Paresis is usually called a feeling of weakness of individual muscle groups caused by a violation of their connection with the central nervous system.
Such conditions are the results of various disorders of brain functioning. In this case, the cause may be instability in the functioning of peripheral nerves if they lose the ability to transmit brain impulses aimed at activating the work of muscle tissue.
There are two main types of paraparesis. This may be an organic or functional form of the disorder.
Organic paraparesis is caused by the influence of certain factors, as a result of which the nerve impulse does not reach the muscle tissue. In the functional form, disorders of inhibition, balance, as well as excitation and maneuverability are observed in the cerebral cortex itself.
Often this type of disease is characterized by an increase in muscle tone or the appearance of reflexes. The symptoms may be related to the formation of pathological reflexes, as well as some other unnatural movements.
Why does pathology occur?
Prosoparesis is a lesion of the facial nerve in which a person becomes unable to control the muscles of the face. In other words, paralysis sets in. It can be partial or complete.
The most common cause of a distorted face is:
- polio - an acute viral disease that affects the central nervous system;
- herpes virus;
- mumps (mumps) - an infectious disease that affects the glandular tissue of the body;
- various head injuries;
- nerve damage, which can occur with severe otitis media - an inflammatory process in the ear;
- mechanical damage to the nerve fiber caused by incorrect surgical intervention;
- syphilis;
- tuberculosis;
- multiple sclerosis;
- ischemic stroke - acute cerebrovascular accident;
- hypertensive crisis;
- diabetes mellitus
In addition, there are frequent cases of damage to the facial nerve due to dental operations such as the removal of molars and opening of abscesses.
Causes
Mobility in the lower extremities depends on the functioning of the brain: when the signal does not pass through the central or peripheral parts of the nervous system, paraparesis is formed. When 2 limbs are affected, the provoking factor should be sought in the spinal cord, spinal column or lower back. Failures may be caused by:
- various injuries to the head and spinal column;
- intervertebral hernia;
- spinal canal stenosis;
- tumor-like neoplasms;
- vascular diseases in the legs;
- lack of B vitamins;
- spinal artery thrombosis;
- consequences of hematomas;
- pathological processes of an autoimmune nature;
- abscesses;
- multiple sclerosis;
- myelopathy and its types.
The disease also occurs as a result of an infectious disease or disturbances in the genome, which is often of hereditary origin. The pathology needs to be treated and get rid of the root cause, since the disease can progress in the shortest possible time, causing paralysis and complete loss of mobility.
Situations of paraparesis in children due to trauma during childbirth are often observed. Each situation is individual and requires a high-quality and timely examination.
The pathological process is quite common. Lower paraparesis can be congenital (due to disorders or damage inside the womb, infectious diseases of a woman during pregnancy) and acquired (due to tumors or damage to the spinal cord). It is observed in adults and children, regardless of gender.

Types of pathology
There are 3 types of facial prosoparesis after a stroke or other diseases:
- Peripheral - when part of the face is affected, most often it is the left or right half.
- Central prosoparesis is a lesion of the muscle structures of the lower part of the face. In this case, a person feels sagging of the facial muscles that are located below the nose.
- Congenital variety. Diagnosed extremely rarely. Characterized by its appearance immediately after birth.
Each type of prosoparesis has its own characteristic features, which help to correctly diagnose the pathology.
Degree of damage
The consequences of brain stroke and other serious diseases can be divided into 3 degrees:
- Mild is expressed in a slight deviation from the norm in the form of a slight drooping of the mouth, where prosoparesis is localized. In addition, a person needs to make some effort to close an eye or frown.
- The average is characterized by the inability to puff out the cheeks or move the lips. Outwardly, the affected side looks more drooping.

In addition, lagophthalmos occurs - the inability to completely close the eyelid.
- The severe one looks like a completely distorted face on one side. In this case, half of the lip and eyelid are lowered as much as possible.
Depending on the degree of damage, adequate treatment is prescribed.
Classification
Symptoms of paraparesis of the lower extremities are characterized by certain features, determined by the degree of damage and its severity. These indicators are determined by a specialist during a clinical examination. Taking into account where the pathology is formed, the following types of paraparesis are distinguished:
- Central or spastic. Spastic paresis occurs when the first motor neuron is damaged. It originates in the motor area in the brain and ends in the anterior horns of the spinal cord.
- Peripheral or sluggish. Flaccid paraparesis is considered a manifestation of damage to the 2nd motor neuron. Its body is located in the lumbar enlargement at the level of L1–S2, and its processes are directed to the lower extremities as part of the peripheral nerves.
When it comes to talking about the severity of changes of a pathological nature, paraparesis of the legs is classified as follows:
- Easy.
- Moderate.
- Deep.
The level of strength reduction is determined by a specialist, based on the results of a clinical examination of the patient. This is done for any type of damage (central and peripheral type). Within one leg:
- there is flaccidity in one muscle;
- a muscle group is weakened;
- parts of the limb (distal or paroxysmal).
During a medical examination, it is necessary to determine the degree of damage to the central nervous system and the level of decrease in muscle strength. The classification of paraparesis is based on this.
Symptoms
Prosoparesis is a pathological condition that can be identified by the following manifestations:
- drooping corner of the mouth on the side of the affected nerve;
- smoothing the nasolabial fold;
- inability to completely close the eye;
- drooping lower and upper eyelids;
- difficulty keeping food and water in the mouth due to the affected nerve;
- smoothing wrinkles on one half of the forehead;
- decreased intensity or complete loss of taste;
- hearing loss;
- lacrimation from one eye;
- inability to put lips together in a “tube”.
In addition, there is severe pain behind the ear during the first time after the onset of the pathology.
Diagnostics
In order to determine facial paralysis, a personal consultation with a specialist is often necessary, since the symptoms are too obvious. However, to complete the clinical picture, additional studies may be prescribed, such as:
- computed tomography, which will show the degree of brain damage if prosoparesis appeared as a result of problems with this organ;
- Electromyography is the study of the bioelectric potential of muscles by passing an electric current through them.
Additionally, a consultation with an otolaryngologist may be prescribed in order to exclude the possibility of diseases of the ENT organs.

Drug treatment
How to recover from a stroke and other diseases that have serious consequences? First of all, treatment should be aimed at fully restoring body functions that have been partially or completely lost. For these purposes, the following medications may be prescribed:
- painkillers (most often analgesics are used);

- decongestants;
- vitamin complexes to support the immune system;
- vasodilators;
- eye drops and artificial tears for mechanical hydration of the affected eye;
- sedatives.
In addition, it is important to carry out competent treatment of the disease that led to prosoparesis of the facial nerve.
About symptoms
It is very important to identify the signs of spastic paraplegia in time; this will greatly help in the treatment of such pathology. Determining the characteristic signs of paresis can be done during a medical examination, however, most often people themselves notice that their legs begin to gradually weaken. So, people themselves come to the hospital because weakened legs create serious problems in everyday life.
It should be noted that weakness in the muscles of the lower extremities is far from the only sign of such an illness; the clinical picture suggests the presence of other symptoms. Thus, spastic paraparesis can be characterized by the following symptoms:
- the muscles can be subject to hypertonicity, in other words, the legs themselves fold like a jackknife;
- tendon and superficial reflexes begin to intensify and become depressed;
- Signs may appear that are clearly pathological in nature, this applies to flexion and extension functions.
When a peripheral motor neuron is damaged, other disorders may also occur. Paresis of a flaccid type can form, and they manifest signs that have the opposite form to those present in the spastic form of the disease. And here the symptoms are:
- muscle tone is greatly reduced (that is, we are talking about hypotension), or it may be that there is no muscle tone at all (then we are talking about atony);
- tendon reflexes are depressed;
- lower limbs undergo hypotrophy;
- individual muscle fibers begin to twitch fascicularly.
All this becomes the cause of disturbances of a static-dynamic nature, that is, a person begins to feel insecure when walking, and from time to time he even falls. Neurological disorders lead to the progression of the disease; if at first there was simply a feeling of weakness in the muscles, then the lower limbs can simply be completely paralyzed. That is, a person cannot walk, cannot stand up, and essentially becomes disabled, and cannot cope without outside help.
Paraparesis of the lower extremities is characterized by the presence of pronounced symptoms, which provides the opportunity to independently determine the pathology. With the disease, there is a loss of sensitivity of the skin on the legs. Lower paraparesis is accompanied by swelling. Most patients complain of pain in the legs.
Paraparesis of the lower extremities is characterized by severe muscle weakness. In pathology, an unsteady gait is noted. Patients say that with lower paraparesis it is difficult for them to bend and straighten their legs and hips. During the course of the pathology, a decrease in the knee reflex is observed. If paraparesis of the lower extremities occurs, the patient cannot step on the heel.
The symptoms of lower paraparesis are characterized by rapid manifestations and persistence for a long period of time. During the pathological process, disturbances in the performance of the pelvic organs are observed.
With lower spastic paraparesis, patients are diagnosed with sleep disorders. During the course of the disease, appetite decreases, which leads to weight loss. Patients complain of weakness and fatigue even when performing usual activities. Lower paraparesis is accompanied by diarrhea.
When the above symptoms of lower paraparesis occur, a decrease in the performance of the immune system is observed. This leads to an increase in the body’s vulnerability to the development of various infectious diseases.
With lower paraparesis, complete loss of sensation in the legs is diagnosed. The patient does not even feel severe bruises and burns. That is why it is recommended to provide special care for people with lower paraparesis.
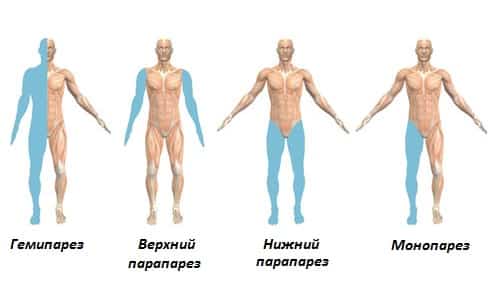
What paraparesis is and what mechanism of its development is known in detail only to a doctor. That is why, when the first symptoms of the disease occur, it is recommended to seek help from a doctor. Only a specialist, after carrying out appropriate diagnostics, will prescribe effective treatment for lower paraparesis.
Physiotherapy
Auxiliary procedures include physiological treatment, including the following methods:
- facial massage, which is carried out under the supervision of a doctor by a qualified massage therapist; independent kneading of the face is not recommended for prosoparesis;

- phototherapy with a Sollux lamp, the ultraviolet and infrared rays of which have the ability to penetrate into the deep layers of the skin and muscles;
- paraffin therapy, which involves covering the face with a layer of warm paraffin;
- phonophoresis - treatment using ultrasound technology.
All procedures must be performed in a clinical setting. The course of treatment depends on the degree of nerve damage and starts from 10 procedures, the interval between which is selected individually.
Spastic paresis of leg muscles due to spinal hernia
Paresis of the leg due to a hernia can be unilateral or bilateral (paraparesis). This depends on the localization of the hernial protrusion of the nucleus pulposus through a crack in the fibrous ring. When the hernia is located posteriorly, compression of the spinal cord is observed, resulting in paraparesis of both lower extremities.
Unilateral leg paresis due to spinal hernia is observed with lateral localization. The cause of muscle weakness is compression of the radicular nerve. This condition requires immediate medical intervention. Neurological syndrome can be eliminated only by eliminating its cause - compression of the dural membrane of the spinal cord or radicular nerve.
Spastic paresis of the legs can develop with traumatic lesions of the spine or nerves responsible for the motor skills of the lower extremities. These can be tumors, inguinal hernias, inflammatory abscesses. But most often, spastic paresis of the leg muscles is associated with strangulation of an intervertebral hernia - as a result of compression, increased muscle tone occurs. It is accompanied by cramps, the inability to independently bend or straighten the leg at the knee, ankle or hip joint.
If paresis develops against the background of an intervertebral hernia, it is necessary to seek medical help as soon as possible. In this case, it is impossible to predict spontaneous improvement in the patient's condition. The longer compression of the radicular nerve or cauda equina is observed, the higher the likelihood of developing complete paralysis of the lower extremities. It will be very difficult to restore innervation in the future.
Paresis of the lower extremities due to intervertebral hernia can be eliminated using the procedure of traction traction of the spinal column. This manipulation allows you to effectively and safely remove compression from the radicular nerve or dural membrane of the spinal canal. After the first 2-3 sessions, the patient notes a significant improvement in his condition.
Flaccid paresis of the lower extremities can be functional or organic. In the first case, damage to the nerve fiber occurs when conduction along the motor type of axons is disrupted. An interruption of this pathway of transmission of nerve impulses from the brain can be observed both at the level of cerebral structures and when the spinal canal is narrowed. Often the cause is pinching or compression of the radicular nerve due to an intervertebral hernia.
Exercise therapy and massage treatments
Therapeutic exercise helps to quickly recover from an illness. Even the simplest movements help restore the nervous response due to irritation of proprioceptors in the area of the muscular-articular apparatus. Exercises prevent the formation of contractures, maintain muscle tone, and stimulate neurotrophic processes.
The doctor will tell you what paraparesis is. He will take into account the course of pathological processes and the individual characteristics of the patient’s body. Exercises should be done slowly, gradually expanding the volume and increasing the load.
Set of classes:
- Lie on your back. As you inhale, raise your right leg, and as you exhale, lower it. Perform similar movements with the left leg.
- Lying on your back, imitate swimming. Perform movements with the lower limbs using the breaststroke technique.
- Bend and straighten your legs at the knees.
- Take turns drawing circles in the air with your feet. Perform exercises while lying on your back.
- Pull your feet towards you or turn them in different directions. Can be performed with both legs at once or in turns. It is allowed to lie on your back or sit.
- Bend one leg at the knee and press it as tightly as possible to the chest. Stay in this position for a while. Straighten the limb and repeat the exercise with the other leg.
- Lie on your back. Take turns bending and straightening your toes, spreading them out. It is important to maintain consistency.
Exercises are performed slowly, in a calm state. If your health deteriorates, you should stop exercising. For some exercises you can use additional equipment. Exercise therapy lasts no more than 20 minutes; for weak patients, 10 minutes is enough. The exercises are repeated 3-4 times.
Along with physical therapy, patients are recommended to attend massage treatments, after which blood circulation is restored and muscles are strengthened. Sessions help prevent degenerative changes. The massage is carried out by 2 specialists at once, starting from the feet and gradually moving to the hips.
Surgical
Only surgery can completely eliminate the cause of paraparesis of the limbs. Neurosurgeons perform decompression of nerves and the spinal cord, eliminating pathologies: hernias, tumors, disc displacements, hematomas, etc.
After surgical treatment of paraparesis, the patient is prescribed a course of rehabilitation to restore motor activity.

Folk remedies can also be used as an additional measure. However, traditional medicine is wary of this method of treating paraparesis and recommends trusting only the prescriptions of a specialist and not self-medicating.
It is important to understand that only competent and timely treatment carried out under the supervision of a qualified specialist can provide the most optimal prognosis for the patient.
In conclusion, it should be noted that paraparesis of the limbs is a pathology that is one of the manifestations of the primary disease. Even small changes in muscle strength and the ability to actively move should be a reason to go to the hospital, since these symptoms often accompany serious illnesses that are dangerous not only to the health, but also to the life of the patient.
Traditional methods of treatment
Prozoparesis is a pathological condition that requires complex therapy. In some cases, folk remedies can be added to conservative treatment methods, the action of which is aimed at maintaining immunity, weakening paralysis, and restoring muscle functions.
Various teas from plants such as lady's slipper, verbena, and motherwort are often used. They can be brewed either separately or together. Drink daily.

An hour before breakfast, it is recommended to drink 0.5 cups of freshly squeezed celery juice.
100 g of dried sage must be poured with 200 ml of boiling water and left for 8 hours. Drink the resulting liquid 1 teaspoon after meals with a glass of milk.
In addition, it is important to avoid drinking strong black tea and coffee, as well as alcoholic beverages during treatment, as their effect can not only interfere with treatment, but also aggravate the existing pathology.
Paraparesis, how to treat paraparesis of the lower extremities?
Many diseases associated with disruption of the nervous system are a big problem for people. One of these ailments is the neurological syndrome of paraparesis. In medical practice, the disease occurs quite often.
The essence of this pathological process is that the spinal cord and brain are damaged, which in turn makes it impossible for nerve signals to pass through the limbs. As a result, the sick person experiences muscle weakness, which in severe cases ends in complete paralysis.
Spastic paraparesis has no age restrictions. It can appear in newborns due to disruptions in the development of the fetus during pregnancy, infectious diseases suffered by the mother, and due to other reasons. The disease can also be diagnosed in an adult, regardless of gender.
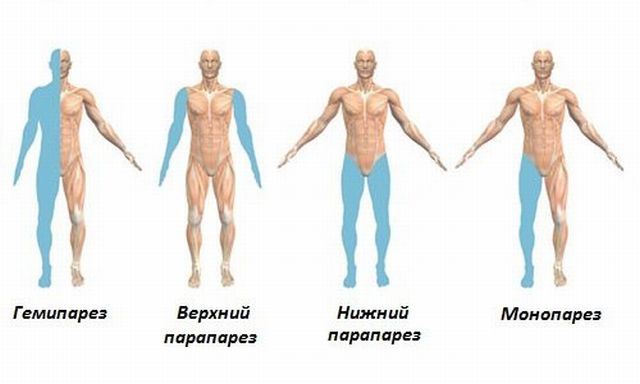
There are two types of this disease - upper, when problems spread to the arms, and paraparesis of the lower extremities.
The disease can occur in several forms. Most often, patients experience spastic paraparesis. To diagnose it, a comprehensive study is necessary.
In case of timely contact with specialists and proper treatment, doctors are able to restore partial motor activity to a person, but this requires a long course of treatment.
Diagnostics
The appearance of one of the above signs should be a cause for concern and seek medical help. To create a complete picture of the disease, all necessary clinical studies are collected. With their help, all possible causes of the pathology are established, which further helps to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment.
To determine paraparesis of the lower extremities, a neurologist prescribes the following diagnostic methods:
- X-ray of the spine.
- CT and MRI.
- Myelography.
- Neuromyography.
- Cerebrospinal fluid analysis.
- General and biochemical blood test.
- Blood serum analysis for vitamin B12 concentration.
- Analysis of urine.
In addition, the doctor recommends donating blood for tumor markers. Only after receiving all the results of the study, the neurologist determines the extent of the damage and selects therapy.
Physiotherapy
For flaccid paralysis and other problems with the musculoskeletal system, treatment with physiotherapeutic procedures is not the least important. Thanks to these methods, the patient’s blood circulation is normalized, spastic disorders are reduced and have a positive effect on nerve fibers.
The most commonly used physiotherapeutic methods are:
- Electrophoresis.
- Magnetotherapy.
- Hydrotherapy.
- Laser treatment.
- Reflexology.
- Procedures using mud and paraffin.
Each of these methods has its own specific contraindications, so their use is permitted only as prescribed by a doctor and after a thorough examination. It is important to remember that during tumor processes, muscle tissue cannot be stimulated. This is fraught not only with their growth, but also leads to worsening paraparesis.
Physiotherapy
The exercises included in the complex of therapeutic exercises are an integral part of the treatment of this disease.
After their use, the nerve roots are activated, and the muscular-articular apparatus gradually comes into action.
It would seem that a very simple exercise in the form of bending and extending the leg, if performed with a certain frequency, helps the patient quickly achieve a positive result in the treatment of paraparesis of the limbs.
Due to the fact that the causes of the disease are different, each patient requires an individual approach. This also applies to the issue of selecting therapeutic exercises. When performing them, the patient should not experience serious stress or rush. Everything should happen slowly, with a gradual expansion of the range of movements and an increase in load.
Massage
With the help of massage, it is possible to keep the leg muscles toned, reduce static manifestations in the limbs and improve the general condition of the limbs.
When performing a massage, specialists in most cases use classic techniques, consisting of stroking, rubbing, kneading and light pressure.
In this case, massage is useful not only for the legs, but also for the back. In combination with other methods, it not only helps to heal faster, but is also a necessary method during the rehabilitation period, when recovering from an illness.
Folk remedies
There are many traditional medicine recipes that help alleviate the patient's condition. Infusions and decoctions containing chamomile, laurel, and marjoram are considered beneficial. They are recommended to be taken orally.
Juices from plantain, celery, dandelion and nettle help the patient get rid of toxins in the body, the accumulation of which occurs during the disease.
Purified natural clay has proven itself to be excellent, which traditional healers recommend using not only in the form of applications, but also internally.
Representatives of traditional medicine do not always trust traditional medicine recipes, so before deciding to try one of the listed recipes, you should consult a doctor. This will help you not harm yourself and avoid possible complications of the disease.
Operation
If all of the above methods do not bring positive results, paraparesis is treated with neurosurgical intervention. During the operation, formations in the form of osteophytes, hernia, tumors that caused the problem are removed. Displacement of the vertebrae is treated in the same way.
After the operation, a long rehabilitation period is required to restore previous activity, including physiotherapy, massages and therapeutic exercises.
Prevention
Every patient diagnosed with paraparesis must understand the complexity of the current situation. You cannot turn a blind eye to the symptoms of the disease listed above. Even a slight decrease in the strength of the muscles of the limbs should alert a person. Treatment must be competent and timely. Only in this case do doctors predict a positive result.
The disease can be avoided if you adhere to a healthy lifestyle, avoid heavy stress on the body, stressful situations and injuries.
Complications
How to recover after a stroke or other illness? It is important to carefully and timely follow all the instructions of the attending physician who prescribed the treatment package. Prosoparesis of the left, right halves or lower part of the face with insufficient treatment or a combination of other negative factors can lead to complications such as:
- Irreversible damage to the nerve fiber. In this case, complete restoration of the performance of facial muscles is not possible.
- Improper restoration of the nerves threatens only a partial return to the former mobility of the face.
- Partial or complete blindness is possible if the optic nerve is damaged.
Such dire consequences can result not only from incorrect treatment, but also from untimely consultation with a doctor.
Clinical picture
Lower paraparesis is characterized by individual manifestations, which are a significant factor in the procedure for diagnosing neurological diseases. The main symptoms include:
- deterioration of sensitivity of the skin of the lower extremities;
- pain and swelling in the legs;
- weakening of muscle tissue;
- difficulty working the lower leg;
- sensations of discomfort during flexion and extension of the hip joint;
- worsening knee reflexes;
- while walking it is impossible to step on the heel normally;
- uncertain movement.
Such symptoms always appear very quickly and can have a long duration of action. In difficult situations, paraparesis in adults is combined with difficulties in the functioning of the pelvic organs.
In this case, a serious feeling of weakness in the muscles can be diagnosed, apathy is clearly expressed in the patient’s behavior, the person may hardly eat and sleep very poorly. In such situations, fever, mood swings, and disruption of normal bowel function often occur.
Due to the deterioration of the protective mechanisms in the human body, infection begins to develop at an accelerated pace.
In children's bodies, such diseases are often diagnosed after injury during childbirth. But there are cases when the diagnosis is determined incorrectly even in the real absence of a specific disease.
When the child becomes older, the established diagnosis must be confirmed or removed. Usually these issues are dealt with by a neurologist. In this case, several main degrees of paresis are determined:
- insignificant;
- moderate pathology;
- expressed;
- pronounced.
As the patient progresses to lower spastic paraparesis, tactile sensations deteriorate in the affected limbs. Therefore, patients with symptoms manifesting themselves in this way require special attention, as well as proper care. This condition mostly progresses when the spine in the chest area is damaged.
Lower flaccid paraparesis is the result of damage not only to the lumbar area, but also to the thoracic area.