All infections are dangerous to varying degrees, and even more so are neuroinfections. The most dangerous neuroinfections are those that affect the brain. There can be no “frivolous” diseases here. Every pathogen that can cross the blood-brain barrier poses a huge danger to human health and life.
Types of Brain Infections
The variety of neuroinfections affecting the brain can be divided into five groups:
- bacterial;
- parasitic;
- viral;
- prion;
- fungal.
Routes of transmission and infection
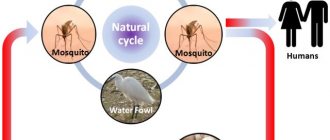
The main route of transmission is airborne droplets: infection most often occurs through contact with a virus carrier, a sick person, during coughing or sneezing.
The infection is transmitted, including through a kiss, if saliva gets on the mucous membrane of healthy people. A predisposing factor is the presence of erosions on the gums or their inflammation, as well as microscopic injuries to the mucous epithelium of the oral cavity - if the above circumstances are relevant, it will be easier for the pathogen to penetrate the body and begin to circulate in it, developing an infection.
The hematogenous route of infection is no less common. The pathological process spreads to the brain and spinal cord when there is a focus of chronic infection in the body, including damage to the vessels supplying these important centers. Such predisposing pathologies are otitis media, brain abscess, and thrombosis of the cerebral sinuses.
Neuroinfection develops, among other things, due to the lymphogenous transmission route, when hidden complications of traumatic brain and spinal cord injuries are present in the patient’s body. Especially if it is aggravated by liquorrhea.
The infection is not transmitted through household contact, therefore, if you use the personal means and belongings of a virus carrier, infection will not occur. The seasonality of the pathology - hot summer - this condition is the most favorable for the spread of infection, therefore populated areas with a dry, hot climate are more susceptible to neuroinfection.
Treatment methods for brain encephalitis
A presumptive diagnosis of encephalitis requires prompt and aggressive treatment as it can progress rapidly and lead to severe and irreversible neurological damage .
Viral encephalitis is treated with antiviral drugs such as acyclovir and ganciclovir.
Seizures may require specific drug treatments. Brain swelling can be treated with corticosteroids. Artificial respiration can be used in cases of difficulty in natural breathing.
Autoimmune encephalitis is treated by administering immunosuppressants and searching for a possible tumor, if appropriate.
It is necessary to assess what kind of rehabilitation is necessary, what can preserve and restore cognitive and physical after the elimination of the acute phase of encephalitis.
Causes of defeat
In general, it should be noted that an infection that affects the nervous system can be caused by both viral, bacterial and fungal etiologies.
Voicing the diagnosis, taking into account the origin of the pathogen, the penetration of which into the body gave rise to the infection. Therefore, they specify “bacterial”, “viral”, “fungal” (meningitis, encephalitis, etc.)
The causes of neuroinfection of the brain are:
- previous traumatic brain injuries (especially those accompanied by prolonged compression);
- hypothermia (staying in low temperature air without a hat);
- if during surgical interventions on the brain or spinal cord, medical instruments or consumables were used of poor quality sterilization ;
- if the surgical or therapeutic intervention was complicated by a violation of the integrity of the doctor’s gloves or was carried out without their use;
- past viral diseases (usually influenza).
Neuroinfection often occurs as a hospital-acquired disease and can result from visiting a dentist who used insufficiently disinfected instruments during work.
Predisposing factors include:
- low immunity (especially if the patient has HIV, tuberculosis, syphilis or other diseases that undermine the body’s protective properties);
- the presence of foci of purulent infection (tonsillitis, otitis), their latent course or rapid transition from the acute stage to the chronic form;
- ignoring follow-up examinations after illnesses , as well as traumatic or spinal injuries.
Classification
Neuroinfections are classified according to individual development factors. Based on the timing of penetration of the infectious agent into the tissues of the nervous system, neuroinfections are divided into:
- fulminant pathologies, when the infectious process proceeds in rapid development, the duration of which can take from a couple of hours to several minutes;
- acute diseases characterized by increasing symptoms over several days;
- subacute pathologies, characterized by a milder onset of pathological development, turning into the main symptoms within 3-7 days;
- chronic diseases characterized by a long, often delayed onset of the disease.
In cases where an infectious disease arises directly from exposure to a pathogenic agent, the disease is considered primary. When damage to nerve tissue occurs against the background of an existing or previous infection localized in other organs (lungs, liver, kidneys, etc.), this pathology has a secondary nature of occurrence.
The main types of infectious brain lesions
In neurosurgical and neurological practice, the following types of infections of the nervous system are encountered.
Dangerous meningitis
Meningitis is an inflammation of the membranes of the brain and/or spinal cord. Infection occurs by hematogenous, lymphogenous or airborne route.
Pathogenic agents – viruses, bacteria, fungi; predisposing factors are the presence (including hidden) of purulent or inflammatory chronic processes in the sinuses of the nasopharynx or auditory canal, as well as hypothermia of the body.
The symptoms of meningitis are quite specific: by visualizing them, you can quickly diagnose this type of neuroinfection and begin its treatment.
The most pronounced manifestations:
- stiffness of the neck muscles (the patient cannot tilt his head forward);
- intense headache, which is always accompanied by vomiting (this symptom raises doubt among experts as to whether the patient has meningitis or a concussion - the determining factor is the medical history);
- increase in body temperature to a high level.
Treatment involves bed rest and antibiotic therapy with broad-spectrum antimicrobial drugs. The prognosis is favorable.
Features of arachnoiditis
Arachnoiditis is an inflammatory process localized in the arachnoid membrane of the brain. The development of arachnoiditis is caused by head injuries, the presence of rheumatism, and an untreated ENT infection in a timely manner.
Symptoms of this type of neuroinfection are:
- severe, persistent headache, making it impossible to perform even basic actions;
- blurred vision;
- weakness;
- nausea, the attack of which ends with vomiting;
- increased body temperature;
- possible development of nosebleeds due to cerebral circulation disorders;
- insomnia;
- in severe cases - impaired consciousness or its absence.
The prognosis for the patient is favorable only if the diagnosis is made in a timely manner and treatment is carried out. Therapy for this disease is aimed at eliminating the inflammatory process, stabilizing cerebral circulation and generally strengthening the patient’s body.
Encephalitis
Encephalitis - inflammation of brain tissue is a consequence of tick-borne infection, as well as the penetration and exposure of bacteria and viruses. If the patient neglects to seek medical help, the prognosis is unfavorable and even fatal. The symptoms of this type of neuroinfection are pronounced:
- headache worsens when lying down, is persistent (poorly and briefly relieved by analgesics);
- there is an increase in body temperature;
- weakness and a feeling of exhaustion increase, as manifestations of general intoxication of the body.
Oculomotor disorders are part of the symptom complex characteristic of this type of neuroinfection: the patient develops ptosis (drooping of the eyelid), a feeling of double vision, and general blurred vision.
Dyspepsia is manifested by nausea, which especially often occurs after traveling by transport; vomiting occurs.
Hospitalization involves further therapy with antibiotics, hormonal drugs and restoratives.
Symptoms of brain encephalitis
Often the disease manifests itself with very mild symptoms. In more serious cases, a person affected by encephalitis may have:
- speech or hearing disorders
- double vision
- hallucinations
- personality changes
- loss of consciousness
- loss of sensation in some parts of the body
- muscle weakness
- partial paralysis of arms and legs
- sudden severe dementia
- convulsions
- memory loss
Young children often experience:
- fever
- lethargy
- vomit
- body rigidity
- unexplained irritability
- a tense or protruding fontanelle (soft spot at the top of the head)
Diagnosis and treatment
The most informative type of study is an MRI, as well as an encephalogram. The laboratory part of the diagnosis involves testing blood and urine.
An analysis of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is also carried out, in which an increased level of protein is determined. Each of these diagnostic procedures allows you to visualize the state of the brain and spinal cord, determine the localization of the pathogenic process, the degree of infection and involvement of tissues in the inflammatory process.
Treatment of neuroinfection is as follows:
- Having established a diagnosis, the patient is hospitalized .
- Vein catheterization is performed (a permanent intravenous catheter is installed).
- Antibiotic therapy is prescribed . The antimicrobial drug is selected by the doctor taking into account which pathogen provoked the development of the neuroinfection: only by adhering to this can one count on the success of the treatment. Antibiotics are administered intravenously or drip (via infusion), since this ensures that the drug immediately enters the bloodstream, as opposed to intramuscular injections. Commonly used drugs include Cefepime, Medaxone, and Ceftazidime.
- The patient is prescribed hormonal drugs - mainly Prednisolone and Dexamethasone, the dosage of which is determined by the severity of the patient and the form of the pathology. If the neuroinfection is combined, then the dosage of the hormonal substance should be higher than for a separate infectious disease of the nervous system.
- The patient's immunity is supported by the introduction of vitamin complexes.
- Correction of blood pressure levels is carried out by administering magnesium sulfate.
- In order to reduce the degree of cerebral edema , the patient is administered diuretics: Furosemide, Lasix.
- Throughout the patient's stay in the hospital, the vital signs of his body are monitored . Maintaining them at a normal level is ensured by constant infusion therapy of the patient with saline solutions and glucose.
- Monitor diuresis .
- In order to prevent exhaustion, the patient is given parenteral nutrition ; carry out hygienic care.
Development mechanism
The pattern of development of the infectious pathological process depends on the form of formation of the neuroinfection. In most cases, pathogens enter the cells of the nervous system through the perineural spaces, blood or lymph. Localized in neurons, the pathogen begins to influence it both directly and through the release of its own toxins.
When the peripheral parts of the nervous system are damaged, infectious agents begin their pathogenic effects by damaging neurolemmocytes (cells of the myelin sheath), which are the main protection of the axon of the nerve cell. During long-term and sluggish infectious processes, pathogens can reach the axon itself.