Apraxia is a disease that is characterized by impairment in the performance of goal-directed actions.
At the same time, despite the fact that there is a desire, as well as physical ability, a person cannot perform any gestures or body movements. In addition, the disease proceeds in such a way that there are completely no disturbances in coordination, as well as signs of paresis.
The disease affects the cerebral hemispheres and along with it the pathways of the corpus callosum. Apraxia can develop as a result of a number of pathologies, and currently experts divide the disease into several types, which are distinguished depending on certain factors, such as location and others.
Some forms of the disease can only be diagnosed by observing a person perform certain tasks. Thus, as an example, we can note the loss of skills:
- drawings that were previously present;
- write;
- tie shoelaces;
- playing a musical instrument and others.
Kinds
Apraxia is a neurological disease that comes in many varieties. Each type of this pathology is distinguished by its individual symptoms, as well as the localization of focal damage to brain tissue.
Apraxia in speech therapy. Types of disease.
In this case, the development of the disease may be due to the negative influence of various factors.
Frontal
Frontal apraxia is characterized by damage to the prefrontal areas of the cerebral cortex in the frontal lobe. The disease is characterized by severe impairment of complex and sequential movements. Moreover, this type of apraxia can be limited or total in nature with dysfunction of individual groups of muscle fibers, or with absolute immobility of the limbs. Frontal apraxia can develop as a consequence of a stroke or severe trauma to the skull.
Motor
The motor type of apraxia is characterized by the fact that the child is able to independently formulate an action plan for performing certain tasks, but is not able to fully realize the functions of individual elements of the musculoskeletal system. In this case, the patient requires help from strangers (for example, lifting a toy or moving any environmental object).
Premotor
Premotor apraxia occurs in children who have signs of damage to the premotor areas of the cerebral cortex. A more detailed examination of the patient reveals that the child has symptoms of inertia and lack of automation of movements. Children with premotor apraxia can perform elementary motor acts, but lack the ability to transform them into more complex actions.
Cortical
This type of apraxia develops in case of damage to the tissues of the dominant hemisphere of the brain.
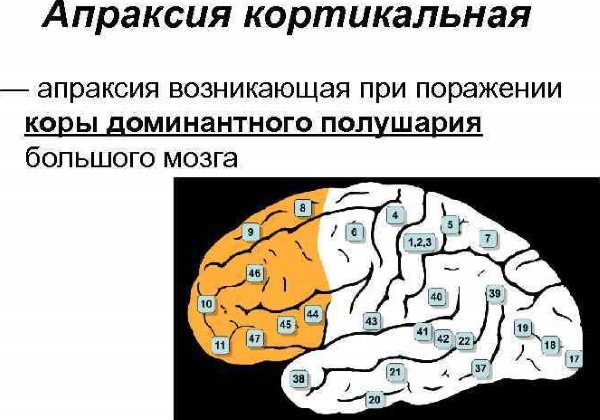
In this case, the pathological condition of the central nervous system can be manifested by disturbances in the motor activity of the limbs or muscle groups on only one side of the body.
Bilateral
Bilateral apraxia is the result of severe bilateral damage to the cerebral hemispheres. In this case, the main focus of pathology is localized in the parietal region of the central nervous system. The disease is characterized by multiple dysfunctions of the musculoskeletal system.
Akinetic
Akinetic apraxia is a separate type of this neurological disorder in which the child’s psychomotor activity is affected. The main manifestation of the pathology is the complete or partial absence of stimulation of the central nervous system to active movements, to perform certain actions that are necessary to achieve set goals. This type of disease is detected in the early period of child development.
Amnestic
Amnestic apraxia is characterized by complete or partial loss of the ability to perform independent voluntary actions. At the same time, the child actively imitates the behavior of adults and other children in his immediate environment.

This type of pathology negatively affects not only the physical development of the patient, but also leads to impairment of the psychomotor and cognitive functions of the brain.
Ideatorial
Ideation apraxia is different in that, due to focal lesions of certain areas of the central nervous system, the child is not able to independently outline a clear plan of action to complete the assigned tasks. The symptoms of this pathology appear especially clearly when children with a similar diagnosis try to implement complex motor acts.
Ideokinetic
Ideokinetic apraxia is a neurological disorder in which a child is able to perform random movements of individual parts of the body or muscle groups, but is unable to carry out simple actions that develop into a more complex motor act. In terms of symptoms, this type of disease resembles cerebral palsy with signs of periodic remission.
Kinesthetic
Kinesthetic apraxia develops in children who have damage to the postcentral part of the central nervous system with the spread of pathology to the dominant hemisphere of the brain. This type of disease leads to disturbances associated with the performance of voluntary movements. The child cannot independently decide what actions he needs to perform in a particular situation.
Constructive
Constructive apraxia affects the cognitive functions of the brain. A child with this type of neurological disorder is not able to independently assemble a separate object from its component parts. For example, collect a multi-colored cube, or an elementary picture consisting of several puzzles.
Apraxia
This type of disease develops in children who have focal lesions of the cerebral cortex in the parieto-occipital region. Most often, the right hemisphere is in the zone of a progressive pathological process. Apraxia of dressing is characterized by the fact that the child completely or partially lacks the ability to dress independently.
Oral apraxia
Oral apraxia is a series of disorders of the motor activity of the facial muscles, motility of the lips and tongue tissues, which ultimately leads to the absence or improper development of the speech apparatus. In speech therapy, this type of pathology is considered a serious disease that is difficult to treat.

The severity of oral apraxia depends on the extent of damage to the centers of the brain.
Spatial
This type of neurological disorder is distinguished by the fact that as the child grows up, he does not develop the ability to navigate in the surrounding space. This pathology may be accompanied by attacks of dizziness and a lack of understanding of simple things that are necessary for independent movement. For example, a child is already quite old and cannot understand where the right or left side is.
Apraxia of walking
Apraxia of gait is a neurological disorder in which the child has preserved the functions of all elements of the musculoskeletal system, there are no symptoms of vestibular disorders, but there are clear signs of walking impairment. A similar pathology occurs in children with local lesions of the frontal lobe of the brain.
Cause of apraxia
Today, there are several main reasons that explain the occurrence of apraxia. And the main one is brain damage, which occurs during trauma, and can also be a consequence of a tumor or heart attack. And apraxia is caused by a degenerative process in which the lesion is localized only in the parietal lobes. After all, it is there that all the action programs that have been learned throughout life are stored. It also happens that apraxia appears due to damage to other parts of the brain, such as the corpus callosum, frontal lobes, and premotor cortex.
To eliminate the cause that caused this disease, the doctor conducts a thorough examination of the patient, for which he asks him to perform some simple steps. For example, the patient should wave his hand in greeting or clap his hands. And at this time, the specialist simultaneously checks his muscle strength, which is observed in those muscle groups that were involved during the exercises. This is necessary so that the doctor can rule out paresis, which may be the cause of the existing disorder. And if apraxia occurs in a severe form, then a neuropsychological study is used to identify it.
Most often, the doctor asks the patient’s loved ones whether he can perform the simplest actions without outside help. For example, can he brush his teeth independently, use cutlery and can he write independently. To clarify the causes of this disease and to make the correct diagnosis, the doctor prescribes CT and MRI, which helps to identify the nature of the lesion. For example, this could be hemorrhage, focal atrophy, heart attack and other reasons. After a physical examination, the presence of certain neuromuscular diseases is usually revealed, which are very often confused with apraxia.
Symptoms and signs
Apraxia in speech therapy is a dysfunction of certain brain centers that are responsible for the motility of the facial muscles, synchronous mobility of the lips and tongue tissues. The first signs of pathology appear in the early stages of a child’s development and also depend on his age.
In children under 3 years of age
In a child of this age group, the main signs of apraxia are the following deviations in the development of the speech apparatus:
- in infancy, children with this pathology do not babble, and also do not make any other attempts to verbally express their emotions;
- the first simple words appear too late, or are completely absent, despite the fact that, due to his age, the child should already be able to pronounce them (for example, mom, dad, baba);
- when trying to speak, a child with oral apraxia is able to produce only a few consonant or vowel sounds that are unintelligible and do not resemble words;
- when pronouncing sounds, the child makes too long pauses;
- in the presence of mild oral apraxia, the child is able to reproduce individual simple words, but at the same time replaces sounds that are difficult to pronounce with easier ones.

Oral apraxia in children of this age group may be accompanied by an unauthorized change in the structure of the word. For example, when a child pronounces the names of objects in a way that is more convenient for him to pronounce the letters of which they are composed. The presence of such symptoms should be the first alarming signal for the child’s parents and kindergarten teachers. In this case, immediate involvement of a speech therapist is required.
In children over 3 years old
Apraxia in speech therapy is a dysfunction of the brain centers that are responsible for the full functioning of the speech apparatus.
In children over 3 years of age, the symptoms of this pathology manifest themselves as follows:
- the child makes immediate mistakes in the process of reproducing sounds, which are not signs of age-related immaturity;
- children with a similar disease understand the language of the people around them, understand the meaning of the words that are spoken to them, but at the same time cannot repeat what was said;
- there are pronounced signs of imitation in the reproduction of heard words, during which this speech is clearer than words spoken after making an independent conclusion;
- hypersensitivity or too low sensitivity of tissues located in the corners of the mouth;
- while attempting to say a word or reproduce a sound, the child gropes certain parts of the face and touches the surface of the lips, which indicates complete or partial dysfunction of the motor skills of these parts of the body;
- poor assimilation of information that comes from loved ones or teachers of educational institutions;

- impairment of fine motor skills of the upper limbs;
- with partial oral apraxia, the child manages to pronounce simple and short words, but at the same time he faces significant difficulties when pronouncing complex word combinations (the ability to construct sentences is practically absent).
The above symptoms can be aggravated at a time of excitement or the presence of a new person in the child’s immediate environment. Children over 3 years of age who suffer from mild oral apraxia may have irregular, choppy, or severely slurred speech. Quite often, children with signs of pathologies of the speech apparatus have other developmental disorders. For example, problems with learning to read, write, dysfunction of muscle groups of the musculoskeletal system.
Benefits of rehabilitation in
Extensive experience and attentiveness allow our specialists to find an approach to patients and select optimal rehabilitation methods in a particular case. We believe that there can be no trifles in medicine: our center employs only competent, qualified specialists (from administration staff and nurses to doctors), we use new, modern and at the same time proven effective equipment and techniques, we adhere to an individual and multidisciplinary approach, our psychologists and psychotherapists are always ready to help patients cope with depression and accept new living conditions. We also thought through the architecture of the center: wide doorways, threshold-free anti-slip coating, ramps and handrails are especially important for people with disabilities.
We want your well-being to not depend on circumstances!
Causes
Apraxia in speech therapy is a neurological disorder that must be detected as early as possible. The main reason for the development of this pathology is the presence of focal damage to areas of the central nervous system responsible for the mobility of the muscles of the face, lips and tongue.
The development of such a disease can provoke the negative impact of the following factors:
- damage to the fetal brain by infectious microorganisms that were able to overcome the placental and blood-brain barrier;
- damage to the central nervous system by chemical or biological substances that have pronounced toxic properties;
- birth trauma of the skull, or brain damage resulting from a fall from a great height or blows;
- pathological influence of drugs and alcoholic beverages, if the child’s mother had harmful addictions throughout the entire period of intrauterine development of the fetus;
- abnormalities of intrauterine development;
- genetic predisposition, if similar pathologies of the cerebral cortex were previously encountered in blood relatives of the child’s parents.

The causes of oral apraxia or another type of this disease can be determined by a neurologist at the stage of preliminary examination of the child in order to establish the nature of the origin of dysfunctions of the speech apparatus.
Diagnosis and assistance
In order to diagnose the disease, a number of measures are taken:
- analysis of medical history and pathological complaints;
- examination by a neurologist;
- examination by a neuropsychologist;
- Magnetic resonance and computed tomography are performed;
- Often the patient visits the office of a neurosurgeon and psychologist.
In this case, there is no drug treatment, and the drugs are not even able to slow down the development of the disease. In addition, to combat pathology and its consequences, the following actions are carried out:
- blood pressure is monitored and medications are prescribed that can improve nutrition and blood flow in the brain;
- surgery (tumor is removed).
The specialist who observes the patient draws up an individual plan for a therapeutic program, which involves the following procedures:
- physiotherapy;
- occupational therapy;
- cognitive method of rehabilitation;
- classes with a speech therapist.
Methods of helping with the disease largely depend on the details. For example, the age of the patient, the degree of damage and the nature of the pathology are very important.
Despite the fact that there is no treatment as such today, the above procedures make it possible to at least partially restore functioning. Physiotherapy is the most effective method, as improvements in body functions are observed over time.
Treatment, or rather maintenance therapy, is a rather difficult and lengthy process that requires persistence and patience.
Therefore, you should not delay going to the doctor if you suspect a disease. Depending on the reasons, a referral to a psychiatrist or neurologist will be made.
In addition to the fact that an individual set of restorative and supportive procedures is developed for the patient, he should be surrounded with care. An additional psychologist and nurse will be required, because relatives and a social worker will not always be able to be with the patient.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of apraxia is carried out with the participation of an audiologist and speech therapist. A specialist of the first profile assesses the child’s hearing level in order to exclude pathologies of the inner ear, the presence of which affects the quality of development of the speech apparatus. After this, a certified speech therapist who has practical experience working with children suffering from apraxia begins to examine the patient.
The table below describes the main types of examination techniques that are used to make a final diagnosis:
| Type of diagnosis of oral apraxia | Principle of the survey |
| Oral-motor assessment | An oral-motor assessment involves diagnosing signs of low tone of muscle tissue responsible for the mobility of certain areas of the face, lips, lower jaw or root of the tongue. During the diagnosis, the speech therapist asks the child to show how he moves his tongue from the right to the left, and whether he can touch its tip to the surface of the palate. Assessment of the level of coordination of movements of all elements of the speech apparatus is carried out by repeating complex phrases or playing a number of sounds. For example, quick pronunciation of tongue twisters, or simple words in the form of “pah-tuh-kah”. At the moment when the child reproduces test words and sounds, the speech therapist monitors the mobility of the patient’s lips, tongue and facial muscles. |
| Melody of speech | Assessment of speech melody is one of the stages of complex diagnosis of children with signs of this disease. The specialist listens carefully to the words and sounds that the child reproduces, paying special attention to the correct composition of syllables. The main purpose of assessing the melody of speech is to determine the patient’s ability to form sentences of various types (interrogative, narrative). |
| Speech sounds | This method of diagnostic examination, which is also carried out by a speech therapist, involves assessing the ability to pronounce consonants and vowels. The specialist asks the child to reproduce individual words that contain the largest number of sound combinations. Based on the results of communication, an appropriate conclusion is drawn up about the presence or absence of oral apraxia. If this diagnosis is confirmed, the severity of the neurological disorder is assessed. |

The average cost of a comprehensive examination by a speech therapist is 1,100 rubles. The duration of diagnosing a child for the presence of apraxia varies from 45 minutes. up to 1 hour
Treatment methods
Apraxia in speech therapy is a complete or partial dysfunction of the speech apparatus, which excludes the full development of the child. The main and only treatment for oral apraxia is regular sessions with a certified speech therapist. To achieve a positive effect in reducing the severity of pathological symptoms, as well as improving speech, the child should attend 3 to 5 therapeutic sessions per week.
Classes with a speech therapist are conducted on an individual basis, depending on the severity of apraxia or the clinical manifestations of this disorder.

For example, if a child cannot pronounce a certain set of sounds, then the specialist draws up a lesson plan so as to emphasize the reproduction of words where there is a defective sound. In addition, regular sessions with a speech therapist can prevent atrophy of the muscles responsible for facial expressions, mobility of the lips, tongue or lower jaw.
The duration of therapy depends on the dynamics of restoration of normal functions of the child’s speech apparatus. The average cost of 1 lesson with a speech therapist is 700 rubles.
Symptoms of apraxia
Symptoms characteristic of apraxia depend on the type of disease and are as follows:
- inability to control facial expressions;
- inability to draw simple shapes;
- difficulties with choosing and using tools;
- problems with performing a set of coordinated movements (tying shoelaces);
- inability to make precise movements with your hands or fingers;
- inability to get dressed;
- shuffling gait;
- slouch;
- inability to step over an obstacle.
If you notice similar symptoms, consult a doctor immediately. It is easier to prevent a disease than to deal with the consequences.
Possible consequences and complications
The lack of treatment aimed at restoring and improving the quality of a child’s speech threatens the development of the following complications and negative consequences:
- violation of the child’s socialization;
- progression of dysfunction of the facial muscles, which is responsible for the mobility of the lower jaw, lips and tongue (this complication will only aggravate the existing signs of oral apraxia);
- the need to receive individual education due to the lack of ability to reproduce words and correctly construct sentences;
- retardation in physical and mental development;
- lack of communication skills with peers and other people around them;
- the emergence of a tendency to aggression, the emergence of outbursts of rage and signs of an unstable psycho-emotional state due to limited abilities to express thoughts;
- the development of complexes and self-doubt that appear in a child due to incorrect reproduction of words and sounds, as well as ridicule from other children;
- preservation of speech apparatus defects, which remain with children at all stages of their growing up, significantly reducing their quality of life.

Apraxia is a severe neurological disorder that develops due to focal lesions in individual areas of the central nervous system. In speech therapy, this disease is characterized by oral apraxia, the symptoms of which are manifested by impaired mobility of the facial muscle tissues responsible for the synchronous interaction of the lips, lower jaw and tongue.
The main symptom of this disease is that the child completely or partially lacks the ability to reproduce most sounds and words. An audiologist and speech therapist are involved in diagnosing pathology.
Prevention and prognosis
It is possible to prevent the development of a pathology such as kinetic apraxia (and other types of disease) only with the help of general recommendations. This is due to the fact that currently there are no specific preventive measures.
Following these rules will help reduce the risk of developing pathology:
- complete renunciation of addictions;
- regular exercise and walking in the fresh air;
- normalization of diet;
- preventive massage of the limbs, which can be performed at home;
- control over blood tone indicators;
- avoiding traumatic brain injuries;
- conducting regular examinations in a medical facility.
Apraxia and agnosia do not threaten the life of patients, but the outcome of the disorder depends on the severity of the disease, its type and the age of the person.
If left untreated, complications may develop: inability to self-care, disability, impaired social and labor adaptation.
If you think you have Apraxia
and the symptoms characteristic of this disease, then doctors can help you: neurologist, pediatrician, psychologist.
Source
Did you like the article? Share with friends on social networks: