Paresthesia is a condition in which there is a burning, tingling and crawling sensation on the skin. This phenomenon is associated with loss of sensitivity, which can occur due to pinching and damage to peripheral nerves, the spinal cord or the brain.
Paresthesia is not a primary disease. It develops as a symptom in various diseases. A similar phenomenon can also appear as a result of metabolic disorders, poisoning, impaired blood supply to the nerves, and so on.
Many people often experience temporary paresthesia when certain parts of the body are compressed, which is also accompanied by numbness. Pathological paresthesia, whether present constantly or appearing periodically, develops solely as a result of the appearance of primary diseases.
Goosebumps all over my body...
The main feature is that the “goosebumps” can be localized in different places. This is influenced by the cause of the phenomenon and the characteristics of the course of the primary disease.
The following areas of the body are most often affected by paresthesia:
- hands;
- legs;
- fingers and toes;
- lips;
- language;
- head.
Some patients in dental clinics experience temporary paresthesia localized in the jaw, cheeks of the tongue or pharynx.
A decrease in sensitivity can occur as a result of improper treatment or tooth extraction. The dentist may snag or damage the nerve fiber. Usually the phenomenon goes away on its own within a few days. Sometimes re-treatment is required.
Causes
Paresthesia of the skin area innervated by the nerve is a consequence of irritation of the latter. Paresthesia can occur when a nerve located, for example, next to tumors is compressed. Compression can occur from the outside, for example, when the brachial nerve is compressed with a tourniquet (with intravenous injections), paresthesia of the skin of the palms and forearm can occur.
The cause of paresthesia can be osteochondrosis of the spine, which leads to compression of the nerve roots.
This phenomenon also occurs with nerve injuries, inflammation of blood vessels supplying the nerves, poisoning, diabetes mellitus and lack of B vitamins.
Causal complex
There are various causes of paresthesia, ranging from pinched nerves and neurological diseases to toxic poisoning and chronic illnesses. Usually the causes and place of manifestation of the phenomenon are interrelated.
Tongue on cheeks - blunder-blunder
Numbness and paresthesia of the tongue, as well as decreased sensitivity and the inability to distinguish tastes, occurs under the influence of external factors, neurological abnormalities and due to internal disorders in the body.
Most often, tingling and burning in the tongue occurs as a result of the development of the following pathologies:
- concomitant disease of the nervous system;
- disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- disease of the endocrine system and so on.
In addition, the phenomenon may occur due to a lack of vitamin B or mechanical damage to tissue from teeth or artificial dental structures.
If your legs are taken away
Paresthesia of the limbs can occur as a result of the following factors:
- spinal cord injurieslocalized in the lumbar region or below, usually the patient also experiences other unpleasant symptoms: decreased sensitivity, weakness, pain, impaired motor function, and so on;
- surgery performed on the spinal cord, spinal nerves or spine;
- tumors on the spinal cord (nerve endings can be pinched, and the blood supply to nerve fibers and the spinal cord is also disrupted);
- multiple sclerosis , especially in cases where its foci are localized in the parietal part of the brain;
- polyneuropathy caused by taking medications, alcoholic beverages or chemical poisoning.
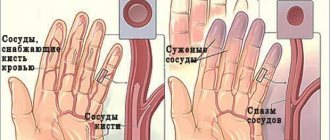
- Raynaud's disease;
- blood pressure disorders in the lower extremities.
Hand Wars
Unpleasant sensations in the hands can occur in the presence of the following pathologies:
- osteochondrosis (when intervertebral discs are destroyed, nerve endings become pinched);
- damage to individual nerves in the neck by an inflammatory process;
- disruption of the blood vessels that supply food to the brain (sometimes paresthesia is one of the first signs of a stroke);
- multiple sclerosis;
- neck muscle inflammation;
- decrease in calcium levels in the body.
With excessive alcohol consumption, certain infectious diseases, diabetes and intoxication, damage to nerve fibers can occur. As a result of the development of pathology, paresthesia in the hands may occur as one of the symptoms.
Loss of sensitivity in fingers
Often the phenomenon appears only on the fingers (hands or toes). The reasons for this phenomenon are usually no different from the reasons that cause paresthesia in the arms or legs. It could be:
- osteochondrosis;
- spinal cord injury;
- alcohol or other poisoning;
- Raynaud's disease;
- vitamin B deficiency;
- lack of calcium and other microelements.
The lips don't seem to be your own...
Tingling, burning or crawling in the lips may occur as a result of neurological or other diseases. Among the most common reasons it is worth noting:
- neuritis of the facial nerve;
- cervical osteochondrosis;
- multiple sclerosis;
- hypertensive crisis (a sharp increase in blood pressure is also accompanied by shortness of breath, severe headache, vomiting, loss of consciousness and other symptoms);
- lack of vitamin B;
- decrease in glucose.
In Bell's palsy, paresthesia and numbness of the lips are the first symptoms of the disease, followed by paralysis.
When you have goosebumps all over your head
Neurological disorders can cause paresthesia of the entire head. The most common reasons include:
Sometimes the phenomenon appears before a migraine attack.
Paresthesia can be a side effect of certain medications.
The phenomenon can be caused by taking medications to lower blood pressure and antieliptic drugs, as well as some other drugs.
Paresthesia of the hands
Hand paresthesia is the most common complaint with which patients consult a doctor. The patient often feels an unpleasant tingling sensation in the hands, crawling insects, etc. This symptom is most common in older people. Their nerves are not able to recover at the same speed as in young people.
Most often, paresthesia of the hands occurs as a result of compression of the limb. The nerve, in response to compression, begins to send multidirectional impulses, which are felt by the person as numbness. It can occur after a person has been in an uncomfortable position for a long time, as well as after sleep.
Typically, paresthesia of the limbs goes away quickly. However, if it occurs very often and bothers a person, then he should see a doctor. Sometimes numbness of the upper extremities is a sign of a serious disorder of the cardiovascular system. It is also important to examine the spine, since cervical or thoracic osteochondrosis is the most common cause of numbness in the upper extremities.
Paresthesia often occurs as a response to stress and overexertion.
It is necessary to urgently contact a neurologist if paresthesia is combined with other circulatory disorders.
Features of the clinical picture
Paresthesia is manifested by a decrease in sensitivity, which causes unusual sensations. The patient feels a tingling, slight burning sensation on the skin, as well as goosebumps.
The main feature is that a person experiences such sensations when different electrical impulses occur in the nerve fibers (or one fiber) that transmit information to the brain.
This happens most often due to disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system.
Paresthesia of the head
Paresthesia of the face or part of it is most often associated with circulatory failure and is always an indication to consult a doctor. Paresthesia is much less dangerous if it is caused by prolonged exposure to an uncomfortable position.
Facial numbness can be a symptom of the following diseases:
- migraine;
- trigeminal neuritis;
- cerebral circulatory disorders;
- herpes zoster;
- osteochondrosis.
But paresthesia of the tongue is rare. It is necessary to consult a doctor, as it may be a symptom of the following diseases:
- oncology of the larynx;
- anemia;
- diabetes;
- stroke;
- brain damage.
Establishing diagnosis
In case of prolonged or frequent paresthesia, you should consult a neurologist. After collecting an anamnesis and a detailed interview with the patient (complaints, chronic diseases, other symptoms, etc.), the doctor prescribes a series of clinical or instrumental studies that help establish the cause of the development of this phenomenon.
In most cases, the patient is prescribed electroneuromyography. Using this study, the passage of electrical impulses along nerve fibers is monitored. The method allows you to determine not only the location, but the degree of disruption of the passage of nerve impulses.
Depending on the accompanying symptoms, the doctor may also prescribe:
- ECG;
- MRI of the brain or spinal cord;
- Ultrasound of the heart;
- radiography of the spine;
- taking a blood test for toxins;
- EEG;
- Dopplerography of blood vessels and so on.
A complete examination allows you to determine the cause of the disorder and prescribe the correct treatment.
Disease prevention
In order to prevent further development of the disease, it is necessary to start leading a healthy lifestyle:
- rejection of bad habits;
- healthy, full sleep;
- a balanced diet including vegetables and fruits;
- light exercises to ensure limb mobility;
- walks in the open air;
- alternation of work and rest;
- timely treatment of chronic diseases that can cause hypoesthesia.
So, we found out that hypoesthesia is a rather serious disorder of the body , which cannot be left to chance, expecting that it will go away on its own.
Because sometimes this disease can lead to the most tragic consequences.
Therefore, if you often feel signs of numbness in any part of the body, you should consult with an experienced doctor, and, if possible, get rid of bad habits that contribute to the development of hypoesthesia.
How to get rid of unpleasant symptoms
The treatment regimen is directly related to the disease or pathology that causes paresthesia. The main goals of therapy are to eliminate the irritating factor, as well as restore the functioning of the nervous system and blood supply.
Among the main goals it is also worth noting the stimulation of the transmission of nerve impulses in the affected area.
Methods used
Treatment of paresthesia depends on the location and cause of its occurrence:
- If tingling and burning of the skin occurs as a result of the appearance of a tumor, surgical intervention is recommended.
- If the functioning of peripheral nerves is disrupted or the spinal cord or brain is damaged , therapeutic actions are aimed at restoring performance (taking medications and prescribing procedures depends on each specific case).
- For diabetes mellitus, the patient takes medications to restore normal blood glucose levels. For metabolic disorders, medications may also be prescribed.
- When nerve endings are pinched, therapeutic actions are aimed at eliminating the problem. In case of deficiency of vitamin B or microelements, a special diet and vitamin complexes are prescribed.
Physiotherapeutic procedures are highly effective in the treatment of neurological diseases. The doctor may prescribe:
- electrophoresis;
- acupuncture;
- diadynamic currents;
- magnetic therapy;
- mud therapy and other procedures.
Physiotherapeutic procedures help restore normal transmission of electrical impulses, which helps get rid of unpleasant numbness and tingling.
Difficulties of therapy
The doctor is not always able to immediately determine the cause of the phenomenon, which delays the prescription of the correct treatment. In addition, it should be taken into account that in most cases, paresthesia is associated with disorders in the nerve fibers, spinal cord or brain.
Restoring the functioning of the components of the nervous system requires a special approach, and is not always possible in full. In some cases, surgery is required (tumors, pinching, etc.).
Sometimes diseases, the symptom of which is paresthesia, develop rapidly and can lead to dire consequences. That is why, if this phenomenon occurs repeatedly, it is necessary to consult a doctor.
Therapy for paresthesia in neuroses is complicated by excessive irritability and excitability of the patient. In this case, treatment is carried out comprehensively and includes medications, physical procedures and other methods.
Paresthesia of the legs
Numbness of the lower extremities and loss of sensation are quite common. Most often, the feet become numb as a result of an uncomfortable posture or being in an uncomfortable position for a long time. This type of digital paresthesia is usually not a cause for concern and goes away quickly.
Paresthesia of the lower extremities can be permanent or transient. Permanent loss of sensitivity in the lower extremities occurs as a consequence of severe pathologies of the brain and spinal cord. Sometimes it develops after spinal cord injuries. And transient paresthesia of the lower extremities develops as a consequence of migraine and taking certain medications.
Paresthesia of the lower extremities occurs most often in the feet. If paresthesia occurs in the calf muscles, it is often accompanied by a cramp. But if paresthesia in the legs appears after sleep, then this indicates a circulatory disorder and is an indication to see a doctor. Especially if numbness is accompanied by cramps and pain in the leg muscles. A comprehensive examination of the heart, spine and blood vessels is also indicated.
Diagnostics
If one or more of the above symptoms occur, you should seek help from a neurologist. The only exception is the localization of unpleasant sensations in the oral cavity - in such situations, diagnosis and treatment are carried out by a specialist in the field of dentistry.
Establishing a final diagnosis involves conducting a wide range of laboratory and instrumental examinations, which are preceded by manipulations performed directly by the clinician. Thus, the first stage of diagnosis includes:
- studying the medical history - to establish the most characteristic predisposing factor for a particular person;
- collection and analysis of life history - this is necessary in cases of the development of paresthesia due to reasons that do not have a pathological basis;
- a thorough neurological examination - aimed at assessing the condition of the skin and its sensitivity, as well as identifying areas of paresthesia and numbness;
- a detailed survey of the patient - to determine the severity of symptoms and compile a complete symptomatic picture.
Instrumental procedures involve the implementation of:
- electroneuromyography;
- radiography of the spine;
- Ultrasound of the peritoneum;
- ECG and EEG;
- CT and MRI of the spinal cord or brain;
- rheovasography.
Laboratory diagnostics are limited to:
- general clinical analysis and blood biochemistry;
- toxicological blood test.
Symptoms of sensory disorders
Patients describe sensitivity disorders with different sensations: the illusion of goosebumps, a feeling of tingling, numbness, pain, increased or decreased susceptibility to real stimuli. They can appear in any part of the body, but most often occur on the limbs, back, and face. The most common symptoms include:
- hyperesthesia - heightened sensitivity to mechanical, chemical, temperature, pain stimuli;
- hypoesthesia is a condition in which the sensitivity of the skin to touch and external irritants decreases;
- paresthesia - the disorder is transmitted through sensations of numbness, tingling, crawling;
- analgesia - reduction of pain sensitivity;
- dysesthesia - perverted, inadequate sensations, for example, warmth is perceived as cold or pain;
- allocheiria - the actions of a stimulus on one side of the body are asymmetrically perceived on the opposite;
- hyperalgesia - increased sensitivity to pain;
- Senesthopathy is an unpleasant bodily sensation localized in internal organs or on the surface of the body, a common symptom of mental disorders.
Treatment of paresthesia
First of all, treatment of paresthesia comes down to eliminating the irritating factor. The patient should:
- stop drinking alcoholic beverages;
- control sugar levels. If the glucose level is high, you should take hypoglycemic medications and also adhere to a diet;
- carry out detoxification measures in case of poisoning, in particular, ensure drinking plenty of fluids and taking B vitamins;
- apply warming ointments to the affected area.
In the presence of tumors and other formations that compress the nerve, surgical removal of the tumor is indicated.
Drug therapy for paresthesia includes taking B vitamins, as well as drugs that improve the rheological properties of blood - antiplatelet agents and vasoactive drugs.
Physiotherapeutic treatment for paresthesia may include magnetic therapy, electrophoresis and mud therapy.
Etiology
Paresthesia acts as the body's response to damage or irritation of the nerve root or nerve endings located in the spinal cord or brain.
The disease can involve both the skin and mucous membranes, often the oral cavity. Depending on the affected segment, predisposing factors will differ. For example, paresthesia of the tongue occurs against the background of:
- irritation of its surface with sharp edges of teeth;
- incorrectly selected dentures by the dentist;
- changes in bite, which can occur due to the absence of several or all dental units;
- increased wear of the dentition;
- galvanization, which is a consequence of the installation of prostheses made of different materials.
However, involvement in paresthesia of the tongue occurs only in cases where the above reasons are supplemented by the following internal pathological factors:
- arachnoiditis or other pathologies of the central nervous system;
- ulcerative lesions of the duodenum or stomach;
- gastritis of any nature and other pathologies of the digestive tract;
- hypovitaminosis, in particular, lack of B vitamins;
- disruption of the functioning of the endocrine system;
- malignant hypertension;
- ailments of the cardiovascular system;
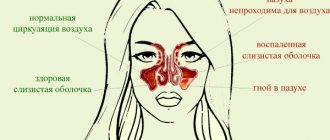
- diseases of the ENT organs, for example, sinusitis and rhinitis.
In addition, paresthesia of the oral mucosa can be caused by:
- wisdom tooth removal;
- entry of filling material into the tooth canal.
The lower and upper extremities are most often affected by paresthesia. In the first case, the provoking factor may be:
- any medical intervention in the spinal cord area, namely open surgery on the spinal nerves, spine or spinal cord, as well as improperly performed procedures such as lumbar puncture;
- injury to the lumbar spinal column;
- the course of diabetes mellitus;
- the formation of malignant or benign formations in the spinal cord in the lumbar region;
- Raynaud's disease;
- obliterating endarteritis;
- polyneuropathy of alcoholic, diabetic or intoxication nature;
- rabies and neurasthenia;
- multiple sclerosis.
Paresthesia of the upper extremities is often caused by:
- osteochondrosis;
- wide range of injuries;
- formations of a malignant or benign course;
- damage to the cervical spine;
- the presence of an inflammatory process in the neck muscles;
- banal overwork;
- acute or chronic circulatory disorders;
- stroke;
- abuse of alcoholic beverages;
- decreased calcium levels in the blood;
- multiple sclerosis and diabetes mellitus.
Paresthesia of the lips is not uncommon, and most often develops against the background of:
- hypovitaminosis;
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine;
- neuritis of the facial nerve;
- lowering blood glucose levels;
- hypertensive crisis;
- inflammatory lesions of the gums. Most often, such paresthesia occurs after tooth extraction;
- chronic migraine;
- multiple sclerosis;
- herpes zoster;
- Bell's palsy.
Paresthesia of the fingers and toes most often results from:
- osteochondrosis;
- tunnel syndrome;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- lack of vitamin B in the body, as well as substances such as calcium and magnesium;
- polyneuropathy of various nature;
- Raynaud's syndrome.
The most common causes of scalp paresthesia:
Involvement of the nose in the pathological process occurs against the background of frostbite, the formation of atherosclerotic plaques, and diseases affecting the cardiovascular system. However, most often a similar variant of paresthesia occurs with osteochondrosis in the area of the cervical spine.
It is extremely rare for testicular damage to occur; provocateurs for this may include:
- oncology in the scrotum area;
- inflammatory process of this localization;
- cauda equina syndrome;
- bladder dysfunction;
- benign tumors;
- testicular torsion.
In addition, the disease can be triggered by:
- prolonged stay in a forced and uncomfortable position associated with prolonged compression of the limbs;
- prolonged exposure to stressful situations;
- a state of intense fear;
- poisoning by chemicals or heavy metals;
- the influence of external factors, for example, squeezing the shoulder with a tight tourniquet;
- overdose of drugs, in particular antiepileptic drugs, as well as substances aimed at lowering blood tone;
- an inflammatory process localized in the vessels that provide blood supply to nerve fibers - a similar condition is also called vasculitis.
It is advisable to relate the above reasons for the appearance of such a disease to absolutely every person, regardless of gender and age category.