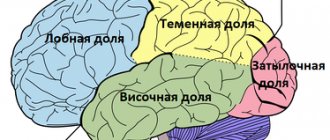
Onset of the disease
According to WHO, at least 50 million people worldwide suffer from dementia, although it is difficult to give an exact figure due to the large number of patients who neglect to seek medical help.
The onset of dementia in most cases develops gradually, and the symptoms are often vague, especially when it comes to senile (senile) dementia. For this reason, it can be problematic to notice it in the early stages.
The development of dementia is preceded by many factors on which the symptoms of the disease, its manifestations and course depend:
- atrophic processes of the brain (Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, Pick's disease);
- vascular diseases;
- head injuries or tumors;
- poisoning with toxic substances;
- severe kidney disease;
- infectious diseases.
The main symptom of the onset of dementia, an Alzheimer's type disease, is memory impairment. The patient forgets simple things, gradually loses the ability to learn and remember new information. In addition to forgetfulness, the patient is disturbed by mood swings, and negative character traits that were previously present to a small extent become sharpened and aggravated. Irritability, melancholicity, and anxiety may develop.
Sometimes the patient develops bad habits: theft, grumpiness, aggression towards others. A characteristic symptom of “Alzheimer's surprise” also occurs (facial expressions as if in surprise, with the eyes wide open, blinking infrequent).
Against the background of problems with the blood vessels of the brain (atherosclerosis, hypertension, vasculitis, after a stroke, heart attack), vascular type dementia develops. Its first symptoms are mild forgetfulness, decreased intellectual abilities, mental changes, and apathy. At the first stage, disturbances in speech, thinking, and writing may also appear.
If other types of dementia occur, then patients, in addition to memory problems and decreased intelligence, may experience impaired coordination of movements, tremors of the limbs, isolation, and loss of interest in life.
Why does the disease affect women more?
The issue is disputed in scientific circles, but despite this, statistics do not lie - the incidence of dementia among women over 60 years of age is significantly higher than that among men. There may be several reasons for this. Firstly, the cause of dementia may be hormonal levels - a sharp decrease in the level of sex hormones, mainly estrogen, that occurs during menopause. The likelihood of the first signs of dementia in this condition can be reduced with the help of properly selected hormone replacement therapy. Secondly, such a disease is a common cause of senile dementia. In turn, this pathology is also more common in women. There is an opinion among scientists that the onset of menopause, when combined with diabetes mellitus, leads to a more pronounced manifestation of signs of dementia in women.
Thus, the slightest irritation can take on unusual proportions and have serious consequences for the human condition. Almost half of patients suffer because of this. External circumstances often accentuate anxiety: alone at home, for example, or, conversely, located in the city. When these situations are known to the person and are likely to be repeated, anxiety may arise due to fear of another anxiety attack.
Practicing physical activities such as yoga, tai chi can help control his anxiety. France. Parkinson's volunteer committees may offer this type of activity. The proportion of people with depression is much higher in Parkinson's than average. This seems understandable because of the difficulties associated with symptoms, changes in relationship with the environment, and awareness of evolution.
Moderate stage
Everything we listed above is an early stage of the disease. But depending on the lesion, a person may experience:
- Severe mental disorders.
- Hallucative reasoning (when a conversation is conducted with fictional characters).
- Inability to remember past events.
- Complete collapse of personality.
- Impaired speech and ability to recognize things.
- Insanity, in which mental and physical work declines.
In addition, you can easily check for shifts by type of activity. If there is a driver in front of you, then pay attention to the following:
- how he navigates familiar terrain;
- does he drive according to the signs?
- how it reacts to force majeure circumstances;
- which turn signal turns on when changing traffic;
- what is his behavior during traffic jams, will he calmly wait for passage or will he overtake on the side of the road;
- whether control mechanisms are confused.
If the disease was not detected at an early stage, and therefore it was not possible to stop its further development and alleviate the course, rapid progression of dementia occurs. Symptoms get worse depending on the type of dementia. The patient loses professional and some household skills, does not want to engage in personal hygiene, and denies the presence of the disease.
A triad of neuropsychological syndromes may occur:
- Apraxia is a disorder of motor activity; the patient is unable to perform complex actions.
- Agnosia is the loss of certain perceptions, for example, the inability to identify sounds, colors and objects, or the faces of familiar people.
- Aphasia is a speech disorder that occurs in dementia associated with Alzheimer's or Pick's disease.
Partial or complete loss of short-term memory occurs, problems with orientation in time and space develop, and the inability to determine the left and right sides the first time. Handwriting changes, the desire to communicate with family disappears.
Dementia at the last stage is very difficult. The patient completely loses his personality, as well as:
- does not recognize loved ones and himself;
- does not understand where he is, what year it is, what time of day it is;
- stops moving fully and is often bedridden;
- loses control of the sphincters;
- loses all skills, ceases to cope with food intake, and in the last days before death he may lose chewing and swallowing reflexes.
Sometimes the “mirror symptom” occurs when the patient looks in the mirror for a long time and talks to it.
Also, at the last stage, the process of dementia can be complicated by psychoses: hallucinations, delusions, persecutory delusions, severe phobias.
Comparison of disease symptoms
| Function type | Early stage | Moderate stage | Severe stage |
| Memory | Development of easy forgetfulness | Partial loss of short-term memory | Loss of short-term memory, and in severe cases, complete amnesia |
| Emotions | Exacerbation of personal traits, slight changes in character | Apathy, depression, isolation from society | Aggression, anger or complete depression develops, the patient loses his personality, ceases to resemble his former self |
| Thinking and speech | Thinking becomes slightly dull and speech slows down | A person tells the same information several times, the “gramophone” symptom develops, speech is fast, some words are forgotten | Incoherent speech, without essence and logic, thoughts are confused |
| Movements | Rarely impaired, except in cases where alcoholic dementia occurs, the stages of development of which are characterized by motor disorders | Hand tremors, loss of coordination (sometimes may not occur) | Development of apraxia, problems with coordination, and in some cases, inability to move |
The gradual development of the disease leads to death, which occurs due to the cessation of brain activity, extinction of vital functions, and less often due to pneumonia, strokes, heart attacks, and intestinal dysfunction. In the severe stage, before death, three more periods are distinguished: terminal, preagony and agony.
The terminal period is characterized by complete apathy, the person is not active, does not respond to sounds, and functions fade away. The development of predagonia can be suspected if the patient’s blood pressure and heart rate have decreased, and breathing has slowed down.
Dementia develops suddenly and sometimes ends in agony with a sharp but short-term improvement in the patient's condition. The person comes to his senses, memory, breathing, and blood pressure temporarily improve. After agony, clinical and later biological death always occurs.
Male manifestation
In men, vascular dementia most often develops, usually manifesting itself in the age period from 60 to 75 years. A cheap remedy for improving memory In order to restore cerebral circulation you need... Folk remedies Treatment Diets YaZdorov.ru
This pathology is formed due to impaired blood circulation, which is caused by damage to brain cells. Vascular dementia develops in the presence of vascular diseases of the head. Medicine can detect pathology by reduced metabolic rates with elevated lipid levels.
As a result of damage, nerve cells suffer and die due to lack of nutrients. For a short time, the patient’s body copes with the help of compensation, then the potential is depleted and negative changes occur, affecting speech, memory, and thinking. Male dementia is often accompanied by weakened limbs and differences in reflexes between the limbs of the right and left sides. Men with this disease suffer from a shuffling gait, instability, and dizziness. Male dementia has the following symptoms:
Manifestations of dementia lead to complete loss of skills and intellectual degradation. At this stage, it is impossible to stop the course of the disease, but if relatives notice the initial clinical picture in a man, then it is possible to stop the rapid course of the disease. The first signs include:
- decreased outlook;
- change in character;
- the patient becomes more greedy;
- aggressiveness;
- malice;
- impulsiveness;
- the patient seems to freeze when choosing the right word;
- irritability.
Many of these signs are attributed to a person’s mood and current circumstances, but they are the ones that indicate impending trouble.
Development of dementia in young and elderly patients
Another factor influencing the symptoms of dementia is the age at which the disease began. In the vast majority of cases, it appears after 65 years of age, although sometimes it is diagnosed at an earlier age.
Moreover, the older the patient is, the more favorable the prognosis. Scientists have proven that dementia, which develops in people under 50-60 years of age, has a severe course and more severe symptoms than the senile form of the disease. Early dementia develops quickly, is less tolerated by the patient, and death occurs within 1-5 years. Senile dementia, on the other hand, develops gradually, manifests itself to a lesser extent and can last 10-15 years with good care.
Younger people are more likely to develop rapidly progressing dementia. Its causes may be head injuries, tumor formations, infectious processes, alcohol poisoning, hormonal imbalances, and lack of vitamins and minerals.
At the early stage of dementia, young people experience problems with memory and concentration, and the ability to engage in professional activities is gradually lost. Apathy, depression and loss of interest in life progress rapidly. The development of dementia can be recognized by the sudden isolation of the patient from society.
Often the first and second stages are almost indistinguishable, the disease suddenly turns into a severe form, and it is very difficult to care for the patient, who is still physically healthy. Young people often develop psychosis, they become distrustful, may refuse to eat, and show aggression towards loved ones.
The onset of senile dementia is much more difficult to notice, since most patients over the age of 65 perceive the symptoms as a natural process.
The disease is most often caused by Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, vascular lesions, or occurs against the background of hormonal disorders. Therefore, the main symptoms that accompany the development of dementia in older people are:
- forgetfulness, absent-mindedness, problems with short-term memory;
- replacing memories with fantasies;
- mental changes;
- problems with thinking and speech.
The moderate stage of senile disease is manifested by increased emotional problems and partial memory loss. When severe dementia begins, it is aggravated by the loss of all skills, motor activity, memory, orientation in space, time and self.
Dementia in children is a serious pathology that leads to the decay of intelligence. The problem usually appears in children over two years of age. Until this moment, the child does not lag behind his peers in growth and development. If you experience symptoms of cognitive decline, seek medical help.
What causes
The pathological process develops due to the influence of various factors that disrupt the functioning of the brain. Sometimes a child is already born with a problem, but manifestations arise as they grow.
The occurrence of the disease is associated with:
- Genetic diseases that can only be identified within several years after childbirth. Dementia accompanies Lafora disease, Newman-Pick disease, and neurodegeneration.
- Infectious processes that spread to the brain. Dementia is a complication of meningitis and encephalitis.
- Head injuries.
- Serious disruptions in the functioning of the immune system.
- Disruption of blood flow in the vessels.
- Drug poisoning.
Other diseases can also create favorable conditions for the formation of pathology.
Severity
The development of the pathological process occurs in several stages:
- Easy. There is a smoothness of symptoms. Therefore, the problem in preschool children is often not identified. There is a preservation of everyday skills. Schoolchildren do not succeed in their studies and suffer from low social activity.
- Moderate. The child needs adult care and support.
- Heavy. Speech impairment and loss of self-care skills occur.
Symptoms depend on the severity of the problem.
Manifestations
Dementia can be progressive or residual. Pathology is characterized by a gradual increase in signs of the disease. The problem in this case is related to genetic diseases. The development of the underlying pathology contributes to the development of dementia.
The last stage of development is considered to be the organic form, in which stable deviations in mental activity are observed and the situation no longer worsens. This problem is associated with injuries, poisoning, and meningitis.
Depending on age, the disease can have different manifestations:
- If a problem arises in a small child, then he loses all the skills that he acquired during his short life, his vocabulary narrows, and difficulties arise in expressing his thoughts. He no longer needs loved ones, does not feel affection. Gradually the baby stops walking.
- During the primary school period, a decrease in working capacity is observed, and difficulties with memorization arise. Speech skills do not deteriorate, but you can often notice that the child confuses colors and shapes.
- An older child has a problem in the form of constant repetition of the same actions.
- Dementia in adolescents is accompanied by deterioration in concentration, memory impairment, and difficulty comprehending information and creating inferences. Performance decreases and speech becomes unclear and blurred.
In the first years of life, the problem does not reveal itself in any way, and it is discovered only in adolescence.
Sometimes the pathology leads to a deterioration in vital functions and children do not live to the age of ten. This occurs in Lafora disease.
It is impossible to stop the development of the pathological process, just as it is impossible to reverse the lesions. With the help of modern therapeutic techniques, you can only slow down its course.
How to make a diagnosis
Dementia at a young age requires careful examination to confirm the diagnosis. Confirm the presence of a problem using laboratory, instrumental and pathopsychological methods. The process of diagnosing a disease consists of:
- Neurologist consultations. The doctor interviews the patient, examines him, checks the child for reflexes and collects anamnesis. To confirm the presence of damage and atrophic processes, echoencephalography, magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography and other instrumental techniques are used. Based on the examination results, a diagnosis is made and dementia is identified.
- Psychiatrist consultations. During its course, emotional, personal and cognitive disorders are identified. A child psychiatrist talks to the child. He draws conclusions about the state of mental abilities, evaluates behavior and emotional response. To clarify the depth of the lesion, they resort to pathopsychological examination.
- Conversations with a pathopsychologist. He selects methods for examining intellectual characteristics, memory, and thinking.
Treatment
Clinical dementia in children is determined by a number of diagnostic techniques, on the basis of which the disease is confirmed and suitable treatment options are selected.
The pathology requires long-term systemic treatment and parental organization. With the help of properly selected therapeutic procedures, disorders of memory, intelligence, and emotional state can be corrected.
They resort to psychological and pedagogical assistance, which promotes the development of thinking and the ability to remember. The educational load is selected depending on the degree of development of the pathological process.
To slow down the development of the pathological process, they resort to symptomatic medications.
Treating dementia is challenging. With this disease, memories, mental activity, practical skills, speech, will are completely lost, and character deteriorates.
Depending on the cause of the problem, symptoms and stage of development of degenerative disorders, they resort to using:
- antioxidants;
- memory enhancing agents;
- drugs for the restoration of nervous tissue;
- medications that improve blood flow through the vessels of the brain.
Symptoms of dementia in young people are reduced using traditional medicine. Alleviating symptoms and slowing down degenerative processes is achieved with the help of decoctions and infusions based on medicinal plants.
You cannot resort to such methods without the knowledge of the doctor, since only he can select products that are harmoniously combined with the drugs and do not cause allergic reactions. Good results are observed when using elecampane root, ginseng, rowan bark, Chinese lemongrass, peppermint and other plants.
The child’s nutrition plays an important role in the treatment process. From birth to one year, it is advisable for the baby to receive breast milk. Mom should eat properly so that the milk contains a lot of vitamins, proteins, fats and carbohydrates.
At an older age, it is important to provide a varied diet for your child. He should eat meat, cereals, fruits and vegetables, and dairy products. During adolescence, emphasis should be placed on dairy products, since during this period bones are actively growing and need a lot of calcium.
It is worth giving up fatty and fried foods, smoked foods, and excessive consumption of sweets.
Physical exercise plays an important role in the process of restoring cognitive functions. Gymnastics and massage help improve memory, speech activity, and the ability to solve everyday problems.
For people of young and adult age, learning a new profession, solving puzzles and tasks helps to stop dementia.
Dementia in children is a serious pathology that requires long-term treatment and constant monitoring by a specialist. Lasting improvement cannot be achieved immediately, and not everyone can wait for relief.
Thanks to medications, they normalize metabolism at the cellular level and accelerate blood flow through the vessels of the brain. These measures help reduce the rate of development of the pathological process. With residual organic dementia, only psychological help and work with teachers is sufficient.
In severe cases, it is necessary to constantly care for the child.
Since a pathological process develops in the brain, mental development also deteriorates. The formation of the nervous system organ continues, but with deviations from the norm. For this reason, the body loses the ability to adapt normally to external and internal environmental factors. Psychopathic attacks, epileptic seizures and other complications develop.
Causes, types and stages of senile dementia
The exact causes of dementia are not fully understood. Doctors say one of the main reasons is hereditary predisposition. There is a concept of “familial dementia”, which appeared as a result of the observation of dementia in men and women in different generations. The death of parts of the brain due to a stroke can also lead to dementia.
When the nutrition of brain cells is disrupted, neurons die. This condition is attributed to primary senile dementia. In case of serious diseases associated with disorders of the nervous system, secondary senile dementia manifests itself.
The brain is the lever for controlling the physical and mental processes of a person. Sufficient blood supply is a necessary condition for its normal functioning. In addition, it must be protected from inflammation, injury and exposure to toxins.
The mental functions of the brain decline with age. The reasons for this are the changes that occur to a person throughout life:
- Brain injuries sever neural connections, the restoration of which does not always occur in full. In this case, in places of damage, the nervous tissue is replaced by connective tissue.
- Atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels, resulting from the formation of atherosclerotic plaques on the vascular walls. This leads to a narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels, slows down the movement of blood through the arteries, and impedes the flow of oxygen that nourishes brain cells.
- Degenerative changes, atrophy - shrinkage of the brain mass.
- Necrotic degradation of brain tissue caused by serious injuries or radiation for malignant tumors.
Secondary senile dementia can occur not only due to serious injuries and infections, but also due to drug addiction, alcoholism, hypothyroidism and metabolic disorders. Long-term depression can also accompany senile dementia. Depressive states in older people are caused by a loss of meaning in life associated with aging.
Senile dementia, as we have found out, occurs primarily due to damage to the human brain. This is accompanied by the death of cells responsible for the full functioning of our body. But there are other diseases that lead to dementia:
- cancerous tumors of the head;
- heart attacks;
- ischemic strokes;
- severe traumatic brain injury;
- prolonged forms of hypertension;
- concussions;
- severe infections: meningitis, AIDS, etc.
Often, dementia can be caused by such serious diseases as renal and liver failure, Yatsenko-Cushing syndrome, multiple sclerosis, disorders of the endocrine system, lupus erythematosus. Obesity, insufficient intellectual activity, and diabetes mellitus can also lead to dementia. Alzheimer's type of senile dementia, according to many studies, most often occurs in women.
Heredity is a common cause of senile dementia. Dementia in your grandparents is a worrying symptom. Most likely, both your parents and you yourself will suffer from this disease. Prevention has weight in the fight against the disease, but a healthy body is not immune from dementia.
The following symptoms are the harbingers of senile dementia: fatigue, difficulty switching from one type of activity to another, impaired concentration.
With dementia, elderly and senile people experience a slowdown in intellectual activity and impaired goal setting. Patients often complain about the difficulty of planning and organizing routine activities.
The death of brain cells is an inevitable reaction of the body to the aging process. A decrease in brain activity is observed in every elderly and elderly person. But not everyone experiences senile dementia with pronounced symptoms; in some people, dementia develops slowly and is considered a manifestation of aging.
Senile dementia affects older people over 70 years of age. At this age, the disorder is observed in 10% of people; by the age of 80, this number increases to 50%. Signs of dementia progress as a person ages.
Types and stages of senile dementia
Types and stages of senile dementia
Senile dementia is characterized by several stages.
Easy.
The patient is able to care for himself, his coordination of movements is preserved, the person is well oriented in time and space. Apathetic states often appear, interest in what is happening around is lost, and depression appears. Sometimes the patient withdraws and strives for solitude.
Average.
Memory and thinking suffer greatly. A person begins to act not consciously, but automatically. In everyday activities, it can cause harm to yourself and your home. Communication with relatives is disrupted. At this stage it is necessary to provide control and assistance to the patient.
Heavy.
A person stops acting consciously. Complete isolation leads to the need for sanitary and hygienic care.
The emotional sphere is also undergoing changes. The patient's mood deteriorates and a depressive state occurs. Depression is typical for 30% of patients. She is characterized by inconstancy - tears suddenly give way to joy.
According to the signs, senile dementia is divided by specialists into several types:
This form is characterized by pronounced memory disorders and emotional state. The person suffers from increased weakness and fatigue. In this case, a predominantly depressed mood is observed.
This type is characterized by gradual development. Distinctive features are fine detail of events, vindictiveness, rancor and pedantry. A person’s horizons sharply decrease, speech becomes poor. Epileptic symptoms can often be observed.
- Schizophrenic dementia.
This type of dementia requires immediate hospitalization of the patient to prevent a complete personality change. In such a state, a person is characterized by complete isolation, emotional coldness, loss of connection with the external environment, decreased activity, and isolation from reality.
In medicine, senile dementia is classified into the following types:
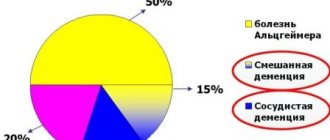
- Atrophic. Dementias of this type include Alzheimer's and Pick's diseases. Initial degenerative reactions affecting the cells of the central nervous system cause atrophic dementia.
- Vascular. Dementias of this type are considered to be atherosclerosis and hypertension. Diseases arise due to pathological conditions of the circulatory systems and blood vessels of the brain
- Mixed. Signs of both types are observed
Forecasts
In almost 99% of cases, dementia is incurable due to irreversible processes that have occurred in the brain, which means the prognosis is extremely unfavorable. Death occurs not from the disease itself, but from the development of complications, 1-15 years after the appearance of the first symptoms.
Comparison of disease types and estimated life expectancy after diagnosis
| Type of dementia | Duration forecast |
| Alzheimer's disease | Without maintenance treatment 5 years, with timely detection up to 15 years |
| Vascular | Depending on the degree of brain damage - from several months to 10 years, dementia progresses especially quickly in older people |
| Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease | 8 months – 1 year |
| Lewy body disease | 5 – 7 years |
| Frontal form | From 1-2 years to 15-20 |
| Pick's disease | Up to 10 years |
Thus, the prognosis depends on the type of dementia and the age of the patient. Another important factor is the timely detection of the disease, as well as the correct prescription of medications.
Thus, with adequate treatment, a disease caused by infectious processes, injuries or tumors can be completely cured. An interesting example is one of the most atypical types of dementia - the rare Creutzfeldt-Jacob disease. This dementia progresses rapidly and in most cases is fatal after about 1 year, but sometimes it can resolve spontaneously.