A pituitary cyst in the brain is a rather insidious disease. Most often, this pathology occurs unnoticed by the patient. A person does not feel any painful manifestations for a long time. The pituitary gland is the central gland of the human body, which controls the entire endocrine system. Neoplasms in this area lead to serious hormonal imbalances, which occur only in the later stages. How to detect a cyst in time? And how to treat this pathology? We will consider these questions in the article.
What it is?
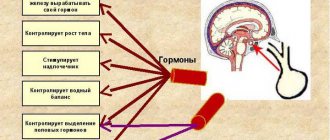
The pituitary gland is an appendage of the brain that produces tropic hormones. These substances regulate the secretion of other endocrine glands. The pituitary gland is responsible for the function of the following organs:
- thyroid gland;
- adrenal glands;
- gonads.
The pituitary gland also produces hormones that affect bone growth and water balance in the body. Therefore, any neoplasm in the appendage of the brain can lead to serious disorders in the functioning of various organs and systems.
A pituitary cyst of the brain is a benign formation. It looks like a spherical tumor consisting of epithelial cells. Its cavity is filled with liquid. In most cases, young men suffer from this pathology.
If the size of the cyst is small (up to 1 cm), then the patient does not feel any unpleasant symptoms. The tumor is discovered accidentally during an MRI or CT scan of the head. Neurological symptoms and hormonal disorders appear only when the tumor grows strongly.
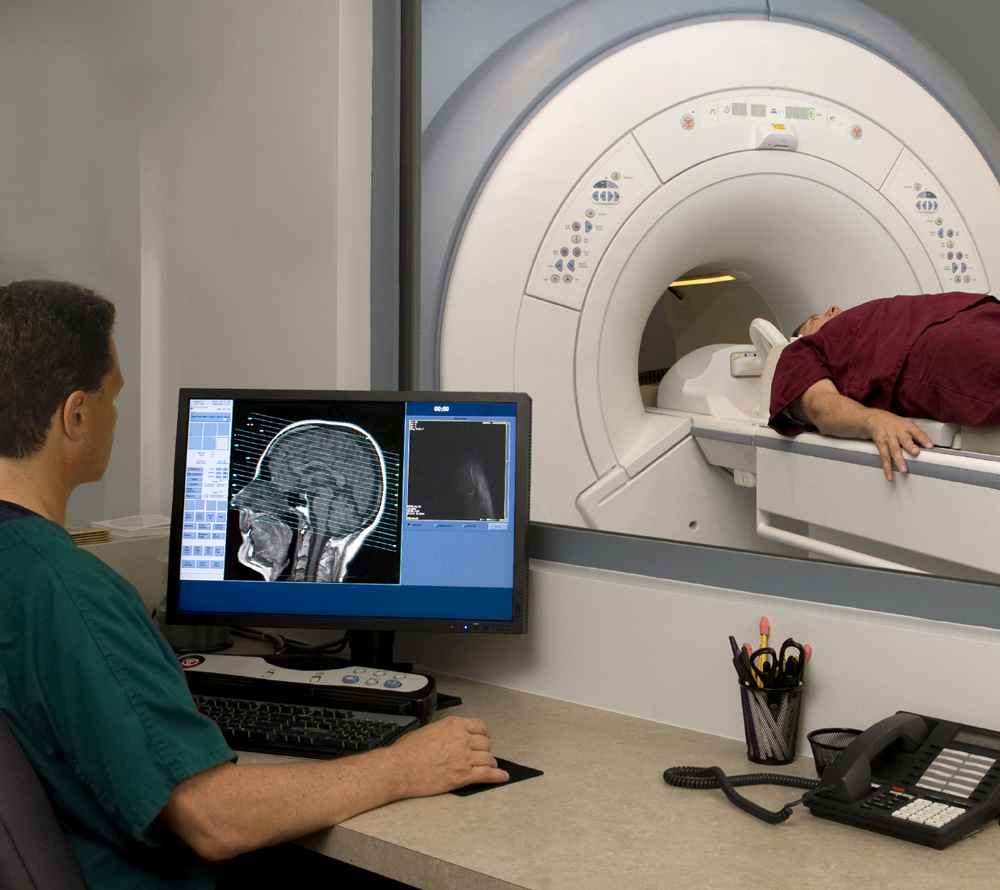
MRI and other diagnostic methods
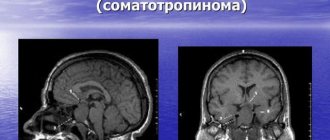
To identify a cyst in the pituitary gland, tomography (CT or MRI) is of greatest diagnostic value. It is usually recommended after detecting changes on an x-ray (deformation or expansion of the sella turcica, destruction of the processes) or examination by an ophthalmologist (swelling of the optic discs, blurred vision).
With tomography, you can see a cavity with a clear capsule in the shape of an oval, ball or dumbbell. Its contents have a density equal to or slightly higher than the surrounding tissue. Unlike adenoma, cysts accumulate contrast agent only in the capsule area.
An important stage of diagnosis is a blood test for hormone levels:
- somatotropin;
- adrenocorticotropic and cortisol;
- thyroid stimulating and thyroxine;
- follicle-stimulating, luteinizing, estradiol, testosterone.
When the pituitary gland is compressed, a decrease in all indicators is found, only prolactin in the blood increases.
Causes
At present, the exact causes of pituitary cysts in the brain have not been established. Endocrinologists suggest that the following factors can provoke the occurrence of a tumor:
- hereditary predisposition;
- infectious and inflammatory processes in the brain;
- head injuries;
- neurosurgical operations.
However, quite often such neoplasms appear for no reason. There have also been cases in medicine where the cyst resolved on its own. However, such a favorable outcome is possible only with small tumor sizes.
Neurological symptoms
In 80% of cases, neurological symptoms of a pituitary cyst in the brain do not appear. The patient’s health remains normal, and the person does not even suspect the presence of a neoplasm.
If the size of the cyst is more than 1 cm, then it begins to put pressure on the brain tissue. The patient's circulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is disrupted. This leads to increased pressure inside the skull, which is manifested by the following symptoms:
- bursting pain in the head (especially in the morning);
- nausea;
- visual disturbances;
- a feeling of pressure on the eye sockets from the inside;
- dizziness.

If treatment is not started at this stage, then the patient will develop serious hormonal disorders in the future.
The pineal gland (epiphysis) is also located in the skull. This organ is located near the pituitary gland. A small cyst of the pineal gland of the brain can give similar symptoms. The exact location of the tumor can only be determined using tomography.
Signs of hormonal disorders
If the tumor is large, the patient may experience serious complications. The consequences of pituitary cysts in the brain in an advanced form are various hormonal disorders. After all, the pituitary gland controls almost all endocrine glands. Pathological changes in this organ negatively affect the endocrine system.
Symptoms and treatment of a pituitary cyst in the brain depend on the location of the tumor. The central gland of the human body is divided into several lobes. Each of them produces certain types of secretions. It is important to determine with the help of analysis: which hormone is produced in increased or decreased quantities. The clinical picture of endocrine disorders will depend on this.
Patients with a pituitary cyst in the brain may experience the following hormonal disorders:
- Thyrotoxicosis and hypothyroidism. These pathologies develop due to a disruption in the formation of the hormone TSH, which is responsible for the functioning of the thyroid gland.
- Itsenko-Cushing's disease. Excessive production of the hormone ACTH impairs adrenal function. This leads to obesity, high blood pressure, and infertility. Women experience excess facial hair growth and irregular menstruation.
- Hypofunction of the gonads. This is the result of improper production of gonadotropic hormones - FSH and LH. As a result of this, ovulation is disrupted in women and infertility occurs, and in men, spermatogenesis is inhibited and potency deteriorates.
- Acromegaly. The cyst can provoke increased production of growth hormone. This leads to a disproportionate increase in the bones of the face, hands and feet in adults.
- Diabetes insipidus. This pathology is caused by a deficiency of the hormone vasopressin. The patient suffers from extreme thirst and excessive urination. 6 - 15 liters of urine can be released per day, which significantly exceeds the norm. This disease leads to severe dehydration.
- Hyperprolactinemia. Prolactin is a hormone that is responsible for the formation of milk during breastfeeding. If it is produced in increased quantities outside of lactation, then women stop having periods and white discharge appears from the nipples. In men, hyperprolactinemia leads to gynecomastia, infertility and a sharp decrease in potency.
Pituitary cyst: how it is treated in Israel
Israeli schools of neurosurgery and oncology are considered one of the best and most progressive in the world.
Since the late 80s of the 20th century, a medical field such as neuro-oncology, which is still not represented in the countries of the former USSR, began to develop in the Promised Land. Neuro-oncologists specialize in the treatment of tumor diseases of the spinal cord and brain, as well as tumors of the peripheral nervous system, coordinating the work of an entire team of doctors consisting of neurologists, oncologists, neurosurgeons, endocrinologists, radiologists, etc. Thanks to modern treatment methods, new technologies and qualified specialists (chief neurooncologists) treatment of pituitary cysts in Israel is performed at the highest level.
During pregnancy
If a woman has endocrine disorders due to a pituitary cyst, pregnancy is not always possible. Many patients suffer from ovulation disorders and infertility. They need treatment with hormonal drugs to normalize reproductive function.
If pregnancy does occur, then the cyst is not treated during gestation. This neoplasm does not in any way affect the development and health of the unborn child. Therapy is started only after childbirth. During pregnancy, the tumor usually stops growing, and sometimes even resolves on its own.

Diagnostics
Neurologists and endocrinologists treat pituitary cysts in the brain. It is these specialists who should be contacted if a tumor in this area is suspected. For diagnostic purposes, doctors prescribe the following examinations:
- electroencephalogram;
- ECHO-gram of the brain;
- MRI or CT scan of the head;
- X-ray of the skull.
Consultation with an ophthalmologist and fundus examination may be required. This study reveals signs of increased cerebral pressure.
A blood test for pituitary hormones is required. This helps determine the presence of endocrine disorders.
Diagnostic methods
The presence of a large cystic formation can only be determined using an x-ray. But the results of this study can only be obtained if the case is extremely advanced.
If a formation has been detected in the pituitary gland, its condition should be monitored by an endocrinologist. If the presence of a cyst is suspected, the doctor confirms the diagnosis using:
- Magnetic resonance imaging. During the procedure, it is possible to image a mass larger than 10 mm and detect a smaller tumor.
- Blood tests to determine hormone levels. Such diagnostic methods make it possible to determine in which part of the organ the tumor is located.
The following hormones in the blood are usually tested:
- adrenocorticotropic hormone;
- cortisol;
- luteinizing hormone;
- prolactin;
- somatropic hormone;
- testosterone;
- thyroid hormones;
- thyroid-stimulating hormone;
- estrogen and follicle-stimulating hormone.
Through these studies, it is possible to understand whether the cyst contributes to the production of hormones that can negatively affect the functions of the body.
Conservative therapy
How to treat a pituitary cyst in the brain? If the symptoms of the pathology are not pronounced and the cyst is small in size, then dynamic observation is recommended. The patient must regularly visit the doctor and undergo diagnostics. This allows you to monitor the growth of the tumor.
If the tumor is large, then it can only be removed surgically. But for many patients surgery is contraindicated. In this case, drugs are prescribed that stop the growth of the tumor:
- "Bromocriptine."
- "Dostinex".
If the patient has signs of cerebral hypertension (headache, nausea, visual disturbances), then diuretics are indicated:
- "Diakarb."
- "Veroshpiron".
- "Furosemide".
In case of secondary disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine glands, hormonal medications are required. Their choice depends on the type of endocrine disorder.
Physiotherapeutic methods are not used. However, there are cases when patients are prescribed physiotherapy for treatment of other diseases. Will this lead to the growth of a pituitary cyst in the brain? Physiotherapy can be carried out only after consulting an endocrinologist. Not all types of procedures are indicated for such patients. Only a doctor can assess all possible risks.
Operation
If the cyst is large and compresses the brain tissue, then this is an indication for surgery. Surgical intervention is performed using low-traumatic methods:
- Endoscopic. A small hole is made in the bones of the skull. The cyst is removed through it. The progress of the operation is monitored using a device with a camera.
- Transnasal. This method of operation allows you to do without craniotomy. Surgery is performed through the nasal passage. The doctor makes a small hole in the septum of the sinus and gains access to the pituitary gland. The cyst is removed piece by piece. After the operation, the patient recovers quickly. Such intervention is possible only for small tumor sizes.
Surgery is a radical way to get rid of a cyst. However, in approximately 20% of cases, recurrence of the tumor is observed.
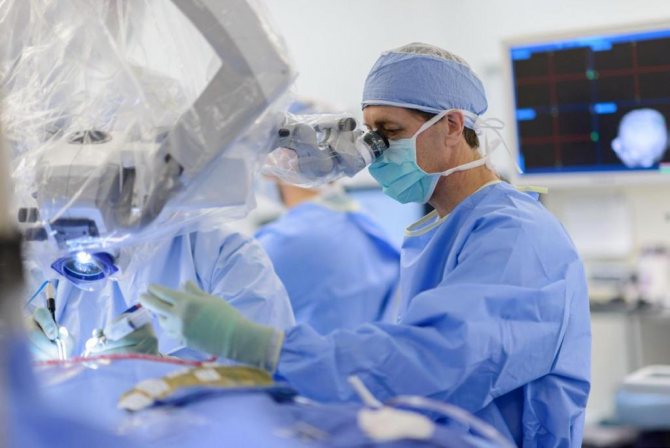
Treatment methods
If the cystic formation is small in size and does not manifest itself, therapy is not required. Conservative treatment of cysts that cause a deterioration in the patient’s quality of life is usually ineffective. The priority treatment method for pituitary cysts, the course of which is accompanied by impaired brain function and the appearance of severe neurological symptoms, is surgical intervention for the purpose of resection (removal) of a space-occupying formation.
The operation to remove a pituitary cyst is performed using a transnasal (through the nasal passages) or transcranial (through the frontal part of the skull) approach. In the first case, an incision is made in the mucous membrane in the area of the posterior part of the nasal septum. The surgeon gains access to the cystic formation through the sphenoid bone and sphenoid sinus.
Endoscopic equipment is usually used to control surgical procedures. The surgeon sees an image of the surgical area on the monitor. Transcranial access operations are rarely performed. Indicated in cases where the cystic formation is large in size and it is impossible to remove the cyst through the nasal passages.
After removing the cyst that has formed on the pituitary gland, it is sent for histological analysis to exclude an oncological process. The doctor may prescribe a course of radiation therapy in cases where large-diameter cystic cavities are detected or the course of the disease is recurrent. After surgery, the patient's condition improves significantly:
- Pain in the head area disappears (82% of cases).
- Visual function is restored (70% of cases).
- The menstrual cycle is normalized (65% of women).
Neurological symptoms are eliminated in 70% of cases. After surgery, a test for hormone levels is performed, based on the results of which the doctor prescribes temporary or lifelong therapy with hormonal drugs. The treatment program is developed taking into account the nature and severity of functional disorders in the pituitary gland.
If there are contraindications to surgical intervention with large cystic formations, the development of mass effect and neurological symptoms, therapy with steroid drugs in high doses is carried out. If the diameter of the cystic formation does not exceed 10 mm, there are no clinical signs of pathology, observation is indicated.
Folk remedies
It is impossible to get rid of cystic formation in the pituitary gland using traditional medicine recipes. However, home remedies can be a good complement to medical or surgical treatment. Before using them, you should consult with an endocrinologist or neurologist.
Herbal medicines that stop the growth of cysts can be purchased at pharmacies. These include:
- "Hemlock tincture."
- "Bedbug tincture."
- “Zdrenko’s collection of herbs No. 99” (a complex of plants with antitumor effects).
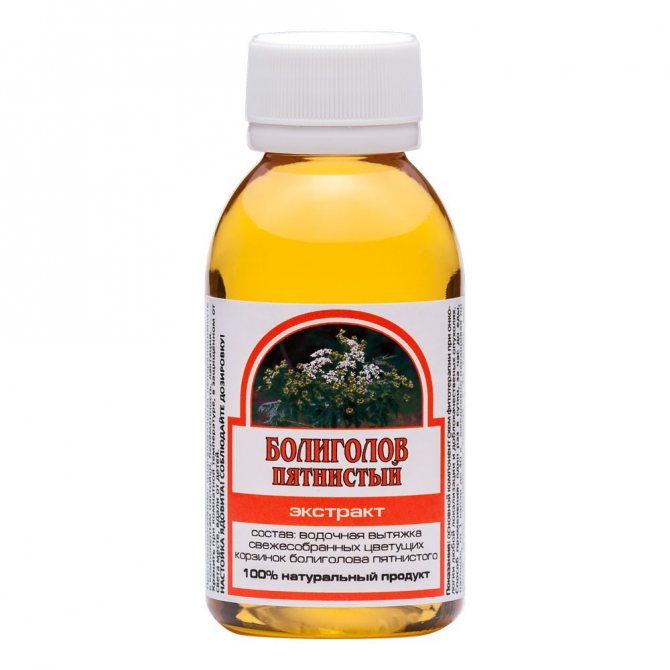

When using preparations based on hemlock, great care must be taken, as this plant is poisonous. Under no circumstances should you allow an overdose of such drugs, otherwise you can get seriously poisoned.
Features of a pituitary cyst
Usually the cyst does not have any effect on the functioning of the body systems. Treatment of a cystic formation in the pituitary gland is necessary only if the size of the cyst increases and it begins to negatively affect neighboring areas and neurological consequences appear.
Why do cysts appear in the pituitary gland?
According to statistics, a tumor forms most often in young patients, and women have a higher risk of formation than men. This type of tumor is extremely rare in children.
There are several reasons for the appearance of such neoplasms:
- Heredity - some people are genetically predisposed to this type of disease.
- Pathologies of infectious etiology - occurring directly in the cerebrospinal fluid (encephalitis).
- Traumatic head injuries.
- Surgeries performed on the brain.
A cyst in the pituitary gland tends to form for no apparent reason, so pay close attention to the manifestation of symptoms; while the tumor is small, its signs are weak.
Symptoms
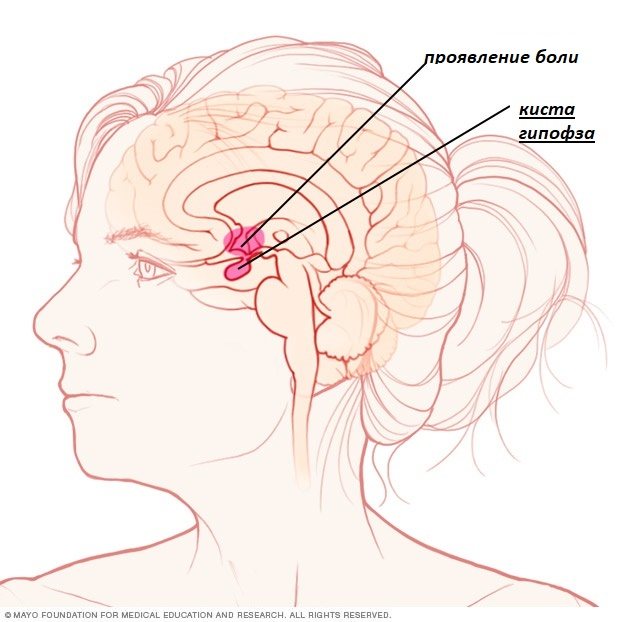
While the cyst is in its infancy, and its size does not exceed 1 cm, it does not manifest itself in any way, but as soon as it grows even a little, it begins to affect all processes in the body, especially the functioning of the brain.
Visible symptoms causing the main complaints:
- Headaches that do not decrease and bother the patient, it may seem that the eyes hurt.
- Efficiency is significantly reduced, fatigue is felt even after short work.
- There may be noise in the ears.
- The patient's vision may deteriorate, sharpness decreases, and there is double vision.
- Increased excitability or, conversely, drowsiness.
- Depending on which part of the pituitary gland, a negative effect on the reproductive functions of the body may occur: in women - scanty periods or their absence, in men - impotence, disorders of the genitourinary system.
- If pathology of the pituitary gland is detected, the work of the hypothalamus may also be disrupted, which affects the general hormonal background of the patient, various diseases appear, for example, Itsenko-Cushing's disease, caused by excessive production of adrenocorticotropic hormone.
Pregnancy and pituitary cyst
Any pathology and pregnancy are poorly combined, and even more so a cystic pituitary adenoma, which usually follows the prolactin scenario; such tumor development can lead to involuntary termination of pregnancy.
Timely and comprehensive therapy will help maintain pregnancy and give birth on time.
Typically, the doctor tries not to prescribe unnecessary medications; only medications aimed at normalizing prolactin levels are used. Basically, the course of pregnancy is monitored and the dynamics of growth of pituitary microadenoma is monitored.