What is a CT scan?
Computed tomography is a study based on the ability of X-rays to illuminate tissue. Thanks to this technique, it is possible to obtain not just a clear image of the organ, but a layer-by-layer image, which, after computer processing, allows you to see the organ being studied in volume, down to the smallest detail.
Two types of examination are used:
- Spiral CT (SCT), in which synchronous movement of the X-ray source and the surface with sensors occurs.
- Multilayer examination (MSCT), which is carried out on a device with several rows of sensors. Here read the article about PET CT and what are its differences.
Experts recommend doing multislice computed tomography of the brain. Unlike SCT of the brain, it makes it possible to notice even beginning pathologies, since it allows you to scan up to 300 layers. In addition, using this technique, you can track processes occurring at a specific point in time.
Video
Faced with a complex abbreviation, the patient often asks the doctor what it is - RCT? Decoding in medicine using professional terminology is presented too difficult. In fact, this is an informative diagnostic method similar to X-rays with more advanced technology. With its help, you can obtain a three-dimensional image of an organ and a view of a millimeter section of tissue in good quality. This is the simplest explanation of what RCT is.
Anatomy of the brain
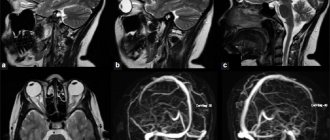
This is what a CT scan looks like.
Thanks to the clarity of CT results, the anatomy of the brain in general terms will become understandable even to a person far from medicine. This is the main organ of the central nervous system, consisting of a large number of neurons and performing a number of important functions:
- Processing information that comes from the senses.
- Coordination of movements.
- Making decisions.
- Attention.
- Thinking.
- Memory.
- Speech generation.
Since the structure of the organ and the functions it performs are very complex, a CT scan of the brain can be recommended by doctors of several specialties involved in its study:
- A neuroscientist who studies the activity of neurons.
- Neurologist who treats diseases of the central nervous system.
- Neurosurgeon responsible for surgical treatment of the central nervous system.
- Psychiatrist specializing in the treatment of mental disorders.
Rules for conducting RCT (MSCT) of the brain
There is a certain set of rules on how to act before and during this diagnosis. Therefore, the following necessary recommendations should be followed:
- The patient should lie comfortably with his back on the transponder table, while remaining completely still. If this method is prescribed to a child or a patient with a disorder in which he cannot remain still, a number of sedatives are administered.
- The procedure does not take more than 15 minutes, except in the case of the introduction of a contrast agent;
- Metal objects are removed to avoid possible image distortion;
- The possibility of performing the procedure on pregnant women exists only if it cannot be avoided;
- If the brain is being examined, no additional preparation is required;
- MSCT is also contraindicated in children due to the radiation received, but in some cases diagnosis is still necessary;
When comparing RCT with other similar methods (MRI, X-ray and others), it is the resonance computed tomography method that has the highest accuracy. One of the main disadvantages of RCT is the increased risk of developing cancer during re-diagnosis in the coming days after the first procedure.
What does a CT scan of the brain show?
Assessing brain activity in its various aspects, which can be done using CT, is the most important step in diagnosing brain diseases. This technique allows you to detect:
- Anomalies in the structure of blood vessels, the presence of aneurysms.
- Problems in the middle ear.
- Stroke and its consequences, primarily brain damage.
- Consequences of traumatic brain injury, are there any hemorrhages, swelling. Detailed article about CT scan of the skull.
- Diseases of infectious etiology.
- Tumors.
- Dropsy.
Advantages of the diagnostic method
Compared to radiography, RCT is superior. The main advantages of the modern method are:
- expansion capacity is 20 times greater than that of x-rays;
- no blurred image;
- obtaining an image in three dimensions.
The similarity with X-rays is that both are sources of radiation. The average radiation dose is 2-11 m3v (this figure may change for various reasons).
Indications and contraindications
Computed tomography of the head is the definitive diagnostic method in the following situations:
- Prolonged headaches that occur without a specific cause.
- Patient complaints of dizziness, convulsions and other symptoms that suggest neurological pathologies.
- Loss of consciousness and its changes.
- If necessary, plan surgery.
- Treatment of brain diseases. In this case, a CT scan of the head is done to evaluate its effectiveness.
- Control during biopsy.
At the same time, RCT of the brain is an X-ray method, so it is important to remember that there are a number of contraindications for its use:
Doctors of several specialties may recommend a CT scan of the brain.
- Any stage of pregnancy.
- Age under 14 years.
- Severe endocrine diseases.
If CT diagnostics requires additional contrast with the introduction of an iodine-containing substance, contraindications are also liver and kidney failure and an allergy to products that contain iodine. Breastfeeding is not considered a contraindication, and a certain period of time must pass before the next breastfeeding - at least a day.
Carrying out diagnostics
The examination of a pathological focus can be carried out using the introduction of a contrast agent; as a rule, this is carried out to detect pathology in hard-to-reach areas, or without the introduction of contrast. Contrasting allows you to reproduce a more accurate image and accurately determine the required area.
The doctor must identify all contraindications for this study that the patient may have. Complete information about the patient and his medical history should be the primary decision to proceed with further action.
No additional preparation is required for RCT of the brain, which allows you to begin the examination immediately. The patient lies down on a moving transponder table, which then moves to the required point, depending on the area being examined.
Next, the diagnosis is carried out directly. In some cases, the patient will need to hold their breath for more accurate images.
Tomography of cerebral vessels
There are many structures in the human body that are difficult to visualize using X-rays. Sometimes additional enhancement is necessary - the introduction of a substance that, when accumulated, enhances the contrast with the surrounding tissues. Most often, contrast is used if the study aims to study blood vessels:
- The doctor needs to visualize the vascular pattern to make a diagnosis.
- It is necessary to assess the condition of the blood vessels and the circulatory system as a whole.
- It is important to understand the sufficiency and adequacy of the blood supply.
Advantages of conducting RCT
What is RCT of the brain, it can be carried out using a special, so-called multispiral technology (MSCT). Which allows it to have advantages in the following cases:
- High scanning speed, which also allows you to obtain a complete image of the pathological area;
- The ability of MSCT to examine several areas at once;
- Significant improvement in contrast resolution;
- Advanced imaging allows you to examine the coronary arteries from almost any angle, obtaining high-definition images;
- Possibility of conducting research on patients who have built-in mechanical implants;
- Reducing radiation exposure from radiation pressure. The method is significantly safer than others that use X-rays.
A particularly important point to note is that this method provides reconstruction in a three-dimensional system. Therefore, this specialist, for example, reconstructive plastic surgery, works with an accurate picture of the areas with which they have to work.
Computed tomography capabilities
Brain diseases lead to malfunction of various organs and systems of the body. Among them are the following ailments:
- Alzheimer's disease.
- Brain stroke.
- Tumor.
- Epilepsy, etc.
A modern approach to diagnosing diseases allows a specialist to conduct a detailed analysis by studying what a CT scan of the brain shows. Both dysfunctions of different parts of the brain and the root cause of their occurrence are identified.
One of the most popular examination methods today is computed tomography, which allows for accurate X-ray analysis of the skull. The MRI procedure is no less widely used. With its help, it is possible to diagnose the blood vessels of the brain, performing it in several projections: full face and in profile.
Recently, computed tomography of cerebral vessels has been actively used. The principle of the procedure is that X-rays penetrate the brain tissue with maximum intensity. Based on the results obtained, a specialist can give a certain prognosis regarding the dynamics of the development of a particular disease, the effectiveness of the therapy used, etc. Using a tomogram, it is possible to identify the location and nature of pathologies, and determine the degree of expansion of the cerebrospinal fluid-containing system of the brain.
Thanks to the procedure, it is possible to identify:
- Anomalies such as edema, meningioma, bruise, cancer, etc.
- Inflammation.
- Fractures of the skull.
- Brain injuries.
- Vascular dysfunction.
- Hemorrhages.
There are a number of indications for the procedure, namely:
- Disorders of brain development, as well as various pathologies.
- Presence of head injuries.
- Various vascular diseases in the brain area.
- Concussion.
- Diseases of the ENT organs and eye sockets.
- Suspicion of neoplasms.
- Diseases of the salivary glands.
- Analysis of surgical results.
- Diseases of the temporal part.
CT scan of the brain: questions and answers
First of all, of course, you need to decide what a CT scan of the brain is? Computed tomography of the brain is a scan of the human body or its organs using x-rays to identify possible diseases. This procedure belongs to the category of diagnostic measures.
Are there differences between an MRI or CT scan of the brain?
Yes, X-ray radiation is the basis of CT examination and this differs from magnetic resonance imaging, which scans the human body by studying the magnetic properties of its hydrogen molecules. In addition, MRI provides an image of the scanned organ in several projections as a three-dimensional image. And computed tomography makes a layer-by-layer scan of the body.
But both MRI and CT are carried out using computer technology and computer programs that allow you to see the image, provide the specialist with certain data about the state of the organ during the scan, as well as the ability to print the image and save it on disks or other media thanks to computer recording devices.
In addition, it is believed that computed tomography is not safe if performed frequently.
In what cases can a CT scan of the brain be performed on children?
It is considered especially unsafe for children. There is evidence that after the second CT procedure in children under 15 years of age, the risk of blood cancer increases, as well as the emergence and development of tumor processes in the brain.
Therefore, computed tomography should be prescribed to children as a last resort, if an urgent scan is needed or if it is impossible to make a correct diagnosis without a CT scan. In addition, a CT scan of the head is prescribed for suspected hydrocephalus and pathological development of the skull bones.
So, a CT scan of the brain is performed in children if they receive head trauma to assess tissue injury and the resulting consequences, as well as to determine the presence of formations in the brain tissue.
What are the reasons for performing a CT scan of the brain in adults?
The need to do a CT scan of the brain or CT scan of the brain vessels arises in the following cases:
- for head injuries (if internal hematomas and bleeding, bruises are suspected);
- if the presence of neoplasms is suspected;
- to confirm the presence of a stroke and its consequences;
- to confirm the presence of changes in cerebral vessels, the presence of aneurysms and their changes;
- with regular severe pain in the head, dizziness and fainting.
In addition, computed tomography may be prescribed:
- before surgical reconstruction of the skull and facial bones - to plan reconstruction; to analyze the temporal bone for hearing problems;
- to examine the sinuses in case of inflammation, pain and other processes associated with the nose;
- for planning and monitoring treatment in the case of tumor formations and changes in blood vessels in the brain.
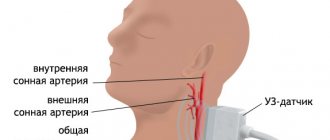
What is CT angiography of cerebral vessels?
Angiography is an examination of blood vessels using a contrast agent that is injected into the blood. CT angiography of cerebral vessels is carried out using X-ray radiation and a tomograph with the necessary computer software.
In the case of angiography, CT scans of the brain have contraindications that should be taken into account. For example, angiography of cerebral vessels is not performed without a contrast agent.
A contrast agent can provoke allergies, it is also contraindicated in case of renal failure, and, in general, angiography should not be done if the body is weakened, so as not to worsen its condition.
Contraindications for angiography
It is strictly forbidden to do a CT scan on pregnant women.
How is a CT scan of the brain done?
Externally, a computed tomograph is practically no different from an MRI. The patient is placed on the tomograph table in a horizontal position. Then the table moves inside under the annular part of the device, where the head is scanned with X-rays.
The scan represents a layer-by-layer penetration into the examined organs and the same display of their condition occurs on the tomograph monitor screen or on media, thanks to which a specialist will be able to conduct a full analysis of the condition.
Computed tomography allows you to see changes in blood vessels and tissues, the presence of inflammation, blood clots and tumors in them.
What is the price of a CT scan of the brain?
For many patients, the price of a CT scan plays a big role. So, a CT scan of the brain - its cost in Russia varies and is a minimum of 2000 rubles without the use of a contrast agent and a maximum of 7800. The cost of a CT scan of the brain in Moscow varies from 3200 to 13000 rubles.
But the main thing is that there is always a choice – prices, devices. But you cannot choose between health and money. After all, tomography is a real saving of time, effort, nerves and, of course, money.
What is CT brain perfusion?
PCT or perfusion computed tomography is one of the progressive methods for examining cerebral blood flow. According to research, this is a more advanced or improved version of CT without the use of a contrast agent, which allows examination of the condition of blood vessels at the capillary level.
Modern CT scanners have a built-in PCT function and can perform CT perfusion of the brain. PCT is used to determine the state of blood circulation in cases of acute and chronic disorders, blood circulation in the human brain or cerebrovascular diseases.
The fact is that recently cerebrovascular diseases (atherosclerosis and arterial hypertension) have become significantly “younger” and now they can be found not only in older people, but also in younger people.
According to statistics, 20–30% of people of pre-retirement age have problems with cerebral vessels. And it is no secret that the deterioration of the cerebral vessels will lead to a deterioration in the condition and functioning of the entire human body. It is also necessary to take into account the fact that the percentage of people with allergies is constantly growing, and the number of patients suffering from renal failure is increasing.
The procedure for performing a CT scan of the brain - photo
Therefore, the role of perfusion computed tomography of cerebral vessels is very valuable, especially since it is carried out without the use of a contrast agent and allows those in need to undergo the necessary examination.