Neurology is a field of medicine that studies the human nervous system, its structure and functions under normal conditions and during the development of a particular neurological disease.
Neurology is divided into general and specific. The general division is based on the study of the functions and structure of the nervous system, as well as diagnostic methods. Private neurology deals with specific diseases of the nervous system.
The central system consists of the spinal cord and brain. The peripheral system includes all kinds of structures that connect the central nervous system and other organs and tissues of the human body.
The nervous system is responsible for the normal functioning of the entire body and the response to changes in the external and internal environment.
Diseases and complications that require consultation with a neurologist
The help of a neurologist is required for various diseases of the nervous system. In particular, it is necessary to regularly consult a doctor after a stroke, severe traumatic brain injury or spinal injury. Thus, observation is necessary for cystic-glial changes in the brain, high blood pressure, liquor hypertension, unstable intracranial pressure, asthenoneurotic, proboscis and other syndromes.
Other diseases requiring clinical observation by a neurologist:
- consequences of contusions, skull fracture, subarachnoid hemorrhage, subdural hematomas;
- suffered a stroke;
- aneurysms, cysts;
- brain tumors;
- diseases of the peripheral nervous system (sciatica, lumbodynia, neuritis);
- vascular diseases of the spinal cord and brain;
- neuroinfections;
- progressive and hereditary diseases (shaking paralysis, multiple sclerosis, myasthenia gravis, BAK, syringomyelia, myopathy);
- parasitic diseases of the nervous system (neurocysticercosis).
For diseases of the spine and joints, the help of a neurologist is necessary in the event of severe pain, sensory disturbances, weakness and dizziness, a feeling of “current through the body,” decreased obedience of the body and limbs, numbness or temporary paralysis, paresis. Also, this doctor should be involved in the treatment of protrusions and intervertebral hernias in case of damage to the nerve roots.
What symptoms require the services of a neurologist?
Urgent assistance from this specialist is necessary if the patient, after a fall or blow, experiences dizziness, periodic vomiting, weakness, confusion, memory impairment, severe headache, nosebleeds, numbness or decreased sensitivity of the body, poor coordination of movements, or changes in gait.
If these disorders are present, an examination by a neurologist is required even if, after examination by emergency physicians or x-rays, no signs of brain or spinal cord injury were detected. Consultation with a neurologist is also necessary if symptoms such as:
- headache;
- nausea or vomiting not associated with gastrointestinal disorders;
- pain in the spine;
- memory impairment;
- temporary change or loss of vision;
- numbness of any parts of the body;
- nervous tics (involuntary movements, sounds or words “escaping” against the will);
- irregular confusion or slurred speech (for example, in the morning or when moving from the street to a warm room);
- disobedience of limbs, lack of coordination of movements;
- sharp spasms, short-term severe headache when moving;
- uncontrolled behavior (for example, the sudden appearance of a grasping reflex).
People often ignore early signs of neurological disorders, attributing them to fatigue, waking up too early, or stress. For example, a person cannot immediately name a familiar object depicted in a painting or photograph, or is unable to walk through a doorway in the morning without touching the wall. It is necessary to consult a doctor when the very first deviations in behavior, memory, and body obedience appear.
Neuroscience Center
- Primary appointment with a neurologist
1600 ₽ - Repeated appointment with a neurologist
1400 ₽
A neurologist is a doctor involved in the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of diseases of the central and peripheral nervous system, as well as some pathologies of the musculoskeletal system. You can get advice from an experienced specialist and undergo a comprehensive examination at a medical center in Moscow. We use advanced treatment methods that are practiced in leading foreign clinics and offer patients a personal approach.
Advantages
Experienced neurologists
The center employs specialists of the highest qualification categories, including candidates of medical sciences
Help for adults and children
“Miracle Doctor” is a multidisciplinary family medical center, we accept patients of any age
Modern laboratory
A number of diseases of the nervous system are infectious in nature, and we have the capabilities to diagnose them
Instrumental examination
We perform ultrasound, duplex scanning of the brain, computed tomography, radiography and other studies
Treatment of organic pathology
Our specialists have successful experience in treating patients with various neurological diseases
Rehabilitation after strokes
We offer effective programs for restoring sensitivity and movement for patients after a stroke
Comfortable hospital
Our patients have modern equipped wards with round-the-clock medical and nursing supervision.
VIP service
We strive to create the most comfortable service conditions for patients
What symptoms should you consult a neurologist for?
The central nervous system controls the activities of all other systems and organs, uniting them and ensuring an adequate response of the body to changes in the internal and external environment. There are no minor neurological disorders; any disturbance can significantly reduce a person’s quality of life and, over time, lead to serious consequences. It is necessary to make an appointment with a neurologist even after a single attack of severe headache or other atypical condition.
Most often, patients consult a doctor with the following complaints:
- fainting, headaches and dizziness;
- hearing, vision, speech, smell and taste impairments;
- periodic loss of balance, falls;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- episodes of short-term memory loss;
- changes in facial expressions, asymmetry of the face, smile and eye movements;
- pain in different parts of the spine with irradiation to different parts of the body;
- abdominal pain not associated with gastroenterological diseases;
- changes in the sensitivity of fingers and toes, individual areas of the skin;
- sleep disturbances, frequent awakenings at night, daytime sleepiness, etc.;
- obsessive involuntary movements, nervous tics, tremors;
- frequent mood swings, increased anxiety, etc.
If treatment is not started in time, the disease will progress. Uncontrolled use of painkillers will also not help eliminate the causes of the pathology; the patient requires qualified medical care.
How is an examination by a neurologist performed?
In our clinic there are practically no queues at the reception desk or in front of the doctors’ offices. We offer patients the most comfortable and convenient service. You will not need to get a referral to a neurologist from a general practitioner, and if necessary, you will be able to undergo diagnostics and visit doctors of other specialties on the same day.
1
Make an appointment
Select a convenient date and let us know when you plan to visit the doctor. We work seven days a week. You can make an appointment with a neurologist by phone or through an online form.
Make an appointment
2
Diagnostics
First, the doctor talks with the patient and clarifies the existing complaints. After this, the neurologist conducts a general examination, checking reflexes and higher brain functions. If necessary, the specialist will prescribe additional examinations, which you can undergo in our center.
3
Treatment
The clinic's doctors work in accordance with the standards of evidence-based medicine. Patients are prescribed effective medications and physiotherapeutic techniques, drug blockades and other modern procedures are carried out.
Methods for diagnosing diseases of the nervous system
Laboratory research. They are used to clarify or exclude a disease, check the effectiveness of treatment, and obtain general information about the patient’s condition. A neurologist may prescribe a cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis, a clinical blood test and the homeostasis system (ESR, hemoglobin, number of red and white blood cells, etc.), a biochemical blood test (protein, cholesterol, glucose, etc.). Laboratory diagnostics are indispensable if cerebral meningitis, multiple sclerosis and other diseases are suspected.
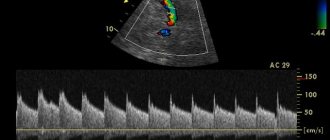
Ultrasound Doppler. Doppler ultrasound allows you to assess the state of blood flow in the main arteries and veins of the neck and head. The examination is quick, safe, painless and has no contraindications. During examination, a specialist can identify a deficiency of blood flow through the main vessels, signs of space-occupying formations in tissues and other pathologies.
Duplex scan of the brain. The study differs from conventional ultrasound by a combination of two techniques: Doppler (assessment of the speed and direction of blood flow) and B-mode ultrasound (scanning organs in a flat projection). The technique allows you to determine the condition of the capillaries, detect the abnormal arrangement of blood vessels, determine damage to the internal walls or narrowing of the lumens of arteries and veins.
EEG. Electroencephalography is a non-invasive diagnostic method that is based on recording electrical impulses from individual areas of the brain. The technique allows a neurologist to confirm the presence of epilepsy and brain dysfunction resulting from injury.
ENMG. Electroneuromyography is a complex examination that allows you to evaluate the features of the peripheral nervous system, skeletal muscles and spinal cord. Only an experienced specialist can perform ENMG, so we recommend contacting the neurology department of our clinic. Diagnostics allows us to identify damage to the nerve roots, myasthenia gravis, multiple sclerosis, polyneuropathy, damage to the trigeminal nerve and other diseases.
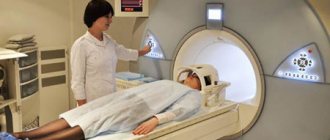
CT. Computed tomography is based on x-rays. The examination allows you to obtain highly accurate layer-by-layer images of any part of the body. In neurology, the technique is used to obtain images of the skull and spine, as well as the brain and spinal cord. In some cases, a contrast agent is used during the examination. Using CT, you can diagnose neoplasms, metastases and other pathologies.
MRI. Magnetic resonance imaging is an informative method for diagnosing any neurological diseases. The examination allows the neurologist to establish the exact size and location of the hernia, assess the degree of deformation of the intervertebral discs, visualize the internal structures of the brain, etc. In addition, MRI is used to diagnose vascular pathologies, acute periods of stroke, etc.
Radiography. It involves radiation exposure to the body and has some limitations. Radiography is widely used to diagnose osteochondrosis, vertebral displacement, and identify metastases in the bones of the skull and spine. The specialists of the Miracle Doctor clinic work with a new generation X-ray machine, which allows you to obtain detailed informative images.
Nervous system diseases
Migraine
This is a specific type of headache, which manifests itself with high intensity, often localized in one half of the head, nausea and vomiting, photophobia and other manifestations. Migraine is quite difficult to treat, however, modern methods can successfully combat the disease. Among them are botulinum therapy, stimulation of the vagus (vagus nerve), transcranial magnetic stimulation of the brain, etc.
Neuropathies
The pathology is characterized by degenerative-dystrophic damage to nerve fibers. Neuropathies affect both peripheral and cranial nerves, so there are many types of the disease. Symptoms associated with loss of sensation in any part of the body, persistent pain or seizures require immediate consultation with an experienced neurologist.
Neuralgia
The pathology is a lesion of the peripheral nerves, which manifests itself as acute pain. There is no decrease in sensitivity or impairment of motor activity. There are costoclavicular, intercostal, occipital and other types of neuralgia. The neurology department uses medications and physiotherapeutic methods to treat pathology, as well as nerve blocks.
Epilepsy
A complex neurological disease that is accompanied by regular attacks associated with disturbances in motor, mental or mental functions. At the same time, seizures that occur during encephalitis, acute cerebrovascular accident and other conditions are not epilepsy. Specialists adhere to international standards for the treatment of this disease.
Multiple sclerosis
A chronic progressive disease characterized by simultaneous damage to different parts of the nervous system. Thus, the patient may experience motor and visual disturbances, dizziness and vomiting. The combination of symptoms is always individual. The prognosis for treatment of multiple sclerosis largely depends on timely diagnosis. In the early stages, drug therapy shows good results.
Osteochondrosis
The disease represents degenerative changes in the vertebrae and the intervertebral discs located between them. There are osteochondrosis of the cervical, thoracic and lumbar regions. The main symptoms of the disease are pain and limited mobility of adjacent joints. The patient requires long-term complex treatment, which in some cases may involve surgery.
Herniated discs
This pathology is one of the consequences of osteochondrosis, in which protrusion of the intervertebral disc occurs between the vertebral bodies. A hernia can compress the spinal cord, nearby vessels and spinal roots. The neurology department uses modern medications and physiotherapy, as well as time-tested manual techniques for treating the disease.
Methods for diagnosing diseases of the nervous system
Many diseases of the nervous system were considered irreversible 15–20 years ago. Modern treatment programs make it possible to successfully relieve pain and achieve long-term remission for such diagnoses as intervertebral hernia and epilepsy. Neurologists use the following diagnostic methods:
Drug therapy. A specialist can develop a regimen for the patient to take painkillers, anti-inflammatory, antiepileptic, antiviral, hypnotic, nootropic and other drugs. Modern drug therapy makes it possible to restore the functions of the central and peripheral nervous system, as well as prevent exacerbations of a number of diseases.
Physiotherapy. To treat neurological diseases, neurologists use techniques such as electrophoresis, magnetic therapy, laser therapy, ultraphonophoresis, darsonvalization, etc. Physiotherapeutic procedures can eliminate pain, swelling, muscle spasms, normalize blood circulation and lymph exchange, and also achieve restoration of nerve tissue.
Therapeutic and diagnostic blockades. These are effective methods of pain relief that help to significantly improve the patient’s quality of life without the use of radical measures. The procedure involves injecting the drug directly into the source of pain. Therapeutic blockade allows you to achieve a long-lasting therapeutic effect.
Auxiliary non-drug methods. These include massage, manual therapy, osteopathic treatment techniques, acupuncture, reflexology, kinesio taping, shock wave therapy and other procedures that do not involve the use of drugs. This group of techniques is auxiliary and cannot be used instead of drug therapy.
Diseases of the nervous system require timely diagnosis and treatment by a good practicing neurologist. These are the specialists who work at the Miracle Doctor clinic. The total work experience of some of our doctors exceeds 30 years. We invite you to make an appointment and personally evaluate the quality of medical care in our center.
Reasons for visiting a pediatric neurologist?
Dispensary observation In the 1st year of life, dispensary observation plays an important role in maintaining health and preventing developmental delays in the child. Recommended terms of examination by a neurologist: 1 month, 3 months, 6 months. and 12 months These dates are associated with the main stages of development of movement skills and psycho-pre-speech development in the baby, as well as with the preventive vaccination calendar. It is important to show the child to a neurologist just before the main stages of vaccination to determine the presence of neurological contraindications to vaccinations. After all, neurological complications due to vaccination take second place after allergic ones. Also, a pediatric neurologist is the main specialist who determines whether the timing of motor and mental development corresponds to age standards. The reasons for delays can be different; they require timely diagnosis and treatment. After 1 year of life, dispensary observation is carried out at 1.5 years and then once a year.
Children born prematurely; with a complicated history of pregnancy and childbirth (intrauterine hypoxia, during childbirth, severe and moderately severe condition after birth, mechanical ventilation after childbirth, pneumonia, birth trauma), hospitalization in the neonatal pathology department, convulsions, abnormalities according to brain ultrasound ( NSG), etc.
Disturbances in the rate of motor and psycho-speech development. The reason for contacting a neurologist is that the child’s development rate lags behind age norms: later he began to crawl, walk, talk, understand spoken speech, simple instructions, etc. There are many reasons for such disorders: from brain damage during pregnancy and childbirth to genetically determined disorders of the structure of muscle tissue, etc. All these reasons require timely diagnosis and correct treatment. It is also necessary to show your child to a neurologist if you notice a loss of previously acquired skills: he has stopped walking or speaking, certain parts of his arms and/or legs have stopped working, etc.
Headaches, pain in the back, pain in the limbs, violent uncontrolled movements (blinking, twitching of the wings of the nose, spasms of the limbs and the whole body), stuttering, freezing, etc.
Poor school performance, fatigue, restlessness, moodiness, hyperactivity, attention deficit and memory impairment, any other types of school failure.
Reasons for an emergency visit to a neurologist: concussions, head impacts; loss of consciousness; sudden loss of function of one or more limbs, facial muscles; sudden speech disturbance; convulsions (newly occurring).
In the event of an emergency, a neurologist in our center will accept you for a consultation without waiting in line!
A neurologist is also the main specialist in the treatment of diseases such as cerebral palsy, consequences of stroke (stroke), injuries, infectious and inflammatory diseases of the central nervous system; epilepsy, diseases of the neuromuscular spectrum, tics, stuttering, headaches, mono and polyneuropathy of various origins, radiculopathy, attention disorders and hyperactivity, developmental disorders of various origins, degenerative diseases, etc.
methods for examining the functioning of the central nervous system in children
Among the many methods for examining the functioning of the central nervous system in children, one of the most important is electroencephalography (EEG).
EEG monitoring reveals functional and organic pathologies of the brain!
This is a harmless and painless diagnosis of brain function. It is carried out for children of any age according to indications.
A comfortable cap with sensitive electrodes is placed on the child’s head, which should be in contact with the scalp. Next, the brain impulses enter the computer, which reflects them on the monitor.
The doctor deciphers and gives a conclusion. Indications for an EEG are convulsive seizures, any paroxysmal conditions in children, delayed psycho-speech development, developmental regression, progressive sleep disturbance in children, and other disorders of the central nervous system in children. Contraindications to EEG: severe health conditions, skin diseases of the head.
At the multidisciplinary medical center President-Med in Vidnoye, electroencephalography is performed for children. The examination is interpreted by a neurologist and epileptologist.
Neurosonography (NSG) is an ultrasound examination of the brain and blood vessels of young children.
This also harmless and painless diagnostic procedure is prescribed to children in the first months of life in order to ensure the correct formation of the brain.
In cases where deviations from the norm are detected, re-examination is required. NSG is prescribed by pediatricians and pediatric neurologists and is included in the list of mandatory examinations during the medical examination of a child at the age of 1 month.
At the President-Med clinic in Vidnoye you can undergo all the necessary examinations for this age.
SERVICE COST*
| NAME | PRICE (Kolomenskaya) | PRICE (Vidnoe) |
| Primary appointment (examination, consultation) with a neurologist (persons under 18 years of age) | 2000 rubles | 1800 rubles |
| Repeated appointment (examination, consultation) with a neurologist (persons under 18 years of age) | 1900 rubles | 1650 rubles |
We accept payment:
Make an appointment by phone: +7,,, +7 (498) 547-29-20 or leave a request on the website.
You can also get advice and do the necessary examinations at the President-Med Medical Center on Kolomenskaya.
Make an appointment by phone: +7,+7,+7 (499)-618-83-43 or leave a request on the website.
Lavrova Nina Avenirovna
Deputy General Director for Medical Affairs Graduated from the Yaroslavl State Medical Institute with a degree in General Medicine Medical work experience - 25 years Make an appointment with a doctor
Objective study of vertebroneurological patients
Questioning the patient (collecting anamnesis)
The examination and neurological examination of the patient is preceded by a thorough collection of information about the history of the disease, aimed at identifying characteristic data indicating a primary lesion of the spine as the cause of pain and movement disorders.
Anamnesis is one of the most important research methods that helps to make a correct diagnosis, determine the prognosis, and choose the best treatment and prevention options. Anamnesis collection is carried out according to a specific plan. Initially, they clarify the patient’s complaints, his feelings, obtain information about the onset of the disease and its subsequent course, then about the patient’s life preceding the disease, heredity, previous illnesses, marital status, bad habits (drinking alcohol, smoking, etc.), conditions everyday life, work, etc. Incorrect information provided to the doctor can lead to an erroneous diagnosis of the disease, and consequently to incorrect treatment.
Spine studies
After anamnesis has been collected, complaints and the nature of the pain syndrome have been assessed, the doctor begins to examine the patient.
Posture and statics The patient must be examined stripped down to his underpants, since only in this case can one get a complete understanding of the characteristics of posture, the statics and dynamics of the spine, the presence of skin changes (with neurofibromatosis and other phakomatoses, with rheumatic diseases, with psoriasis, skin neoplasms, mammary gland), burn marks, dry skin, ichthyosis, swelling, etc. Symmetrical skin folds, the presence of stretch marks on the lower back, varicose veins (on the legs, above the spine), hemangiomas; the presence of bone deformations (consequences of trauma, rickets, joint deformities due to arthrosis, urate deposits due to gout, varus or valgus deformities of the limbs, etc.). Many of these signs can be decisive for making a diagnosis.
The examination is carried out from all sides (front, back and side), from head to toe in a standing position. When examining the front surface of the body, attention is paid to the position of the head relative to the midline, the symmetry of its location, the elevation or depression of the shoulder girdle, the shape of the chest, sternum , symmetry of the costal arches, abdomen, location of the navel (deviates towards the tense oblique abdominal muscle), iliac crests; on the shape and length of the legs (O-shaped, X-shaped), the position of the feet (toes spread or brought together, support on the outer or inner part of the foot). When examining the patient from behind, we draw an imaginary vertical from the middle of the crown of the head to the middle of the distance between the feet and record the deviation of the line of the spinous processes of the vertebrae in one direction or another (scoliosis), the displacement of the head from the midline. We note the asymmetry of the location of the shoulders (raised or lowered shoulder), shoulder blades (wing-shaped shoulder blade, spaced from the chest). We pay attention to the length of the neck (short neck), the protrusion of the spinous process of the seventh cervical vertebra and other vertebrae. The shape of the chest, the presence of a rib hump in scoliosis, kyphosis (round or flat back) are studied; symmetry or oblique position of the pelvis, sacrum in the shape of the sacral rhombus, height, symmetry of the location of the wings of the iliac bones. It is important not to lose sight of the presence of transverse stretch lines, skin folds, drooping gluteal folds, the presence of areas of atrophy and hypertrophy of the paravertebral muscles and leg muscles, and flat feet. Waist triangles formed by the lines of the arms, hips and waist should be the same shape on both sides; their asymmetry indicates significant disorders in the musculoskeletal system. Examination from the side clearly reveals defects in posture, deviations of the head, abdomen, and pelvis from the center of gravity, increased physiological bends or the formation of a hump, hyperlordosis, hyperextension of the legs at the knee joints. The most common deviations are a forward head, hyperextension in the cervical spine, stoop (corrected by tension in the back muscles), kyphosis of the thoracic spine, hyperlordosis of the lumbar spine, protruding or hanging belly, posterior distance of the pelvis, shortening of the distance between the lower ribs and the pelvis is observed with weakness of the gluteal muscles and abdominal muscles, tension in the paravertebral muscles of the lumbar region. Examination in a sitting position provides additional important information about the statics of the spine. In this case, features of the sitting posture are noted, increased anterior displacement of the head, its tilt to the side, accentuation of thoracic kyphosis, scoliosis, smoothing of lordosis or the formation of kyphosis in the lumbar spine, symmetry of support on the buttocks or its violation. In a sitting position, the patient’s predominant type of breathing (upper and lower thoracic, abdominal or mixed) is clearly revealed.
Study of active movements in the spine Study of active movements in the spine (its dynamics) is the most important differential diagnostic technique, allowing one to judge the severity, location and often the nature of its damage. In a standing, sitting and lying position, the patient performs flexion, extension, lateral bending and rotation to the right and left in various parts of the spine. Movements in the cervical and thoracic regions are best studied in a sitting position. Mobility in the lumbosacral spine is examined with the patient in an upright position. The examination reveals a limitation in the range of motion, fixation of the spine or its enlargement, hypermobility (range of motion is increased), and instability. Fixation is most often caused by muscle tension, which provides a protective anti-pain posture (myofixation). This situation is typical for reflex pain and root syndromes caused by osteochondrosis and herniated intervertebral discs. In this case, movement is limited in the direction of pain, that is, an attempt to tilt or straighten the spine in this direction increases or provokes pain. Limitation and increase in the mobility of the spine is determined visually by changes in the curvature of its arches. In the cervical region, the range of movements is established by the approach of the chin to the notch of the sternum when tilting the head (normally, the chin should touch the chest), the scales of the occipital bone to the spinous process of the seventh cervical vertebra during extension (normally, the gaze should be directed straight up), the ear to the shoulder when tilt to the side (normally, the upper edge of one ear should be at the same level as the lower edge of the other ear), rotation is assessed by the arc of rotation relative to the shoulder girdle (normally, the head should be turned to the side so that the gaze is directed to the side). With hypermobility, the range of motion is increased. Local instability is detected against the background of blocked adjacent segments and a relative decrease in the total range of movements in the studied part of the spine, deformation of the spinal arch. When bending in an unstable segment, a characteristic crunch may occur, which can be heard from the side. The movement is intermittent due to instantaneous closing and opening of the affected segment with a short-term increase in pain. More often, the same phenomenon is more pronounced when the body returns to its original position.
Palpation (palpation) Palpation is the main method of research, allowing the doctor to obtain complete information about painful changes in muscle tissue, tendons, ligaments, joints, muscle tone, the condition of the skin and subcutaneous tissue, the presence of pain and trigger points, pain in peripheral nerves trunks. First, superficial palpation of the skin in the area of the affected motor segment is performed, which may reveal local thickening and hyperhidrosis. The skin fold in this area is poorly formed. These changes are defined as a stripe above the damaged segment or cover a significant area of skin located below. Next, the spinous processes, interspinous ligaments, projection sites of the intervertebral joints, and transverse processes are palpated separately. At the same time, palpation becomes deeper and more intense. The most painful points are recorded, the effect of pain being transmitted to other parts of the body.
Neurological examination
When examining a neurological patient, the main symptoms of damage to the nervous system, which are directly related to the patient’s status with vertebrogenic pathology and various neurological complications associated with it, allow the doctor (orthopedist) to independently understand the syndrome of damage to the nervous system and its possible connection with spinal disease.
Cranial nerve examination
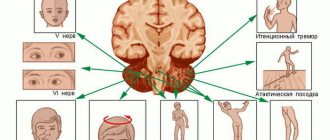
There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves connected to the brain, which provide sensitivity to the skin of the face, mucous membrane of the eyes, nasal cavity, mouth, pharynx, larynx, as well as motor reactions of the muscles of the face, eyes, tongue, pharynx and larynx. Autonomic nerve fibers of the cranial nerves control the activity of the lacrimal and salivary glands and are involved in ensuring the function of the respiratory organs, cardiovascular system, and gastrointestinal (digestive) tract. In addition, the cranial nerves provide the functioning of the senses, maintaining communication between the central nervous system and the receptors of smell, vision, hearing and taste.
Vestibular function study
Ataxia is a disorder of balance, standing, coordination and rhythm of movements, and gait.
Dizziness is a false sensation of moving surrounding objects or one’s own body, combined with imbalance. The cause of dizziness is a violation of the parts of the nervous system that are involved in regulating the balance of the body, the vestibular apparatus, located in the inner ear.
Nystagmus is jerky horizontal, vertical or rotational movements of the eyes, following one after another and independent of the will of the patient. Nystagmus is usually bilateral, very rarely unilateral. In healthy people, it occurs when observing objects moving quickly in front of the eyes or during rapid rotation, for example, in a special chair. Nystagmus is also noted when rinsing the ear with water at a temperature higher or lower than body temperature. Nystagmus can also be caused by diseases of the inner ear and various lesions of the central nervous system.
Research of the motor sphere
Examination of muscles and joints External examination allows you to detect deformities of the spine, joints, feet, hands, asymmetry of skeletal development, and leg length.
Palpation of soft tissues, muscles, bones and joints Painful areas, areas of deformation of joints, bones, subcodal tissue, areas of edema are palpated (dense edema in hypothyroidism, soft edema in venous insufficiency).
Assessment of range of motion Range of motion is the most important characteristic of the function of the spine, osteoarticular, and muscular systems, determines the severity of motor neurological defect, and allows you to objectively evaluate the results of treatment of patients with orthopedic and neurological pathologies. Assessing muscle strength allows you to determine the severity of paresis (partial decrease in muscle strength) of the limbs and weakness of individual muscle groups or muscles.
Study of reflexes (the body's response to irritation from the environment and internal environment, with the participation of the central nervous system; manifested by the emergence or cessation of any activity of the body, contraction or relaxation of muscles, constriction or dilation of blood vessels, etc.).
Study of sensitivity (the ability of a living organism to respond to stimuli coming from the external and internal environment).
Gait study
The study of a patient’s gait provides the key to many diagnostic hypotheses; by its nature, a number of neurological and orthopedic syndromes can be easily distinguished. During the examination, the patient should be dressed lightly; shoes should be removed. The patient's stability when supporting on both legs, posture, and readiness to walk are assessed. A push test is performed. The doctor lightly pushes the patient's shoulder. Normally, body deviation is easily compensated by muscle balance. If the patient’s legs are brought together at the moment of the push, a support reaction is observed: the leg distant from the place of application reflexively moves to the side, preventing a fall. In the process of walking, pay attention to its speed, rhythm, smoothness, symmetry of the change in phases of support and transfer of the leg. Important parameters of walking are the width and length of the step, the synchronization of the knee and ankle joints, the degree of abduction of the leg to the side when moving it, the stability of the joints when supporting the leg. The participation or exclusion of movements of individual parts of the patient’s body during walking is studied. The adequacy of friendly movements, their suppression, redundancy or asymmetry are noted. The position of the head and shoulder girdle is assessed; synchronization of hand movements when walking or their tense, protective posture; flexion of the hips, rocking of the pelvis; hyperextension of the leg at the knee joint; resting on the full foot, toes, or tucking the foot inward, outward. Walking on your toes and heels reveals hidden weakness of the extensors and flexors of the feet.
Symptoms for which you should consult a neurologist
- Headaches are sudden, sharp, increasing.
- Dizziness, fainting, presyncope.
- Pain in the limbs, back, neck, body.
- Shooting facial pain - with gusts of wind, touch, while talking or chewing food.
- Muscle weakness.
- Unsteadiness of gait, general lack of coordination of movements.
- Sleep disorders, including insomnia.
- Visual impairment – double vision, loss of parts of the visual field, blurred contours of objects and people, “islands” of blindness.
- Speech disorders - inability to control the tongue and lips, inability to form competent phrases, lack of speech, altered voice volume.
- Uncontrolled movements of the arms or head, speech tics, uncontrollable coughing or sniffling during a conversation.
- Drooping eyelid.
- Memory impairment.
What does a neurologist do during an examination?
The appointment begins with a conversation with the patient and collection of anamnesis. It is imperative to inform the neurologist that there were diseases of his profile in the family, tell in detail about the symptoms, say when and how they began, etc. You must bring all available medical documentation to the appointment - examination results, an outpatient card, if you have it on hand. If it is impossible to speak clearly with the patient, a relative or accompanying person should come to the appointment and answer questions. Based on the results of the initial conversation, the doctor will understand whether there are any speech or consciousness disorders.
Then an external examination of the patient is carried out. The neurologist pays attention to the symmetry of the shoulders and limbs, posture, motor activity, and notes trembling of the hands or body. The doctor will ask you to squeeze their arm to test muscle strength. With neurological pathology, it can be different in different hands.
The neurologist examines reflexes - cutaneous, periosteal, pupillary, tendon, meningeal. Tendon reflexes are tested by lightly hitting the tendon of the target muscle with a hammer. Pupillary - by moving the hammer in front of the patient's face, who must follow it with only his eyes.
Types of mucosal reflexes and ways to test them:
- pharyngeal - if you act on the mucous membrane of the pharynx, swallowing will occur;
- palatal - the palate tightens when you touch it;
- corneal - when the doctor touches the cornea of the eye, the eyelids close;
- anal - the sphincter contracts when there is tingling around the anus.
Skin reflexes are tested by irritating the skin with a specific object. As a result, the muscles contract locally. There are the following skin reflexes:
- plantar – the toes bend when the skin of the foot is applied;
- cremasteric - if you act on the skin of the thigh from the inside, the testicle is tightened;
- abdominal - the doctor quickly moves the handle of the hammer along the skin of the abdomen, in response to which the oblique and rectus muscles contract.
Temperature sensitivity of the skin is tested by applying test tubes with liquid of different temperatures to the body.
Pain sensitivity is tested by lightly pricking the skin with a needle. Tactile sensitivity is assessed using a piece of fabric or a brush.
All these tests are tests of surface sensitivity. Next, the neurologist checks the deep. To test the sensation of pressure, objects of different weights are placed on the skin. Normally, a person feels a pressure of up to 0.02 g with the palm and inner side of the forearm. To study the deep muscle-articular feeling, the doctor makes passive movements in different joints of the patient.
Then combined sensitivity, or complex sensitivity, is checked. This includes testing: coordination, the ability to reproduce graphic patterns “drawn” with a blunt object on the skin, a sense of localization - the ability to correctly assess one’s spatial position.
Cerebellar function must be examined. The neurologist checks stability in the Romberg position (the patient stands, feet shifted, eyes closed, arms extended straight in front of him), asks to touch the tip of the nose with one finger with eyes closed.
A test for diadochokinesis is also performed: the patient stands with his eyes closed and rotates his hands in different directions; if the cerebellum is damaged, the amplitudes of movements on different hands will vary.
Another test is the heel-knee test: the patient lies on his back and touches the knee of the other with the heel of one leg.
The doctor also performs a pointing test - you need to touch the hammer with your index finger.
Study of a neurological patient
CRANIAL NERVES I pair – olfactory nerve
(N. OLFACTORIUS)
Subjective data – sense of smell is preserved, decreased (hyposmia), lost (anosmia), increased (hyperosmia), distorted (dysosmia). It is determined whether there are olfactory hallucinations (sensations of non-existent odors).
The study of smell is carried out using a set of aromatic substances (mint, valerian, perfume, etc.), each half of the nose is examined separately. You should not use substances such as acetic acid or ammonia, which irritate the endings of the trigeminal nerve.
II pair – optic nerve
(N. OPTICUS)
It is necessary to find out whether there are any complaints about decreased visual acuity, limitation or loss of visual fields, a feeling of fog, dark spots, sparks, flickering before the eyes; whether the patient distinguishes colors; Are there any visual hallucinations? Visual acuity is examined using Golovin-Sivtsev tables. Impaired visual acuity can occur in the form of decreased vision (amblyopia) or blindness (amaurosis). Visual field testing is usually done using a perimeter. The results of the study are sketched on a special diagram. To roughly determine the visual fields, you can use the following technique: the patient is seated with his back to the light and asked to close one eye with his palm, and with the other to look at the bridge of the nose of the doctor, who is located opposite him (at a distance of one meter). Then the doctor slowly moves his finger from the periphery to the center of the visual field, alternately in different directions - above, below, outside, inside - until the patient sees the finger. It is necessary to ensure that the patient does not deviate his gaze to the sides. The field of view of each eye is examined separately. Normally, the border of the field of vision for white color is: upward – 50–60°, downwards – 60–70°, outwards – up to 90° and inwards – 55–60°. Thus, the visual field is the space that is perceived by a fixed eye. With pathology, concentric narrowing of the visual fields, loss of half of the visual fields - hemianopsia - can be detected. Hemianopsia is distinguished: homonymous - loss of the right or left halves of the visual fields of both eyes, bitemporal - loss of the temporal and binasal - loss of the nasal halves of the visual fields, and quadrant - loss of a quarter of the visual fields. Loss of certain areas of the visual fields – scotomas – may also be observed. Color perception is studied using special polychromatic Rabkin tables or multi-colored threads, pieces of paper, etc. Impaired ability to distinguish colors is called achromatopsia, the inability to perceive individual colors is called dyschromatopsia (for example, inability to distinguish between red and green is color blindness). Examination of the fundus is carried out using an ophthalmoscope. In the fundus, neuritis, congestive papillae of the optic nerve, primary or secondary atrophy of the papilla, retinal hemorrhages, and angiopathy can be detected.
10
Types of diagnostics prescribed by a neurologist
Based on the results of the examination and tests, the doctor may refer the patient for some examinations from this list:
- MRI – regular or with contrast, in the second case the accuracy of visualization of nerve structures is higher;
- CT head;
- echoencephalography;
- PET (positron emission tomography);
- cerebral angiography;
- lumbar puncture;
- Ultrasound Doppler scanning;
- myelography;
- Ultrasound of the spine;
- electroneuromyography;
- gammaencephalography;
- laboratory tests - clinical and biochemical blood tests, general urine analysis, etc.
How is treatment done by a neurologist, what methods are used?
The choice of treatment method depends on the disease, its stage, age and general health of the patient. Basic techniques:
- manual therapy;
- different types of therapeutic massage;
- physiotherapy;
- acupuncture;
- biofeedback therapy;
- traction therapy (spinal traction with rings, blocks, belts);
- kinesitherapy;
- osteopathy;
- drug therapy;
- blockades
To relieve muscle-tonic syndromes and pain, periarticular and joint blockades are prescribed.
In the treatment of neuroses and sleep disorders, special medications and psychotherapy are prescribed. In this case, a neuropsychiatrist or psychotherapist is involved in treatment.
For vascular disorders, epilepsy, concussion, consequences of surgery, etc., a medicinal method of treatment is used, that is, based on the patient taking medications prescribed by a neurologist.
Treatment is always individual, and many factors are taken into account when developing a treatment plan. And only with this approach can patients count on the effectiveness of therapy and its minimum duration.
The most commonly used techniques from the above:
- Manual therapy is a treatment method based on manual manipulation. It is used mainly for the treatment of internal organs and the musculoskeletal system.
- Physiotherapy – individual selection of physiotherapeutic techniques for each patient – temperature, ultrasound, electromagnetic, electric current, vibration and other types.
- Osteopathy is a gentle influence on the patient’s body to restore biomechanics. Neurology uses craniosacral and structural osteopathy, which regulate bone relationships and affect the musculoskeletal system.
- Acupuncture is the effect of ultra-thin needles on biologically active points of the human body. Simply reflexology can also be used - acupressure, laser techniques, cold treatment, etc.
- Kinesitherapy – the patient works on special decompression machines, which reduce the load on the joints and allow you to do exercises without pain.
Neurological status in Parkinson's disease
Are we talking about Parkinson's disease? Then it is necessary to find out the state of the neurological status. An example of symptoms is listed below.
What is this disease? It is considered chronic and disrupts the functioning of the nervous system. Most often, older people are susceptible to this disease. Often the cause of this disease is considered to be problems with the musculoskeletal system.
The first manifestations or symptoms are generally normal: we are talking about the presence of ptosis, mydriasis, lack of reaction to sunlight or natural bright light. There may also be double vision. In addition, less common symptoms are sometimes present. We are talking about a visual disorder, ankylosing spondylitis, which patients are quite afraid of.
Prevention of neurological diseases
There are only four rules, if followed, you will not encounter neurological problems:
- Exercise regularly or at least do daily exercises.
- Get proper rest - sleep at least 8 hours a day, but at night, and not during the day or evening.
- Eat right so that your diet contains all the necessary vitamins and minerals, avoid junk food, alcohol, and fast food.
- Walk in the fresh air as often as possible, at least 20-30 minutes a day, and preferably 1 hour.
When is it necessary to contact a neurologist?
Patients usually focus on their condition. Complaints that are directly related to the neurological specialty are the following:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- Noise in ears;
- facial pain;
- double vision;
- loss of visual areas (scotoma), or narrowing of visual fields, especially in young people
- unsteadiness of gait;
- high blood pressure and hypertensive crises, in which, as a rule, neurological abnormalities are found;
- loss of sensitivity (a person has ceased to feel any part of the body - an arm, leg, face or part thereof);
- feeling of “pins and needles” (paresthesia);
- difficulty swallowing or choking on food;
- lower back pain;
- leg pain ;
- pain in the neck;
- pain in the thoracic spine;
- pain in the back and interscapular area;
- arm pain;
- pain is a neurological disorder. Of course, there are pains that are related to other specialties. But we must remember that the sensation of pain is provided by nerve conductors;
- dysfunction of the pelvic organs (sudden onset of urinary or fecal incontinence, false urge to urinate: the urge is pronounced, but there is little discharge);
- a lot others.
Examination of the cervical and spine
When a doctor examines the neck, he must pay attention to its basic position and how mobile the spine is. The carotid artery, nodes and thyroid gland are examined by palpation. In order to examine the veins and vessels, it is necessary to perform auscultation. At the same time, the occipital muscles are checked for tone, as well as for the presence of Lhermitte’s symptom. If everything is normal, then they continue the examination further, trying to find out the neurological status of the patient.
The doctor proceeds to examine the chest and abdominal cavity. The spine should be examined very carefully. The doctor must evaluate the mobility of the vertebrae. This is done by bending the patient in different directions. This will also allow you to determine how tense your back muscles are and whether they react painfully to movement. The lumbar vertebrae are also examined in the same way.
When examining the neck, pay attention to the position and mobility of the head and neck. The thyroid gland, carotid arteries, and lymph nodes are examined by palpating. The carotid and subclavian arteries are examined by auscultation. Determine the tone of the occipital muscles, whether there is a Lhermitte symptom. Next, the chest and abdominal cavity are examined.
A thorough examination of the spine is very important. They pay attention to various types of spinal deformities, assess the mobility of the vertebrae, tilting the patient in different directions, determine the degree of tension in the back muscles and their soreness, as well as the condition of the lumbar vertebrae.
How is an examination by a neurologist performed?
Diagnosis begins from the moment of the first contact between the doctor and the patient. The neurologist looks at the patient’s gait: are there any difficulties when moving, how does the patient sit down. At the beginning of the conversation, the neurologist evaluates how the patient conducts the conversation, whether the vocabulary is reduced, pays attention to memory, reaction speed, etc.
Anamnesis is important - the history of the development of the disease, the history of the patient himself. Even seemingly insignificant facts about relatives or the patient himself can play a significant role in establishing a diagnosis.
Next, the neurologist begins to examine and test the patient using a variety of neurological techniques, such as: taking into account coordination tests, the patient’s motor and sensory spheres, checking reflexes, muscle strength, pupil reactions, etc.
After this, the consultation with a neurologist comes to the key stage - making a primary diagnosis, or preliminary diagnosis (in a hospital - “diagnosis on admission”). This is the diagnosis on which, in the era before MRI and ultrasound, not only any neurologist in Kyiv, but also his foreign colleagues began treatment.
Now neurologists all over the world use hardware diagnostics to clarify and establish a final diagnosis.
Purposes of the neurological examination
What a neurologist checks and evaluates:
- examination and general assessment of the functioning of all organs and systems in the human body;
- the skin is examined;
- body type is determined;
- when communicating, the specialist pays attention to the shape, symmetry and size of the head;
- then the neck is diagnosed and the stiffness of the neck muscles is checked;
- chest examination;
- the peritoneal organs are palpated;
- the spine is examined.
Specifically, the neurological examination includes the following parameters:
- assessment of the state of consciousness and the presence of its disorders;
- how the patient can navigate space, his own personality and time;
- assessment of cerebral symptoms;
- checking the function of the cranial nerves;
- study of the motor sphere;
- reflexes are checked.
The nervous system performs many functions in the body and controls the functioning of all organs and systems. Therefore, examination of a neurological patient, depending on the patient’s condition and the necessary diagnostic methods, can last from 15 minutes to several hours.
The qualifications of a specialist are very important when undergoing an examination and making a diagnosis.
Diagnostic methods in neurology
Any neurologist in Kyiv with 15-20 years of experience remembers the times when there was no MRI equipment in the city. There was no ultrasound, which can be used to determine the condition of the blood vessels. There was rheovasography - an insufficiently accurate outdated method. Any neurology in Kyiv must be equipped with MRI, ultrasound, x-ray and other diagnostic equipment.
- Clinical examination conducted by a neurologist
- MRI of the brain, MRI of the spine, MRI of the joint and periarticular tissues that can cause pain.
- MRI of head vessels. A very important method. It shows congenital or acquired vascular defects in which blood flow to the brain may be reduced.
- MRI of the spinal cord is performed predominantly at 1.5 Tesla MRI
- Vascular ultrasound
- Ultrasound of nerve trunks
- Ultrasound of muscles and tendons
- Electrophysiological diagnostic methods (EEG, somatosensory visual potentials, brainstem and visual potentials, electromyography)
- Laboratory research methods
- — others
Study of higher brain functions
When collecting anamnesis, the doctor will be able to quickly determine the patient’s mood, his attention, his manner of answering questions, and the nature of his clothing. When the patient listens carefully to the neurologist, specifically answers the questions, and understands their meaning, then this behavior of the patient is assessed as normal, and there is no point in further testing.
If, on the contrary, the patient does not behave adequately, his thoughts are confused, aggression manifests itself, then an in-depth study of cognitive functions should be prescribed. The specialist’s task is to conduct a differential diagnosis between disorders of brain function and mental disorders.
The patient is also additionally prescribed the following tests:
- cranial nerves;
- voluntary movements;
- coordination of movements;
- sensitivity;
- movement pathologies;
- autonomic nervous system.
Laboratory research methods are used after collecting anamnesis and general examination of the patient. If necessary, the patient undergoes a lumbar puncture. It is designated for the following purposes:
- measurement of cerebrospinal fluid pressure and to obtain a sample of cerebrospinal fluid for a number of studies;
- as a therapeutic manipulation for introducing a number of drugs directly into the spinal cord;
- injection of air during myelography.
Treatment methods in neurology
There are a lot of treatment methods in neurology. The use of each of them is determined by the established diagnosis.
There are generally accepted and exclusive methods of treatment in neurology. The generally accepted methods include drug treatment (allopathy). There are different methods of introducing medications into the body:
- Tablets, capsules
- intramuscular, subcutaneous and intradermal injections (the method of administration depends on the medication and the desired speed of its absorption)
- intravenous methods of administering medications;
- intra-articular;
- paraneural (near the nerve trunks)
- paraarticular (periarticular)
- paravertebral (paravertebral)
- epidural (into the epidural space)
- periganglionic (to the nerve ganglia)
- medicinal paravertebral blockades
- epidural
- paraaricular
- paraneural
- paraapophyseal
- neuromuscular
- and etc
Cell therapy.
Efferent therapy.
Physiotherapeutic interventions at the Meddiagnostika clinic:
- ultraphonophoresis
- paraffin
- magnetotherapy
- laser therapy
- magnetic laser therapy
- electromyostimulation
- electrical neurostimulation
- shock wave therapy for pain syndromes
Other methods of physical rehabilitation at the Meddiagnostika clinic
- development of muscle contractures
- various types of massages
- kinesiotherapy
- manual therapy,
- osteopathy
- chiropractic elements
- reflexology
- Acupuncture
- Dr.
All of the listed diagnostic and treatment methods are available at the Meddiagnostka clinic.
What is the autonomic nervous system?
The autonomic nervous system (as opposed to the somatic nervous system) is a complex regulatory mechanism that is not subordinate to consciousness, which is millions of years old. It supports blood circulation, heart rate, blood pressure, sleep and wakefulness, response to stress and weather changes, daylight and nightfall. The autonomic nervous system regulates blood flow to the brain and heart, muscles and internal organs. It ensures the constancy of the environment and largely determines human health. You can read a little more about the autonomic nervous system and related diseases in the section on autonomic-vascular dystonia.
Advantages of the Meddiagnostika clinic
- Experience and traditions of the clinic since 1978 (more than 40 years)
- Academic approach to diagnosis and treatment: the clinic has always been the base of the National Medical University.
- All diagnostics and all available neurological treatment methods are concentrated in one building. Thus, the patient will be able to conveniently and quickly undergo all tests without wasting time traveling to undergo diagnostics in other areas of Kyiv.
- The diagnostic standards at the Mediagnostika clinic are so high that our studies are accepted abroad. At the same time, our specialists conduct a number of studies that are not yet used in foreign practice.
- The clinic has all the amenities for our patients, starting with a nearby metro station, own parking near the building, microclimate, cafe, wi-fi and ending with the most modern equipment.
- Modern MRI 1.5 Tesla (Japan), special open MRI for people with claustrophobia (Japan), expert class ultrasound equipment (Netherlands), modern Japanese X-ray machine with digital technologies and much more.
Cost of services
How is an examination by a neurologist carried out?