Hallucinations in older people: main types
There are true and pseudohallucinations.
The first group includes pathological conditions that an old person perceives as realistically as possible. It seems to him that perception involves the senses. The second group of hallucinations, which are also called false, do not have this property, and the visions are transmitted directly to the brain. True hallucinations are divided into the following groups:
- Spontaneous, appearing independently of sensory organ receptors.
- Functional, developing when various stimuli affect sensory endings.
- Reflex, appearing when a stimulus affects one sense organ, but is regarded as stimulation of another organ. For example, when exposed to noise, an old patient experiences images.
Often hallucinations in older people begin unnoticed and are not clearly expressed. But if treatment is not carried out or the wrong drugs are taken, then the symptoms intensify, becoming more vivid and lasting. Impaired sensory perception gives rise to the following types of hallucinations:
1. Visual.
Non-existent images appear before an old man; sometimes he speaks with an invisible interlocutor. The nature of visual hallucinations is not fantastic. Everything really exists, but not now and not here.
"Visual hallucination"
It rarely happens that an old person sees fantastic images such as angels, demons and other characters.
2. Auditory.
These disorders manifest themselves in different ways. An old patient can hear rustling, knocking, talking, and music in complete silence. There is an imperative form, when an elderly person thinks that voices are ordering him something. The orders are predominantly destructive in nature.
A voice sounding inside can give an order to put your hand in boiling water, or to kill the “demon” sleeping on a nearby bed. If the disease is in the initial stage, then the old patient drives away the voices. As the disease progresses, without proper treatment, the voice becomes intrusive, and the patient plunges into a state of madness.
3. Olfactory and gustatory.
The whims of old people about tasteless food, over-salted or poisoned food are not a whim. When an elderly person has hallucinations of this kind, he begins to feel different kinds of tastes and “recognize” poisons. These sensations can lead to a panic attack or an attack of paranoia.
Olfactory hallucinations are common in old people who have lost their significant other. They hear a familiar smell, so they begin to believe that they have been visited by the ghost of a deceased life partner. These visions are dangerous, as an old person can fall into a depressed state. Due to stress, he will want to die quickly in order to get to a loved one.
4. Tactile hallucinations.
Such hallucinations are also called “delusions of skin parasites.” This type is typical for people of “early old age.” Old patients complain of itching, pricking, soreness, and burning.
It seems to them that someone is crawling or rolling under the skin. These tactile sensations can be either local (on the hands, face, feet, genitals, mucous membranes) or spread to the entire body.
The reasons cited by old patients are quite specific: lice, fleas, helminths, glass fragments, small pebbles.
In some cases, hallucinations are detailed, when the patient describes the shape, color, size of objects that bother them. Hallucinations are expanded by the presence of visual perception.
In these cases, old people see worms crawling out from under the skin or insects running over the body.
Most tactile hallucinations are accompanied by hypochondriacal delusions. Old patients sincerely think that they have an incurable disease.
They visit doctors and traditional healers and are treated using traditional and folk methods. Patients constantly wash and disinfect areas of the body “affected” by the disease.
After some time, the manifestations of hallucinations become easier and the symptoms decrease. But there is a possibility of relapse.
5. Paranoid hallucinations.
Paranoid hallucinations
They begin with a mild form of paranoia. Old patients may develop obsessive ideas about robbery, persecution, and poisoning.
All their immediate surroundings (neighbors, relatives, friends) become subjects of these events. Over time, the symptoms are aggravated by the addition of verbal hallucinations.
Audible voices “tell” the old man who wants to rob or poison him and in what way.
If the disease has taken a severe form, then taste hallucinations may also appear, when the patient thinks that he has been poisoned. Such “visions” already take on the character of schizophrenia.
The illusion of mental openness and controllability appears. Ideas related to causing harm become complete fantasy.
An important clinical manifestation is impaired thinking, which is subsequently supplemented by memory problems.
- Useful materials about medicine are here!
- What to do in retirement so you don't get bored?
- What types of hearing aids are there for older people?
- What to do if an elderly person's legs swell?
- Mobile toilet for the elderly: 3 main types!
How to get rid of hallucinations: a review of drugs
Identifying the cause and selecting therapy for loss of reality is a difficult issue for psychiatrists. To correctly prescribe pills for hallucinations, you need to carefully collect anamnesis, conduct an examination, and exclude hereditary mental disorders, neuroinfections and brain tumors.
What is a hallucination?
Hallucinations are a loss of reality that manifests itself in the form of unreal sensations, images and sounds.
They can be symptoms of pathological mental disorders, hereditary and acquired pathologies, as well as a reaction to lack of sleep.
They should be distinguished from illusions and pseudohallucinations, which also refer to disturbances in the perception of the surrounding world that occur in severe mental disorders.
Types of hallucinations
Depending on which analyzer the disorder occurs, hallucinations are divided into auditory, visual, motor, tactile, and gustatory.
Visual hallucinations
Visual hallucinations occur spontaneously, without the desire or will of the patient. Sometimes they frighten him, but they can attract and enchant him, causing patients to stare into emptiness for a long time.
Visions can be transparent, color or black and white, large or small, moving or stationary. Sometimes the patient sees something as simple as a flash or spot. Visions may also contain complex images in the form of people, animals, unreal creatures or detailed scenes.
Auditory hallucinations
Auditory hallucinations are manifested by sound phenomena of two types:
- Simple - noises, crackling, grinding, creaking, as well as shouts and fragments of words.
- Complex - divided into verbal - monologues, dialogues, phrases, and musical - singing, melodies.
Verbal hallucinations are divided into three types: commentary, imperative and threatening. Commenting voices express an opinion about the patient’s actions, threatening voices intimidate the patient. More dangerous are imperative ones - they establish prohibitions or give orders, for example, to attack other people or commit suicide.
Alcohol hallucinations
The second most common alcohol psychosis after delirium tremens is alcoholic hallucinosis, which often becomes chronic. Patients hear voices ordering them to harm loved ones or commit suicide. Against the background of alcoholic hallucinosis, a feeling of constant persecution, anxiety, and unreasonable fear is formed.
Hypnagogic hallucinations
Images that appear at the moment of falling asleep or waking up, when a person is on the border between sleep and reality, are called hypnagogic hallucinations.
It is a rare phenomenon and is often confused with other types of perceptual disorders.
People facing this problem indicate that hypnagogic visions appear much more vividly than dreams and remember them in great detail.
Hallucinations in children
According to research, about 10% of children of early and early preschool age experience various forms of the disorder, but many parents attribute them to wild childhood imagination.
Attention! If the child’s visions become systematic and there are signs of anxiety, you need to show him to a psychiatrist, as this may be the first sign of neurosis or psychosis.
Often the first signs of loss of reality appear in the 1st grade, when an additional load is placed on the student’s nervous system. A change in the children's team, a lot of new information, and fear of bad grades lead to the child developing false visual images or hearing whispering voices.
The development of hallucinations in adolescence is associated with the onset of drinking alcohol and drugs, which, acting on a fragile body, can lead to severe mental disorders.
When is treatment for hallucinations required?
But treatment is not always carried out with drugs against hallucinations. If the disorder is caused by lack of sleep, severe stress or overwork, it is enough to take a vacation, adjust your sleep patterns and get proper rest for the visions to disappear. If after rest the symptom returns again, the presence of mental disorders must be excluded.
Treatment methods for hallucinations
In each case, an individual treatment regimen is prescribed. For hallucinations, symptomatic therapy is prescribed, aimed at reducing anxiety and suppressing visions. Most often, patients are prescribed Aminazine, Haloperidol, Trisedil, Amisulpride, Risperidone.
For visions caused by taking medications and drinking alcohol, it is necessary to detoxify. After cleansing the body, antipsychotic drugs are prescribed.
In addition to drug treatment, all patients are recommended to undergo a course of psychotherapy in order to restore their psycho-emotional state, eliminate depression caused by being in hospital, and suppress the fear that false images will return again.
Anti-hallucination pills for older people
Medicines for hallucinations in older people are selected with extreme caution, after a full examination of the patient, since they cause undesirable reactions from the central nervous system and other body systems.
Neuroleptics
Among the anti-hallucination pills for older people, antipsychotics are most often chosen, which are prescribed for neurological and psychotic disorders.
Haloperidol, Chlorpromazine, Thioridazine have an antihallucinogenic effect, but they often cause undesirable reactions.
Therefore, recently doctors have been prescribing modern antipsychotics that rarely cause side effects - Abilify, Quetialin, Triftazin.
Tranquilizers
Tranquilizers for loss of reality are prescribed if it is caused by depression, or each attack is accompanied by fear, anxiety or panic attacks. They relieve internal tension without affecting intellectual activity. The most effective tablets include: Gidazepam, Seduxen, Grandaxin.
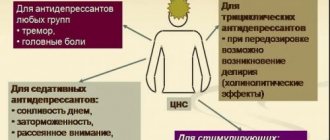
Antidepressants
Antidepressants are prescribed for loss of reality, accompanied by weakening of motor activity, autonomic disorders, prolonged depression and mental disorders. Commonly prescribed antidepressants include Amitriptyline, Paroxetine, and Tianeptine.
What pills are available without a prescription?
There are a number of drugs that can be purchased without a prescription, but psychiatrists do not recommend self-medication. An incorrectly selected medicine and its dosage lead to undesirable consequences, including the development of chronic hallucinosis.
The names of pills for hallucinations that are available without a prescription are Afobazol, Buspirone, Mexidol, Phenibut. But it should be remembered that in some pharmacies, before selling such drugs, the pharmacist may ask for a prescription and, if it is not available, refuse to sell it.
Antidepressants: list of the safest and most effective drugs
Psychotropic drugs that have an antidepressant effect can be divided into several groups:
- tricyclics (“Amitriptyline”, “Imipramine”, “Clomipramine”, “Tianeptine”);
- tetracyclic (“Mianserin”, “Maprotiline”);
- serotonergic (“Citalopram”, “Sertraline”, “Prozac”, “Fluoxetine”);
- MAO inhibitors (“Moclobenide”);
- specific serotonergic (“Milnacipran”).
The most prescribed and relatively safe (with a minimal list of side effects and contraindications) are the following antidepressants:
- “Fluoxetine” has a mild stimulating effect, reduces appetite, increases resistance to life’s adversities, and improves psycho-emotional state.
- “Zoloft” has a sedative effect, but at the beginning of use it has a stimulating effect on many patients. Compared to “Fluoxetine”, it is rather calming (the action sometimes resembles “Aminazine”, the instructions for use confirm this). When taking Zoloft, patient monitoring is necessary, since the drug has a rather different effect on each person.
- “Stimuloton” has a mild stimulating effect, while being able to have an anti-anxiety effect and soften the severity of phobias and paranoia.
Nootropics are the most harmless class of psychotropic drugs. Many of them can be purchased at a pharmacy even without a prescription from a psychiatrist.
Nootropics have a positive effect on cognitive functions. Capable of stimulating learning and memory processes, increasing the brain’s resistance to various adverse factors (in particular, hypoxia) and extreme stress.
However, they do not have a direct stimulating effect on mental activity. In rare cases, during nootropic therapy, the patient develops causeless anxiety and sleep disorders.
Tablets with nootropic effects, which are prescribed to adults, children and adolescents to stimulate cerebral circulation and improve cognitive function:
- pyrrolidone derivatives (“Piracetam”, “Phesam”);
- cyclic derivatives, GABA (“Pantogam”, “Phenibut”, Aminalon”);
- acetylcholine precursors (“Deanol”);
- pyridoxine derivatives (“Pyritinol”, “Riridoxine”);
- drugs with neuropeptide action (“Vasopressin”, “Thyroliberin”, “Cholecystokinin”);
- antioxidants (“Mexidol”).
Almost any of these drugs can be purchased at any pharmacy without a prescription, since they are not included in the list of potent drugs.
Many of the above drugs are used in the treatment of children with mental retardation, with moderately severe delay in psycho-speech development. Psychiatrists often prescribe nootropics for suspected early childhood autism and manifestations of schizophrenia in children and adolescents.
Many nootropics have proven to be effective in preventing the progression of senile dementia.
Nootropics can effectively counter the development of toxic encephalopathy in drug addicts and people with alcohol addiction.
You should be extremely careful when taking it without authorization: nootropics have quite a few contraindications and in some cases can provoke acute psychotic states (if the patient is predisposed to this). In this case, emergency assistance for mental disorders will be required to relieve psychosis.
- tricyclics (“Amitriptyline”, “Imipramine”, “Clomipramine”, “Tianeptine”);
- tetracyclic (“Mianserin”, “Maprotiline”);
- serotonergic (“Citalopram”, “Sertraline”, “Prozac”, “Fluoxetine”);
- MAO inhibitors (Moclobenide);
- specific serotonergic (“Milnacipran”).
- “Fluoxetine” has a mild stimulating effect, reduces appetite, increases resistance to life’s adversities, and improves psycho-emotional state.
- Zoloft has a sedative effect, but at the beginning of use it has a stimulating effect on many patients. Compared to Fluoxetine, it is rather calming (the action sometimes resembles Aminazine, the instructions for use confirm this). When taking Zoloft, patient monitoring is necessary, since the drug has a rather different effect on each person.
- "Stimuloton" has a mild stimulating effect, while being able to have an anti-anxiety effect and soften the severity of phobias and paranoia.
Nootropics are the most harmless class of psychotropic drugs. Many of them can be purchased at a pharmacy even without a prescription from a psychiatrist.
- pyrrolidone derivatives (Piracetam, Phezam);
- cyclic derivatives, GABA (“Pantogam”, “Phenibut”, Aminalon”);
- acetylcholine precursors (“Deanol”);
- pyridoxine derivatives (“Pyritinol”, “Riridoxine”);
- drugs with neuropeptide action (“Vasopressin”, “Thyroliberin”, “Cholecystokinin”);
- antioxidants (Mexidol).
Hypnotic psychotropic drugs belong to the group of psycholeptics. Their task is, as a rule, short-term treatment of sleep disorders. Some hypnotic psychotropic drugs, such as zolpidem and zaleplon, act on receptor systems similar to benzodiazepines, although to a much lesser extent.
On the other hand, nootropic psychotropic drugs are called pro-cognitive drugs, they have properties that improve cognitive function. They have found particular use in improving concentration and memory. They facilitate cerebral blood flow; some drugs from the group of psychotropic nootropics are inhibitors of the enzyme that decomposes acetylcholine (they are used for dementia).
What are the causes of illness in elderly patients?
The appearance of any hallucinations indicates a significant impairment of mental activity, which can develop with:
- various mental pathologies, for example, epilepsy or schizophrenia;
- psychoses of infectious origin;
- hallucinations due to acute or chronic intoxication;
- with organic brain damage, especially in the presence of tumors;
- when exposed to hallucinogens;
- when taking certain medications (certain antibacterial and antiviral drugs, sulfonamides, drugs used to treat tuberculosis, anticonvulsants, antihistamines and antihypertensive drugs, psychostimulants, tranquilizers and many others);
- with sensory and social isolation;
- temporary visual hallucinations in older people can be caused by taking medications with psychodysleptic properties;
- with disturbances in the mechanism of alternation of sleep and periods of wakefulness.
It is worth noting that psychopathological symptoms among elderly patients are observed under various conditions. The clinical manifestations of these disorders depend on the underlying disease.
The acute onset of senile hallucinations is characteristic of delirium; it can also develop with various somatic diseases, as well as with substance abuse or when taking certain drugs that can cause psychosis. The chronic course of hallucinations and their stable nature are characteristic of chronic schizophrenia, as well as psychoses developing against the background of chronic somatic pathology or Alzheimer's disease.
In addition, hallucinations are quite common in Parkinson's disease. Thus, approximately 20−60% of patients develop psychotic disorders. In most cases, they are caused by external influences, although they can also occur due to internal disorders, for example, during the development of a neurodegenerative process that develops in the nerve cells responsible for the synthesis of dopamine.
It is worth noting that most antiparkinsonian drugs, if taken incorrectly, can cause the development of psychotic symptoms.
When treating hallucinations that develop against the background of Parkinson's disease, we must remember that older people have increased sensitivity to antipsychotic drugs.
In this case, clozapine becomes the drug of choice in most cases.
In addition, cholinesterase inhibitors can be used, which lead to a reduction in psychotic symptoms and improve cognitive function in this pathology. It is worth noting that there are a number of other factors that increase the likelihood of hallucinations in old age:
- damage to the cerebral cortex in the frontal or temporal region, which is caused by age-related changes;
- neurochemical disorders associated with the aging process;
- social isolation of older people;
- insufficiency of sensory organs;
- pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic age-related disorders;
- polypharmacy, which can also cause hallucinations in the elderly.
Hallucinogenic drugs, or which pills cause hallucinations – Site about poisoning
A hallucination is an image that occurs as a result of an error in the perception process of one or more senses.
Such an image exists only in the head and has no connection with reality (external stimulus), but at the same time it can have a sensual coloring and be very convincing.
Alcoholic epilepsy - what is it and how to treat it? Find out about this from our article.
Causes
- Who is susceptible to hallucinations?
- The appearance of hallucinations is directly related to the state of the brain , in which images, voices, smells and images that do not correspond to reality arise.
- Very often, hallucinations are a symptom of schizophrenia or the result of using hallucinogenic drugs.
The brain is still not fully understood by science and is a mystery to scientists .
Therefore, all the processes occurring in it cannot be explained precisely and unambiguously, nor can the causes of emerging disorders be studied in detail.
But all the reasons can be divided into three categories:
- internal (hereditary diseases that affect the human brain and nervous system);
- external (acquired diseases and pathologies, such as severe concussions, poisoning and infectious lesions of the body, etc.);
- temporary (metabolic disorders of a non-pathological nature, such as lack of sleep or stress).
Visual hallucinations develop against the background of alcoholism, drug and psychotropic substance abuse, taking certain medications, and even food poisoning.
Visual and auditory hallucinations appear complexly against the background of mental illnesses, such as schizophrenia, hallucinosis, psychosis and some types of seizures.
Olfactory hallucinations occur with brain lesions/injuries.
The cause of the disorders may be an infection (encephalitis, malaria, typhus, etc.) or a blow/bruise to the temporal region, as well as schizophrenia and other diseases.
Tactile hallucinations appear as a result of withdrawal syndrome due to alcohol abuse. False sensations on and inside the body can also be provoked by encephalitis and schizophrenia.
Risk group
There are groups of people who, as a result of their lifestyle or current state of the body, are predisposed to hallucinations.
- Aged people. The aging process is inevitably associated with changes in the body and irreversible processes in the brain.
After 60 years of age, a patient may be diagnosed with paranoia or dementia, which is the cause of hallucinations.Rheumatic diseases and cardiovascular pathologies in the stage of decompensation also provoke false images.
- People suffering from alcoholism . Severe alcohol poisoning leads to delirium tremens and hallucinations. Alcoholic psychosis and delirium are acute psychotic conditions associated with disruption of the brain and sensory organs.
- susceptible to depression. A depressed state of mind, an increased level of anxiety, a depressive view of reality and phobias can lead to the appearance of hallucinations and various visions.
- People who may have genetically inherited mental disorders . If a person has a family history of schizophrenia, hallucinations may be the first sign of inheriting the pathology.
- People taking drugs . Even if taking narcotic drugs does not lead to hallucinations directly during the action of the drug, disturbances in perception may occur after (during the period of withdrawal, due to withdrawal syndrome).
What to do: which doctor should I contact?
Hallucinations are an unhealthy state of the body that signals disorders that require correction.
At the same time, disturbances in perception are not an independent illness, but a symptom of various pathologies (physical or mental).
To treat a symptom, it is necessary to find out the cause that provoked the hallucinations. You cannot ignore medical help and self-medicate, even if hallucinations appear in a mild form.
First of all, a person with perception disorders should contact a therapist, psychiatrist and neurologist .
As part of the accompanying examinations, the therapist can refer the patient to an oncologist, narcologist and other specialized specialists who will analyze the patient’s condition and confirm/refute the presence of diseases that caused hallucinations.
Grandmother's hallucinations after a stroke
A stroke is a serious condition that requires long-term treatment and recovery.
But even with proper treatment, complications can be detected (impaired blood circulation in the brain, irreversible processes and delirium). Against the background of these pathologies, perception disturbance occurs.
Post-stroke hallucinations appear as incoherent speech, illusions, and delusions. The patient may complain of strange visions and images, realizing his condition, or believe in hallucinations, considering them real.
- In the event of post-stroke hallucinations, the patient’s relatives must ensure the safety of both the person with a perception disorder and the people around him.
- to call an ambulance without the patient noticing, so as not to provoke an attack of aggression or an increased level of anxiety.
- are strictly prohibited , as all this can aggravate the situation.
- In a state of psychosis, sick people are in a state of excitement and experience a surge of physical strength .
Therefore, it is necessary that there be at least 3 people in the room who can pacify the patient. In some cases, even weak elderly people and patients in the postoperative period can reach a window or door and cause physical harm to relatives (against the background of psychosis).
Sharp and heavy objects should not be left in the patient’s room. Also, a person with hallucinations should not be left unattended .
It is strictly prohibited to use drugs to relieve hallucinations without medical advice. All actions must be agreed with a specialist.
How to help yourself if visions arise?
How to get rid of hallucinations?
If you suspect you are hallucinating or are sure you are experiencing a perceptual disorder, try not to panic.
First of all, contact a loved one who can refute the frightening visions/voices, etc. Enlisting support can help reduce anxiety.
- If visions occur due to poisoning, taking psychotropic substances, or drinking alcohol, you must immediately go to the hospital .
- Even if hallucinations are not associated with illness/pain or illness, seeking medical help and finding out the root cause is essential.
- In the later stages, it is very difficult to cure hallucinations or alleviate symptoms.
High temperatures can cause hallucinations. In this case, antipyretics (Ibufen, Paracetamol) will help to quickly cope with the unpleasant symptom.
Stress, lack of sleep and extreme fatigue lead to hallucinations. If you understand that the body is on the verge of exhaustion, you need to rest (go to bed, turn off instant messengers and take a break from business).
It is important to admit to yourself in a timely and honest manner that the help of a specialist is necessary. A person with hallucinations cannot help himself on his own , since the line between the real and the unreal is erased.
A substitution of perception occurs, and the patient becomes increasingly immersed in his world of visions.
It is almost impossible to get out of this vicious circle, since with progressive diseases a person begins to get confused in sensations and believe in hallucinations.
Treatment methods
Hallucinations caused by triggers (psychotropic substances, poisoning, hypnosis, drugs) are treated by getting rid of the harmful effects (the triggers themselves).
The only exceptions are those situations in which external factors led to changes in the body or provoked withdrawal symptoms.
Hallucinations against the background of psychotic disorders are treated by correcting the underlying pathology that provoked the perception disorder. For this purpose, antipsychotics are used.
If the underlying pathology cannot be treated (senile dementia), then therapy is aimed at
stopping the acute phase of hallucinations.
If hallucinations were caused by taking drugs or alcohol, the patient must undergo a course of rehabilitation .
Scheme
How to treat pathology? What medications will help?
Treatment for hallucinations is individual therapy. Drugs are selected based on the clinical picture, type of hallucinations, underlying pathology and emotional state of the patient.
The list of mandatory measures includes:
- taking medications according to an individual regimen;
- isolation of the patient during the acute period (directly hallucinations);
- individual psychotherapy for the patient’s rehabilitation and return to normal life.
Drug names
What pills should the patient take? Antipsychotics (neuroleptics) are used to combat hallucinations
- Clozapine;
- Quetiapine;
- Risperidone;
- Olanzapine;
- Ziprasidone.
To relieve attacks of acute agitation and delirium, intramuscular injections :
- Tizercin;
- Aminazine;
- Haloperidol;
- Trisedil.
If the patient is depressed, he is prescribed antidepressants . To combat anxiety, tranquilizers , and in case of weakness, stimulants .
- It is very important not to panic when hallucinations appear and not to try to hide the fact of a perception disorder from others.
- Often, reluctance to seek help is caused by fear of upcoming treatment, shame, or the belief that the case is isolated and does not pose a danger.
- However, in the long term, such a strategy will only lead to a worsening of the patient’s condition and a complete loss from normal life, loss of control over reality and one’s own actions.
- When hallucinations do not require treatment:
Source:
What pills can cause hallucinations
For a person of any age with symptoms of a mental disorder (eg, hallucinations) or delirium, careful consideration should be given to whether the symptoms are caused by the medication before starting antipsychotic medication.
For a person 60 years of age or older, there is a good chance that hallucinations, delirium, or other symptoms similar to those of schizophrenia may be caused by taking the following drugs or abruptly stopping alcohol, barbiturates, or other hypnotics or tranquilizers.
Source: https://bdc03.ru/infektsii-i-zabolevaniya/gallyutsinogennye-preparaty-ili-kakie-tabletki-vyzyvayut-gallyutsinatsii.html
Neuroleptics
Therapy for hallucinations is most often carried out with the help of medications belonging to the group of antipsychotics, which cope with this problem quite successfully. Antipsychotics are psychotropic drugs designed to treat neurological and psychological problems.
New generation drugs help not only cure hallucinations, but also relieve muscle tension, provide a mild hypnotic effect, and clarify the thought process. The most popular drugs that help treat hallucinatory-delusional syndrome today include:
Abilify. Prescribed simultaneously with antidepressants for dementia, schizophrenia, depression. However, it must be remembered that this drug may cause increased anxiety. Typically, for schizophrenia, the drug is prescribed from 10 to 15 mg per day; for the treatment of bipolar disorders, the recommended dose varies from 15 to 30 mg per day. The usual treatment course is from 1 to 3 months.
Contraindications for use are children under 16 years of age and individual intolerance to the drug. Patients also with cardiovascular diseases should be subject to special monitoring. Adverse reactions include dizziness, drowsiness, pneumonia, and decreased appetite.
Quetiapine. It is used according to the following scheme: on the first day, 50 mg is used, on the 2nd day - 100 mg, on the 3rd day - 200 mg, on the 4th day - 300 mg. The dosage then varies in mg per day. Elderly patients initially take 25 mg per day, then the dose is increased by 25 mg daily. The same dosage is also prescribed for patients with renal or liver failure.
These tablets for hallucinations are contraindicated for use if you are intolerant to them, in children under 18 years of age, or during breastfeeding. In patients with a history of convulsive phenomena or cardiovascular diseases, use should be carried out under the supervision of a physician.
Etaperazine. Not indicated for endocarditis, brain disease, central nervous system disorders, during pregnancy, lactation, children under 12 years of age. This medicine is used starting from 10 mg daily; if the patient has previously taken treatment with this drug, then it is possible to prescribe 40 mg daily.
Then the daily dosage is increased to 80 mg and taken for a 4-month course. Etaperazine has many side effects, the most common of which are dizziness, muscle weakness, anxiety, increased blood pressure, nausea, tachycardia, frequent urination, fever, and urticaria.
Hallucinogens of synthetic origin
LSD is one of the most common drugs. It was first obtained in 1938 from ergotamine. Only in the 60s this drug was included in the list of prohibited drugs, but to this day it is produced in illegal laboratories. According to doctors, LSD is excellent for migraines. Consumption of this drug provokes a distortion of sensations.
This drug is common in nightclubs and discos. It is in such places that they can offer to try this psychedelic. Ecstasy was first created in Germany in 1912 and only in the 90s it was added to the list of prohibited substances. This drug provokes depression caused by serotonin deficiency. Many experts continue to study this drug as a treatment for post-traumatic stress.
The most dangerous psychedelic. In medicine it is referred to as phencyclidine. Initially used as an anesthetic. But later they stopped using it because there were many different side effects. Drug addicts who use this drug can easily injure themselves; it is not uncommon for people under the influence of angel dust to jump from the windows of high-rise buildings. The consequences of use are very similar to the symptoms of schizophrenia.
Consequences
Hallucinogenic drugs are often purchased by drug addicts for their further synthesis with other harmful substances. By combining substances with chemicals, a person turns them into poison, which can destroy him in a few years. The most popular drugs are Desomorphine, Koldakt, Vint. Hallucinogenic drugs are often purchased by drug addicts for their further synthesis with other harmful substances. By combining substances with chemicals, a person turns them into poison, which can destroy him in a few years. The most popular drugs are Desomorphine, Koldakt, Vint.
A drug addict can develop an addiction very quickly. A strong craving to get pleasure and eliminate bad health forces him to use hallucinogens. During so-called withdrawal, a drug addict experiences the following symptoms:
- fever or chills;
- panic attacks;
- tendency to diarrhea;
- lacrimation, nasal discharge;
- abdominal cramps;
- excessive sweating;
- attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- confusion;
- sleep disturbance or drowsiness;
- deterioration of coordination;
- restless behavior, anxiety, depression, irritability.
Systematic intake of a hallucinogen causes the brain to gradually adapt to it, and the body’s addiction leads to the need to increase the dose.
Hallucinogenic substances can be persistently addictive. Moreover, psychological dependence is usually stronger than physical dependence.
In addition, regular use of drugs entails severe damage to the central nervous system, a mental disorder that is expressed by symptoms similar to schizophrenia. This is especially pronounced in old age: older people are more prone to accidents and injuries under the influence of drugs.
Drugs have a negative impact on overall health and can destroy the liver and brain. The likelihood of developing dependence increases several times when using drugs in high doses, combining them with alcohol and painkillers.
Pharmacy drugs are medications with a powerful analgesic or sedative effect that are highly addictive and are used for other purposes. Preparations containing narcotic substances are available in every pharmacy, and many of them are available without a prescription.
Impact of psychedelics
There are many medicines that have psychedelic properties. The popularity of medicines is explained by the fact that they contain hemp. The most common are diethylamide, psilocybin, and mescaline.
These are accessible types of drugs that allow a person to escape from the real world. Long-term use of the drug leads to serious consequences, the patient ceases to understand where he is, and also does not distinguish an imaginary life from reality.
List of pharmaceutical drugs - 2020
Lyrics
This is a medicine for epileptics that relieves seizures. In the past, it was used by narcologists to combat withdrawal symptoms - withdrawal symptoms.
Lyrica is similar in action to morphine, heroin or methadone. It is also highly addictive and puts you into a state of euphoria, which drug addicts prolong by drinking the pills with alcohol.
Signs of addiction to lyrics:
- Nervous, aggressive behavior.
- Mood swings - from hysterical joy to tears.
- Unsteady gait, poor coordination.
- Dilated pupils.
- Increased sweating.
- Skin rash.
Consequences of abuse of lyrics:
- Chronic fatigue syndrome: drowsiness and feeling of weakness, confusion.
- Apathy and thoughts of suicide.
- Impotence in men, hormonal imbalances in women.
- Migraines and memory impairment, fainting.
- Cramps, muscle pain.
- Tremor.
- Confused speech.
An overdose of Lyrica causes coma and death.
Terpinkod, Nurofen plus
This popular cough suppressant clears mucus from the respiratory tract.
Terpincode contains the psychostimulant codeine. To achieve euphoria, addicts drink 2-5 packs at once, or extract crude codeine from tablets and inject it intravenously. A cheap analogue of Terpinkod - Nurofen Plus, practically does not differ in psychotropic effects. Addiction sets in after 3 packs.
Signs of dependence on terpin code:
- Sallow or gray skin, flaking skin.
- Frozen in one position, motionless gaze.
- Red eyes.
- Severe weight loss.
Consequences of terpincode abuse:
- Poor eyesight.
- Development of heart diseases.
- Migraine.
- Rotting of the skin.
- Epileptic seizures.
- Death of brain cells, dementia.
- Development of mental disorders and suicidal tendencies.
Terpinkod is superior to cocaine in destructive power. A fatal outcome is possible after just a few months of use - a person dies from sudden respiratory arrest.
Tropicamide
Tropicamide - eye drops.
Ophthalmologists use it when examining the fundus of the eye and prescribe it for inflammation. In large dosages, Tropicamide immerses you in a state of euphoria and provokes auditory and visual hallucinations. Drug addicts inject it through the veins and muscles, drink it as a solution, and mix it with opiates. Persistent addiction to Tropicamide develops in just a month.
Signs of trapicamide addiction:
- Dilated pupils.
- Increased sensitivity of the eyes to light.
- Yellowish skin tone.
- Distracted attention.
- Memory loss.
Consequences of trapicamide abuse:
- Serious visual impairment. Problems with focusing and clarity, pain in the eyes from sunlight, partial and complete blindness.
- Cardiovascular diseases. Arrhythmia, development of deadly infective endocarditis. The appearance of blood clots after intravenous injections.
- Nervous system problems. Cramps, burning sensation in muscles.
- Mental disorders. Psychosis, panic attacks, schizophrenia, depression, suicide.
- Liver and kidney diseases. Hepatitis and cirrhosis of the liver, acute renal failure, urinary incontinence.
- Purulent inflammation. Abscesses appear at injection sites, which spread infections throughout the body.
Exceeding the dose leads to paralysis of the respiratory center of the brain, coma and death.
Tramadol
It is a powerful analgesic and is prescribed for severe pain in cases of injury and serious illness, or to reduce pain during diagnosis.
Drug addicts take tablets in increased doses, or make solutions for intramuscular and intravenous injections. The drug gives a surge of vigor, a feeling of relaxedness, a desire to sympathize and help people. However, the peaceful mood quickly gives way to aggression and apathy when the effect of Tramadol wears off. After 2-3 doses of the medicine, a strong attachment appears.
Signs of tramadol addiction:
- Pale skin with red spots.
- Red eyes.
- Constant thirst.
- Dizziness, difficulties with orientation in space.
- Rapid transitions from apathy to excitement.
- Decreased performance.
- Drowsiness or insomnia.
Consequences of tramadol abuse:
- Headaches, muscle pain, joint aches.
- Tremor, epilepsy.
- Arrhythmia, tachycardia, acute heart failure.
- Cirrhosis of the liver.
- Nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, abdominal pain.
- Dementia.
- Panic attacks.
- Psychoses, aggressive antisocial behavior.
- Hysteria.
- Depression, suicidal tendencies.
Tramadol quickly wears out all body systems. A drug addict who is addicted to it lives no more than 3-4 years. In case of an overdose, blood pressure drops sharply, suffocation, pulmonary edema and sudden cessation of breathing occur.
Coaxil, Prozac, Zoloft, Aurorex
These are powerful antidepressants with almost identical effects on the psyche.
Drug addicts use them to escape withdrawal symptoms, and as a result they become addicted to a new drug. Increasing the dosage gives a pronounced sedative effect: the person relaxes, feels joy and carelessness, and loses a sense of reality.
Signs of antidepressant addiction:
- Mood swings, inappropriate behavior. The addict is often overexcited, laughing or crying for no apparent reason.
- Nervousness and aggressiveness. Without a new dose, the addict feels deeply unhappy, becomes nervous and suspicious, and lashes out at others.
- Bad feeling. Fainting, dizziness and nausea become more frequent.
Consequences of antidepressant abuse:
- Acute psychosis, uncontrollable rage.
- Severe depression.
- Tachycardia and arrhythmia, heart failure.
- Chronic fatigue and insomnia.
- Blood clot formation.
- Stomach ulcers, gastritis, diarrhea and constipation.
- Epilepsy attacks.
An overdose of antidepressants results in sudden cardiac arrest or lethargy with death.
Treatment of drug addiction
The Solution Drug Rehabilitation Center offers effective treatment for drug addiction. The rehabilitation program includes:
- Intervention. Most often, the addict denies his problem and refuses the help of doctors. In this case, our psychologists come to the patient’s home and, together with relatives, gently convince him to begin rehabilitation.01
- Detoxification. To eliminate the effects of withdrawal symptoms, we cleanse the body of toxins using special medications and a balanced diet. Detoxification is the first step to recovery and provides relief from physical addiction.02
- Hospital treatment. During rehabilitation, the patient lives in a comfortable suburban hospital. He is temporarily isolated from society and is completely focused on the course of treatment. Residents of the hospital learn the details of their illness, attend group and individual psychotherapy sessions. They learn to analyze and control their emotions, build healthy relationships with people around them, and resolve stressful situations without drugs. Psychologists help patients gain healthy life values, regain self-respect and trust of loved ones.03
- Ambulatory treatment. At this stage, the patient lives outside the center and regularly attends classes with a psychologist. Specialists help him adapt to sober life in society and improve relationships with family and friends. We control the condition of the former drug addict, so we can prevent a relapse in time.04
- Return to a full life. Throughout the program, residents gain valuable professional and social skills, and upon completion of the course, we can employ them in our center. Our specialists also prepare graduates for interviews if they want to grow and develop elsewhere.05
Pharmacy addiction is more dangerous than any other, because medications are always readily available within walking distance of your home. The risk of relapse among pharmacy drug addicts is high. Therefore, in case of failure, our clients can undergo a second course of treatment free of charge.
And most importantly, all our patients and their loved ones receive a lifetime right to support our drug treatment clinic: they can turn to us for help and advice at any time.
You can learn more about the dangers of pharmacy drug addiction from a narcologist in this video:
Statistics
Many researchers believe that statistics are underestimated for several reasons:
- Fear of being branded “crazy”;
- Some types, mainly in the elderly, have not been sufficiently studied;
- Many people are afraid to admit to taking drugs.
Based on a few studies (13 thousand adults surveyed) in 2000, the following statistics are known:
- 6% of adults experience once a month, 2% - once a week;
- 27% experience hallucinations during the day;
- 3% experience tactile hallucinations, 3% visual, 0.6% auditory. Tactile, associated with drug use.
There is no evidence that hallucinations occur more frequently in certain ethnic groups and are not associated with gender. Demographic characteristics are as follows:
- The child has. Hallucinations occur in children under eight years of age. About 40% have schizophrenia (all types), the child has visual or auditory predominance;
- Eye diseases – 14% of patients receiving medications for glaucoma or age-related macular degeneration experienced distinct vision vision;
- Alzheimer's disease - in 40% in the later stages;
- Addiction. Among schoolchildren and students, hallucinogens are the third most consumed drug (after marijuana and alcohol). The highest level is in the Caucasus, in men aged 18-25 years;
- In healthy people, they occur during the transition from wakefulness to sleep or vice versa. This condition is not considered pathological;
- Migraine. 10% of patients experience visual visions before the onset of an attack;
- Epilepsy. 80% of sufferers experience visual, olfactory, and auditory disturbances before an attack;
- Post-traumatic – after traumatic injuries, 60% experience auditory injuries.
Sources
- https://otravlenye.ru/vidy/alko-i-narko/preparaty-kotorye-vyzyvayut-gallyutsinatsii.html
- https://kurenie.me/alkogolnaya-zavisimost/kak-izbavitsya-ot-gallyutsinatsij.html
- https://oinsulte.ru/preparaty/kak-izbavitsya-ot-gallyucinacij.html
- https://smart-log.ru/kakie-lekarstva-vyzyvajut-galljucinacii/
- https://dekto.ru/kak-izbavitsya-ot-gallyucinacii-v-domashnih-usloviyah/
- https://stopzavisimosti.ru/gallyucinogennye-preparaty.html
- https://narko-kliniki.ru/stati/narkotiki-gallyucinogeny.html
- https://atlasplay.ru/preparaty-vyzyvajushhie-galljucinacii/
- https://www.schoolcenter48.ru/poyavilis-gallyucinacii-chto-delat-tabletki-ot-gallyucinacii/
- https://medilo.ru/otitis/kak-vyzvat-silnye-gallyucinacii-v-domashnih-usloviyah-kak-vyzvat.html
- https://psyholic.ru/psihiatriya/tabletki-ot-gallyutsinatsij.html
[collapse]
Tranquilizers
Often, treatment of hallucinations requires the use of tranquilizers that have a sedative effect. Tranquilizers relieve panic, anxiety, stress, depression, and help eliminate hallucinations. These drugs will help relieve internal tension without affecting cognitive processes.
- Gidazepam. Refers to “daytime” drugs that do not cause drowsiness. The usual dosage is 0.02 to 0.05 g three times a day. The duration of the course varies depending on the patient’s condition and ranges from 4 months. This drug is contraindicated in cases of kidney and liver pathology, muscle weakness, or employment at work that requires reaction speed. The most common side effects are dizziness, itching, decreased libido, and nausea.
- Grandaxin. It is used for increased tension, fear, autonomic disorder, and decreased activity. Usually prescribed 5 mg. The average dosage for adults is 0.01 g three times with a typical therapeutic course of no more than 2 months.
If necessary, subsequent repetition of the use of the drug is possible after 1 month. The most common side effects include various digestive disorders and itching. Contraindications for the use of Grandaxin are the 1st trimester of pregnancy, psychopathological disorders. If there is a need, it can be prescribed for children from 1 year of age, but the doctor should select the dose based on the baby’s weight.
- Seduxen. Calms the central nervous system, relaxes muscle tone, relieves emotional stress, anxiety, increased irritability, hallucinations against a background of fear. This drug is prescribed with 0.0025 mg twice, with a gradual increase in which it is possible to bring it up to 5 mg per day. In case of increased fears accompanied by auditory hallucinations, an increase in the drug to 20 mg daily is allowed.
The daily dosage is divided into 3 doses. If there is persistently disturbed sleep, then the medicine is given at night. Can be used from 1 year of age, with the dose selected exclusively by the attending physician. Side effects include nausea, dizziness, and tremor. Contraindicated for use during pregnancy, in the presence of renal failure and cardiovascular diseases.
Symptoms:
Hallucinations are divided by analyzers (visual, tactile, auditory, etc.) and by the nature of their occurrence. The most important in practical terms are the following. Hypnagogic - visual and auditory hallucinations that occur when falling asleep (with eyes closed!) and often serve as a harbinger of developing alcoholism. Visual hallucinations most often occur in acute exogenous psychoses and in impaired consciousness. They are observed mainly in the evening and at night. Microptic - visual hallucinations in the form of images of people or animals that are very small in size (common in alcoholic delirium). Imperative - auditory hallucinations, “voices” commanding to perform certain actions, often dangerous for the patient or others; sometimes they forbid the patient to talk, force him to resist examination or examination, etc. The danger of these hallucinations is that patients are often unable to resist the “order.” Auditory hallucinations often occur in silence, when the patient is alone and not distracted. Auditory hallucinations are especially common in alcoholic hallucinosis. Olfactory hallucinations are expressed by various imaginary odors, often unpleasant; usually found in schizophrenia and presenile paranoids; their appearance in the clinical picture of schizophrenia usually means a tendency towards an unfavorable course of the disease with resistance to treatment. With tactile hallucinations, the patient experiences a feeling of insects, goose bumps, small objects crawling under the skin (with delirium alcohol, cocaine). With taste hallucinations, patients experience an unusual taste that is not typical for a given food or the appearance of unpleasant taste sensations in the mouth without eating. There are true hallucinations and false hallucinations (pseudohallucinations). A patient with true hallucinations is convinced of the reality of their existence, since for him they are projected in the surrounding space, no different from ordinary sounds, voices and visual images. Pseudohallucinations are localized within the patient’s own body and are accompanied by a feeling of alienation and madeness (they hear voices in their heads that are transmitted to them from space; they “have visions”; they are convinced of an outside influence on their thoughts and feelings, often expressing their thoughts about the nature of such influence - “hypnosis”, “laser”, etc.). Pseudohallucinations are usually combined with delusions of influence. If true hallucinations are more typical for alcoholic, traumatic and organic psychoses, then pseudohallucinations are only for schizophrenia. Hallucinosis is a psychopathological syndrome characterized by pronounced, abundant (various types) hallucinations that dominate the clinical picture. Hallucinosis is often accompanied by delusions, the content of which depends on “voices” or visions (hallucinatory). Acute hallucinosis usually develops during infectious or intoxication (usually alcoholic) psychoses. With an unfavorable course or insufficient treatment against the background of organic or vascular diseases of the brain, acute hallucinosis becomes chronic, in which auditory and less often tactile hallucinations predominate. With it, the behavior of patients is more orderly, perhaps a critical attitude towards “voices”, patients can even remain able to work.