Astheno-neurotic syndrome has many synonyms, among which the most famous is the name “chronic fatigue syndrome”. But even this term does not provide a complete understanding of the nature of the disorder, although it largely explains its appearance and nature. In general, astheno-neurotic syndrome is understood as a special type of neurosis, to which people with a sensitive, vulnerable psyche are most susceptible.
In recent years, there has been a sharp increase in the number of cases of diagnosis of this disease, also called neurasthenia. Moreover, among the patients there are not only adults, but also children of different ages! This is a clear reflection of the modern lifestyle, but astheno-neurotic syndrome cannot be called a harmless condition, since in advanced cases it leads to total apathy, deep depression or even suicidal tendencies. Therefore, it is very important to pay attention to the creeping trouble in time and find an effective way to cope with it.
Causes

Children who experience increased stress at school or who have recently had an infectious or other serious illness are susceptible to asthenia.
There are many reasons for the development of asthenia in children:
- Overfatigue: if a child gets tired of studying at school and then attends additional sections or classes with a tutor. At the same time, there is no time left for proper rest, since you still need to do your homework.
- Children with weakened immune systems are especially susceptible to asthenia, especially after suffering an infectious, neurological or endocrine disease.
- Changes in hormonal levels in adolescents.
- Incorrect daily routine, insufficient sleep.
- Mental overload, excessive flow of information, unregulated time spent at the computer or watching TV.
- A stressful situation (a change in the usual way of life when entering kindergarten or school, conflicts in the family, in a team, watching a horror movie, etc.).
- Treatment with certain medications that depress the nervous system.
- Oxygen starvation in brain tissue in the absence of walks in the fresh air.
General information about asthenic syndrome
Asthenic syndrome or asthenia is a painful condition, neuropsychic weakness, manifested by a discrepancy between the body’s energy expenditure and the efforts made.
In the development of the disease in question, considerable importance is given to insufficient blood supply to the brain , leading to imbalance of neurotransmitters and, as a result, the appearance of symptoms such as anxiety, irritability, disruptions in the functioning of the autonomic nervous system, sleep disorders, and skeletal muscle weakness.
Based on the predominance of certain manifestations, two main subtypes of asthenia can be distinguished:
- hypersthenic asthenia - fatigue is combined with high irritability, mental excitability, and sleep problems;
- hyposthenic asthenia – mental weakness, inactivity, lack of initiative, decreased motor and speech activity, impaired attention and memory.
Manifestations of asthenia in children
Asthenic syndrome can develop even in infants. The child becomes capricious and easily excitable. Manifestations of asthenia at this age may include causeless tearfulness and fearfulness from faint sounds.
The child gets tired when interacting with him for a long time, rocking him in his arms. The baby has difficulty falling asleep, his sleep is restless, he often wakes up and is capricious. A child with asthenic syndrome will fall asleep faster in the absence of parents; he just needs to be put in his crib and left the room.
Psychological exhaustion can easily be caused by separation from the mother when registering the baby for kindergarten. Entering school at the age of 6, new requirements, the need not only to sit through all the lessons, but also to remember the material heard cause asthenia, the manifestation of which is:
- nervousness;
- isolation;
- fear of contact with strangers;
- fear of bright lighting;
- increased fatigue, the child may even refuse his favorite game;
- memory impairment;
- difficulty concentrating when required;
- headache when hearing loud noises;
- frequent dizziness;
- decreased appetite.
In adolescents, asthenic syndrome can manifest itself with the following symptoms:
- violation of the rules of communication with others: they are rude to parents, conflict with peers;
- decline in academic performance;
- desire to argue about anything;
- absent-mindedness, impaired attention;
- increased fatigue;
- poor appetite;
- weakness and lack of desire to do anything;
- periodic headache;
- frequent mood changes;
- sleep disturbance.
All these manifestations can be combined with symptoms of the disease that caused asthenic syndrome. Asthenia is not a single symptom noted, but a complex of increasing manifestations.
If a child has 3 or more of the listed signs, you should seek help from a psychologist and pediatrician. Diagnosing asthenic syndrome in children is not always easy; its manifestations sometimes do not differ from personal characteristics.
What is asthenia
Asthenia (chronic fatigue syndrome, CFS) is a disease of the nervous system , according to the definition of the international classification of diseases.
It falls under the category of other nervous system disorders. Typically, this syndrome is considered in the context of medicine, so the diagnosis should only be made by an experienced and competent specialist.
Key symptoms include persistent fatigue, mild fever, enlarged lymph nodes, headache, muscle pain, joint pain, depression or even memory loss. For diagnosis, it is important that these signs are present for at least 6 months. Asthenia is believed to be caused by a viral infection, but the origin and progression of the disease are not fully known.
Asthenia is chronic fatigue syndrome
Treatment

There is no specific treatment. It is important to identify the cause of the asthenic condition and eliminate it. The help of a psychologist can be very tangible.
If the child's workload is excessive, it should be reduced if possible (perhaps by canceling clubs or other additional loads). With severe manifestations of asthenia, there may be a need for an additional day of rest during the week. It is equally important to reduce computer games to a minimum or completely eliminate them. You should pay attention to creating a warm, comfortable environment at home and in the family.
If asthenic syndrome is caused by any disease, the help of a specialist to treat it is necessary. In some cases, the doctor may prescribe medications, adaptogens, and vitamin complexes. Be sure to provide your child with regular outdoor walks and good nutrition.
How to treat asthenia
Sports and a healthy lifestyle counteract asthenia
The first question parents ask when symptoms of CFS appear in a teenager is who treats asthenia? First of all, you need to contact a neurologist or therapist (he will refer you further to a specialized specialist).
Due to the unknown etiology, treatment is symptomatic, often pragmatic. Since the disease has a significant mental superstructure, it is often significantly improved by any treatment, even if it does not affect the body.
Because in many cases the effects of infection are evident in the development of the disorder, it is still unclear whether they play a role as a cause, trigger, or complication. How to treat asthenia, which specialist should you contact if an infection is detected?
Typically, the neurologist refers the patient to an infectious disease specialist; treating the current infection may improve the patient's condition.
Drug treatment
Pharmacotherapy is a last-line therapeutic approach.
Various medications are used from the groups of antidepressants, anti-inflammatory drugs, psychostimulants, antiallergic, antihypotensive drugs.
The administration of immunoglobulins is rarely prescribed ; but such treatment has conflicting results, in some cases there is obvious benefit for the patient, in others there is no therapeutic effect.
The range of substances used is not limited to medications - vitamins, minerals, herbal remedies, and nutritional supplements are also recommended (also without clear evidence of effectiveness).
Non-drug treatment
, a number of non-pharmacological therapeutic procedures are used in practice .
Various sports and physical activities are recommended for teenagers . Some alternative medicine methods, such as acupuncture or homeopathy, are sometimes used, but their effectiveness is uncertain and controversial.
Psychotherapeutic methods
Psychotherapy for asthenia
Psychotherapeutic procedures also occupy a special place in the treatment of asthenia in adolescents. According to a meta-analysis by J.R. Price and colleagues published in the Cochrane database in 2008, cognitive behavioral therapy appears to be the most beneficial.
However, recent statements related to the PACE trial, a study examining the effectiveness of various treatments, cast doubt on its effectiveness.
Lifestyle change
In the treatment of asthenia, a varied and balanced diet with sufficient amounts of vitamins and minerals is important. It is advisable to take nutritional supplements aimed at maintaining energy, reducing fatigue, and strengthening the immune system.
Proper nutrition
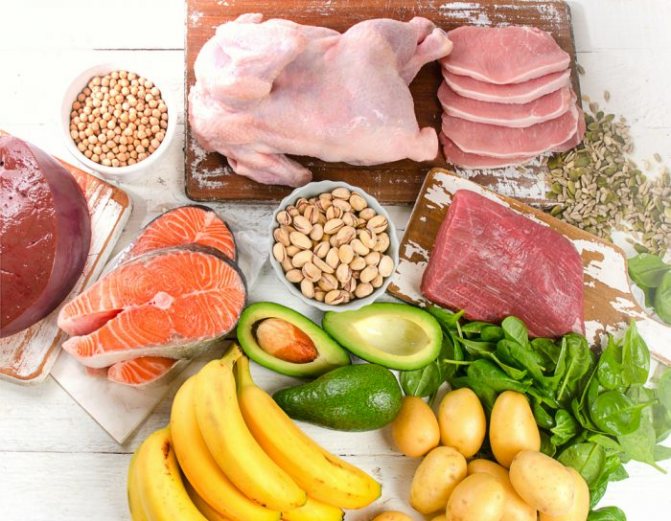
When asthenic syndrome occurs, nutrition must ensure that the body receives not only nutrients, but also essential microelements and vitamins. A child needs to eat 5-6 times a day.
In order to improve brain activity, you should include in your child’s diet foods rich in natural nootropics - amino acids proline, glycine, tyrosine, taurine, glutamic and y-aminobutyric acids.
These products include:
- beef;
- poultry meat;
- liver;
- fish;
- goat and cow milk;
- sour cream;
- cottage cheese;
- dairy products;
- cheese;
- chicken eggs;
- seafood (crabs, squid, seaweed, oysters, clams);
- cereals – oatmeal, buckwheat, rice;
- fruits: avocado, bananas;
- soy;
- pumpkin seeds;
- almonds and peanuts;
- sesame;
- gelatin;
- greens: parsley and spinach.
Eating the following foods will help you get rid of low mood and depression:
- dishes from mackerel, salmon, herring, cod, sardines, salmon;
- chicken bouillon;
- seaweed;
- buckwheat or oatmeal;
- cheese of any kind;
- fruits and vegetables with bright colors (eggplants, beets, carrots, bell peppers, bananas, oranges, persimmons, tangerines, apples);
- chocolate and cocoa;
- nuts.
Eating the following can help relieve tension and recover from stress, and improve concentration in children:
- foods rich in magnesium: potatoes, legumes, pumpkin seeds, green vegetables, seaweed, buckwheat, millet and oatmeal;
- whole grain bread;
- nuts;
- papaya and avocado;
- tea with mint and lemon balm.
The intake of glucose from food increases brain performance. It will improve if children eat raspberries, grapes, watermelons, cherries, strawberries and cherries. Glucose is also contained in cereals and grain crops, vegetables (potatoes, carrots, pumpkin, white cabbage).
Preparations of ginseng, Rhodiola rosea, Eleutherococcus, Chinese lemongrass, and golden root will help cope with increased fatigue. These drugs can only be selected and prescribed by a doctor. Self-medication is dangerous.
Drinks with caffeine (coffee, strong tea) should be avoided, especially with severe excitability and a tendency to increase blood pressure in adolescents. Carbonated drinks are not allowed.
Traditional medicine recommends for children freshly prepared juice from 2 carrots and 1 grapefruit, take 2 tbsp. l. 2 times a day.
Healthy foods in the diet should be selected depending on the severity of the main manifestations of asthenia.
Diagnosis of asthenia
Diagnostic criteria for identifying asthenia were developed by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
When diagnosing a disorder, the following 2 conditions must be met:
- Unexplained constant fatigue inadequate to the previous load. After rest, only a slight improvement occurs.
- At least 4 of the following symptoms present for at least 6 months:
- memory disorders, impaired concentration;
- severe and prolonged states of exhaustion or even illness after physical or mental stress;
- sleep does not lead to refreshment;
- muscle pain;
- joint pain not accompanied by swelling or redness;
- headaches of varying nature or intensity;
- frequent sore throat;
- tender cervical or axillary lymph nodes.
Summary for parents

Asthenic syndrome in children is a secondary condition that develops against the background of illness, excessive stress, and stress. The task of parents is to help their beloved child cope with the problems that have arisen. Some help with this can be obtained through proper nutrition.
First children's medical center, educational video about asthenic syndrome:
Failure of the autonomic system
Manifestations of neurasthenia from the autonomic nervous system can mask the pathology of internal organs. How does astheno-neurotic syndrome occur in children?
The main manifestations include:
- unpleasant sensations and a tingling feeling in the heart area, these manifestations are most expressed during stress, mental and emotional overload;
- presence of tachycardia;
- increased sweat production.
Sometimes asthenia may be accompanied by a slight increase in body temperature to 37.5º C, especially if a malfunction of the central nervous system was caused by an increase in the production of thyroid hormones.
As for manifestations from the cerebral cortex, first of all, changes of a psychological nature should be included here.
Among them are:
- increased level of fatigue, fatigue does not give the child the opportunity to perform mental work;
- inability to sit still and concentrate;
- disturbances in the sphere of memory and attention (short-term memory suffers first, the child cannot remember information because he is not collected);
- altered emotional background of the child, which manifests itself in increased irritability, tearfulness and hot temper;
- sleep disturbances (the child cannot fall asleep for a long time and has difficulty waking up in the morning);
- frequent mood swings.
In general, astheno-neurotic syndrome in children has clear manifestations:
- hyperactive behavior of the child;
- decreased attention;
- capriciousness and disobedience.
The appearance of such symptoms should be a reason to contact a specialist who can determine a possible violation.
It should be noted that in childhood the signs of the disease are more pronounced than in adults. This is due to insufficient development of higher nervous activity. Sometimes the impetus for the development of neurasthenia is minor emotional or mental stress.
How else does astheno-neurotic syndrome manifest itself? Symptoms in children include general malaise. For example, while in transport, a child complains of motion sickness, nausea, and dizziness. Such a child often experiences fainting.
If we talk about the symptoms of neurasthenia in children of primary school and preschool age, then they often have enuresis. As the pathology develops, the child may complain of pain in the neck and eye twitching. The limbs may be cramped.
This symptomatology characterizes an advanced form of astheno-neurotic syndrome, when the parents did not take any radical steps for treatment. In this case, the child is characterized by hysteria and increased aggression.
As for the signs of the disease in schoolchildren and adolescents, they are expressed in the inability to concentrate. Such children experience difficulties both at school and at home.
In this case, parents should show maximum patience, not raise their tone at the child, and not punish him for mistakes and excessive nervousness. Punishment and speaking in a raised voice will only aggravate the situation and become fertile ground for the rooting of a psychological problem. In this case, the child may completely lose sensitivity and memory.
Clinical manifestations depending on age
Today, symptoms of the disease can be observed in children of various age groups. Even the youngest children are no exception. The clinical manifestations of the disease depend on the age of the child.
Infants up to one year old
Infants suffering from asthenia often cry, fall asleep worse, and experience constant fatigue while communicating with their parents, playing, or being held. Signs of asthenia in young children are:
- The child is often capricious and cries for a long time, even if he is well-fed and healthy.
- The baby does not fall asleep well when rocked to sleep, but becomes calmer when he is alone in the room.
- Frightened by sounds, even fairly quiet ones.
- Gets tired of talking to people quickly.