries to walk, making movements with his arms, moving his back or side.
Patients with oculomotor disorders benefit from visual exercises. The patient tries to fix his gaze on a certain object or point, while changing the position of his head and body.
What symptoms should you be wary of?
The number and intensity of symptoms of ataxia vary from person to person. The greatest number of alarming manifestations is observed in the mixed form of the disease, when not one, but several varieties are diagnosed.
At the puppy's
In the congenital form, the first symptoms can be detected at 4-5 weeks of life. Sick babies are very clumsy. They constantly fall over on their side after a couple of steps and have difficulty getting up on all 4 legs.
If by 4-6 months the puppy still cannot maintain balance and constantly falls, contact your veterinarian. Such clumsiness is normal only in the first months of life.
You should also monitor feeding. If your pet strangely twists its neck and body without getting its muzzle into the bowl, hurry up and schedule an examination.

In an adult dog
Most often, the disease develops in animals older than 6-7 years. It is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- sudden loss of coordination, manifested by body collapse and squatting when turning;
- increasing weakness, decreased activity and loss of appetite;
- hearing impairment and periodic involuntary movements of the eyeballs;
- erratic head rotation and muscle tremors;
- falling out of the blue for no reason;
- problems with climbing stairs or jumping onto vertical surfaces.
If you notice only one of the listed symptoms, do not wait for the condition to worsen and rush to seek help. Timely treatment will help prevent the development of complications.

Disability in cerebellar ataxia
With Pierre-Marie ataxia, a person partially or completely loses the ability to work. Therefore, he has the right to receive a disability group.
The patient is unable to perform many types of work. Due to ataxia, a person cannot stand on his feet for a long time. Impaired hand coordination interferes with work that requires precision movements. Speech problems interfere with activities related to communication (for example, with clients). If the disease is complicated by intellectual impairment, then the person cannot engage in mental work. The symptoms of the disease impose great restrictions on the patient’s work.
The degree of disability is determined individually, depending on the patient’s condition.
When is a cerebellar stimulation program useful?
If you notice the following features in your child:
- started walking or talking late, missed the crawling stage in development;
- quickly gets excited and tired, there are difficulties in self-control;
- often distracted by extraneous stimuli, it is difficult for him to concentrate;
- he has poor memory and attention difficulties;
- behavioral disorders, frequent mood swings, impulsivity;
- reduced school performance, difficulties in mastering the school curriculum;
- delay in the development of motor skills, motor clumsiness;
- lack of coordination (clumsiness, lack of coordination).
The cerebellar stimulation program is effective for the following diagnoses:
- attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD);
- minimal brain dysfunction (MCD);
- speech development delay (SDD) of varying severity;
- mental retardation (MDD) and psycho-speech delay (PSRD);
- dyslexia and dysgraphia;
- autism and autism spectrum disorders;
- Asperger's syndrome;
- logoneurosis (stuttering).
Disease prognosis
Pierre-Marie ataxia is a progressive disease. Over time, symptoms increase. We can say that this disease has a poor prognosis.
The disease does not affect life expectancy and is not fatal. But changes in the cerebellum are irreversible, and over time the patient loses his ability to work.
Today, medicine cannot cure this disease, like many other genetic pathologies. However, medical assistance will help somewhat slow down the development of the disease.
How is ataxia treated in dogs?
It is impossible to cure such brain damage in a pet. There are no effective means that would have a selective effect on the cerebellum and would correct its functions. All that a veterinarian can do in such a situation is to prescribe treatment aimed at relieving the factors that caused ataxia. It provides:
- Prescription of antibacterial therapy for the treatment of acute and chronic infectious diseases.
- Taking symptomatic medications to improve the dog’s general condition (this category includes vitamin complexes, sedatives that relieve panic, and diuretics).
- Surgical treatment (surgery is prescribed for tumors and traumatic brain injuries).
The presented treatment methods can improve the general condition of the animal, get rid of symptoms of ataxia such as increased nervousness, and also slow down the further development of the disease. Only a veterinarian should prescribe certain medications to a dog and determine the duration of therapy. An incorrectly chosen strategy to combat the disease will not only not bring relief to the pet, but can also lead to its death.
A dog that has been diagnosed with cerebellar ataxia needs to be provided with the most comfortable living conditions.
Under no circumstances should it be kept outside (even if a comfortable kennel is made for the animal); the pet should be placed in a room where there are no traumatic objects. If the dog's condition worsens significantly over time, he will need to be euthanized.
Video: What is cerebellar and vestibular ataxia in dogs? Their symptoms and treatment.