There are basic innate reflexes that appear in the baby and indicate the normality of its development. There are more than seventy such unconditioned reflexes in a newborn, and all of them are designed to ensure the child’s adaptation to living conditions.
Among the most important oral automatisms, the proboscis reflex should be highlighted. This is a contraction of the orbicularis oris muscle that occurs automatically in response to a brief touch of the lips. Reacting to the touch, the baby's lips extend into a tube, like a proboscis, hence the name of this phenomenon.
The sucking act is vital in the first months of life, which explains the importance of the proboscis reflex as a component of the sucking process. In neurology, the results of testing this reflex can be used to determine compliance with age standards and detect pathologies of the nervous system, depending on diagnostic purposes.
The concept of pathological reflex
When the main neuron of the brain or neural pathways are damaged, pathological reflexes occur. They are manifested by new connections between external stimuli and the body’s response to them, which cannot be called the norm. This means that the human body reacts inadequately to physical contact, compared to a normal person without pathologies.
Such reflexes indicate any mental or neurological diseases in a person. In children, many reflexes are considered normal (extensor-plantar, grasping, sucking), while in adults the same ones are considered a pathology. At the age of two years, all reflexes are caused by an immature nervous system. Both conditioned and unconditioned reflexes can be pathological. The former manifest themselves as an inadequate response to a stimulus, fixed in memory in the past. The latter are biologically unusual for a given age or situation.
Norm and pathology
If in early childhood reflexes of oral automatism are a normal physiological phenomenon, then in adults their presence is considered a sign of the development of pseudobulbar palsy.
On this basis, according to N. Bogolepov’s definition, these symptoms are called pseudobulbar reflexes.
Their presence is due to the fact that, against the background of various negative factors, the GM cortex is disinhibited. Among the reflexes that become positive are:
- Proboscis reflex.
- Palmomental reflex.
- Mandibular reflex.
- Nasolabial reflex.
In the presence of pathological cerebral anomalies, these signs appear in isolation. In some cases, they appear in separate combinations. Some experts in the field of neurology believe that the retinal structure of the trunk takes part in the formation of signs of oral automatism.
Causes
Pathological reflexes can result from brain lesions and pathologies of the central nervous system, such as:
- damage to the cerebral cortex by infections, spinal cord diseases, tumors;
- hypoxia - brain functions are not performed due to lack of oxygen;
- stroke – damage to the blood vessels of the brain;
- Cerebral palsy (cerebral palsy) is a congenital pathology in which the reflexes of newborns do not fade over time, but develop;
- hypertension;
- paralysis;
- coma state;
- consequences of injuries.
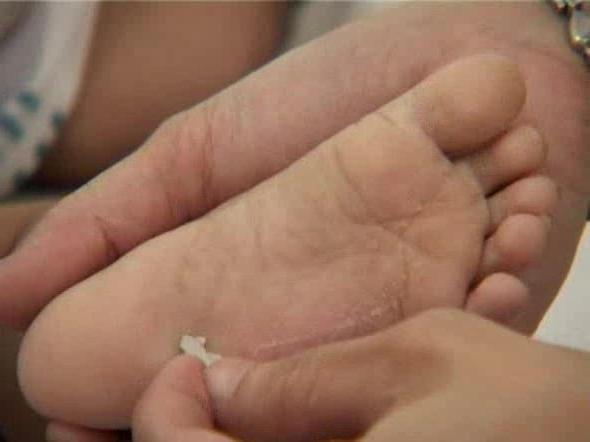

Any diseases of the nervous system, damage to neural connections, or diseases of the brain can cause incorrect, unhealthy reflexes.
Pathological reactions of unconditioned reflexes
In addition to pathological reflexes of the upper, lower extremities and oral muscles, pathological reactions of unconditioned reflexes are also distinguished:
- Reflexes are perverted
. Such reflexes provoke the formation of a dominant focus in the area of the main center (for example, bending the arm). When the tendons are stretched, at the moment of irritation due to the dominant focus, the limb will not flex, but extend. This pathology can be triggered by intoxication with tetanus toxins, injury to nerve endings and pressure on the nerve fibers of scars. - Reflex contractures
. They appear in the area where the dominant focus has stagnated. Nerve impulses that will be transmitted through the joints from the area of injury will first create and later strengthen this focus in the spinal cord itself. As a result of this process, strong flexion of the injured limb occurs, which, if prolonged, causes severe pain and discomfort. - Reflex paralysis
. They appear due to the slowing down of motor neurons in the impulses of more sensitive neurons. An example is the formation of scars in the area of sensitive nerve endings. With strong pressure and pinching of the nerve, paralysis of the limbs and body can develop. - Reflexes exhibiting nonspecific reflex projection
. One of the striking examples of this type of reflex is Babinski’s symptom. It involves bending the toes when a stimulus is applied to the area from the end of the heel to the beginning of the toes.
Classification of pathological reflexes
Pathological reflexes are divided into the following groups:
- Reflexes of the upper limbs. This group includes pathological carpal reflexes, an unhealthy response to external stimuli of the upper extremities. May manifest as involuntary grasping and holding of an object. They occur when the skin of the palms at the base of the fingers is irritated.
- Reflexes of the lower extremities. These include pathological foot reflexes, reactions to tapping with a hammer in the form of flexion or extension of the phalanges of the toes, and flexion of the foot.
- Reflexes of the oral muscles are pathological contractions of the facial muscles.
Reflexes of a newborn.
Understanding what reflexes are inherent in a newborn from the first minutes of life helps the mother better adapt to his needs and distinguish the entire palette of the child’s emotions.
Newborn reflexes are divided into conditioned and unconditioned. To express the first, no time or even basic training is required: the baby breathes from the first seconds after birth, can grab his mother’s finger with his palm, and suck the breast. In other words, do everything necessary to maintain your own life. Indeed, despite the apparent fragility of a newborn, reflexes can provide him with great strength to live.
Reflexes of a newborn baby.
The first month of life, which in pediatrics is called the newborn period, is difficult and at the same time the most educational for the baby. The reflexes of a newborn baby help him to master the world and adapt to it without much effort. Some unconditioned reflexes are replaced by conditioned ones, which are based on the experience experienced by the baby.

Unconditioned reflexes of newborns.
The main unconditioned reflexes include:
Protective reflex. The child reflexively turns his head to the side if he is placed on his stomach. This reflex is developed in all children whose central nervous system is not damaged.
Support reflex and automatic gait. When you place your baby's legs on a flat surface, supporting his shoulders, he will rest on his feet, despite the fact that he will not yet be able to stand on his own. If you pull the hanger forward, the child will take steps, although the legs will periodically cross.
Crawling reflex. For the first time it is clearly expressed approximately on the fourth day of life. Namely, in a position lying on the stomach: on the back and side the reflex will not work. The baby's movements, when he pushes off the surface with his lower limbs, are called spontaneous crawling. It is especially noticeable if you place your palm under the newborn’s feet. In healthy children, this reflex disappears around the 4th month. The baby needs it only as a transitional method of transportation until he learns to walk.
Grasping reflex. It manifests itself in the fact that the newborn clasps the finger of the mother (or another person) if you press on his palm. The grip force is so strong that the child can even be lifted on a finger. This phenomenon is also called the Robinson reflex .
The root of this adaptation lies in the need of our ancestors - monkeys - to stay on their mother's fur independently with the help of their own brushes.
It’s the same with the toes: after pressing on the ball of the foot, the toes bend. The so-called Babinski reflex , on the contrary, speaks of the fanning of the toes due to dorsiflexion of the foot.
This reflex, like the previous one, manifests itself in children only up to 4-5 months, after which it transforms into voluntary grasping of objects, which then becomes conscious, facilitated by educational games.
You can often observe manifestations of the Moro reflex : when the baby lies on his back and his legs are raised, he spreads his arms to the sides and after a couple of seconds returns them to their previous position. The same thing will happen if you lightly hit the bed 15 cm from the baby’s head.
From the 5th-6th. , the Galanta reflex develops . It means that when the skin along the spine is irritated, the baby’s back arches, as if to avoid the unpleasant sensation.
And the Perez reflex , for example, means that running your hand along the spine with light pressure causes negative emotions in the baby: he may cry, scream and squirm.
The above unconditioned reflexes concerned the musculoskeletal system of the newborn. In addition to them, there are oral reflexes, which play an equally important role in the life of the baby.
Proboscis reflex. With a light blow to the lips, they protrude forward. Search reflex. Stroking the lip leads to the opening of the mouth, lowering of the lower lip and turning the head towards the stimulus. Depending on where you press the sponge, the reflex will manifest itself in different variations, but its goal is the same: to find the mother’s breast.
Palm-oral reflex. If you press the middle of both of your baby's hands, he will open his mouth and bend his head. The sucking reflex is very important in the life of a baby, which will be discussed separately below.
All parents need to know the unconditioned reflexes of newborns well, because understanding many details will protect the baby from the careless actions of those closest to them.

Conditioned reflexes of newborns.
In the first months of life, the child’s central nervous system quickly gets tired, so the baby sleeps almost all the time: this is how his body rests from external stimuli. During this period, the cerebral cortex of the newborn is not mature enough to ensure the development of conditioned reflexes.
The simplest of them can be observed no earlier than 2-3 weeks of life. The vestibular reflex appears first as a reaction to rocking. Conditioned reflexes of a more complex type appear in newborns only by the fourth month.
Parents should pay attention that the development of conditioned reflexes in a baby depends not only on age, but also on the state of the senses: eyes, ears, sense of smell, touch, taste. A reflex is a direct physiological reaction to irritating factors of the external world, and if a child is deprived of the ability to feel some of its elements, the development of reflexes will be corresponding.

Sucking reflex in newborns.
Everyone knows that every newborn can suck on his mother’s breast or pacifier without any training or habituation and completely independently, that is, reflexively.
The sucking reflex is perhaps the most important for the survival of a newborn. Therefore, it is observed from the first hours of life. It is more pronounced when the baby is hungry, and fades away for a while after feeding.
Interestingly, the sucking process calms the baby. This is explained simply: he knows that he has access to food, and besides, there is a mother nearby who will protect him from all the hardships and difficulties of this world. The sucking reflex in a newborn weakens by the age of one year and completely disappears by 3-4 years.
Foot reflexes
Extensor reflexes of the foot are an early manifestation of damage to the nervous system. The pathological Babinski reflex is most often tested in neurology. It is a sign of upper motor neuron syndrome. Belongs to the group of reflexes of the lower extremities. It manifests itself as follows: a stroking movement along the outer edge of the foot leads to extension of the big toe. May be accompanied by fanning out all the toes. In the absence of pathology, such irritation of the foot leads to involuntary flexion of the big toe or all the toes. Movements should be light and not cause pain. The reason for the formation of the Babinski reflex is the slow conduction of stimulation along the motor channels and impaired excitation of segments of the spinal cord. In children under one and a half years of age, the manifestation of the Babinski reflex is considered normal; then, with the formation of gait and vertical body position, it should disappear.
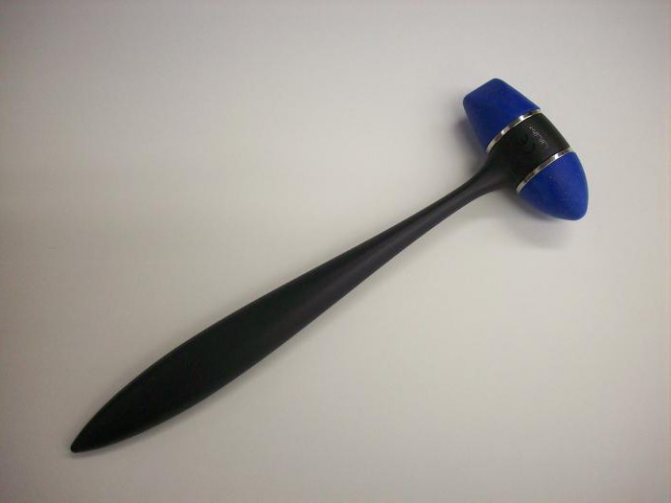

A similar effect can occur with other effects on receptors:
- Oppenheim reflex - extension of the finger occurs when pressing and moving from top to bottom with the thumb in the area of the tibia;
- Gordon's reflex - when the calf muscle is compressed;
- Schaeffer reflex - when the Achilles tendon is compressed.
Pathological flexion reflexes of the foot:
- Rossolimo reflex - when exposed to abrupt blows of the hammer or fingertips on the inner surface of the phalanges, rapid flexion of the II-V toes occurs;
- ankylosing spondylitis reflex - the same reaction occurs when lightly tapping the outer surface of the foot in the area of the metatarsal bones;
- Zhukovsky reflex - manifests itself when struck in the center of the foot, at the base of the toes.
Sucking reflex
This unconditioned reflex of the newborn is necessary for breastfeeding, but it works not only when sucking the breast.
If you insert your finger or pacifier 3-4 cm into the baby's mouth, he will begin to make rhythmic sucking movements.
This is one of the most important reflexes, which can be absent only with paresis of the facial nerves, severe somatic condition and severe mental retardation. Some pediatricians believe that the sucking reflex fades by the age of one year, others believe that it lasts until 3-4 years of life, which means the need for sucking and breastfeeding persists until preschool age. American anthropologist Katherine A.
Dettweiler even noted that the natural period of breastfeeding is much longer - this unconditioned reflex of a newborn can persist even up to 7 years if the mother continues to feed.
Oral automaticity reflexes
Oral automatism is the reaction of the oral muscles to a stimulus, manifested by their involuntary movement. Pathological reflexes of this kind are observed in the following manifestations:
- The nasolabial reflex, which occurs when the base of the nose is tapped with a hammer, is manifested by stretching the lips. The same effect can occur when approaching the mouth (distance-oral reflex) or when lightly hitting the lower or upper lip - oral reflex.
- Palmomental reflex, or Marinescu-Radovic reflex. The stroke movements in the area of the thumb from the side of the palm cause a reaction of the facial muscles and cause the chin to move.
Such reactions are considered normal only for infants; their presence in adults is pathological.
Total information
The essence of oral automatism reflexes comes down to the fact that the baby’s body is always ready to eat food. If the reflexes of oral automatism are poorly developed, control of nutritional functions can be seriously difficult.
As soon as the nipple approaches the baby's lips, his lips extend into a tube or proboscis. Next, sucking movements arise. In the absence of pathological reactions, these mechanisms disappear in the second or third years of life.
Synkinesis and defensive reflexes
Synkinesis are reflexes characterized by paired movements of the limbs. Pathological reflexes of this kind include:
- global synkinesia (when the arm is bent, the leg is extended or vice versa);
- imitation: involuntary repetition of movements of an unhealthy (paralyzed) limb after the movements of a healthy one;
- coordinator: spontaneous movements of an unhealthy limb.
Synkinesis automatically occurs during active movements. For example, when moving a healthy arm or leg, a spontaneous muscle contraction occurs in a paralyzed limb, a flexion movement of the arm occurs, and an extension movement of the legs occurs.
Protective reflexes arise when a paralyzed limb is irritated and are manifested by its involuntary movement. An irritant can be, for example, a needle prick. Such reactions are also called spinal automatisms. Protective reflexes include the Marie-Foy-Bekhtereva symptom - flexion of the toes leads to involuntary flexion of the leg at the knee and hip joint.
Search reflex
The search or Kussmaul reflex is another condition for successful breastfeeding.
If you stroke the corners of a baby's lips, he will lower his lip, deflect his tongue, and turn his head toward the stimulus. If you press on the middle of the upper lip, his mouth will open and his head will straighten. Press on the middle of the lower lip - the head will bend and the lower jaw will drop.
In a hungry baby, the reflex is especially clear and manifests itself symmetrically; it is most pronounced at the age of 3-5 months.
Tonic reflexes

Normally, tonic reflexes appear in children from birth to three months. Their continued manifestation even in the fifth month of life may indicate that the child has cerebral palsy. With cerebral palsy, congenital motor automatisms do not fade away, but continue to develop. These include pathological tonic reflexes:
- Labyrinthine tonic reflex. It is checked in two positions - on the back and on the stomach - and manifests itself depending on the location of the child’s head in space. In children with cerebral palsy, it is expressed in increased tone of the extensor muscles when lying on the back and flexor muscles when the child lies on the stomach.
- Symmetrical cervical tonic reflex. In cerebral palsy, it is manifested by the influence of head movements on the tone of the muscles of the limbs.
- Asymmetrical cervical tonic reflex. It manifests itself as increased muscle tone in the limbs when turning the head to the side. On the side where the face is turned, the extensor muscles are activated, and on the side of the back of the head, the flexor muscles.
With cerebral palsy, a combination of tonic reflexes is possible, which reflects the severity of the disease.
Reflexes and speech function
Many experts believe that there is a connection between speech function and the oral reflex. It is believed that it is necessary to train oral automaticity reflexes. This should be done at the appropriate age for this. so that the speech function is well developed.
For this, it is extremely important to stimulate the distance-oral, proboscis and sucking reflex. This can be done both naturally and artificially. It is recommended to stimulate key reflexes of oral automatism when the child is at the pre-speech stage of his development.
The process of stimulating reflexes is as follows:
- first you need to gently touch the baby’s tongue or lips with a clean pacifier;
- As soon as the baby “takes the breast”, it is important to help him learn to latch on and hold the nipple;
- It is also important to teach the child to hold the pacifier (to do this, you need to gently hold his lips).
If a young mother practices artificial feeding, then the hole in the bottle or nipple should be enlarged as sucking and swallowing are activated.
Tendon reflexes
Tendon reflexes are normally caused by hitting the tendon with a hammer. They are divided into several types:
- Biceps tendon reflex. In response to a hammer blow on it, the arm bends at the elbow joint.
- Triceps tendon reflex. The arm is bent at the elbow joint, and upon impact, extension occurs.
- Knee reflex. The blow falls on the quadriceps femoris muscle, under the kneecap. The result is extension of the leg at the knee joint.
Pathological tendon reflexes manifest themselves in the absence of a reaction to hammer blows. They can occur with paralysis, coma, or spinal cord injuries.
Finally
Training the appropriate mechanisms plays a huge role in a person’s future life. It is believed that if in early childhood all the necessary manipulations are performed correctly, then the necessary facial muscles will also be formed correctly. It is this factor, considered key, that influences speech development as the child grows up.
It is for this reason that it is recommended to listen to experienced pediatricians, who believe that important skills must be learned by the baby in a timely manner.
Rate this article:
(votes: 1 , average: 5.00 out of 5)
Loading...
Related posts:
- Basic examples, signs and features of the classification of unconditioned reflexes
- Conditioned reflex: mechanisms of formation and classification of acquired reactions
- The main features of the manifestation of obligatory reflexes in newborns
- The main features of the manifestation of the Moro reflex in newborns
- What is included in the classification of reflexes?
- What are the consequences of a violation of the knee reflex of vital functions?
Is treatment possible?
Pathological reflexes in neurology themselves are not treated, since this is not a separate disease, but only a symptom of some mental disorder. They indicate problems with the functioning of the brain and nervous system. Therefore, it is necessary, first of all, to look for the reason for their appearance. Only after a doctor has made a diagnosis can we talk about specific treatment, because it is necessary to treat the cause itself, and not its manifestations. Pathological reflexes can only help in determining the disease and its severity.
Moro reflex
Also known as the “hug reflex.”
Hearing a sharp sound, the child first spreads his arms to the sides, unclenches his fingers and straightens his legs, and then returns to his previous position and even hugs himself a little. This biphasic reflex is observed until the age of five months.
In premature babies, babies with mild asphyxia, injuries received during childbirth or illness, the manifestation of motor reflexes may weaken. Therefore, assessing reflex reactions can tell a lot about the baby’s condition.
However, do not be afraid, especially if you do the check yourself. Perhaps the manifestation of unconditioned reflexes is hampered by the fact that the baby is simply well-fed and sleepy. In any case, a medical specialist will tell you whether everything is okay.
Synkinesis
Synkinesia is a reflex during which one reflex movement of the upper or lower limb is accompanied by a reflex reaction of the other.
Synkinesias are divided into:
- global (flexion of the paralyzed arm together with extension of the paralyzed leg);
- imitation (involuntary motor acts of paralyzed limbs, movements familiar to a healthy person);
- Coordinating (production of various movements by paralyzed parts of the body during the performance of other complex motor acts).
To avoid the development of pathological reflexes, both in childhood and in adulthood, it is very important to devote a lot of time to your health. Particular attention should be paid to the daily routine, healthy eating, alternating rest and physical activity.
If nonspecific signs of the disease appear, you will urgently need to consult a neurologist.
Proboscis reflex in children and adults: what it indicates and how it is caused
The proboscis reflex is the stretching of the lips into a characteristic tube. In some cases, sucking movements are provoked. The proboscis reflex can be provoked by touching or delicate tapping of neurological instruments on the lips of the subject.
The proboscis reflex was first described by the great Russian neurologist V. Bekhterev at the beginning of the twentieth century.
Important reflexes
The main reflexes that provide a baby with a comfortable existence in the first months of his life in new conditions include:
- Sucking reflex.
- Swallowing reflex.
- Proboscis reflex.
- Ref. Babkina.
- Search refl-s.
- Upper protective refl.
In newborns
The proboscis reflex in newborns is characterized by a specific protrusion of the child’s lips. In response to the stimulus, the baby’s lips take on a specific “tube” or “proboscis” shape. This mechanism is caused by a quick, sharp touch to the actual areas of the fingers of the parent or doctor.
The proboscis reflex in newborns is caused by the automatic contraction of the orbicularis oris muscle of the newborn. The orbicularis muscle is a key muscle called the sucker.
According to experts, the proboscis reflex is relevant in the first two to three months of a child’s life, after which it fades. There is also an opinion that normally the proboscis reflex in newborns can occur until the baby reaches the age of two and a half to three years.
In this case, the mechanism is presented in the form of a protective-adaptive reaction.
In adults
The proboscis reflex in adults indicates deformation of the structures of the cerebral cortex. If such a symptom is present, the researcher may suspect:
- Traumatic brain injury.
- Stroke.
- Encephalopathy.
- Bulbar syndrome (relevant in case of damage to the tenth pair of cranial nerves).
The proboscis reflex in adults is the most common sign of oral automatism. Also, the proboscis reflex in adults can be detected with diagnosed pseudobulbar palsy. Sometimes this symptom is detected with diffuse lesions of the brain.
In addition, the risk group includes mentally ill individuals and people suffering from neuropathic disorders. To avoid negative consequences, it is recommended to undergo regular examinations in a neurologist’s office.
Particular attention should be paid to this mechanism.
The presence of this mechanism does not always indicate the presence of an abnormal process in the body.
A moderately pronounced proboscis reflex in adults is often caused by older people who care about their health.
How is it called
The proboscis reflex can be detected using a special neurological instrument. A specialist who wants to identify this mechanism gently taps the relevant area with a hammer. This zone is considered to be the upper lip of the subject. The area is at the level of the gums.
The response should be considered a protrusion of the lip. In some cases, the person being examined protrudes both lips. In this case, the shape of the lips takes on a characteristic shape. This is why the reflex was called proboscis.
Researchers note that the intensity of the reaction can vary greatly. Sometimes it persists for a certain time.
Sometimes, simultaneously with the protrusion of the lips into the proboscis, the lower jaw also moves. Specific movements similar to the act of swallowing are often provoked.
This mechanism is recognized by medical experts as pathological.
The presence of the proboscis reflex is noted in the presence of pathological foci on the opposite side of the posterior part of the frontal lobe.
Many researchers working on this issue, including Dr. S. Karchikyan, believe that the presence of this mechanism may be due to a high level of idiomuscular mechanical excitability. The human orbicularis oris muscle is at risk.
In addition to V. Bekhterev and S. Karchikyan, this issue was studied in detail by A. Epstein. The main theses were put forward in the thirties of the twentieth century.
Important to remember
Using important reflexes, including the proboscis reflex in newborns, the doctor checks how the baby’s central nervous system works. It is important to remember that the absence of vital reflexes may indicate the presence of a serious pathological process. This is also evidenced by the long “life” of a particular mechanism.
When to sound the alarm bell
In some cases, important mechanisms in a newborn are turned on at the wrong time or appear very weakly. Sometimes the anomaly can be caused by injury resulting from a difficult delivery. It also happens that the “inhibition” of reflexes is associated with an individual reaction to a particular drug.
The weakness of the proboscis and other oral mechanisms is usually associated with the fact that the child born was premature or suffers from a mild degree of asphyxia.
If the baby is full, there is no need to sound the alarm, since pronounced oral mechanisms appear when he experiences a feeling of hunger.
Pathology is the complete absence of reactions. This is a significant reason for immediate rehabilitation. This manipulation should only be carried out by qualified personnel.
There are several reasons for this anomaly:
- intrauterine pathologies;
- umbilical cord strangulation;
- birth injuries.
It is important to remember that the reserves of a growing organism are practically inexhaustible. Most often, the child recovers quickly and even surpasses his peers in development.
Assessment of the proboscis reflex in newborns and other important reflexes is carried out in a well-lit and warm room. The surface should not be too soft and not too hard. The subject must be rested, well-slept and well-fed.
Source: https://VashNevrolog.ru/fiziologiya/xobotkovyj-refleks-u-detej-i-vzroslyx-o-chem-on-svidetelstvuet-i-kak-vyzyvaetsya.html