What kind of disease is this?
Migraine is a systematic throbbing pain in any part of the head. This neurological disease is accompanied by several symptoms depending on the type and phase of its course:
- photophobia and distortion of visual images;
- hyperacusis (sound fear);
- hyperosmia (aversion to smells);
- nausea and vomiting;
- dizziness;
- noise in ears;
- mood changes;
- intestinal disorder;
- drowsiness;
- painful thirst and craving for sweets;
- violation of speech coherence;
- confusion of consciousness;
- numbness and paralysis of some parts of the body.
Many factors can trigger a migraine attack:
- severe stress and overwork;
- hypothermia and changes in weather conditions;
- pungent odor, loud noise, flickering light;
- alcohol intake, eating disorders, consumption of certain foods.
In women of childbearing age, migraines can be caused by hormonal changes - ovulation and menstruation, taking hormonal contraceptives.
Basic recommendations
If you notice symptoms of migraine or individual signs, it is recommended:
- cancel all planned events, free yourself from household chores;
- create the most tranquil environment in the apartment;
- darken the room, provide access to fresh air;
- place pets with relatives and friends;
- take a remedy recommended by a specialist at the aura stage;
- try to fall asleep, it’s not without reason that they say that sleep is the best treatment for migraines;
Each person knows what best helps him cope with a migraine attack, but following the above recommendations best alleviates the condition, treatment takes a shorter period of time.
Duration of migraine depending on its type
There are several systematizations of migraine; the difficulty in determining the nature of the headache is that the patient does not immediately come to the doctor, describing in detail the details of the attacks. The course and duration of the disease depends on its type:
- Simple migraine, or migraine without aura, is the most common type of disease, occurring in 80% of headache attacks (cephalalgia). It lasts from 4 hours to several days. A migraine of this type almost never lasts a week. In children, the illness usually does not last more than a day.
- Classic migraine or migraine with aura. An aura is a warning sign of pain that appears half an hour to an hour before a migraine attack. The cephalalgia itself lasts from 4 hours to several days.
Headaches are divided into several main types:
- simple,
- classical,
- associated (complicated),
- group.
Each of them has a different duration, as it differs in a special mechanism of passage.
Simple type of migraine
A simple type of headache is characterized by rapid development. Pain comes suddenly, replacing good health. This ailment does not have the first two stages: prodromal and aura. Most often, the throbbing pain during such an attack is localized in the frontal or temporal part of the head, less often - a headache in the back of the head. In addition, it may be accompanied by nausea or vomiting, fatigue and dizziness.
If a simple migraine has no complications, it can last up to several hours. An attack that lasts longer is caused by something more serious than a spasm of cerebral vessels and, if repeated, requires mandatory contact with a specialist.
Acute attacks that do not have an aura are considered more dangerous because they occur suddenly, and before their onset it is impossible to take medicinal measures to relieve pain.
Classic migraine is a headache preceded by an aura. During the painful period, symptoms such as weakness, nausea, and irritability may be added. Sometimes the pain is accompanied by hypertension, as well as impaired reflexes.
The duration of an attack of such a migraine without an aura period is from half an hour to three hours. Taking into account the aura, the headache can last up to four to five hours. In some cases (most often these are advanced or chronic forms), classic migraine can last up to several days and is difficult to treat.
This type of headache differs in that it has certain complications. According to the nature of complications, associated pain is divided into several subtypes:
- ophthalmological (damage to the optic nerves);
- hemiplegic (complicated by hemitype sensitivity disorder);
- vestibular (dysfunction of the vestibular apparatus, dry ears and dizziness);
- cerebellar (mechanical injuries or oxygen starvation of the cerebellar part of the brain, impaired coordination and balance);
- cardiac (complicated by disruption of the cardiovascular system);
- abdominal (digestive disorders).
With a complicated form of the disease, it is impossible to say exactly how long one attack will last. This depends on several factors, in particular on the degree of development of the complication and its nature. For example, cerebellar migraine can be observed as short-term attacks of painful attacks and parallel loss of coordination that last only 5-10 minutes. And ophthalmic or cardiac headaches can last longer than several days if the complicating disease has an acute form of development.
In order to get rid of the associated disease, it is necessary to cure not only the headache itself, but also the causes and consequences of its formation.
Group or histamine pain in the head area are all names for Bing-Horton disease. This problem differs from others in its sudden progression, as well as darkening of the skin and conjunctivitis. During histamine attacks, as a rule, only one half of the head hurts.
The duration of such a headache varies from ten minutes to several hours. In addition, the pain may return as a repeated attack. Recurrences most often occur on the same day.
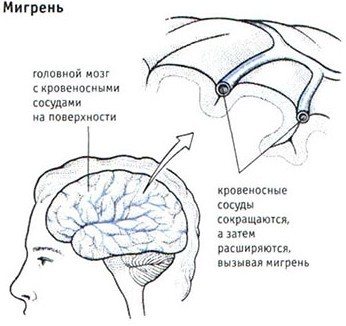
The brain does not experience pain, since it does not have nerve endings responsible for this. However, migraines often occur due to disruptions in the occipital cortex. Headache is divided into primary (independent) and secondary (against the background of another disease). The first group is the main one and accounts for 2/3 of all cases.
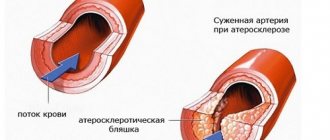
The emerging illness should not be attributed to overwork or other factors, as the cause may be more serious. You can find out through a brain examination. If a migraine is diagnosed, then no one can name its exact mechanism of occurrence, but there are general theories. The main cause of the pathology is considered to be a failure in the regulation of the walls of the cerebral (brain) vessels.
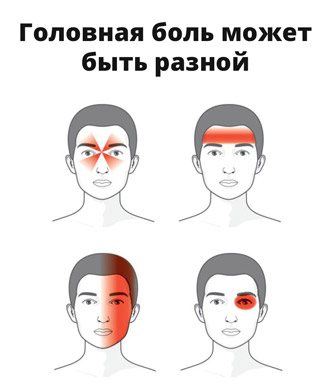
Sometimes it can appear due to an incorrectly drawn up daily schedule, as the body will begin to experience overload over time. Pain sensations are localized mainly on one side of the head and radiate to the eye and temporal region. The nature of the pain is sharp and throbbing, and it intensifies during movements.
Migraine aura
It could start with:
- photopsia, as fear of flashes of light;
- paresthesia - numbness in the fingertips, goose bumps;
- visual hallucinations – lightning flashes and zigzags before the eyes;
- uncharacteristic previously expressed general weakness;
- loss of adequate perception of surrounding objects - like Alice in Wonderland.
Such negative sensations bother the patient 5-20 minutes before he is overtaken by a migraine attack. The intervals between auras are no more than 1 hour.
Certain types of pathology are more prone to the appearance of an aura, for example, the cervical variant. It happens that the patient does not experience a previous deterioration in health at all, but is immediately overtaken by an attack of acute headache.
Phases of the disease
The stages of migraine development were divided into the following phases:
- Prodromal. Symptoms characteristic of this phase can warn a person of an impending attack. It manifests itself as excessive impulsiveness, anxiety, depression, general weakness and drowsiness. Symptoms may appear a day before the expected seizure, which will allow you to prepare or provide an opportunity to avoid it;
- Aura. Immediately before a seizure, many patients experience its precursors. They manifest themselves in the form of various neurological symptoms. Visual aura is the most common and is characterized by blurred vision, flashes before the eyes, etc. In more rare cases, the muscles of the limbs weaken, tingling sensations appear in the fingers and speech defects occur (swallowing letters, stuttering, etc.). After this stage, a migraine attack begins. It is already extremely difficult to stop it, but you can prepare medications and lie down in a dark and quiet place to quickly stabilize the condition;
- Painful. This phase is the attack itself. Because of it, a person becomes irritable and cannot bear even a small load. Without treatment, this condition can persist for several days, so it is advisable to see a doctor to draw up a treatment regimen.
In the absence of an aura, phase 3 may begin immediately, so people suffering from migraines should always be prepared for this.
The disease has several stages:
- Prodromal stage. Some people don’t even notice this phase, which lasts from an hour to a day, attributing the symptoms to fatigue and overwork. During this period, a person experiences exhaustion, loses dexterity, feels thirsty or cravings for sweets, and often yawns.
The person also becomes irritable, sensitive to light and loud sounds, and has increased tone (rigidity) of the neck muscles.
- Stage of aura (harbinger of pain). The phase lasts several tens of minutes. When it occurs, a person experiences difficulty speaking, his hands lose sensitivity, and his vision may be distorted (blindness, flashes, double vision).
- Painful stage (migraine attack). During this phase, the person begins to experience intense to moderate pain in one part of the head. He wants to sleep, he feels tired and overwhelmed. In addition, he reacts sharply to bright light and loud sounds.
- Postdromal (thermal) stage. During this period, the headache and other symptoms subside, and when the migraine passes, the person experiences muscle pain and improved mood.
- prodromal stage,
- aura stage,
- pain stage,
- postdromal stage.
Conventionally, migraine is divided into four stages of development:
They are present in every attack of illness, forming the so-called attack pattern or mechanism of action. How many days a migraine can last depends on the development of these stages of the attack and the duration of each of them.
The initial phase of the disease precedes the appearance of pain. At this moment, a spasm of cerebral vessels occurs. You may experience the following symptoms:
- sudden change in mood;
- high irritability;
- a feeling of fatigue and drowsiness (for some people, on the contrary, a surge of efficiency and hyperactivity);
- excessive appetite and thirst;
- decreased attentiveness and information processing time.
This period lasts from one to three hours, after which it is replaced by an aura of pain. Some patients suffering from chronic illness already feel the onset of an attack based on the signs of this stage. For some types of pain, there is no prodromal phase, as is the migraine aura.
Aura stage

This stage does not appear with every attack. According to various sources, it accompanies from fifteen to twenty-five percent of headaches. Most often, an aura can be distinguished by disturbances in the functioning of the sensory organs, most of all this concerns vision:
- the appearance of white and dark spots before the eyes;
- short-lived “outbursts”;
- change in the field of vision in one eye or in both eyes at once;
- incorrect perception of shape, color, size of objects.
Also, during the period of an aura, the body’s speech function and sense of touch may be upset (the sensitivity of the limbs decreases).
The aura period lasts no more than one hour. Sometimes, at the moment when the disruption of the sensory organs has already begun, it is also accompanied by weakness and drowsiness, that is, a prodromal period. This means that these periods can seem to merge into one.
Painful stage
The migraine stage can begin immediately after the end of the aura, or maybe 5-10 minutes after the end of the previous period. The painful part of the attack is always accompanied by sharp or pulsating, and sometimes aching discomfort. They can either spread throughout the entire head or be localized in a certain part of it. The following symptoms may accompany the malaise:
- disruption of the senses: vision, hearing, touch;
- photophobia, dislike of loud sounds and strong smells;
- poor spatial orientation;
- numbness of the limbs and tingling in them;
- weakness, dizziness;
- fatigue and drowsiness;
- nausea and vomiting;
- fainting.
Depending on the cause that caused the pain, and on its timely treatment, the main period of an attack of malaise can last from several hours to three days.
Most patients note that if the attack is not treated, then after a couple of days it can go away on its own, however, during these few days there is a decrease in appetite and deterioration in sleep.
This is a period of pain subsiding, when unpleasant symptoms gradually decrease and then disappear completely. The body's recovery time is characterized by fatigue, weakness and drowsiness. It lasts up to twenty-four hours.
Causes
You can find out why migraines occur using this list:
- Sudden change in weather. This reason applies to both sexes and is a consequence of a person’s poor adaptability to external stimuli. Because of this phenomenon, people begin to feel dizzy, their blood pressure increases, their sleep rhythm is disrupted, blood flow is disrupted, and headaches occur;
- Overstrain of the eyeballs. Sitting for a long time at a computer, book, phone, etc. against a backdrop of poor lighting can cause eye fatigue and, as a result, migraine;
- Hormonal imbalances. They affect both sexes, but predominantly women. In males, this problem occurs during puberty;
- Stress. Constant mental stress, anxiety and depression plague many people. They are one of the main factors in the appearance of headaches;
- Cold. As a result of illness, a person often experiences headaches.
Women are 5 times more likely to suffer from migraines. It is not difficult to understand why this happens if you know its types and causes. The trigger or trigger for pathology in women is often a hormonal imbalance. It occurs due to the following factors:
- Puberty;
- Menstrual cycle;
- Pregnancy period;
- Use of contraceptive medications;
- Postpartum condition;
- Menopause.
During puberty, teenagers often suffer from migraines. During this period, the number of patients from it becomes approximately equal in the ratio of women and men.
Signs of an approaching attack
You can recognize an approaching attack by the following symptoms:
- The appearance of an aura;
- Changes in behavior;
- Stuffy nose and excessive tearing;
- Increased appetite;
- Frequent urge to go to the toilet;
- Continuous yawning;
- Feeling of tingling or numbness in the extremities;
- Nausea to the point of vomiting;
- Speech defects;
- Dizziness;
- A split picture before my eyes.
Migraine is a common cause of headaches. This neurological disease has affected many of us. Who is not familiar with throbbing point pain, such that it is difficult to turn your head? Many suffer especially from exacerbations in the off-season. So, let's find out how migraine headaches hurt and what to do about it.
The question often arises: where does a migraine headache hurt? The main symptom is unilateral intense throbbing pain. However, it is possible that it can spread, covering the eyes and neck.
Painful sensations may intensify after bright flashes of light, noise or strong odors. The person may feel nauseous. Many people feel dizzy and it becomes more difficult to navigate in space. You may feel irritable, depressed or agitated.
Taking medications that relieve headaches will not relieve the attack; you should consult a doctor.
The presence of an aura occurs in the classic form of migraine. It was observed by a third of patients. The aura is not dangerous to health, it only reflects certain processes occurring in the brain. Its duration is from 10 to 30 minutes.
An aura is visual - while hallucinations appear as flashes of light, spots or a rainbow line.
If you have problems with vision, you should talk about scintillating scotoma (ocular migraine) - the eyes stop seeing due to circulatory problems.
Ocular migraine occurs in pregnant women and children of adolescence. Sensitive symptoms may occur, such as numbness in your fingertips or a tingling tongue. All this is accompanied by visual disturbances, and sometimes it is difficult to speak or find words. When the aura passes, severe pain pierces the head, which is often localized in one place.
No aura
How does a migraine headache without aura hurt? Women may suffer from illness before the onset of menstruation, this is due to hormonal fluctuations.
A migraine attack is often preceded by precursors - symptoms that warn that there will soon be a “storm”.
An attack without an aura begins instantly (from 10 to 30 minutes) and immediately with painful sensations (often in the right side of the head). A distinctive feature is pulsation, similar to the rhythm of the heart; this nature of pain is due to reverse blood flow. It can intensify with physical activity, so it is better for patients to lie still in bed.
This is a rare occurrence. Neurological symptoms are added to painful attacks - disturbances of the speech apparatus, motor functions, sensory organs, and visceral disorders occur. How does a headache with associated migraine hurt? The following options exist:
- Ophthalmoplegic – headaches are accompanied by problems with the oculomotor nerve, such as strabismus, ptosis, and dilated pupils.
- Hemiplegic – added weakness in the limbs.
- Vestibular – Meniere’s syndrome is added to the pain (dizziness, nausea, tinnitus, hearing problems).
- Cerebellar – problems arise with the vestibular apparatus.
- Cardiac – angina or tachycardia is added.
- Abdominal – pain is accompanied by cramping in the abdomen, possible bloating, and vomiting.
Factors that can trigger an attack can be different:
- Excitement, stress.
- Sudden change of activity.
- Lack of sleep or excess sleep, fasting or low blood sugar.
- Flickering or blinding light, intrusive sounds, intoxicating odors, weather changes, allergens, pressure surges.
- Provoking factors can be foods (chocolate, sausages, cheese, ham) and alcohol.
- Chemical additives such as aspartame, benzene.
- Caffeine, oral contraceptives.
How to distinguish a migraine from a headache? First, it’s worth understanding the classification:
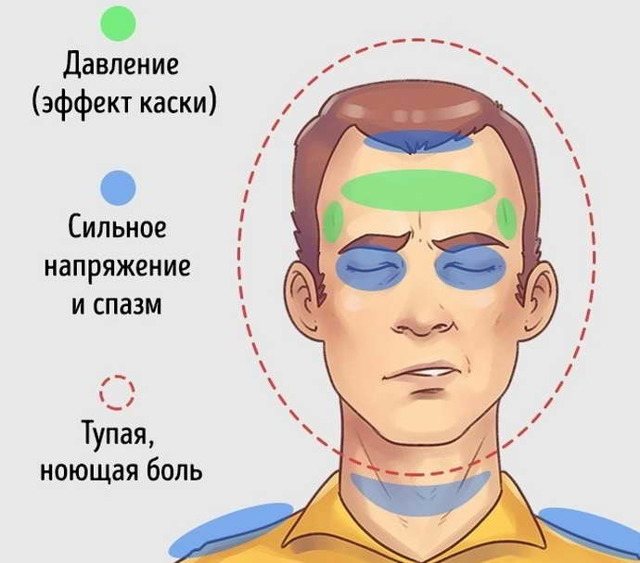
- A common occurrence for us is tension headache (TTH), when aching sensations occur in the temple and back of the head areas. It lasts from 30 minutes to several hours, as if the head is bound with a hoop.
- Cluster pain occurs in the eye. Its duration is from 15 minutes to 3 hours.
- Head pain during migraine can be long-lasting, up to 3 days, and the localization is widespread - the frontal and temporal areas are affected.
TTH occurs when tension occurs in the neck muscles. It develops slowly, cluster pain strikes in the blink of an eye.
The cause of migraine remains a mystery; it is believed that it is provoked by changes in cerebral vascular tone or heredity. Another difference is that an aura can warn about it.
However, without the latter, the disease may not be determined, since cluster pain also occurs on one side. The monotony of attacks, the occurrence of an aura and the genetic factor help to establish a diagnosis.
How to cope with illness during pregnancy?
During pregnancy, especially in the first trimester, most painkillers are not recommended to be taken so as not to harm the development of the fetus. How then to cope with migraines as a pregnant woman. Or will you have to live with migraines until you give birth? Relaxing techniques are suitable for the fight: yoga, meditation, moderate physical activity, herbal teas. Try the following methods:
- Use compresses to combat migraines. Apply a warm or cold compress to your forehead or base of your neck to constrict blood vessels and improve circulation.
- Take a cool shower. This is a simple and effective remedy for headaches.
- Ask your family to give you a relaxing massage, or consult a specialist. Pay special attention to the muscles of the neck, back, and shoulders to relieve tension.
- Make sure you are not thirsty or hungry. A headache may occur due to a lack of glucose in the blood, as well as due to dehydration.
Why do the attacks recur?
Proper nutrition is important for migraines
Chronic migraine is largely a vascular pathology. The real reason why a person experiences frequent migraine attacks is not clearly understood. They may be directly related to abnormal brain activity. They may also be a consequence of developed hypersensitivity of intracerebral arteries.
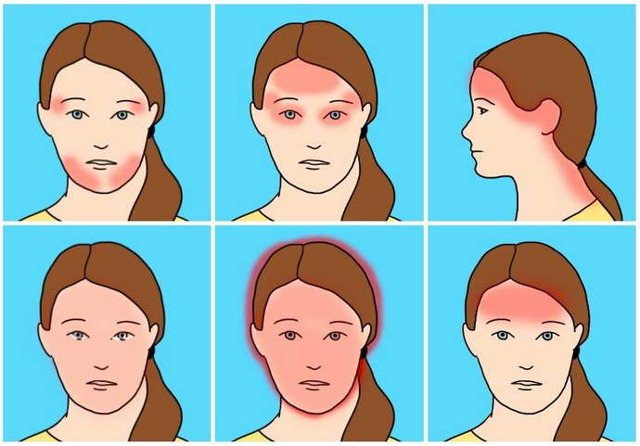
It is still impossible to establish the exact chain of episodes today. But, according to most doctors, chemical processes may be involved in the attack that has begun. Against this background, dangerous changes affecting blood flow in the surrounding tissues, as well as in the brain, can be updated. If migraine attacks a person very often, then there is a risk of vascular changes. This process is diagnosed in people at risk. Frequent migraines can be caused by the following events:
- Alcohol intoxication.
- Stressful situation.
- Severe anxiety.
- Annoying sounds.
- "Aggressive" light.
- Abuse of tobacco products.
- Irritating scents.
Often, a migraine attack is the result of not one, but several provoking factors.
A migraine attack most often attacks young ladies aged 20-45 years. Doctors consider fluctuations in the levels of progesterone and estrogen to be the main provoking factor. For most representatives of the fair sex, a migraine attack is directly associated with the menstrual cycle. This anomaly is most difficult to tolerate during the 1st trimester of gestation. The young lady's condition improves with the onset of the 2nd trimester.
The first migraine attack can make itself felt already when a girl crosses the threshold of her fifteenth birthday. When a young lady turns 18, the headache becomes less intense. But if there is a family history of migraine, then there is a chance that the duration of attacks will be increased. A family history of migraine occurs in approximately 80 percent of patients.
Types of headaches
According to many medical experts, migraine attacks occur in people with poor health. Usually such a person has a whole “bouquet” of chronic pathological conditions. Also, a person who experiences frequent migraines has a depressive character. Often he develops symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia, neurosis or psychosis.
If a migraine attack occurs too often, there is a risk of developing a migraine stroke or status migraine. Status migraine refers to a very prolonged attack, characterized by duration and painfulness.
The painful syndrome, localized in the 1st half of the head, quickly takes on a bursting character. After this, the person begins to vomit violently. This symptom often leads to dehydration.
The person feels tired. Against the background of severe weakness, convulsions appear. This condition requires immediate hospitalization.
Cephalgia most often occurs 2 to 8 times a month. However, there are cases where migraine attacks recur daily, and in some patients - only once a year.
Thus, migraine is not as harmless a disease as it might seem at first glance. It changes a person’s quality of life or even, in the case of migraines lasting several days in a row, leads to disability.
In addition, how long one attack lasts, with migraine it is also necessary to take into account the fact how often the malaise recurs. Of course, this factor also depends on the characteristics of the human body. On average, research experts have identified the following frequency of occurrence of chronic ailments:
- 34% of those suffering from the disease experience attacks less than once a month;
- in 27% pain occurs once a month;
- in 17% of cases, attacks are repeated twice a month;
- 12% have 3–4 attacks during a given period;
- 6% - more than five attacks;
- only 4% complain that the illness takes more than ten days a month.
The average value is 8–10 attacks in one year. Considering that each of them can last up to three days, a migraine in some cases takes away an entire month of a quiet human life in a year. It is worth reducing this indicator by using migraine prevention. For example, eliminate a sedentary lifestyle, walk more in the fresh air, take vitamins B and C.
What medications can I take?
As a medical treatment, the doctor prescribes:
| Name | Recipe |
| Sumatriptan | Used to relieve acute attacks. Adults drink 50-100 mg once. |
| Naratriptan | The dosage regimen is a single dose of 2.5 mg during an attack. If symptoms return, the tablet should be taken no earlier than 4 hours after the first dose. No more than 5 mg per day. |
| Excedrin | An analgesic, antipyretic agent that helps relieve pain. You should drink 1-2 tablets for headaches up to 4 times a day. |
| Voltaren | NSAIDs drink 75 immediately after the onset of an attack. The daily dose is not more than 175 mg. |
| Motilium | An antiemetic drug is prescribed for adolescents and adults 10-20 mg up to 4 times a day. No more than 80 mg per day. |

Varieties
There are several types of migraines that occur due to certain reasons, namely:
- No aura. This form of pathology occurs most often. It is characterized by a gradually increasing headache, localized on one side of the head. The attack lasts from 4-5 hours to 3 days. Migraine without aura is accompanied by nausea and increased sensitivity to noise and light. During a seizure, the patient tends to lie down in a dark and quiet place;
- With an aura. This form occurs in 1/3 of patients. Thanks to the warning of an attack, people can have time to prepare for it. This form is characterized by speech defects, impaired perception, muscle weakness and blurred vision;
- Basilar. It is a consequence of malfunctions in the brain stem and manifests itself in virtually the same way as migraine with aura;
- Hemiplegic. This form appears in children, but goes away on its own over time. Hemiplegic migraine occurs primarily due to head trauma;
- Menstrual. It occurs in virtually every second woman from puberty to menopause. A headache can occur both before or after menstruation, and during it. In women, this condition manifests itself in the form of nausea, depression, chronic fatigue, as well as pain in the mammary glands and lower back.
At-risk groups

Experts identify the following risk groups for migraine:
- residents of large cities – where the level of stressful situations is several times higher;
- symptoms of pathology are more often detected in ambitious people trying to climb to the highest possible level of career growth;
- people with severe emotional instability, prone to depression;
- patients who, due to circumstances, are forced to take medications from certain subgroups for a long period of time, for example, sugar-lowering drugs, estrogens;
- those who abuse alcohol and tobacco products and lead a sedentary lifestyle;
- babies whose parents both complain of migraine attacks;
- Migraine in adolescents is quite possible at the time of rapid hormonal changes; over time, the child may well “outgrow” it.
Having identified individual symptoms or signs of pathology, it is recommended to consult a neurologist and conduct a comprehensive diagnostic examination.
Diagnosis and basics of therapy
If the attacks are mild and occur no more than 2 times a month, then no special examination is carried out. Most often they are caused by fatigue or hardening (rigidity) of the neck muscles. Such attacks can be easily stopped using painkillers.
In the case of moderate to severe headaches, attacks can occur almost every few days due to any irritant. They appear suddenly and are accompanied by neurological symptoms. In such a situation, the help of a neurologist will be required, since the cause of the emerging pathological process can be extremely serious.
Diagnosis of migraine is carried out mainly by interviewing the patient. Due to it, many pathological processes can be excluded. The doctor can finally make sure that they are not there, using the following instrumental examination methods:
- CT and MRI of the brain;
- Taking tests;
- Radiography of the neck area.

After examination, the doctor will be able to make sure that the headache is primary. However, there is no exact marker for identifying migraine.
Treatment of migraine consists of following a strict diet and taking medications from the group of triptans (Sumatriptan) or dihydrogenated ergot alkaloids (Dihydrergot). Antispasmodics like No-Shpa will not help and will only worsen the attack. In severe cases, tablets must be combined with antiepileptic medications and antidepressants. You will have to wait for the result from 30-40 minutes to 1-2 days.
During an attack, you need to take medications and lie down in a dark and quiet place. During an exacerbation of the disease, it is advisable for patients to rest more, give up bad habits and get enough sleep. During the course of therapy, both physical and mental stress should be reduced.
Anyone can find out what causes migraines by spending 10 minutes searching for information or going to a consultation with a doctor. Knowing the factors that trigger an attack will help the patient avoid it. In this case, you can cope with the problem even without drug therapy.
How to treat migraine in women?
It is currently impossible to cure hemicrania or get rid of the disease. The neurologist is faced with the task of determining a set of measures aimed at quickly resolving the paroxysm.
How to prevent the development of attacks?
Compliance with preventive recommendations helps well against migraines:
- Elimination of habitual intoxications (drinking alcoholic beverages, smoking);
- Preference for a balanced diet, additional intake of multivitamin complexes;
- Full sleep;
- Regular exercise;
- Practicing relaxing auto-trainings;
- If indicated, take medications in a timely manner.
First of all, it should be noted that it is necessary to establish control over the causes of migraine paroxysms.
Treatment of migraine and interictal prevention
Treatment of migraine in women consists of choosing a drug that has an analgesic effect when the first symptoms of migraine appear. There are enough medications to treat the pathology.
| Drug group | Example of a drug |
| Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs | diclofenac, xefocam |
| Vitamins | vitamin E, B6 |
| Homeopathy | mastodinon, agnukaston, notta |
| B-blockers | propranolol |
| Tricyclic antidepressants | amitriptyline, tianeptine |
| Quadruple antidepressants | Lerivon |
| Antidepressants selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors | sertraline |
| Vegetotropic agents | grandaxin |
| Ergotamine-containing drugs (true migraine drug ergotamine) | ergotamine, dihydroergotamine |
| Triptans | sumatriptan, eletriptan, zolmitriptan |
The use of antiemetics (cerucal, metoclopramide) can be considered symptomatic to relieve nausea and vomiting.
Drug interictal prophylaxis consists of planned long-term drug therapy:
- Adrenergic blockers:
- β-blockers (propranolol, metoprolol);
- ά-adrenergic blockers (dihydroergocryptine);
- Calcium ion channel blockers (verapamil);
- Antidepressants:
- Tricyclics (amitriptyline, nortriptyline);
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (fluoxetine, sertraline);
- Selective serotonin and adrenaline reuptake inhibitors (venlafaxine, ducoxetine);
- NSAIDs (ibuprofen, diclofenac, ketoprofen);
The need for frequent use of drugs is dictated by the severity of the disease in a woman.
Treatment of migraine with folk remedies
Traditional medicine can help a woman without pills.
- Herbal medicine is the main direction of alternative medicine. Plants that have a sedative and relaxing effect (melissa, chamomile, valerian) are recommended for use in the form of tinctures, decoctions, and teas.
- Apple cider vinegar is a remedy that is actively used in the treatment of the disease. It is recommended to take baths with it, apply body wraps, and consume it internally with eggs and milk.
- Vegetable juices. Juices from carrots, cucumbers, spinach or potatoes have a symptomatic effect.
- Ear drops from a decoction of garlic prepared in milk.
- Therapeutic baths (hydrotherapy). At home, relaxing baths with the addition of sea moth can be used. The method is contraindicated for people with severe somatic diseases.
How can you help yourself?
When attacks recur frequently, patients do not want to use medications all the time, as this risks developing side effects. Possible algorithm of actions to relieve pain.
- Eliminate potential triggers:
- Turn off the lights, TV, computer;
- Lower the curtains, darken the room;
- Create silence (if possible).
- Ventilate the room.
- Massage your head or neck using acupressure points.
- Perform distracting water procedures (irrigation or rubbing of the skin). Water can be replaced with a vinegar-salt solution.
- If conditions exist, take a contrast shower.
- Elastic bandaging of the head with woolen fabric.
- Apply essential oils to your forehead, temples, and behind your ears.