Disease development process
The development of peripheral paralysis is associated with damage to the neuron responsible for movement and its axon. If only the nuclei of the cranial nerves and anterior horns are affected, then spinal muscular atrophy may develop in parallel with flaccid paralysis.
In addition, these two ailments are accompanied by characteristic fascicular twitching. When a peripheral nerve is deformed, there is a high chance that the innervated muscle will be paralyzed.
Peripheral and central paralysis are 2 pathologies that are often mistaken for one disease or even confused.
But these are different violations. With central paralysis, motor functions of the entire body are lost, the muscles are in constant tension. In addition, there are no signs of degeneration and the muscles do not atrophy. In the case of damage to the peripheral parts, the picture is different, or rather completely opposite.
Peripheral paralysis is a disease in which there is a decrease in muscle tone and paralysis of individual parts of the body.
Symptoms of flaccid paralysis, such as loss of motor function, are not an independent disease; they are often caused by concurrent illnesses.
Essentially, paralysis is a disorder in which a person makes involuntary movements. In some cases, patients cannot move part of the body or are completely immobilized.
Partial loss of motor functions indicates paresis. In any case, the disorder is evidence of damage to the nervous system, namely the centers that are responsible for movement and the peripheral parts. The following factors are noted as influencing the development of pathology:
- previous injuries;
- metabolic problems;
- infectious diseases (syphilis, tuberculosis, encephalitis, meningitis and polio);
- nutritional and toxic (pellagra, beriberi, heavy metal poisoning);
- oncological diseases;
- congenital and hereditary factor;
- intoxication;
- disruption of the nutrition system;
- diseases whose etiology remains unknown, for example, multiple sclerosis.
Dangerous and unpredictable
All types of paralysis are a real challenge both for the patient himself and for his loved ones. A paralyzed person is completely dependent on the people around him. He is unable to satisfy his household needs on his own.
During the course of the disease, pain can cause a lot of trouble. Limitation in postures can cause tension to build up in other parts of the body.
The human body has the ability to “write off” those resources that it does not actively use. In particular, muscles in different parts of the body that are not used in life can atrophy over time. Therefore, it is very important to start treatment in a timely manner and bring it to a victorious end.
Since paralysis is always a consequence of other diseases, it is recommended to promptly treat diseases of the cardiovascular system and take measures to prevent stroke.
The mother's lifestyle plays a huge role in the development of infantile paralysis. Women of childbearing age should absolutely not smoke, use drugs or indulge in alcoholic beverages.
Pathogenesis
(Guillain-Barré, Landry, Strohl, Miller-Fisher syndrome,
acute polyradiculoneuritis)
Children are affected with a frequency of 1.1 per 100,000 population. The disease is often preceded by respiratory and
gastrointestinal tract
Campylobacter jejuni (30%)
cytomegalovirus (15%)
Epstein-Barr virus (10%)
Mycoplasma pneumoniae (5%), etc.
acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (AIDP),
acute motor axonal neuropathy (AMAN),
acute motor-sensory axonal neuropathy (ASAN),
Miller-Fisher syndrome
occur without a rise in temperature against the background of a generally satisfactory condition
gradual (over 1-2 weeks) development of neurological symptoms
in children with a feverish onset of the disease, the development of paresis/paralysis occurs against the background of normal temperature
paresis/paralysis begins in the distal limbs
are symmetrical
sensory disorders of the “stockings” and “gloves” type are observed
in the CSF there is often an increase in protein numbers with normal cytosis
by the end of the 3rd week of illness, 85% of patients show signs of segmental demyelination and/or axonal degeneration in an ENMG study
Most often, post-injection mononeuropathies are observed. When collecting anamnesis, it is possible to identify a connection with intramuscular injection that preceded the development of neuropathy
Other causes are less commonly identified: falls and spinal injuries, compression of a limb by a tight bandage, pinching of a limb in a crib or playpen
Loss of reflexes, as well as hypotension, occur due to interruption of the monosynaptic stretch reflex arc, as well as disruption of the stretching mechanism of fast and slow reflexes. Muscle atrophy appears because the anterior horn ceases to have a trophic effect on muscle fibers - this problem appears several weeks after the denervation of nerve endings in the muscles has occurred and can be so severe that after several months or years only connective tissue remains in the affected muscles.
Neuromuscular diseases
congenital muscular dystrophy
spinal progressive muscular atrophies (Werdnig-Hoffman, Fazio-Londe, etc.)
atonic form of cerebral palsy
benign form of congenital hypotension
some other diseases
Absence or decrease in muscle strength; - decreased muscle tone; - hyporeflexia or areflexia; - muscle wasting or atrophy.
Hypotonia and areflexia develop due to interruption of the arc of the monosynaptic stretch reflex and a disorder of the mechanism of tonic and phasic stretch reflexes. Muscle atrophy is caused by a violation of the trophic influence from the anterior horn on the muscle fibers, develops several weeks after denervation of the muscle fibers and can be so pronounced that after several months or years only the connective tissue remains intact in the muscle.
Restorative measures for the development of flaccid paresis or paralysis are aimed, firstly, at restoring (if possible) the function of a peripheral neuron, and secondly, at preventing the development of muscle tissue atrophy and preventing contractures.
Achieved by prescribing neutrotrophic and vasoactive drugs:
- nootropil/piracetam (capsules/tablets 0.4 g-0.8 g three times a day or 20% solution 5-10 ml intramuscularly or intravenously);
- Cerebrolysin (3-5 ml intramuscularly or intravenously);
- actovegin (5-10 ml intramuscularly or intravenously drip once or twice a day; 1 ml contains 40 mg of the active substance);
- trental (in pills, 0.1 g three times a day, or 5 ml intravenously drip once a day; 1 ml contains 0.02 g of the active substance);
- vitamin B1 (solution of thiamine chloride 2.5% or 5% or thiamine bromide 3% or 6%, 1 ml intramuscularly daily, once a day);
- vitamin B12 (400 mcg once every 2 days intramuscularly, can be taken simultaneously with vitamin B1, but not in the same syringe).
If the anatomical integrity of the peripheral nerves is compromised, neurosurgical intervention may be indicated.
This is a very important task, since degeneration of denervated muscle fibers develops very quickly and is often irreversible. By the time innervation is restored (either through natural reinnervation or through neurosurgical intervention), atrophy can reach such a pronounced degree that muscle function can no longer be restored.
Massage
It is aimed at stimulating muscles, so techniques include fairly intense rubbing, deep kneading, and impact on segmental zones. However, massage of paretic muscles should not be done with great force. The massage should be moderate and short-lived, but carried out over many months (short breaks are taken between courses).
Rough, painful techniques can cause increasing muscle weakness. They also use acupressure using a tonic technique. The toning method of acupressure is carried out by applying vibrating, short, quick stimulation with the fingertip sequentially to a number of points that stimulate the desired movement. The topography of recommended points of influence for stimulating active muscle contractions is presented in table 4.5. and in Fig. 4.6.
| Point number | Point name | Location of the point | Muscles that are stimulated |
| Shoulder girdle and upper limb | |||
| 1 | Jian-jin | On a line corresponding to the middle of the shoulder girdle, in the center of the supraspinatus fossa | |
| 2 | Fu-fen | At the inner edge of the scapula at the level of the spinous processes of the II and III thoracic vertebrae | Trapezius muscle (movement of the shoulder girdle up and back) |
| 3 | Gao-huang | At the inner edge of the scapula at the level of the spinous processes of the IV and V thoracic vertebrae | Trapezius muscle (movement of the shoulder girdle up and back) |
| 4 | Jianyu | Above the shoulder joint, between the acromion process of the scapula and the greater tubercle of the humerus | Deltoid muscle (abduction, flexion, extension, supination and pronation of the arm in the shoulder joint) |
| 5 | Xiao-le | In the middle of the back surface of the humerus 5 cun above the elbow joint | |
| 6 | Xiao-hai | On the back of the shoulder between the inner condyle of the humerus and the olecranon | Triceps brachii (extends the forearm) |
| 7 | Yang-chi | On the dorsum of the wrist joint, in the center of the wrist fold | |
| 8 | Wai-guan | 2 cun above the yang chi point | Extensor muscles of the hand and fingers |
| 9 | E-men | On the dorsum of the hand between the metacarpophalangeal joints of the fourth and fifth fingers | Finger extensor muscles |
| Pelvic girdle and lower limb | |||
| 10 | Yin-bao | On the midline of the inner thigh, 5 cun above the knee joint | Adductor muscles |
| 11 | Cheng-fu | In the center of the gluteal fold | Biceps femoris, semitendinosus and semimembranosus (shin flexor) |
| 12 | Yin-men | 6 cun below the cheng fu point (middle of the back of the thigh) | Same |
| 13 | Yin Ling Quan | On the inner surface of the tibia, at the posterior edge of the inner condyle of the tibia | |
| 14 | Yang-ling-quan | At the anterior lower edge of the head of the fibula, in line with the Yin Ling Quan point | Same |
| 15 | Tzu-san-li | 3 cun below the patella outside the crest of the tibia | Extensor muscles of the foot and toes |
| 16 | Jie-si | In the middle of the dorsum of the ankle joint | Same |
| 17 | Shan-qiu | On the inner surface of the foot, in front and below the inner ankle | Same |
| 18 | Qiu-xu | On the dorsum of the foot in front and below the outer ankle | Same |
| 19 | Pu-shen | A series of dots along the outer edge of the foot | Pronators of the foot |
Note: cun is an individual unit of measurement for each person, equal to the distance between two folds formed when bending the second and third phalanges of the middle finger on the left hand in men and on the right hand in women.
Physiotherapy
Aimed at restoring movements of weakened muscles. Initially, in the complete absence of active movements, passive movements are used in all joints of the paretic segment or limb. Passive movements are performed with a small amplitude simultaneously with the volitional sending of a motor impulse to the patient for this movement.
movements are performed in a horizontal plane, on a smooth surface. Another way to get relief is to exercise in water. The patient is taught measured muscle tension and relaxation, gradual increase and decrease of force, differentiation of different degrees of force (for this purpose, visual analogue scales and bars, dynamometers can be used to help the patient).
As muscle strength is restored, training exercises begin to be used. In order to increase the load on the muscles, multiple repetitions of the movement, an increase in the speed of movement and the length of the lever, and resistance to the movement are used (the resistance can be provided by a trainer or a partner; rubber bandages, expanders, and block exercise machines with a suspended load are also used to create resistance).
The exercise should cause some fatigue, but not overwork of the working muscles. Intense, prolonged physical activity is unacceptable, since paretic muscles are characterized by rapid fatigue, and an overdose of exercise leads to an increase in muscle weakness. The load is increased gradually as muscle strength increases.
Electrical stimulation
Electrical stimulation plays a special role in the treatment of flaccid paralysis. Electrical stimulation of motor nerves and muscles is understood as the use of electric current to excite or enhance the activity of these structures [Bogolepov V.M. et al., 1985]. Electric current, changing the concentration of tissue ions near the cell membrane and changing its permeability, acts like natural biocurrents.
The therapeutic effect of electrical stimulation is associated with increased blood flow to contracting muscles and improved venous outflow, which is accompanied by a local increase in metabolic and plastic processes, as well as an increase in the functional activity of the central nervous system. However, the therapeutic effect of electrical stimulation entirely depends on how correctly the parameters of the stimulating electrical current are selected.
The choice of exposure parameters, in turn, is determined by the degree of disruption of the muscle innervation and the condition of the muscle tissue. Therefore, electrical muscle stimulation should always be preceded by a diagnostic study of the degree of muscle denervation. The main question to be resolved is the question of the presence of a complete (anatomical or functional) or partial break of the nerve, since with a intact or only partially damaged nerve, stimulation of the muscle must be carried out through the nerve, whereas with complete denervation of the muscle it is necessary to limit stimulation of the muscle itself. This issue can be resolved using electromyography and/or electrodiagnostics.
Currently, the main diagnostic method for determining the level and degree of damage to nerve conductors is electromyography in its modern versions (stimulation, needle). Let us recall that the main electromyographic signs of partial nerve damage are a decrease in the velocity of excitation (during demyelination) and/or a decrease in the amplitude of the M-response (a sign of axonopathy), as well as changes in the structure of action potentials of motor units.
Signs of complete interruption of a peripheral nerve include the absence of an M response when the nerve is stimulated, as well as spontaneous activity recorded in the muscle at rest. Damage to a motor neuron at the level of the anterior horns of the spinal cord is characterized by the appearance of fasciculations at rest, and with active contraction - a sparse interference curve with individual high-amplitude discharges of long duration.
Characteristic manifestations
Signs of peripheral paralysis:
- complete or partial loss of motor functions;
- decreased muscle tone in the affected part;
- complete or partial absence of any reaction to sudden irritation of paralyzed muscles;
- denervation atrophy is observed, that is, loss of muscle mass;
- a reaction of degeneration or degeneration is also observed.
Over time, if a person does not receive proper treatment, peripheral paralysis can develop into another form, that is, an acute infectious disease. It is often found under the name polio. It is characterized by intoxication, while the nervous system also suffers, paralysis and acute flaccid peripheral paresis develop.
This infection is initiated under the influence of a filter virus, which is quite resistant and has increased sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation, disinfectants and high temperature.
When the virus penetrates a neuron, a dystrophic-necrotic process is triggered, which is accompanied by the replacement of all dead neurons with glial tissue and subsequent scarring. In turn, the more neurons die, the faster paresis or paralysis occurs.
Differential diagnosis
In addition to the basic methods, specialists carry out differential diagnosis of the disease. At the same time, symptoms are identified that are very easily confused with signs of central paralysis.
In addition, do not forget that in some cases, the lack of motor functions can be caused by any kind of injury and such a symptom is not always a sign of peripheral paralysis. Therefore, a complete examination of the patient is carried out to identify such injuries.
During diagnosis, the medical history of the disease is analyzed, as well as the patient’s complaints. It is necessary to answer the following questions: how long ago did the strength in the muscle group disappear; for what reason did this happen; whether such symptoms were observed in other family members; whether at home or at work you have to come into contact with harmful toxic elements.
You need to undergo an examination by a neurologist - the patient’s muscle strength is assessed on a 5-point scale, and in addition, other signs of the disease are searched for (lack of reflexes, facial asymmetry, problems with swallowing function, thinning muscles, the appearance of strabismus).
In some cases, it is necessary to consult a neurosurgeon.
Analyzes
The main tests that the patient needs to undergo are the following:
- Blood for a general analysis to determine markers of inflammation (increased ESR rate, as well as C-reactive protein) or an increase in creatine kinase;
- Blood for toxicological analysis to determine the presence of individual toxic elements in it;
- Sometimes a proserine test is performed to detect the presence of myasthenia gravis (pathological fatigue of muscle groups). The introduction of this drug allows you to quickly restore muscle strength to the body.
The main instrumental diagnostic method for determining the level and degree of destruction of nerve receptors is electromyography (modern variations of this procedure are needle or stimulation).
In the diagnostic process, it is very important to differentiate flaccid (peripheral) paralysis from central. In addition, it should be distinguished from tendon injuries, limited movement due to various injuries, as well as joint contractures.
The main difference between flaccid paralysis and spastic (central) paralysis is the preservation or destruction of the lower motor neuron. If it, as well as its axon, is preserved, the disease will be spastic, and if destroyed, it will acquire a peripheral form.
Symptoms of acute flaccid paralysis
flaccid syndrome is characterized by the following symptoms [Duus P., 1995]: – absence or decrease in muscle strength; – decreased muscle tone; – hyporeflexia or areflexia; – or muscle atrophy.
Hypotonia and areflexia develop due to interruption of the arc of the monosynaptic stretch reflex and a disorder of the mechanism of tonic and phasic stretch reflexes. the muscle is caused by a violation of the trophic influence from the anterior horn on the muscle fibers, develops several weeks after denervation of the muscle fibers and can be so pronounced that after several months or years only the connective tissue remains intact in the muscle.
Acute flaccid paralysis is characterized by the following manifestations:
- the muscle does not resist passive movements;
- atrophy is very pronounced;
- there is a decrease or complete absence of deep reflexes;
- muscle and nervous electrical excitability changes.
Flaccid paralysis of the legs
If there is a disruption in the functioning of the anterior horns located in the spinal cord at the site of the lumbar thickening, flaccid paralysis of the legs may develop. When such a lesion spreads to the cervical or lumbar area of compaction on both sides, simultaneous paralysis of all limbs or a specific area may develop.
Flaccid paralysis usually affects only one leg. In this case, it becomes impossible to move the foot, because the disease affects the tibial muscle group.
Before the onset of flaccid paralysis of the legs, the patient feels a sharp pain in the lumbar region.
Bedridden illness or paraplegia
A paralyzed person in our understanding is a person confined to a wheelchair. But even this phenomenon has a scientific basis. Paraplegia is paralysis of the upper (upper paraplegia) or both lower (lower paraplegia) limbs.
General information
So, paraplegia (para- - two identical limbs, -plegia - paralysis). This disease is a consequence of injury to the lower or upper parts of the spinal cord, as a result of which nerve impulses cease to flow to the limbs and they become paralyzed.
Classification of ailments
In addition to paraplegia, in modern neurology there are such concepts as tetraplegia - paralysis of all four limbs and monoplegia - paralysis of one limb.
If we talk about such a concept as paraplegia of the lower extremities, it is somewhat more common than paraplegia of the upper extremities. The reason for this is the physiological structure of the human body. If a patient’s spinal area in the upper parts of the body is damaged, then it is more likely that not only his arms, but also his legs will fail.
Heredity
In addition to the above-mentioned causes of the disease, there is a special subtype - hereditary spastic paraplegia (Strumpel's paraplegia). This type of disease is transmitted solely through inheritance.
There are two types of hereditary spastic paraplegia:
- Clean (simple).
- Complex.
The pure form is characterized by damage to the extremities, without other pronounced symptoms. The complex form, in addition to paralysis of the limbs, is combined with mental disabilities, visual impairment, hearing impairment, epileptic seizures and other related ailments.
Hereditary spastic paraplegia can develop in people of any age from one year to old age. In the case of a simple form, the patient may not lose the ability to walk at all, but some difficulties will still be present.
In the case of a complex form, the patient is more likely to eventually not be able to move independently.
Health care
First of all, treatment is aimed at getting rid of the causes contributing to the development of the disease. In some cases that are particularly complex, specialists resort to surgical intervention.
In this case, only the part of the spinal cord on which the damaged muscles are located is affected. But we should not forget that peripheral paralysis may not be a consequence of some other disease, but it is quite likely that it will develop as an independent form of pathology.
A whole range of measures is used in treatment. In this case, both medications and more common methods such as physical therapy and massage are used.
The main task of specialists is to fully restore the patient’s motor functions. If this is done, the chance of developing other processes leading to deformation against this background is significantly reduced.
All this time, the patient must be under the supervision of a neurologist and follow all his instructions, including taking individually prescribed medications.
Among the medications that are often prescribed to patients suffering from flaccid paralysis are:
- Prozerin;
- Dibazol;
- Mellictin;
- thiamine chloride solution.
In addition, physiotherapeutic treatment is now actively used. This process takes quite a long time, but, nevertheless, this type of treatment is the most effective. If only this type of treatment is used, motor functions may not fully return, so a whole range of measures is required.
Leg muscle paralysis: causes, methods of diagnosis and treatment
Paralysis of the leg muscles is a symptom of a neurological disease, which is expressed in impaired motor functions and complete immobility. It can be temporary or permanent, depending on the cause of its appearance and the intensity of development.
If motor activity is partially limited, this is leg paresis; it is easier and faster to cure. Pathology is not an independent disease, but a sign of serious problems in the body that need immediate treatment.
You should contact a neurologist; sometimes you may need the help of a neurosurgeon.
Causes
Flaccid paralysis (paresis) develops when a peripheral (lower) neuron is damaged in any area: anterior horn, root, plexus, peripheral nerve.
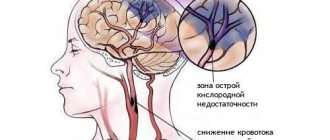
The main cause of flaccid paresis of an arm or leg is a stroke, which results in an acute disorder of cerebral or spinal circulation. In second place in frequency are tumors of the brain or spinal cord, and head or back injuries.
Other reasons include:
- Brain abscess.
- Encephalitis.
- Disseminated encephalomyelitis.
- Poisoning with poisons, salts, alcohol.
- Botulism.
- Epilepsy.
Most often, identifying this symptom does not require any diagnostic measures, since making the above diagnoses already implies a decrease in muscle strength in a person.
The doctor must examine the patient and interview him. The main complaints are identified, from what period the strength in the arms or legs began to decrease, and whether anyone in the family has similar symptoms.
After this, a neurological examination is performed on a five-point scale, which allows you to identify flaccid paresis of the lower extremities and assess the general condition of the muscular system. After this, a general blood test is performed, and, if necessary, toxicological tests.
Other diagnostic procedures include electroencephalography, computed tomography, magnetic resonance angiography. If necessary, a neurosurgeon is consulted.
The main cause of this disease is considered to be various enteroviruses. For example, enterovirus 71 is currently the most dangerous virus of the neurotropic type; it very often leads to the development of epidemics of flaccid paralysis in children.
Difference from peripheral paralysis
Spastic (SP) and peripheral paralysis (PP) differ from each other in a number of characteristics. The main ones are the following:
Spastic paralysis involves damage from the cortex to the cells of the anterior horns of the spinal cord; with PP, damage to the cranial or anterior roots of the spinal cord is observed;
- with SP there is an increase in reflexes , with PP they are absent;
- with SP, abdominal reflexes are absent or weakly expressed, with PP they are normal;
- pathological reflexes are not lost in SP, but are absent in PP;
- muscle atrophy is characteristic of peripheral paralysis, which is not observed in SP;
- electrical excitability remains , but with peripheral it is weak or absent.
Treatment
Restorative measures for the development of flaccid paresis or paralysis are aimed, firstly, at restoring (if possible) the function of a peripheral neuron, and secondly, at preventing the development of muscle tissue atrophy and prevention.
* nootropil/piracetam (capsules/tablets 0.4 g-0.8 g three times a day or 20% solution 5-10 ml intramuscularly or intravenously); * Cerebrolysin (3-5 ml intramuscularly or intravenously); * actovegin (5-10 ml intramuscularly or intravenously drip once or twice a day; 1 ml contains 40 mg of active substance);
* trental (in pills, 0.1 g three times a day, or 5 ml intravenously once a day; 1 ml contains 0.02 g of active substance); * vitamin B1 (solution of thiamine chloride 2.5% or 5% or thiamine bromide 3% or 6%, 1 ml intramuscularly daily, once a day); * vitamin B12 (400 mcg once every 2 days intramuscularly, can be taken simultaneously with vitamin B1, but not in the same syringe).
If the anatomical integrity of the peripheral nerves is compromised, neurosurgical intervention may be indicated.
Prevention of development. This is a very important task, since degeneration of denervated muscle fibers develops very quickly and is often irreversible. By the time innervation is restored (either through natural reinnervation or through neurosurgical intervention), atrophy can reach such a pronounced degree that muscle function can no longer be restored.
Massage. It is aimed at stimulating muscles, so techniques include fairly intense rubbing, deep kneading, and impact on segmental zones. However, massage of paretic muscles should not be done with great force. The massage should be moderate and short-lived, but carried out over many months (short breaks are taken between courses).
Rough, painful techniques can cause increasing muscle weakness. They also use acupressure using a tonic technique. The toning method of acupressure is carried out by applying vibrating, short, quick stimulation with the fingertip sequentially to a number of points that stimulate the desired movement.
Flaccid paresis is a decrease in strength in one or more muscles. It develops only secondarily, that is, it is a consequence of one or another disease. In this case, strength can be measured using a special test, which cannot be said about another condition called paralysis.
Depending on how badly the muscles are damaged, there are 5 types of this condition. To determine one degree or another, you can use a scale specially developed for this purpose.
Acute flaccid paresis is not a separate disease, but only a consequence of other, more serious diseases. Therefore, treating it alone will not give any results. First of all, it is necessary to identify and direct treatment to the cause that caused this condition.
For example, it may require surgical removal of a tumor or hemorrhage caused by a stroke. The same method is used to remove the abscess (abscess) and begin antibiotic therapy.
Treatment can use drugs that improve blood circulation, lower blood pressure, and improve metabolism. Antibacterial therapy may also be carried out if infections of the brain or spinal cord have been diagnosed. For botulism - administration of serum. And, of course, drugs that improve nerve conduction are always used.
It turns out that the treatment of flaccid foot paresis will depend entirely on what causes the pathology, and the therapy itself must be strictly individual.
During treatment, massage, exercise therapy, physiotherapy and other procedures are required that are aimed at preventing the muscles from atrophying.
It is very rare to be completely cured, so in most cases the patient receives disability.
By the way, you may also be interested in the following FREE materials:
- Free books: “TOP 7 harmful morning exercises that you should avoid” | “6 Rules for Effective and Safe Stretching”
- Restoration of knee and hip joints with arthrosis - a free video recording of the webinar conducted by Alexandra Bonina, a doctor of physical therapy and sports medicine
- Free lessons on the treatment of lower back pain from a certified physical therapy doctor. This doctor has developed a unique system for restoring all parts of the spine and has already helped more than 2000 clients with various back and neck problems!
- Want to know how to treat a pinched sciatic nerve? Then carefully watch the video at this link.
- 10 essential nutritional components for a healthy spine - in this report you will learn what your daily diet should be so that you and your spine are always healthy in body and spirit. Very useful information!
- Do you have osteochondrosis? Then we recommend studying effective methods of treating lumbar, cervical and thoracic osteochondrosis without drugs.
Acute flaccid paralysis occurs due to damage to a peripheral neuron in any part of it: on the root or peripheral nerve, in the plexus or anterior horn. With the development of this pathology, muscles lose reflex and voluntary innervation.
With the development of flaccid paralysis, treatment procedures are aimed at restoring (if possible) the functioning of the peripheral neuron, and in addition to preventing the process of muscle tissue atrophy and the possible occurrence of contracture.
Medicines
To improve the functioning of nervous tissue, treatment with vasoactive and neurotropic drugs is necessary:
- nootropil or piracetam (tablet/capsule at a dosage of 0.4-0.8 g 3 times/day or 20% solution at a dosage of 5-10 ml IM or IV);
- Cerebrolysin (in a dosage of 3-5 ml IM or IV);
- Actovegin (in a dosage of 5-10 ml IM or IV through a dropper 1-2 times/day; 1 ml of the drug contains 40 mg of the active ingredient);
- trental (dragées in a dosage of 0.1 g 3 times / day or intravenously through a dropper 1 time / day in a dosage of 5 ml; 1 ml of medicine contains 0.02 g of the active ingredient).
Vitamins
Vitamins are also taken:
- vitamin B1 (solution 2.5% (thiamine chloride) or 5% (thiamine bromide), 3% or 6% at a dosage of 1 ml IM every day 1 time/day);
- vitamin B12 (dose 400 mcg 1 time/2 days IM, can be combined with vitamin B1, but they cannot be mixed in one syringe).
Acute flaccid paralysis can be effectively treated with electrotherapy and other physical therapy methods. Basically, for this disease, balneotherapy and galvanization are prescribed.
In the case of flaccid paralysis, massage is carried out to stimulate the muscular system, which is why deep kneading is used when performing it, and with it rubbing with high intensity, and in addition to this, the massage therapist actively influences the so-called segmental zones. But at the same time, you cannot massage paretic muscles with excessive force - the procedure should be short and moderate.
In addition, acupressure is performed using a tonic technique. In this case, it is necessary to press the necessary points with the tip of your finger in order to cause quick short vibrating irritations that will stimulate the necessary movement.
Roots of the evasive peony. You need to take 1 tsp. dry ingredients and pour boiling water (3 cups), then cover the container and leave for 1 hour, then strain. You need to drink the tincture three times a day. 1 tbsp each before meals (15 minutes before). Alcohol tincture should be taken in a dosage of 30-40 drops. 3 rubles/day before eating.
Dying or tanning sumac (fresh leaves are used). Take 1 tsp. ingredient and pour boiling water (1 cup), cover the container and leave for 1 hour, then strain. Drink 3-4 times a day. 1 tbsp each
Rosehip fruits and roots. A decoction of the roots is used externally - in case of paralysis, you need to bathe your feet in a bath with it.
Surgical treatment
In case of destruction of the anatomical integrity in the peripheral nerve system, the patient may be prescribed a neurosurgical operation.
Paralysis of the lower extremities, paralysis of the legs, types and symptoms, how to cure
Paralysis is a condition in which muscles are unable to perform their functions because... shrink. Paralysis itself is only a sign (symptom). This disease is not independent, but only develops secondary to some illness or component of a condition, disorder, neoplasm, etc.
Classification and types of paralysis
In terms of origin, there are two types of paralysis:
- peripheral (another name for it is flaccid);
- central (aka spastic).
Peripheral is expressed by the destruction of motor neurons innervating muscles, or nerves connected to muscles. As peripheral destruction develops, the tone of the paralyzed muscles decreases, they become thinner and exhausted, which creates complete atrophy.
Central have their own distinctive ability - increasing muscle activity in paralyzed areas and damaging the area above the motor activity of neurons.
There is another classification of paralysis - in terms of the number of affected limbs:
- monoplegia – paralysis of one of the limbs;
- hemiplegia – damage on one side only;
- paraplegia is partial paralysis of the legs or arms (only the upper or lower limbs are affected);
- tetraplegia affects all limbs; it is paralysis of the legs and arms.
Causes
According to statistics, about 2% of the population experience discomfort in the lower extremities when moving. Every year, just over 1 million people injure their backs to some degree. And these numbers are growing every year.
When the capabilities of full motor skills are weakened, and not completely lost, we can talk about paresis. Paresis and paralysis are similar in one thing - they occur when human nerve cells are damaged, when two parts of the motor system responsible for coordination are affected. Complete paralysis can be caused by the following factors:
- spinal and head injuries;
- intoxication with substances: heavy metals and their salts, poisons of various origins, alcohol, narcotic substances, medications, etc.;
- cancerous formations;
- infectious diseases that entail negative consequences in the functioning of the whole organism;
- metabolic disorders in the body;
- botulism (manifested by disturbances in the respiratory system, gastrointestinal disorders, abdominal pain, slurred speech);
- poor nutrition, unhealthy lifestyle;
- alcohol and drug abuse;
- hereditary changes in the body that affect the functioning of the nervous system and are accompanied by poor coordination of movements.
People who have suffered birth trauma can also suffer from paralysis. This, among other things, is a common cause of cerebral palsy.
There are several ailments of unknown origin (for example, Charcot's disease), which manifest themselves as motor impairments; they have very negative consequences. There is a high probability that paralysis may be the result of neurosis and have a psychogenic nature of origin. Such patients definitely need psychological help from a professional.
Pathogenesis
A paralyzed person must be thoroughly examined in order to notice even the slightest changes in the body.
If there are signs of changes in reflexes, then most likely the disease is caused by organic reasons. In this case, there is a risk of developing atrophy and complete disorder of muscle tone.
If the paralysis is temporary, there are no changes in tendon reflexes or muscle tone.
Symptoms
Paralysis can be caused by various reasons, which is why its symptoms can have a different nature and various localizations. The most common changes occurring in the major structural component of the nervous system during paralysis may include:
- degeneration (nerve tissue dies and new ones do not form);
- destruction (in this case the conduction of nerve impulses is disrupted);
- neuroinflammation;
- vascular obstruction, plaque formation, risk of thrombosis;
- development of sclerosis;
- the appearance of demyelination - a pathological process of destruction of the myelin sheath of the nervous system.
With this disease, there are other symptoms: headaches, migraines, fever, lump in the throat, partial loss of vision, nausea and vomiting, increased fatigue, muscle pain or weakness, involuntary urination, inability to control bowel movements.
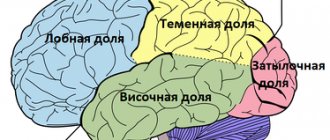
If we consider paralysis from an anatomical point of view, we can divide them into two forms: the first are caused by destruction of the central nervous system (cerebral and spinal), the second - by peripheral nerves.
Symptoms of central paralysis
The symptoms of central paralysis are very diverse: some signs are immediately detected in their pure form, others are confusing due to their combination with some signs of peripheral paralysis. But both are accompanied by sensory changes and atrophy, and pathologies of vascular tone.
During the genesis of an illness of this type, the entire body is exposed to suffering, and not individual parts of the musculoskeletal system, for example, muscles.
Absolute tendon reflexes are preserved and may even intensify, and accelerated spasms of the muscles of the paralyzed limbs are noted. Abdominal reflexes are the opposite: they are reduced or disappear on the paralyzed side.
Symptoms of peripheral paralysis
This form of paralysis occurs when the nerve roots are destroyed, the muscles are weakened, the plexuses or the nerve itself are damaged. This form is usually characterized by vulnerability.
Symptoms of paraplegia
In the process of diagnosing paralysis of the lower extremities, a phenomenon may occur - the pathological Babinsky reflex, in which a response is received to the line irritation of the outer edge of the sole - 1 toe extends. In a paralyzed limb, there is a complete decrease in deep reflexes, there is a possibility of their complete absence. In the same case, clonus are not detected. But you can note the abdominal reflexes, which remain intact.
First aid
In case of sudden damage to the limbs, you must promptly consult a doctor. To do this, the first thing you need to do is call an ambulance. By waiting for a medical team, you can alleviate the patient’s situation.
- If the head, neck or back is injured (or there is a suspicion of injury), the victim should not be moved under any circumstances. The exception is a mortal threat to life - fire, flood, natural disaster.
- Fixation of the spine. To prevent further damage, it is necessary to position the victim’s head in line with the body, using available means.
- Do not give drink. Under no circumstances should you give water until specialists arrive.
Treatment
The primary task that the attending physician sets for himself is to eliminate the cause of the disease.
In all cases, without exception, symptomatic drug treatment, exercise therapy, as well as therapeutic massage are carried out, which will help speed up the recovery of motor reflexes.
For each individual case, its own program is selected, including both medications and preventive exercises.
In the treatment of this dangerous disease, the main emphasis is on physical therapy. During exercise, it is very important to position the affected limb correctly so that contractures do not appear.
Physical education includes vigorous and passive exercises aimed at restoring motor skills and healthy muscle tone.
You need to do gymnastics carefully, moderately, following all the doctor’s instructions.
Before a gymnastic set of exercises for peripheral paralysis, it is necessary to do a special massage.
With the gradual revival of motor functions, active movements are added to the complex aimed at strengthening muscles, normalizing tone and straightening gait. Great success in treatment can be achieved if you add water activities to this complex.
They can be done in the bathroom, or you can sign up for the pool. Water helps reduce stress on the joints, so the healing process will speed up and will not be as painful.
The drug course of drugs is selected individually by a neurologist. Dibazol, Proserin, Mellictin and intramuscular injections of vitamin B1 are usually prescribed.
In case of a dangerous form of paralysis, corticosteroid drugs and salicylates are added to this complex. In extreme cases, electrotherapy is used.
For vascular disorders, there are special drugs to improve the metabolic processes of the brain and saturate it with oxygen.
Spastic paralysis is treated with datrolene in combination with imidazoline and gabaleptin benzodiazepines. There are cases in which Botox is used, which can help damaged muscles relax and return to their former shape.
In the case of spastic paralysis, surgical intervention is also possible. But to resort to this last resort, at least 6 months must pass.
If no changes in a positive direction are observed during this period, the surgeon gets down to business.
//www.youtube.com/watch?v=5v7UVz91D-U
It must be remembered that the main thing for the patient is movement. If the patient cannot do this on his own, he needs help, because the more a person is in motion, the faster he will recover.
When you stay in bed for a long time, blood circulation is disrupted, which leads to frequent dizziness and fainting, the respiratory system, cardiovascular system, joints suffer, skin condition deteriorates, and much more.
It is imperative to actively engage your lungs and perform simple breathing exercises, constantly warm up your body with massage and strengthen it with physical exercise.
Prevention of paralysis
- Have regular medical examinations once a year.
- Complete exclusion of alcohol and drugs.
- Maintaining a healthy sports lifestyle (moderate physical activity, daily morning exercises, walks in the fresh air, healthy 8-hour sleep).
- Following the rules of proper nutrition (excluding fried and smoked foods, eating fruits and vegetables that are rich in vitamins, moderate consumption of sweets).
- Blood pressure control.
Source: //NashiNervy.ru/perifericheskaya-nervnaya-sistema/otchego-byvaet-paralich-nerva.html
Preventive actions
In order to avoid the development of disorders, experts recommend following the following instructions:
- Seeing a doctor at the slightest symptoms of the disease or any other problems;
- blood pressure should always remain under control;
- treating infectious diseases in their early stages, preventing them from causing more serious problems;
- It is best to eliminate all bad habits - alcohol and smoking contribute to the development of many health problems, not only peripheral paralysis;
- effective prevention is maintaining a healthy lifestyle (proper nutrition, rest, adherence to a routine and physical activity).