Types of inattention
Impaired concentration and attention can be divided into 3 categories:
- “Fluttering attention” or absent-mindedness can be characterized as a process of uncontrolled switching of attention to stimuli, as well as poor concentration. This type is usually present in schoolchildren, but can also occur in older people, usually when they are very tired.
- “Scientist’s inattention” is the difficulty of switching attention from one process to another, as a result of very deep concentration on the process or on one’s thoughts. A person with this type is characterized by the presence of obsessive thoughts.
- “Abstract-mindedness of the elderly” is a condition characterized by poor concentration of attention and the ability to switch it. The disease occurs in cases of constant overwork, oxygen starvation of the brain, and also in people, mostly elderly, who suffer from cerebral atherosclerosis.
What is absent-mindedness and inattention?
Many people like to say that absent-mindedness is characteristic of great people. This is repeated by those who do not want to work on their bad qualities and look for excuses for them. In fact, this drawback is not as harmless as many people believe.
Absent-mindedness is a state of attention in which a person cannot concentrate on ongoing events or actions. It is also called inattention, forgetfulness, and is often not considered a vice, but only a character trait.
None of us were born immediately absent-minded or inattentive. Many people consider them "glory flaws," but they can lead to real tragedies: car accidents or factory accidents. Such people also cause a lot of trouble in everyday life, because they also cannot build normal relationships due to constant everyday “accidents,” and they are unlikely to bring much benefit at work.
Absent-mindedness has absolutely nothing to do with memory, it is a violation of attention. This trait is acquired, so you need to get rid of it if you want to change your life for the better and make it easier for those around you, to whom you cause, albeit minor, troubles.
What is attention from a psychological point of view?
Attention is a concept in cognitive psychology that represents the extent to which we process specific information that our brain receives from the environment.
Thanks to attentiveness, the subject’s successful orientation in the surrounding space is ensured, and it also ensures a complete and clear reflection in the psyche. The object of attention falls into the center of our consciousness, other elements are perceived weakly, not clearly, but at the same time the direction of our attention can change.
There are several types of attention:
- Involuntary type. While working with this type of attention, a person does not make any effort of will to concentrate, he does not even set a goal for himself.
- Arbitrary type. During this type, a person makes an effort of will to focus on a specific object.
- Post-arbitrary type. During this type of attention, a decrease in volitional efforts is characteristic, but the goal of being attentive remains.
The presence of this disorder in everyday life can lead to various problems, and sometimes quite serious ones. Communication with such people is quite troublesome; they cannot build normal relationships and have a very difficult time at work. Therefore, this condition must be treated so that it does not lead to more serious consequences.
Distracted attention can be of different types:
- functional type;
- poetic look;
- minimal type.
This type of inattention can occur in almost any person as a result of a monotonous and monotonous work process.
This type of malfunction can occur due to problems with sleep, constant headaches, and also if a person has any illnesses.
Minimal inattention and forgetfulness is caused by the inability to focus one’s attention on important objects due to deep immersion in one’s personal problems.
This type of disorder occurs due to the fact that a person cannot escape from internal experiences. Personal worries distract him from everything he does.
With this disorder of attention, a person is constantly in a state of daydreaming and fantasies. This species has no age restrictions. It applies mainly to people who have a creative character; it is normal for them to be constantly thoughtful, searching, and comprehending.
Distracted attention syndrome can manifest itself in different ways, namely:
- Insufficient concentration - absent-mindedness. As a result of this disorder, there is a decrease in the ability to remember what is seen or heard. Inherent in people who are highly sensitive to various conditions (fatigue, anxiety, lack of sleep).
- Rigidity is slowness, inhibition, in which there are problems with switching from one topic to another. This condition is observed in patients with epileptic syndrome, hypomania, and hebephrenia.
- Unstable - spasmodic attention. This condition is characterized by frequent jumping from one topic to another, which results in memory problems. Instability of attention often occurs in children who have attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), which leads to memory problems and decreased academic performance.
Distraction of attention can be caused by various reasons. To begin with, it is worth highlighting factors of a physiological, not pathological type, which provoke inattention, exhaustion, jumps and inertia of attention:
- Against the background of physical and mental fatigue.
- For chronic lack of sleep, insomnia.
- In a profession that requires performing the same monotonous actions or concentrating on the same object. Often, work behind a conveyor belt or behind the wheel causes disturbances in volume and weakening of attention.
- Sometimes people of certain professions, in the course of their work, develop a habit in which they concentrate on the subject of their scientific research, which entails ignoring everything around them; this is the so-called inertia of attention (switchability disorder). At the same time, memory does not suffer, on the contrary, it improves; it’s just that people working in a scientific field or another field discard everything that is not necessary and try to keep their attention on the most important.
- Age-related changes. With age, especially in old people over 70, the functions of concentrating attention weaken and disorder occurs.
- Sometimes strong anxiety prevents you from focusing your attention, which entails a state of absent-mindedness.
Absent-mindedness, forgetfulness and inattention can occur due to various diseases and disorders in the body:
- during problems with blood supply and nutrition to the brain that are associated with vascular disorders - atherosclerosis, osteochondrosis, dyscirculatory encephalopathy, arterial hypertension, vertebrobasilar insufficiency;
- various tumor disorders, hydrocephalus;
- Alzheimer's disease, vascular dementia;
- various mental problems - depression, schizophrenia, epilepsy;
- the appearance of headaches of various origins - migraine, arterial hypertension, vegetative-vascular dystonia, anemia;
- problems with sleep, insomnia;
- state of hypoxia;
- genetic factors;
- if the body has problems with metabolism - diabetes;
- if the body has a lack of useful components (iron, magnesium) or, on the contrary, an excess (lead).
Often, absent-mindedness and forgetfulness in children and very young people are characterized by an inability to control themselves. A child’s attention depends on many psychological processes that occur in the body. At the very beginning of his journey, he needs motivation and control from his parents.
Confusion and lack of self-control are often one of the main signs of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). If a child has this disorder, then he or she develops absent-mindedness such as “fluttering” attention. The main features of this condition are a low level of concentration and rapid involuntary switching of attention.
Absent-mindedness and forgetfulness in young children can be provoked by seemingly harmless factors and reasons:
- various preservatives, flavorings, and other food additives that are found in large quantities in modern delicacies;
- medications that are derivatives of salicylic acid;
- if there is an increased craving for sweets;
- problems with carbohydrate metabolism;
- the occurrence of allergic reactions to food;
- if there is a lack of necessary chemical components for the child’s body, especially iron and magnesium;
- if there is an increased level of heavy metal - lead in the blood. Its excess can lead to severe pathologies of the central nervous system and mental retardation.
If a child develops ADHD, he or she may exhibit the following symptoms:
- a state of hyperexcitability, restlessness, constant fuss;
- often switches from one activity to another, while not completing the previous task;
- the child cannot concentrate himself on one specific task;
- he has poor memory, jerky movements, absent-mindedness and forgetfulness.
In addition to these symptoms, you should pay attention to other signs:
- the child cannot concentrate on a specific task and is constantly distracted from it;
- often loses or forgets his school supplies, things, toys;
- constantly refuses to perform certain work, during which concentration and perseverance are required;
- problems with academic performance due to the fact that the child cannot complete even simple tasks;
- slowness;
- is in constant daydreaming;
- does not listen to instructions;
- can quickly switch to another task without fully completing the previous one.

The primary stage of diagnosis for attention disorders and absent-mindedness includes the following examinations:
- Examination by a neurologist. During the examination, the doctor should assess the state of fine motor skills, as well as identify neuralgic symptoms.
- Conducting a survey with filling out a diagnostic card.
- Conducting neuropsychological testing. During this examination, the level of attention, intellectual abilities, performance on a long task and other conditions are assessed.
Set of measures
Treatment for ADHD and related disorders should be comprehensive and should consist of the following steps:
- behavior correction techniques;
- psychotherapeutic methods;
- neuropsychological correction.
The main medications that help combat absent-mindedness, forgetfulness and inattention in a child are psychostimulants, which should only be taken under the supervision of a doctor:
- Glycine. This remedy increases performance, improves mental activity, and has a beneficial effect on the central nervous system. Take 1 tablet under the tongue per day.
- Piracetam. Improves mental activity. Take 30-50 mg per day.
- Biotredin. Has a positive effect on cognitive functions. Increases alertness and improves memory. The dose of the drug is 2 mcg per 1 kilogram of body weight, taken for 3-10 days.
- Phenibut. Improves blood circulation in the brain, improves mental activity and memory properties. The dosage is up to 250 mg per day.
All drugs have contraindications and side effects, so be sure to read the instructions for use before use.
During physiotherapeutic treatment the following procedures are performed:
- laser therapy, the full course consists of 7-10 procedures, during each of which 3-5 zones of the body are irradiated;
- DMV therapy, it consists of 8-10 procedures;
- inhalation procedures 5-10;
- UV treatment of the nasopharynx, the full course consists of 3-5 procedures;
- a course of magnetic therapy, which consists of 8-10 procedures.
Parents play an important role when their child has problems with attentiveness and perseverance. They must fulfill the following requirements:
- be sure to adapt to your child’s routine and constantly comply with it;
- control that the child feels calm during the day, so that he does not become overtired; it is also not advisable for him to spend a long time in front of the TV or computer screen;
- try to interest the child in some sports games, you can sign him up for the pool, and also go with him constantly for walks in the fresh air;
- It is advisable to avoid visiting places with large crowds of people and not to invite a large number of guests.
Causes of absent-minded attention
Attention deficit disorder in adults, as already mentioned, is often mistaken for a character trait: “what can I do, I’m absent-minded,” “that’s how inattentive I am,” etc. The main features can be considered:
- frequent change of hobbies (when deeply immersed in a new topic)
- inability to meet deadlines for completing assigned tasks, for example, “deadlines” at work, delays in paying for housing and communal services at home
- inability to plan workday and personal affairs
- ignoring social norms
- impulse purchases
There can be many reasons for absentmindedness. Let's look at the most common of them.
- A number of physiological reasons associated with general fatigue of the body - lack of sleep, busy work schedule, prolonged illness.
- The development of this condition is often promoted by taking certain medications, alcohol abuse, and smoking.
- Sometimes such a symptom can indicate hormonal changes in the body - during pregnancy, PMS, menopause or thyroid diseases.
- Psychological disorders in the human mind - stress, depression, neuroses, panic attacks.
- Age-related changes that inevitably occur in the body.
- Diseases and pathologies of the brain.
- Lack of iodine in the body.
- A characteristic feature of a person.
It happens that a person thinks that he has absent-minded attention, when he may have other abilities (more active).
Absent-minded people are often active. This is not a pathology, but a character trait. You can change if you know what to change in yourself, then your attention will improve.
A person may be distracted due to prolonged stress/anxiety, depression. If you have been somewhat absent-minded since childhood, it means that some processes in your brain are slow or are going poorly, and puzzles and active games can help with this.
Answer these questions for yourself:
- Are you satisfied with yourself? (except attentiveness)
- Are you often sad?
- Do you feel lonely?
- Do you have difficulty waking up in the morning and daytime sleepiness?
- Don't always understand what they want to tell you?
- Do you often answer in fragments (not in detail)?
If many of the answers coincide, then the reason is in the metabolic processes of the head.
Attention deficit in adults
Memory deterioration affects the work sphere and a person’s personal life. Memory is a place where images are stored that help in perception and response. Dysmnesia – memory impairment. Often accompanied by decreased concentration. Find out the reasons for the phenomenon from the article.
Causes
Memory decline occurs with age, but this does not mean that this does not happen in young people.
A recently popular cause of cognitive decline is information overload. Each person analyzes a large amount of information every day; students and teachers, “mind workers,” are especially at risk.
With daily large volumes of data, the brain gradually begins to perceive information superficially and scatter attention, not concentrating on one object. Superficial perception does not allow the material to linger in memory for a long time.
In addition, functional disorders occur against the background of:
- organic, mechanical damage to the brain, deterioration of blood supply;
- viral and bacterial diseases;
- chemical dependence, adverse reactions to taking medications or their incorrect selection;
- unhealthy lifestyle, physical inactivity, bad habits, overeating;
- stress, depression, anxiety;
- asthenic syndrome;
- anxiety disorder;
- fatigue, exhaustion;
- disturbed sleep patterns;
- hormonal imbalance;
- diseases, internal disorders of other systems, for example, digestive, cardiovascular;
- changes in the usual way of life, a traumatic situation.
If you cannot remember a word or date, the name of a new acquaintance, then this does not indicate pathology. This is probably a consequence of fatigue or selective memory.
Selectivity is a natural property of memory. We forget what has no value or significance for us or causes unpleasant emotions. Yes, sometimes these are important work moments, if they are not of subjective interest.
The same thing happens with attention. We easily notice and analyze what interests us. It is not surprising that concentration decreases when you need to write a report at work or tinker with numbers for several hours. Think about what exactly made you think about the deterioration of memory and attention. Maybe something has lost value for you?
Forgetfulness
It is worth suspecting pathology if you do not remember an event of the past day, but accurately describe an incident three years ago. Or if you cannot reproduce the information that was just given to you. In these cases, consult a neurologist. In other cases, we are talking about the idea of forgetfulness caused by overwork.
Forgetfulness has nothing to do with medicine. Forgetfulness can be a character trait or occurs under certain conditions. This is not an independent diagnosis, but it is worth paying attention to possible causes of forgetfulness: stress, chronic fatigue, poor diet, lack of sleep.
Treatment
Neurological disorders are treated with medication after a full examination using diagnostic equipment.
As for the deterioration of attention and memory due to fatigue, I suggest working with the following exercises:
- Try performing a familiar task with your eyes closed. Try to move around the room in the dark. Don’t forget to be careful, secure yourself with a wand or an assistant.
- If you are right-handed, try writing and brushing your teeth with your left hand. If left-handed - right-handed.
- Get to know mnemonics. Mnemonics is the science of ways to remember information.
- Take an abstract concept such as “love.” Come up with as many options for visualizing it as possible using words or touches.
- Play association games. Write down any word, select an associative series for it.
- Make lists, plans, tables. But don't overuse them. Rely on them, but try to remember everything yourself.
In addition, it is useful to play chess, checkers, memorize poetry, prose, solve crosswords, and logic problems. Buy a collection of puzzles and develop your memory.
Reading articles and popular science literature has a positive effect. Start learning a new topic or foreign language that interests you. Give preference to printed publications. Try to watch less TV or work on the computer.
Get rid of the habit of rushing and trying to do several things at once. Otherwise, you will constantly be haunted by a feeling of anxiety, thoughts that you have forgotten something. Eventually, forgetfulness will become real.
Do you know where the comb or keys are now? Try to make even such everyday little things conscious.
Prevention
Don't forget about healthy and adequate sleep. During rest, all body systems are rebooted and restored. The information received during the day is processed and sorted.
Physical activity stimulates blood circulation and saturates the brain with oxygen, which ensures its normal functioning. Walk every day, do feasible exercises, and do a warm-up. If possible, walk more, replace driving with walks.
Don't forget to ventilate the room and do breathing exercises. Good blood supply to the brain and sufficient oxygen are important for normal memory and attention.
Watch your diet. Excess sugar causes memory impairment. Healthy fats and iron improve brain function. Nutrition should be balanced, with a predominance of proteins and complex carbohydrates. Eat nuts, apples, dress your salad with oil, take B vitamins, Omega-3. For a prescription of a mineral-vitamin complex, consult your doctor.
Increase your resistance to stress. Anxiety, stress, and worry interfere with concentration.
Not only a child, but also an adult can have this syndrome. Constant absent-mindedness, poor self-organization, forgetfulness - this is what this can lead to.
To overcome this psychological disease, you must first understand its root cause.
Basically, this diagnosis is made to children at school age, and then it manifests itself at an older age. But sometimes the symptom is first diagnosed in adulthood.
The process of the disease is also unique; the symptoms of adults are categorically different from those of children.
What should parents of an inattentive child do?
Parents play an important role when their child has problems with attentiveness and perseverance. They must fulfill the following requirements:
be sure to adapt to your child’s routine and constantly comply with it; control that the child feels calm during the day, so that he does not become overtired; it is also not advisable for him to spend a long time in front of the TV or computer screen; try to interest the child in some sports games, you can sign him up for the pool, and also go with him constantly for walks in the fresh air; It is advisable to avoid visiting places with large crowds of people and not to invite a large number of guests.
A child’s attention must be trained from childhood so that in the future he does not develop a state of restlessness, loss and absent-mindedness. It is advisable to interest him in various educational games. Even in infancy, you need to show different toys and name them so that he can already focus on them.
If suddenly you have already noticed signs of attention disorder in your child, then it is necessary at the initial stage to begin to independently develop attentiveness and determination.
Buy educational games, construction sets, mosaics. The child must develop perseverance, and each lesson must be completed to the end, and to facilitate this process, parents must help him with this.
Beauty and Health Health
Sometimes we hear that absent-mindedness is a “trait of the great,” but this is said by people who do not want to get rid of their shortcomings, which are not as harmless as they might seem.
Symptoms of poor concentration
“I can’t concentrate on anything” is a fairly common complaint among patients suffering from psychological disorders.
Often patients do not understand that neuroses, worries and fears can negatively affect such cognitive processes as memory, attention and thinking.
In most cases, as a rule, people ignore this problem, not taking into account the fact that the lack of treatment for mental disorders can lead to more serious problems.
Poor concentration is usually accompanied by the following symptoms:
- absent-mindedness, forgetfulness;
- headache;
- instability of mood (depression and apathy towards everything predominate);
- impatience, restlessness;
- decreased performance;
- weakness and irritability, lethargy;
- inability to relax;
- insomnia, loss of strength, drowsiness, lack of energy.
The same symptoms are observed in conditions such as asthenia and neurasthenia. These disorders occur in people with an unstable nervous system. Disorders can develop independently or appear as a result of VSD.
Thus, with neurasthenia, unable to cope with strong psychological stress, patients begin to get irritated and distracted by any little things just a few minutes after starting work. Neurosthenics seem to “freeze” when performing any activity; the information received immediately flies out of their heads.
They can re-read the instructions for the task several times, but in the end they still don’t understand anything. In addition to loss of concentration, patients often experience uncontrollable tears, debilitating weakness, and even outbursts of aggression.
The inability to concentrate also occurs due to uncontrollable fears, neurotic conditions and OCD.
Constant worries, obsessions, anxiety lead to the fact that a person becomes unable to maintain attention on anything other than his own thoughts.
Increased anxiety does not allow a person to collect himself; he has no strength left for either mental or physical work.
Many people, noticing that their attention or memory has deteriorated, try to rest more, not overwork themselves, or resort to special exercises. Undoubtedly, such actions can be beneficial, however, first of all, a person needs to understand the state of his psychological health.
For example, with a disorder such as asthenia, normal well-being after rest does not last very long, and neurasthenics do not feel rested even after a long sleep. Therefore, in order to recover from problems with concentration, first of all, it is necessary to understand the reasons that led to the deterioration of well-being.
No amount of exercise will make cognitive processes work fully if a person is constantly haunted by obsessive thoughts or disturbing phobias. Only a qualified psychotherapist can help to cope with problems of this kind. Independent (additional) help may include following several rules.
- You need to try to protect yourself from stressful situations, to minimize all factors that provoke psycho-emotional stress.
- You should not force yourself to do this or that work when you feel a complete lack of energy and loss of strength. First of all, it is necessary to cope with mental stress that interferes with normal concentration. If you work forcefully, the condition will only worsen, and labor productivity will be extremely low. In addition, attempts to work without strength can lead to unpleasant physiological symptoms (headaches, increased blood pressure, darkening of the eyes, etc.).
- It is necessary to carefully monitor the implementation of all recommendations prescribed by the doctor. It is strictly forbidden to stop taking strong medications on your own or to thoughtlessly change their dosage. These actions can lead to dangerous consequences.
- You should not neglect such preventive measures as proper sleep, proper nutrition, exercise and walks in the fresh air. Positive emotions are also an excellent cure for negative thoughts.
We recommend that you read: Vision problems with VSD - is there any salvation?
The problem of "can't concentrate on anything" can be very serious.
If you don’t deal with it and let everything take its course, not only attention and memory will deteriorate, but also psychological well-being.
In order to return to the usual rhythm of life, start working fully again and fully recover after rest, you need to seek professional help in time.
We've all experienced problems concentrating at some point. It can decrease in both adults and children.
In this article, CogniFit psychologist Andrea Garcia Cerdan will tell you everything about concentration problems: what they are and why they occur, what are the signs, symptoms, and possible causes of low concentration. Should I be worried about this? You'll also receive 11 tips that can help improve your concentration.
Concentration can decrease in people of any age; this is a fairly common problem. In children, this manifests itself in worsening grades and school performance in general.
Therefore, it is extremely important to take the necessary measures in time to solve problems with concentration and improve alertness.
Concentration is the ability to effectively focus our attention on the task we are performing. In addition, with good concentration, we are able to block out various distractions, such as extraneous sounds or even our own thoughts.
When the level of concentration is optimal, it is easier for us to complete our work, we make fewer mistakes and spend less time on it, and we remember information better.
Problems with concentration, decreased concentration is the inability to concentrate and focus on the desired stimulus. At the same time, we may be distracted by noise, the sound of a mobile phone, various thoughts, etc., as a result of which we stop performing the task.
A person's concentration level depends on the following factors:
- Involvement, commitment to the task
- Interest in the task
- Ability to carry it out
- Physical and emotional state
- Suitable environment with minimal distractions
When these conditions are met, it is much easier for the brain to focus attention on important stimuli and block all other unwanted stimuli and distracting thoughts.
Problems concentrating
1) Inability to focus on one task or matter. You can easily be distracted by an object or sound, causing you to switch to another object or perform another task. In this case, there is “freezing” and “wandering” of attention. A person is unable to concentrate on completing a task, does not pay attention to details, and cannot focus, for example, when reading a book or when conducting a dialogue.
2) Another manifestation of the disease is the ability to concentrate on one thing. An example is listening to music or reading a book, during which we do not notice anything around us. In some cases, this disadvantage can be used for work purposes, but we should not forget that this can sometimes cause inconvenience to you and those around you.
3) Poor self-organization, as well as constant forgetting, are a sign of poor concentration. The consequences are:
- Constantly postponing work tasks;
- being late for work, etc.;
- systematic loss of things, forgetting their location;
- poor time orientation, inability to estimate approximate work time, etc.
4) Impulsivity is another sign of the disease. This may be accompanied by not understanding parts of the conversation, or experiencing the interlocutor. You are able to say or do something first, and only then think about the consequences. Tend to perform actions that can cause addiction.
5) Emotional problems can cause anger and frustration in patients. Symptoms of this form of the disease:
- constant change of mood;
- inability to motivate yourself and stay motivated;
- low self-esteem, lack of acceptance of criticism;
- hyperactivity;
- constant feeling of fatigue;
- frequent nervous excitement.
Hyperactivity in adults occurs much less frequently than in children, and this symptom does not always indicate a violation of concentration.
If these symptoms are present, you should contact a specialist in this field for examination and clarification of the problems.

The main doctors who can determine the degree of morbidity are a neurologist, psychologist and psychiatrist.
Only after consulting doctors can the problem and treatment methods be fully determined, since this can only be specified in an individual case.
Need for treatment
Treatment for absent-mindedness depends on the severity of the disorder.
- Internal factors. Organic brain damage. The need for clinical treatment.
- External factors. Overwork or illness.
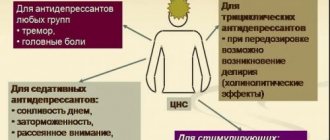
In the first case, inattention is considered a mental disorder, which can even occur with complete loss of memory. Most often this happens due to depression or anxiety disorder. With this diagnosis, drug treatment is prescribed, antidepressants or nootropic drugs are prescribed. At the same time, a psychologist is provided with help to work through emotional situations, if any.
"Fluttering" attention
The second type of attention disorder does not require serious medical treatment. It can be called “fluttering” attention. It is typical for teenagers and older people. This type of inattention is observed in people who are overworked or weakened by illness. Their inability to flutter like a butterfly, switching from topic to topic.
For ordinary people of this type, it is temporary, provided that such inattention is combated and the reasons that cause it. This pathology is affected by a temporary decrease in the mobility of nervous processes. In the clinical case, this occurs due to cerebral oxygen starvation or cerebral atherosclerosis. Most often this occurs in older people.
“How to get rid of absent-mindedness and bad memory? What to do?" - a frequently asked question from anxious patients, which they address to psychologists. They are concerned about whether the disease is serious, whether it needs treatment, and how to deal with absent-mindedness. Often this type of inattention manifests itself in the inability to concentrate and difficulty switching attention from object to object or from one type of activity to another. This type does not need serious treatment for absent-mindedness. The cause may be simple physical, emotional or mental fatigue. In this case, it is clear what needs to be done. Just give your body a rest, perhaps even a change of scenery for a while.
Diseases that cause concentration problems
The list of such diseases includes:
- depression;
- hypoprosexia;
- hyperprosexia;
- paraprosexia;
- epilepsy and head injuries.
Epileptics and people suffering from depression have so-called slow and “stuck” attention. In this case, there is a decrease in the activity of nervous processes and an inability to switch attention.
Hypoprosexia causes decreased concentration. Its variety is aprosexia, in which, in the case of numerous distractions, concentration and the ability to concentrate are completely absent.
Excessive concentration of a person on one thing, for example on just actions or thoughts, is characteristic of hyperprosexia. This is the so-called one-way focus of attention.
With paraprosexia, concentration deviations may occur, which are characterized by the appearance of delusions and hallucinations. This occurs due to the fact that the human brain is constantly tense, and this leads to such consequences.
This effect can be observed even in a completely healthy person, for example in athletes who experience enormous moral stress.
So a runner, waiting for the “start” signal, concentrating very much on this, can hear the signal in his head, even before it sounds in reality.
Varieties of manifestations
Distracted attention syndrome can manifest itself in different ways, namely:
Insufficient concentration - absent-mindedness. As a result of this disorder, there is a decrease in the ability to remember what is seen or heard. Inherent in people who are highly sensitive to various conditions (fatigue, anxiety, lack of sleep). Rigidity is slowness, inhibition, in which there are problems with switching from one topic to another. This condition is observed in patients with epileptic syndrome, hypomania, and hebephrenia. Unstable - spasmodic attention . This condition is characterized by frequent jumping from one topic to another, which results in memory problems. Instability of attention often occurs in children who have attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), which leads to memory problems and decreased academic performance.
Distraction of attention - is it a disease, answers the psychotherapist:
What to do if your concentration has decreased? Symptoms, causes and 11 tips

Distraction of attention is a violation of the ability to concentrate attention on any task, topic of conversation or subject. If the disorder occurs, a person is constantly distracted by extraneous stimuli, cannot engage in one task, is forgetful, is late for work, and cannot organize a work schedule.
The listed symptoms cannot be ignored; prolonged impairment of concentration is harmful to health and has a bad effect on the emotional and psychological state. To prevent complications, it is important to consult a doctor in a timely manner and undergo treatment.
Causes
Causes of absent-mindedness and inattention

To understand how to get rid of absent-mindedness, you need to know where it comes from. It comes in two types: imaginary and genuine. The real one may be associated with health problems such as neurasthenia, chronic fatigue syndrome, or very severe fatigue. A person simply cannot concentrate on one thing, but at the same time he is very easily distracted by extraneous events.
No matter how strange it may sound, imaginary absent-mindedness appears due to concentration, but excessive concentration. A person’s attention is focused on one thing, but he does not notice everything that happens around him. This is precisely the trait that great people have.
Modern technologies are very developed and help make our lives much easier. It is precisely because of the “ease” of life that inattention appears. Because of this, many suffer from insomnia: they seem to be mentally exhausted, but their physiological processes are disrupted, and they don’t want to sleep.
It happens that you are so exhausted at work that by the evening you completely stop thinking, you even lose your orientation in time. How to become more attentive? Move more, play sports, surf the Internet less.
Here's what Wikipedia writes on this topic:
Distraction of attention is acquired during a person's life, and is not congenital. This symptom is not nosospecific and can occur due to various reasons.
It is believed that absent-mindedness may be a reflection of an unconscious reluctance to do what it should be focused on. Distraction of attention can arise from fatigue, insomnia, headache, monotonous and monotonous activity (this occurs more often with the first type of absent-mindedness).
Distraction of attention also appears due to organic brain damage. It occurs in various mental illnesses, such as depression or anxiety disorder, when a person has difficulty concentrating on something.
Prevention
In connection with the reasons stated above, it is clear that the factors influencing the impairment of concentration are quite numerous and varied, and therefore it is impossible to give monosyllabic advice on how to avoid this.
In non-clinical cases, it is definitely recommended to lead a healthy lifestyle, give rest to the body and spirit during regular stress, and change your type of activity during rest.
At the same time, prevention is in your hands. After all, we know that it is better to prevent than to eliminate the consequences. On our resource you can take a course of exercises to concentrate your attention, with the help of which, if possible, you can avoid situations that require the participation of doctors.