The anatomical features of the brain are individual for each person. Some deviations from the norm are considered physiological, while other abnormal manifestations are considered pathological.
Dilatation of the lateral ventricles of the brain is an asymmetry (expansion) of one or both lateral ventricles (ds cavities).
The cerebral specificity of asymmetry in the size of the ventricles is not a separate nosological unit.
Ventriculoasymmetry of the brain is only a sign indicating the presence of pathology or the possible development of a disease. In this case, the clinical MRI picture of symptoms may be absent.
For example, a brain tumor, intracranial hypertension (intracranial hypertension) or internal hydrocephalus can gradually (without any special symptoms) cause the ventricle to deform, expand or increase its volume.
In most cases, ventricular asymmetry is diagnosed in premature infants, newborns or infants in the first year of life.
A similar phenomenon in children is considered a sign of perinatal pathology of the nervous system.
However, quite often lateroventriculoasymmetry of the lateral ventricles is observed in adults, especially in people of the normosthenic type.
Symptoms of the disease
Most often, lateroventriculomegaly in adults has no clinical signs.
Under such circumstances, an anomaly in the cerebral structures of the right or left ventricle of the brain is not considered a pathology. The deviation is detected during MRI and is defined as a concomitant finding.
Pronounced dysfunction of cerebrospinal fluid dynamics is accompanied by the following clinical symptoms:
- headache;
- feeling of heaviness and fullness in the head;
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- vomiting that does not bring relief;
- phobic syndrome - a state of anxiety, fear, panic;
- disturbances of memory, vision, breathing, heart function;
- possible loss of consciousness, dementia, coma;
- sleep disorder, insomnia or, conversely, increased daytime sleepiness;
- disorientation, inability to coordinate movements;
- enuresis;
- depression, apathy.
The clinical MRI picture, in which the lateral ventricles of the brain are asymmetrical, can be supplemented by the symptoms of the disease identified by neuroimaging on ultrasound or CT.
For example, the appearance of cognitive or cerebellar disorder, paresis, decreased or increased sensitivity of organs, etc.
Symptoms of ventricular dilatation
The principle of the development of the disease has general features, without taking into account the characteristic causes. Fluid collects in the ventricles, they enlarge and begin to put pressure on the brain tissue. The pressure in these cavities increases.
Patients experience: headaches, nausea, vomiting, a feeling as if the eyes are being squeezed out, problems with hearing and vision, apathy, fatigue, dizziness, memory deterioration, fainting, coma, disorientation, problems with coordination of movements, enuresis. , depressive state. All these are symptoms of dilatation of the lateral ventricles.

Types of lateroventriculoasymmetry
Cerebral asymmetry of the lateral ventricles is classified into two types:
- symptomatic - the development of pathology occurs due to a specific cause;
- idiopathic - the etiology of the disease is unknown.

In addition to types, the disease varies in severity:
- mild asymmetry - no therapy is required, since no serious deviations are observed;
- moderate lateroventriculoasymmetry - determined by a slight disturbance in the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid, a slight asymmetry of up to 15-17 mm is noticeable;
- severe (or dangerous) form - there is maximum dilatation of the ventricles on the left or right, as well as significant dysfunction of the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid.
With a strong degree of severity, complex symptoms, anomalies and pathology of the brain and nervous system are added to the asymmetry.
Lateroventriculoasymmetry is divided into types:
- isolated type - an increase in the volume of only the lateral ventricles;
- extensive - dilatation of different groups, for example, asymmetry of the anterior horns of the lateral ventricles (ALV);
- hereditary predisposition.
The pathology forecast is made after analyzing all types, forms, types, as well as measuring several altered parameters of the ventricles.
Main reasons
Asymmetry of the lateral ventricles is formed due to dysfunction of the cerebrospinal fluid circulation, which is determined according to the following principles:
- increased production of cerebrospinal fluid;
- increased concentration, accumulation and dysfunction of cerebrospinal fluid absorption;
- disruption of the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid.
Difficulty in the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid and disruption of dynamics occurs with pathology of the ventricular choroidal plexuses and subarachnoid membrane of the brain.
The main reasons provoking ventricular dilatation:
- The most common are neuroinfections (meningitis, encephalitis and others).
- TBI (traumatic brain injury).
- Neoplasms (tumor, cyst or bruise).
- Ideopathic hydrocephalus.
- The presence of a formed hematoma.
- Hemorrhagic stroke.
- Thrombosis of cerebral vessels.
- Atypical embryonic anlage of the ventricular system.
Consequences
Lateroventriculoasymmetry of the ventricles in a child can have various consequences.
With slight asymmetry, there may be a disturbance in the development of mental and motor functions, which will correct and return to normal over time.

The severe form is the most dangerous, as there is a risk of cerebral palsy, serious mental and nervous disorders, deformation of the skull bones with brain damage.
Detection of asymmetry in a newborn signals the need for comprehensive diagnostics and specialist consultation.
Up to three months, neurological disorders are difficult to identify, so the child must be constantly under the supervision of a neurologist.
If you ignore pathology in an adult, the following manifestations are possible:
- development of chronic cephalgia;
- intellectual impairment;
- the appearance of cognitive disorders;
- dementia (brain cell atrophy);
- impaired coordination of movements.
Timely diagnosis and well-chosen therapy are the key to the health of an adult and the normal development of a child.
Ventriculomegaly is dilatation of the lateral ventricles in a fetus, newborn, or infant in the first year of life.
The first signs of pathology can be detected exactly at the 17th week of pregnancy.
Most often, the pathology manifests itself in premature infants; the asymmetry of the ventricles can be seen in the photo.

Typically, such babies at birth have formed ventricles, while the skull has not yet reached the required size.
Correct diagnosis
The simplest method of diagnosing a baby is a monthly measurement of head growth, which even parents can do.
A more informative conclusion can be obtained after a hardware examination.
| Name | Description |
| Ultrasound | In the fetus, an increase in the size of the ventricles of the brain is determined. If the width is more than 10 mm, a diagnosis is possible. In addition, disturbances in the structure of the heart, bone apparatus, and nervous system are determined. |
| MRI | Performed in the presence of severe symptoms of ventriculomegaly |
| Neurosonography (NSG) | Used in infants immediately after birth and at the age of 1 month. This method is very informative and provides detailed information about the course and dynamics of the disease. |
| EEG | Brain Activity Test |
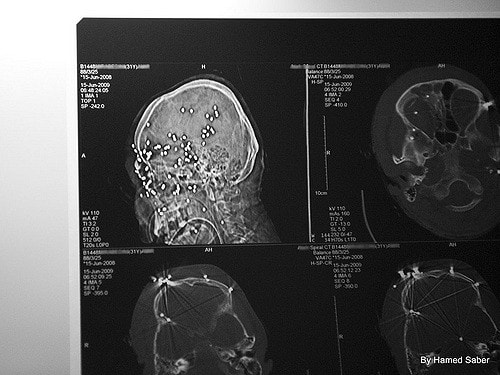
Medical certificate
The main components of the brain are 4 ventricles. They are represented by small cavities. They constantly produce and circulate cerebrospinal fluid. Its main purpose is to transport nutrients to cells and remove waste products. In addition, cerebrospinal fluid plays a kind of shock-absorbing role during head impacts.
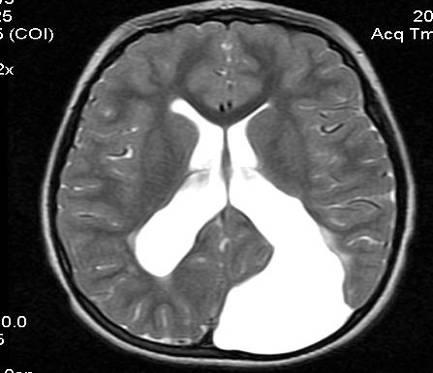
Normally, each ventricle contains about 150 ml of cerebrospinal fluid. It is completely updated three times a day. An increase in its volume provokes an increase in the size of the ventricles and a change in their shape. When the lateral C-shaped curvature disappears, the cavity becomes rounded. In this case, they speak of the initial stage of lateroventriculoasymmetry of the brain.
What it is? Such a terrible diagnosis refers to a disorder characterized by an asymmetric change in the size of the ventricles. To a small extent, such changes are not considered a pathology. However, their noticeable progression can lead to severe brain disorders. Enlarged ventricles begin to put pressure on surrounding elements and structures, causing disruption of the functioning of neurons. In some cases, death of nerve cells is observed.
There is a treatment
Therapy is prescribed only for severe clinical signs. Only the doctor decides how to treat, based on the conclusion, as well as the individual characteristics of the patient.
A specific treatment regimen is selected, aimed directly at eliminating the cause of the pathology.
- diuretics;
- nootropics;
- NSAIDs (anti-inflammatory);
- vasoactive substances;
- neuroprotectors;
- sedatives;
- in the presence of infectious diseases, antibacterial agents are used.

Additionally, massage, therapeutic exercises and physiotherapy are prescribed, which have a positive effect on the dynamics of recovery.
Some people prefer to see an osteopath - a specialist who treats without medication using palpation.
Dr. Komarovsky spoke in detail about the effectiveness of this technique, who devoted a series of programs to this topic.
Reviews
Larisa Vilkova:
After birth, the child was diagnosed with mild asymmetry. I had to do an ultrasound every month. Dilatation does not increase. The doctor said that this happens due to the position of the fetus in the stomach.
Olga Klochkova:
The labor was protracted, the waterless period lasted several hours. The result is hypoxia and the diagnosis is asymmetry of the lateral ventricles. Vikasol was prescribed, and a month later no pathology was detected by the NSG.
The ventricles of the brain are a collection of cavities of the nervous system filled with cerebrospinal fluid. The ventricles perform several functions:
In the brain are located:
- Lateral ventricles;
- Third ventricle
- Fourth ventricle.
How does the disorder develop?
If there is a slight expansion of the ventricles of the brain, this does not affect the patient’s condition. The disease is indicated by pronounced changes or expansion. The patient feels all the signs of the primary disease, leading to dilatation of the ventricles.
Some patients complain of problems with sensitivity and motor function, memory loss and absent-mindedness. When the ventricles of the brain are enlarged, intracranial pressure increases.
This condition is accompanied, firstly, by a headache, more often in the morning. When a person lies down for a long time, ICP increases. Migraines may not occur, but there is a feeling of squeezing. Nausea, vomiting. It doesn't get any easier after vomiting. This symptom occurs even with proper nutrition. Often a person feels sick with high blood pressure. My head is spinning. Anxiety, apathy, and fatigue appear.

This indicates that the disease is developing. The brain shrinks due to problems with the removal of cerebrospinal fluid into the lymphatic system. The result of such a process may be that schoolchildren may also develop such a disorder. Enlargement of the ventricles of the brain is observed due to congenital problems with the development of the organ , infections or genetic abnormalities.
Children experience such problems as movement of the eyeballs becomes difficult, the bones of the skull diverge, after tapping on the skull a specific sound is heard, and development is inhibited.
When minor events occur, the mood quickly changes. Impaired physical activity. Problems with excess weight. Attachment to parents and other close people noticeably deteriorates. In adolescents, asymmetry of the lateral ventricles of the brain occurs after injuries or infections. At the same time, they have severe headaches, nausea, and mental disorders.

What it is
Ventriculoasymmetry is a pathological condition in which the lateral ventricles are asymmetrical in relation to each other. Normally, they have a symmetrical arrangement and the same volume, however, due to external or internal factors, their relative position changes.
Ventricular asymmetry is considered a pathology only if it leads to dysfunction of the nervous system, deterioration of the body’s functioning and the development of symptoms. If the violation of symmetry is minimal and does not lead to disorders, this is considered an anatomical feature of the brain.
In the medical classification there is no such nosological unit (independent disease) as ventricular asymmetry, however, their asymmetry can lead to disruption of the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid, which in turn determines the clinical picture.
Lateroventriculoasymmetry is often latent (hidden) and does not cause symptoms. As a rule, the pathology of this system is determined by chance, by neuroimaging on computer or magnetic resonance imaging during a routine examination or after a head injury.
The change in symmetry itself is not dangerous to humans. The consequences that asymmetry can lead to are dangerous. For example, impaired liquor dynamics (fluid outflow), compression of cranial nerves, increased intracranial pressure. All consequences trigger a chain that develops its clinical picture.
Asymmetry is mainly diagnosed at an early age (up to one year) and in children.
Interhemispheric asymmetry with asymmetry of the cavities is not disturbed.
Causes of asymmetry of the lateral ventricles of the brain and main symptoms
What is asymmetry of the lateral ventricles of the brain and how can it affect health? To understand why asymmetry occurs, it is necessary to become familiar with the structure of the brain and the functions of its individual parts.
What are the lateral ventricles?
The ventricles of the brain are hollow areas in the brain tissue that exist to store or deposit cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). In the presence of certain pathologies, the ventricles increase in volume. The lateral ventricles are the largest in size.
Each has its own serial number. The third ventricle communicates with the lateral ones through the interventricular foramina. The lateral ones contain the occipital horn, the temporal horn, the frontal horn and the central part. Their location is slightly below the corpus callosum.
The left ventricle is called the first, and the right - the second.
The fourth ventricle is located midway between the medulla oblongata and the cerebellum. Because of its diamond-shaped shape, there is another well-established name, the diamond-shaped fossa. The spinal canal is located there.
Such cavities of the brain are created to perform their functions, namely formative and storage, and occupy an important place in the process of formation of cerebrospinal fluid. In the absence of pathological factors, the cerebrospinal fluid created with their help is transferred to the subarachnoid space. If the process does not proceed correctly, hydrocephalus appears.
The asymmetry of the lateral ventricles of the brain is that either one or both ventricles will immediately increase in size. The fact of the increase already indicates the presence of a pathological process.
What causes asymmetry?
Scientists have precisely established that asymmetry of the ventricles of the brain quietly manifests itself with age, during which the ventricles change their size. Diagnoses, some of which entail hydrocephalus, also increase their size. The lateral ventricles may also increase in size in patients with bipolar disorder or in patients with schizophrenia.
At the slightest suspicion that your newborn baby has asymmetry of the ventricles of the brain, do not rush to panic. This condition is also caused by ordinary reasons at the physiological level.
The baby may simply have a head that is smaller than the required size. This is not a common condition for them, but it happens often. There is nothing to be afraid of. A similar disorder can also occur in prematurely born children.
In such children, the volume of the ventricles will be slightly larger than in those born on schedule.
This diagnosis implies its development along two paths - atrophic and hypertensive. In ninety-nine percent of cases, hypoxia is considered the basic condition for the growth of cavities. The remaining people develop extremely rare infections and other diseases.
With insufficient oxygen saturation, the brain of a healthy person always produces cerebrospinal fluid, which also begins to accumulate. Under such conditions, a person develops increased pressure inside the skull - hypertension.
Abnormally enlarged ventricles can be easily noticed during an ultrasound examination.
With the atrophic development of the disease, hydrocephalus appears only after severe hypoxia. Additionally, it is caused by metabolic diseases, which have now become rare diseases, after hemorrhage or when catching an infection. In this case, the brain receives irreversible damage, which is a possible cause for the appearance of cerebral palsy or the development of neurological diseases.
How to detect asymmetry?
Despite all the variety of equipment, it is still impossible to make an accurate diagnosis. The examination is carried out on the following points:
- Monthly head growth is assessed. The method itself is the simplest, carried out by a local doctor or even by the baby’s mother herself. Brings correct information about the development of the diagnosis.
- Ultrasound quickly, clearly and accurately shows the true size of the ventricles.
- Examination by a neurologist. Children under three months are not examined due to the uninformative nature of this method.
- Search for edema of the vascular network, hemorrhages or spasms, examination of the fundus.
- The use of neurosonography is a method that allows you to determine the size of cavities.
If necessary, the specialist sends the patient for serious studies: MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) and CT (computed tomography). Another correct confirmation of the diagnosis is the method of taking a lumbar puncture, the study of which will provide the exact pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid.
What are the typical symptoms?
Depending on the level of intracranial pressure, symptoms change accordingly. The very first thing is discomfort.
Indeed, what disease can proceed comfortably for the patient? Regurgitation appears, but not always. Subsequently, throwing back the head is added - postural reflexes.
Another beacon will be simply an enlargement of the head. In fact, the disease often does not manifest itself, so it can only be detected by ultrasound.
A short list of symptoms:
- Decreased muscle tone.
- Complete refusal to breastfeed.
- Constant worry and crying.
- Hand trembling.
- Weakening of swallowing and grasping reflexes.
- Dehiscence of the sagittal suture.
- Swelling and tension of the fontanel.
- On examination, the iris of the eye is partially hidden behind the lower eyelid - rising sun syndrome.
- Swelling of the optic discs.
Danger of disease
At an early stage, the disease contributes to the development of the above symptoms, which, moreover, like some delay in movements, disappear forever with age. The appearance of such severe effects, for example, cerebral palsy, does not occur in this case.
If the pressure inside the skull is already high, and the cerebrospinal fluid continues to accumulate, then the human brain will inevitably be damaged. With the tireless increase in the size of the ventricles, the very properties of the brain change, reducing nervous regulation.
The child’s brain bones are elastic and not so rigidly connected to each other, so the pressure will always be slightly lower.
How can the disease be cured?
To get rid of the diagnosis, you should contact neurosurgeons and neuropathologists. To avoid the possibility of developing side effects, the child is constantly monitored by attending physicians.
The main methods of combating asymmetry include the use of diuretics to reduce the amount of cerebrospinal fluid produced and the use of neurometabolic stimulants (nootropics) for better blood supply to the brain. In addition, sedatives are also added here.
Additionally, special gymnastics and therapeutic massage are prescribed. Babies up to six months of age are treated on an outpatient basis. Older children are treated taking into account the disease that caused the asymmetry. For example, if it is an infection, then antiviral drugs and antibiotics are added.
Surgeries are performed to treat head trauma and tumors. The course of treatment is long and takes up to several months.
Source: https://glmozg.ru/stroenie/asimmetriya-bokovyh-zheludochkov-golovnogo-mozga.html
Causes
Factors influencing the expansion of the lateral ventricles are divided into several groups:
Direct reasons that directly affect the size of cavities:
- Impaired outflow of cerebrospinal fluid. The phenomenon develops as a result of brain tumors, brain displacement as a result of trauma.
- Excessive production of cerebrospinal fluid is a consequence of the innate characteristics of the body.
- Impaired absorption of fluid by the ventricles.
- Disruption of the formation of the ventricular system and the brain as a whole during the period of intrauterine development of the fetus.
- Head asymmetry – uneven skull.
- Prematurity of the fetus, oxygen deficiency.
- Prolonged and problematic labor: birth trauma, premature birth.
Symptoms and signs
Ventricular asymmetry does not have a specific clinical picture. All symptoms of the pathology are common and are characteristic of many infectious diseases of the nervous system. In terms of symptoms, asymmetry can imitate, for example, intoxication syndrome.
Symptoms of pathology in adults:
- Dizziness and headaches.
- Nausea and urge to vomit.
- Feeling of fullness in the head.
- Fast fatiguability.
- Visual impairment, slower reaction of the eyes to a visual stimulus.
- Diplopia is double vision.
- Hearing impairment, possibly tinnitus.
- Unpleasant sensations in the head when turning the head sharply, sneezing and coughing.
- Mental symptoms: irritability, emotional lability.
- Autonomic symptoms: hyperhidrosis - increased sweating, hot flashes to the extremities.
It is important to remember that the presence of these symptoms does not determine that the lateral ventricles of the brain are asymmetrical and the final diagnosis is made only after instrumental research methods.
Signs of pathology in children:
- Constant crying, anxiety.
- Lack of appetite.
- Throwing the head back.
- Frequent regurgitation immediately after eating, as a result of which the child does not gain weight well.
Symptoms of ventriculomegaly
The first signs of the presence of this pathology in the fetus are the large size of the ventricles of the brain, reaching 12-20 mm. The optimal period for its detection is 24-25 weeks of gestation.
Symptoms of ventriculomegaly in newborns include lethargy, inactive sucking and difficulty swallowing; the child often spits up and cries; sleep intervals are short; on the head and facial part of the skull, blood vessels often appear through the skin; There is protrusion of the fontanel, periodic trembling of the lower jaw and convulsive movements of the limbs. Until the sutures of the skull have fused, there is a rapid increase in its circumference (macrocephaly).
Children of the first two to three years have headaches; the pain intensifies with tension and sudden movements, jumping, bending. Nausea and vomiting occur spontaneously. In the presence of chromosomal syndromes, symptoms acquire characteristics characteristic of them.
Ventriculomegaly in adults can manifest as headaches, nausea, vomiting, increased intracranial pressure, and blurred vision. The latter is caused by swelling of the optic disc - papillodema, which in the early stages may be asymptomatic or cause headache. Over time, this swelling can lead to the appearance of a blind spot, blurred vision, and periodic limitation of the field of view. As a result, complete loss of vision is possible.
If the third ventricle located in the diencephalon enlarges, then due to pressure on the subcortical autonomic centers in the gray medulla of its walls, there may be gait disturbances, paresthesia, urinary incontinence, and deterioration of cognitive functions.
Diagnostics
Symptoms of the pathology do not provide reliable information about ventricular asymmetry, so objective studies are used to make a diagnosis.
- Monthly measurement of baby's head growth. This procedure is carried out by a local pediatrician. The essence of the method is to measure the size of the head. The indicators indicate normal growth, or excessive growth, which indicates a violation of the formation of the GM due to the expansion of the ventricles.
- Magnetic resonance or computed tomography. These neuroimaging methods allow the structure of the brain to be assessed using layer-by-layer images. The data indicate the volume and dynamics of changes in the volume of the lateral ventricles.
- Ultrasound. The method shows volumetric changes in structures, changes in the ratio of the ventricles, the presence of cysts and neoplasms.
- Echoencephaloscopy is an ultrasound method that allows you to assess the presence of volumetric structures (tumors). This procedure provides indirect evidence of changes in ventricular symmetry.
- Cerebrospinal fluid puncture. One of its parameters (the pressure under which cerebrospinal fluid flows out) can indicate a reduction in cavities. If the pressure is high, the ventricle is reduced, if the pressure is low, its size is increased. The remaining parameters (pH, glucose level, color and density) do not matter.
Treatment
Treatment of ventricular asymmetry can be conservative or surgical. Conservative treatment is only symptomatic, since the structural disorder cannot be cured with pills. For this purpose they prescribe:
- Diuretics. Diuretics stimulate diuresis - the outflow of fluid from the body increases. This reduces intracranial pressure and suppresses symptoms.
- Neuroprotectors are agents that protect GM from metabolic disorders. Neuroprotectors also prevent metabolic disorders and irreversible changes in nerve cells.
- Vasoactive drugs are drugs that improve blood supply to the brain and restore damaged tissue.
- Nootropics are drugs that restore parameters of mental functions (speed of attention, volume of short-term memory). Nootropics act only on damaged cells and have no effect on a healthy body.
- Sedatives and anxiolytics. Used to treat agitation in children and to relieve anxiety.
If there is an objective reason, etiotropic therapy is used, aimed at eliminating the nature of the disease that led to changes in the ventricles. For example, for neuroinfections, antiviral, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory agents are prescribed. If the asymmetry is caused by impaired blood supply and acute disturbance of blood flow, drugs are prescribed that improve the rheological properties of the blood.
Surgical treatment is prescribed in the presence of tumors in the brain, complicated traumatic brain injuries, subdural hematoma (hemorrhage under the meninges that compresses the brain and displaces the ventricles).
Ventriculomegaly is a pathology that affects the ventricles of the brain. The function of these parts of the organs is to maintain intracranial pressure and ensure normal blood circulation to the human cerebral cortex.
Most often, the disease occurs in unborn babies, less often in children of preschool and school age. Ventriculomegaly in adults develops in exceptional cases, since the disease is congenital.
Let's take a closer look at what ventriculomegaly is, the causes of its occurrence and how it is treated.
Asymmetry of the lateral ventricles of the brain in children and adults
Quite often, parents of infants are faced with a diagnosis of asymmetry of the lateral ventricles of the brain (lateroventriculoasymmetry). This causes them to panic, but in most cases everything is not as scary as it seems. In adults, this phenomenon is also sometimes diagnosed - but much less frequently.
Ventricles of the brain: types, structure, functions
Ventricles are containers in the brain that synthesize and also accumulate cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). There are four of them in total.
The lateral ones are located to the left (first) and to the right (second) of the midline. They have special holes through which communication occurs with the third and fourth. Characterized by larger sizes than the other two, they resemble the letter S. They are symmetrical in relation to each other.
The cerebrospinal fluid accumulated in the ventricles is transported to the subarachnoid space (the area between the brain and the spinal cord). Next, new fluid is produced. This is a normal physiological process.
Characteristics of the anomaly
Sometimes the system crashes. The removal of cerebrospinal fluid from the ventricles that produce it becomes difficult; excess fluid accumulates in them. The lateral ventricles of the brain begin to enlarge. This phenomenon is commonly called hydrocephalus.
The increase itself is precisely the asymmetry. Sometimes the volumes change for only one of them, and sometimes for both. But their symmetry in relation to each other is always violated.
This condition is not considered a pathology. But it can be caused by various diseases. Often this discrepancy in size is an individual feature. If it is small and does not manifest itself in any way, there is nothing to worry about. In most cases, abnormal development of the ventricles of the brain, diagnosed in newborns, goes away on its own over time.
Reasons for asymmetry
Most often, the deviation is detected in infants. Moreover, the overwhelming majority of cases occur in premature babies. And the more pronounced the asymmetry of the ventricles of the brain in newborns is, the earlier the child is born. This is due to the baby’s head circumference being too small and is not considered a pathology.
Other reasons for enlarged cerebral ventricles in newborns include:
- Hypoxia during intrauterine development.
- Infections that penetrate the placenta.
- Injuries during childbirth.
As for adults, similar brain problems can be caused by:
- New growths in the head.
- Infectious diseases (encephalitis, meningitis, etc.).
- Strokes.
- Thrombosis of cerebral vessels.
- Head injuries.
If an anomaly diagnosed in childhood is often a temporary physiological deviation, then in adults everything is different. Deviation from the norm is usually the result of some serious pathology associated with the brain.
Symptoms and features of asymmetry in children and adults
Asymmetry of the lateral ventricles of the brain in adults does not manifest itself if it is insignificant. In severe forms, people complain of:
- dizziness,
- Headache.
- Darkening in the eyes.
- Increased fatigue.
- Feeling of fullness in the head.
- Nausea.
In children, a slight increase in the ventricles of the brain also often does not make itself felt. In cases where the violation is significant, the child may:
- Cry a lot.
- Refuse food.
- Throw back your head.
- Burp frequently.
- It's bad to gain weight.
If, as a result of the obstructed outflow of cerebrospinal fluid, a lot of the latter has accumulated, the baby’s head becomes enlarged. And this can already be seen with the naked eye. In such cases, cerebrospinal fluid retention leads to hydrocephalus and requires immediate medical intervention.
Diagnostic measures
It is quite difficult to understand whether there is asymmetry of the lateral ventricles of the brain when it is not particularly pronounced. A visual examination by a therapist will not give results here. Therefore, if you suspect a problem, do:
- Computer or magnetic resonance imaging of the brain.
- Neurosonogram.
- Lumbar puncture (in rare cases).
Another common diagnostic method is fundus examination. If hemorrhages, swelling, spasms, etc. are observed, problems with the lateral ventricles are possible. Infant head growth should be assessed monthly.
Treatment of asymmetry
If there are no clinical manifestations of enlarged cerebral ventricles, treatment is usually not carried out. Doctors practice watchful waiting while monitoring the patient’s condition. In those cases where symptoms are present, asymmetry of the ventricles of the brain requires active medical intervention.
Conservative therapy involves taking sedatives and diuretics. Nootropics are also used that activate the cells of the ventricles of the brain.
The development of hydrocephalus often becomes a reason for surgical intervention. A large accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricles is very dangerous.
Asymmetry of the ventricles of the brain in adults requires treatment depending on the causes of its occurrence. If growth is caused by a tumor, it is removed. In cases where the cause is infection, a course of antibiotics and antiviral drugs is prescribed.
The process of combating asymmetry is long and difficult. But if there are indications, treatment is necessary. Otherwise, complications cannot be avoided.
Possible consequences
The consequences of a slight enlargement of the ventricles of the brain in infants can be a slight developmental delay. Usually, over time, the baby catches up with everything. In more complex situations, asymmetry threatens cerebral palsy, severe mental disorders, growth of the skull to enormous sizes, etc.
In adults, the lack of treatment for diseases that provoke changes in the volume of the ventricles means the progression of these pathologies. They often pose a threat to life.
Asymmetry of the lateral ventricles of the brain is sometimes completely harmless and goes away on its own, but the opposite situations are also common. Most often, asymmetry is diagnosed in newborns (especially premature babies). In adults, it usually results from other pathologies. In any case, the anomaly requires the help of specialists. You can’t let everything take its course.
Source: https://BolitGolova.info/mozg/asimmetriya-bokovyh-zheludochkov-golovnogo-mozga.html
Causes and prerequisites for the development of ventriculomegaly in the fetus
According to medical research, ventriculomegaly of the lateral ventricles occurs due to the following reasons:
- Hereditary prerequisites. If any of the child’s close relatives (mother, father, siblings/cousins) suffered from a similar disease, the likelihood of its occurrence in the newborn increases to 25% compared to a baby in whom no one in the family had such a disease;
- Ventriculomegaly in the fetus often develops as a side disease along with another disease, such as Down syndrome;
- Pathology is provoked by intrauterine infections, as a result of which the ventricles of the brain enlarge.
Reasons for appearance
Asymmetry of the lateral ventricles in adults may appear with age due to an increase in their size throughout life.
Diagnoses that entail dropsy of the brain (hydrocephalus) also contribute to enlargement of the ventricles. This deviation can also occur in mentally ill people - schizophrenics and those suffering from biopolar disorder. Do not panic if asymmetry of the lateral ventricles of the brain has been detected in an infant or newborn child. This is a fairly common occurrence and may be caused by the fact that the child's head is smaller than necessary. In addition, premature babies have much larger ventricular volumes than full-term babies. There is nothing to be afraid of here. Asymmetry of the lateral ventricles in an infant is an imaginary fear.
The main reasons for the appearance of newborn children:
- intrauterine infections in the mother;
- asphyxia;
- birth injuries;
- hydrocephalus;
- cerebral hemorrhage;
- hypoxia (oxygen starvation);
- heredity;
- the age of a pregnant woman over 35 years (increased risk of pathology).
The course of fetal ventriculomegaly in pregnant women after 35 years
Ventriculomegaly in the fetus most often develops if the child’s mother is over 35 years old. This happens for the following reasons:
- The risk of genetic disorders (for example, Down syndrome) increases;
- Intrauterine infections occur more often;
- A pregnant woman over 35 years of age is susceptible to complications while bearing a child.
Thus, if the mother is under 35 years old, ventriculomegaly in the child occurs only in exceptional cases.
Diagnosis of lateroventriculoasymmetry of the brain

Depending on the patient’s age, various methods for diagnosing pathology are used:
- The disease can be detected in the fetus starting from the 17th week of pregnancy. For diagnosis, the doctor performs an ultrasound of the mother’s abdominal cavity;
- Ventriculomegaly in an infant is confirmed after an ultrasound of the head;
- To diagnose an adult, an MRI of the brain is prescribed.
All procedures are aimed at examining the ventricles of the brain and identifying lateroventriculoasymmetry (violation of ventricular symmetry).
Severity of ventriculomegaly of the lateral ventricles
Doctors distinguish three degrees of severity of pathology:
At the first stage of development of the disease, there are no pronounced symptoms. Only a neurologist can detect it after diagnosis. Most parents notice that the child becomes excitable and irritable. Unfortunately, no other symptoms appear.
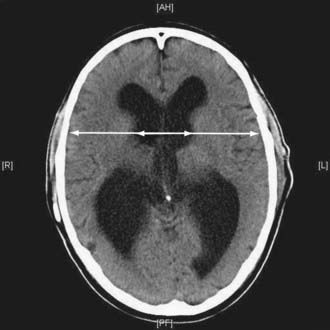
- Periodic convulsions, similar to epileptic seizures;
- Increase in head size;
- The presence of bulging veins on the forehead;
- Slow physical development;
- Mental retardation.
In addition to abnormal expansion of the ventricles of the brain, the following symptoms are present:
- Increased intracranial pressure due to the asymmetric shape of the ventricles;
- Recurrent headaches;
- Speech disorders.
Additional diseases are often added to the pathology: cerebral palsy, Down syndrome or hydrocephalus.
Course of the disease in children
The manifestation of the pathological process in young patients depends on age. Children are usually capricious and do not eat well. Their gaze is directed downward, but their eyes are excessively open. In children, the bones of the skull are flexible and plastic. Therefore, disorders can manifest themselves in an increase in head size. Pulsation of the fontanel and swelling of the veins are often observed.
School-age children also suffer from lateroventriculoasymmetry of the brain. Only a few know what kind of disease this is. Its development may be preceded by congenital disorders of brain formation or failures at the genetic level. At this age the disorder manifests itself:
- divergence of seams between the bones of the skull;
- slow development;
- overweight;
- sudden mood swings;
- impaired ability to move the eyeballs;
- problems with mental activity;
- decreased attachment to loved ones.
In adolescents, this disease is a consequence of cranial injuries or previous infections. It is accompanied by severe headaches, vomiting and nausea, and convulsions. Psychosis cannot be ruled out.

Treatment of ventriculomegaly in the fetus
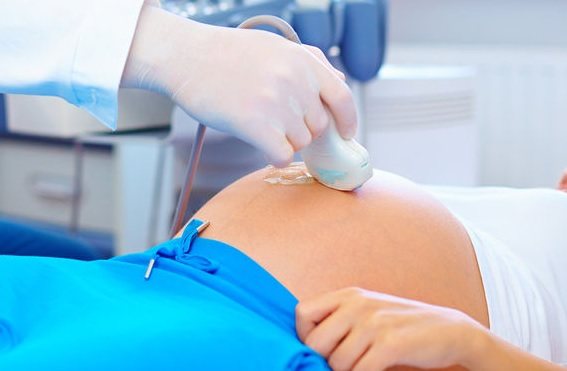
The disease is most often congenital, so it can be detected even before the birth of the child. To do this, the expectant mother undergoes an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, based on the results of which the degree of pathology is determined. In the third degree, the woman is offered an abortion, since the risk of miscarriage is high.
In other cases, doctors begin searching for the cause of the pathology:
- A woman must be tested for infectious diseases;
- The fetus is checked for the presence of congenital pathologies (cerebral palsy, Down syndrome, etc.);
- If no abnormalities are found, the pregnant woman is prescribed potassium tablets. It saturates the fetus with oxygen, which improves its condition.
Treatment options
When, based on research results, it is possible to determine that the patient has dilated ventricles, many begin to worry about the possible danger. Often, when the disease is detected, symptoms do not appear .
Therapeutic procedures are carried out to eliminate the disease, as a result of which the ventricles in the brain have enlarged. After this, the next stage of the procedure is performed. Medicines are prescribed to relieve intracranial pressure and preventive measures are taken.
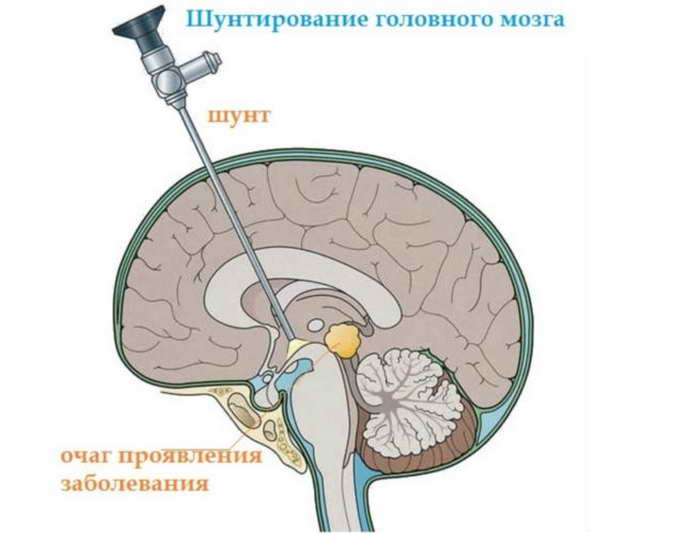
If the use of medications does not produce results, surgical measures must be used. A spinal tap is performed. If the ventricles are dilated due to a brain tumor, the tumor is removed. Ventricular bypass surgery is often performed. The device is inserted into the head and drains cerebrospinal fluid into the abdominal cavity or directly into the bladder.
In most examples, the bypass procedure has not been shown to be effective. The likelihood of inflammation around the shunt, blockage, and infectious process increases. The device has to be changed. During the treatment process, there are quite positive results in children compared to adults.
Medicines: diuretics, nootropics, sedative tablets, antiviral drugs and antibiotics are used in the presence of infections. The operation is performed after the formation of tumors, head trauma, hematomas, etc.
Treatment of ventriculomegaly in a newborn
With a mild degree of pathology, no therapy is prescribed: the mother only needs to carefully monitor the child’s condition and, at the slightest deviation from the norm, contact a neurologist.
The second stage is treated with medication: the child is prescribed drugs that accelerate processes in the brain:
- Vitamin B tablets;
- Diuretics are drugs that remove excess fluid from the body;
- Medicines to improve blood circulation.
To enhance the effect, it is recommended to walk with your child in the fresh air more often and perform minimal physical exercise with him.
The third degree of pathology is treated surgically, since taking medications will not give any results. The asymmetric shape of the ventricles is corrected by performing ventriculo-peritoneal shunting.
This is an operation during which shunts are installed to remove excess fluid. After surgery, children recover quite quickly: insomnia disappears and appetite returns.