There is no need to hide the fact that a diagnosis of convulsive readiness will not lead to a degree of extreme disorder for very few parents. Fortunately, in this case, timely detection of the disease, proper treatment and competent specialists will help both desperate parents and the little creature bravely endure all the hardships of the disease. Convulsive readiness is not a fatal diagnosis. You can fight him. The number of people cured of the disease is increasing every day.
Seizures (convulsive syndrome) - causes, treatment, first aid, types, medications and pills
Statistics show that seizures happen to every person at least once.
You should worry if such a phenomenon goes into the system. The concept of convulsive syndrome is defined as a pathological condition characterized by unaccountable contractions of the muscular system. In this case, cramps can appear in one specific place or spread to an entire muscle group.
There are many reasons for this disease. There are specific medications for each case.
The main thing is to make the correct diagnosis. And only a qualified doctor can prescribe adequate treatment.
Kinds
There are several types of seizures:
- tonic-clonic convulsions;
- myoclonic contractions;
- partial seizures.
Tonic-clonic seizures are manifested by loss of consciousness:
| Tonic spasms occur first | At the same time, the pupils dilate, the eyes roll up and all the muscles tense. |
| Then comes the phase of clonic convulsions | There is an alternating alternation of muscle contractions and relaxations. |
| Sleep or coma occurs | The attack may be accompanied by the appearance of bloody foam as a result of biting the tongue and profuse salivation. |
Children and adolescents may experience myoclonic contractions. The process involves the entire muscle or only a certain group of muscles. For example, the muscles of the fingers or face. Many seizures can cause a child to fall, resulting in injury.
Convulsions of clonic origin without loss of consciousness are called partial. The process can involve the muscles of the face, feet and other parts of the body.
Many people confuse calf muscle spasms during sleep with cramps. This phenomenon is called myoclonus. Often accompanied by contractions of the thigh muscles.
Myoclonic states occur as a result of calcium deficiency, as well as due to the influence of low temperatures.
During sports training, painful contractions occur due to insufficient warm-up, loss of fluid and excessive increase in loads.
Causes
The following causes of seizures in different age groups of the population can be identified:
- the occurrence of various neuroinfectious diseases, for example, meningitis or encephalitis;
- deviations in the development of brain activity;
- hypoxia;
- lack of calcium, glucose and magnesium in the blood;
- the occurrence of gestosis during pregnancy;
- severe intoxication;
- severe forms of dehydration;
- complex diseases of the nervous system;
- high fever and respiratory infectious diseases;
- birth injuries in newborns;
- pathologies of metabolic processes;
- epilepsy;
- various brain tumors;
- traumatic brain injuries.
Even bright light and loud noise can trigger seizures. Hereditary factors also play an important role.
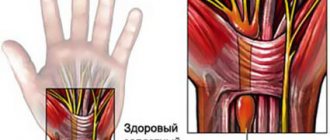
If your hands cramp
Most often, hand cramps appear in people who work a lot at the computer.
Reductions can be caused by the following reasons:
- state of stress;
- poor blood supply to the upper extremities;
- excessive sports activities;
- hypothermia;
- lack of calcium;
- various poisonings.
Coffee lovers should remember that this drink contributes to a significant leaching of calcium from the body, which can also cause cramps.
The following manipulations can help with this problem:
| Gymnastic exercises | In this case, you need to actively move your fingers, as well as clench and unclench your fists. |
| It's worth doing self-massage | Use your healthy hand to stretch your hand. |
To prevent such conditions, you need to follow simple rules:
- Consume foods rich in potassium and calcium.
- Avoid extreme cooling.
- Warm baths with the addition of essential oils have a beneficial effect.
Diseases and consequences
The manifestations of convulsive syndrome are due to the diseases that caused them.
| Tonic-clonic convulsions | May be the result of traumatic brain injury. |
| Febrile spasms | Appear in children with very elevated body temperature. |
| Cramps in the legs above the knee or in the arms | Appear at night. Their cause is considered to be a lack of magnesium, as well as problems with the spinal column. |
In some cases, seizures can even cause death. This is due to associated complications. For example, cardiac arrest, spinal fracture, arrhythmia or various injuries.
Normal muscle spasms are not dangerous.
Convulsive phenomena occur as a result of disorders of the central nervous system, which can occur due to neurological and infectious diseases, toxic processes, disorders of water-salt metabolism or hysteria.
Seizures occur in the following diseases:
| Epilepsy | This is a brain disease that is characterized by periodic seizures. At the beginning of the attack, various hallucinations may occur, and then a seizure occurs. First, the tonic phase occurs, and then the clonic phase:
Frequent seizures lead to the death of brain cells, and personality changes may also occur. It is worth remembering that during such attacks the patient should be protected from bruises, and it is also not recommended to insert plastic or metal objects into the mouth to prevent bites. |
| For tetanus | An exotoxin is produced that affects the medulla oblongata and spinal cord. This disease occurs from infection in a wound. The disease has the following manifestations:
|
| A brain tumor | In the initial stage it is accompanied by convulsive spasms. |
| Rabies | A person can become infected after being bitten by a sick animal.The following consequences appear:
|
| Tetany occurs when calcium levels are low | This condition is accompanied by muscle and nervous excitability. Partial convulsions occur. |
| Chronic alcoholism | It is characterized by increased excitability of the nervous system. In this case, generalized convulsions appear. |
| Eclampsia | It is the last stage of late toxicosis. Contractions of the facial muscles appear first, followed by clonic contractions. |
| Hysterical attack | Occurs as a result of emotional shock. Patients may squirm in an arc. Clonic convulsions develop. After the attack, sleep does not occur. |
What to do if you have seizures
Treatment of seizures occurs in two stages. First, the attack is stopped, and then treatment is given to the underlying cause.
Drug treatment should be carried out only as prescribed by a doctor. Medicines are often prescribed in the presence of a generalized or partial epileptic seizure.
Medicines for stopping an attack of epileptic convulsions
| Group of drugs | Indications | Medicine |
| Gamma amino acid acid and its derivatives. | Rehabilitation after brain injuries and strokes, severe forms of psychosis, seizures. | Sodium hydroxybutyrate by injection. |
| Benzodiazepines. | Generalized and partial convulsions. | Diazepam injections. |
| Anticonvulsant microelements. | Arrhythmia, convulsions in pregnant women and poisoning. | Magnesium sulfate in the form of injections. |
Medications to eliminate the causes of seizures
| Medication group | Purpose | Medicine |
| Barbiturates. | Partial and generalized convulsions. | Phenobarbital sodium. |
| Valproic acid derivatives. | Seizures of varying strength. | Sodium valproate in the form of syrup. |
| Benzodiazepines. | Partial and generalized contractions. | Phenazepam tablets. |
| Neuroleptics. | Complex forms of psychosis. | Aminazine injections. |
| Fibrinolytics. | For ischemic stroke. | Urokinase in the form of injections. |
| Cardiac glycosides. | For heart failure. | Digoxin tablets. |
| Iron supplements. | Convulsive syndrome caused by anemia. | Sorbifer tablets. |
In preventive measures, to avoid the recurrence of seizures, you need to follow the correct work and rest schedule, eat well and avoid excessive physical exertion.
Magnesium and potassium
With a deficiency of magnesium and potassium, muscle contractions may occur. You may also experience tingling and crawling sensations.
A deficiency of these microelements can occur in the following cases:
- if you take laxatives or diuretics for a long time;
- when dehydrated;
- during fasting;
- as a result of poisoning or alcohol abuse;
- with diabetes mellitus.
In order to compensate for magnesium deficiency, the drug Magne B6 is prescribed. You also need to eat foods rich in beneficial microelements. For example, watermelons, milk, oranges, bananas, buckwheat and bran.
First aid
Before providing assistance, it is necessary to find out the exact cause of the seizure syndrome.
| For partial seizures in adults | The person must be seated in a chair to prevent falling. |
| During a generalized attack | An ambulance should be called. Before her arrival, the patient must be placed on his side and his head protected from blows. |
| If the cause of convulsions is not epilepsy | Then it is necessary to give the limbs an elevated state. Massage will help relieve local cramps. |
The sequence of actions when providing assistance is as follows:
- The patient should be seated or laid down.
- Then grab your toes and bend your foot towards your knee. First bend halfway and release. Then bend as much as possible and hold it until the attack stops.
- Perform a muscle massage.
- Ensure complete rest.
After a binge
Convulsive syndrome often occurs after heavy drinking.
There are several reasons for this:
| Drinking alcohol | Leads to dehydration of the body and leaching of magnesium and potassium |
| Hangover syndrome | It affects the nervous system, which leads to changes in the human psyche. |
The last stage of seizures in alcoholism is called alcoholic epilepsy. It is accompanied by severe pain in the limbs, salivation and breathing problems.
You need to pay attention to the systematic occurrence of seizures and promptly seek medical help.
Methods for preventing complications:
- you should start leading a healthy lifestyle;
- you need to monitor the water balance in the body;
- avoid serious physical activity;
- take essential microelements.
If you take care of your health, many problems can be avoided.
Febrile convulsions with fever in a child
It is possible to say that febrile seizures have begun when convulsive or convulsive seizures form. They must be accompanied by a high body temperature (more than 38 degrees) and occur in children who have not previously experienced seizures of this type, up to 6 years of age. It is imperative to differentiate this…
Cramps during pregnancy
The problem of cramps can appear from the first weeks of pregnancy and continue both before the birth of the child and during breastfeeding. To avoid cramping in the future, it is important to determine the cause of the muscle strain and take preventive actions that can help manage and avoid the spasm...
Description of seizures in children
Convulsive syndrome in children develops when a focus of pathological excitation appears in the brain and is accompanied by the sudden appearance of partial or generalized seizures of a clonic, tonic or mixed (tonic-clonic) nature. This pathological condition can develop with…
Description of leg cramps
Cramps are a state of constant contraction of a muscle that does not respond to involuntary relaxation. It leads to a pronounced painful reaction, which is associated with a deficiency of oxygen and nutrients. The muscle also produces a lot of waste products, which irritate the nerves and lead to pain. By…
Source: https://nerv.hvatit-bolet.ru/sudorogi/
Where do cramps come from and what to do about them
A cramp is a sudden and most often involuntary contraction of one or more muscles. Usually the legs cramp: the muscles of the back of the calf, as well as the front and back of the thigh, are affected. But the muscles of the arms, wrists, abdominal wall, and shoulder girdle are also not immune.
In most cases, doctors consider this condition, although painful, to be harmless. Especially if the muscle spasm is one-time in nature and does not last long. However, there are combinations of symptoms that require an urgent visit to the doctor.
But first, let's look at the most common causes of seizures.
Why do cramps happen?
Where muscle spasms come from is not entirely clear to science. Often the cause cannot be established (however, if the cramp is a one-time occurrence, we don’t really try).
But there are situations that often precede a spasm. Here are seven of the most common causes of seizures.
Muscle strain
Often, cramps are the result of an overly energetic approach to equipment in the gym. The resulting sprains and other microtraumas during the healing process can be accompanied not only by pain (soreness), but also by muscle cramps.
Circulatory disorders
A classic example is carpal tunnel syndrome. This is the bane of those who spend too much time with a computer mouse in their hand. Due to the constant fixed and unnatural position of the wrist, blood circulation in the muscles is impaired. The consequence of this can be pain and muscle weakness, as well as cramps.
A couple more common special cases:
- Uncomfortable shoes . Shoes with unusually high heels, uncomfortable lasts, flip-flops that you have to keep on your feet by tucking your toes. The muscles get so used to the unnatural tension that then, when you are finally freed from the “Spanish boot”, they cannot relax, they go into spasm.
- Uncomfortable position while sleeping . Stiff arms, legs, neck - all this is also a sign of poor circulation and can trigger cramps at night.
Overheating and/or dehydration
It doesn’t matter what exactly caused the overheating: summer heat, intense physical activity, or, say, high temperature due to infections. The main thing is that along with the sweat released, the body loses not only moisture, but also electrolytes necessary for the correct transmission of nerve impulses. The muscles react to this, including cramps.
Mineral depletion
Not having enough potassium, calcium, or magnesium can make it difficult for your muscles to relax. And this leads to seizures.
Nervous strain or neurological disorders
In such conditions, it is often difficult for the muscles to relax. You already know the consequences.
Pregnancy
Leg cramps are familiar to many expectant mothers. The reasons for this are still not entirely clear to doctors.
Certain diseases and certain medications
Muscle spasms often accompany ailments such as diabetes, kidney problems, and thyroid disorders. They can also be a side effect of taking certain medications. For example, furosemide and other diuretics, as well as drugs for the treatment of angina, osteoporosis, Alzheimer's disease and others.
What to do if you have seizures
Fortunately, getting rid of cramps is quite easy in most cases. Here are some common first aid measures.
Stretch the affected muscle, give a light massage
This will help the cramped muscle relax. For example, very common leg cramps can be relieved like this: sit down, straighten your legs and pull the toe of the affected limb towards you.
Use cold or hot compresses
Apply a towel or sheet with a heating element soaked in warm water to the muscle. You can take a warm bath or do a hydromassage by directing streams of water from the shower to the spasming muscle.
Cold will be no less effective. Wrap a bag of ice or frozen vegetables in a towel and lightly massage the muscle.
Take a painkiller
For example, ibuprofen. It will also help relax the cramped muscle.
When are seizures dangerous?
Muscle spasm can be a symptom of a serious malfunction in the functioning of one or another internal organ or the body as a whole. For example, liver cirrhosis, type I diabetes mellitus, and developing neurological disorders, in particular epilepsy, often make themselves felt by seizures.
There is another danger. A spasm can affect not only large muscles, but also smooth muscles that make up the membranes of internal organs. Spasms of such muscles are sometimes fatal. For example, spasm of the bronchi can lead to respiratory arrest, and spasm of the coronary arteries can lead to a deterioration in the functioning of the heart, or even cardiac arrest.
Experts at the Mayo Clinic Research Center recommend seeking medical help as soon as possible if seizures:
- They happen often—several times a day or several days in a row. This is a reason to be wary and consult a specialist.
- Cause serious, almost unbearable discomfort.
- Accompanied by swelling, redness or any other changes in the color and structure of the skin.
- Combined with high fever and headache.
- Causes severe muscle weakness.
If you do not observe any of the listed symptoms, you can exhale: most likely, the spasms will not threaten you with anything dangerous. Nevertheless, it is still worth understanding their origin. At least in order to save yourself from such painful sensations in the future.
How to treat seizures
If cramps cause you discomfort (wake you up at night or last for quite a long time, despite massage and compresses), go to a therapist. To identify problems with your body, your doctor will ask you several questions. For example:
- How often do you have cramps?
- What muscles do they affect?
- Are you taking any medications?
- How often do you drink alcohol?
- What is your lifestyle and physical activity like?
- How much fluid do you drink daily?
Blood and urine tests may be required for a more complete diagnosis. With their help, the doctor will find out the level of microelements and will also be able to check the condition of the kidneys and thyroid gland. In some cases, electromyography is prescribed. This is a test that measures muscle activity and diagnoses existing muscle disorders.
As a result, the doctor will determine the disease, the symptom of which is seizures, and prescribe specific treatment.
How to prevent seizures
Considering the most common causes of muscle spasms, prevention is obvious:
- Drink more water to stay hydrated.
- Don't abuse alcohol. Among other things, it is a powerful diuretic and provokes fluid loss.
- Warm up regularly to prevent circulatory problems.
- Wear comfortable shoes.
- Try to avoid stress and nervous tension. You should have proper rest and sleep.
- Make sure your diet is complete and includes foods rich in potassium, magnesium and calcium: fermented milk, cereals, leafy greens, nuts, and so on.
- If necessary, take mineral complexes and dietary supplements. Naturally, do this after consulting a therapist.
Source: https://Lifehacker.ru/sudorogi-prichiny-lechenie/
What are the causes of seizures during loss of consciousness?
Fainting is a sudden loss of consciousness. Often expressed as a reaction to a temporary cessation of blood transport to the brain. Sometimes people experience loss of consciousness with seizures. The causes of this disorder are described below. They are caused by excessive activation of the nervous system and the formed elements of the cortex. The consequence of this will be unconscious contractions of groups of muscle tissues.
What causes fainting?
The most common reasons are shown here. Fainting may have one or more associated precipitating factors.
The list indicates the possible origins of this condition: high pressure in the head, tumors in the brain, neck muscles constantly tense, trauma or concussions, changes in the position of the vertebrae in the neck, infections, prolonged tension of the central nervous system.
In older people:
In children and adolescents:
In ordinary patients:
Necessary actions in case of fainting
There is not always a medical center or doctor nearby when your health condition worsens. Only people around can help a sick person in such a situation.
Let's consider the algorithm of actions that must be executed:
- Eliminate the cause.
- Fainting can be caused by stuffiness, rapid changes in body position, injury, or fear.
- Place the sick person in a prone position. We lower our head below the level of our feet.
- Turn over on its side.
At this time, the patient may be subject to external damage; his body must be protected from such effects. It is necessary to create irritable conditions for the patient that do not imply injury, but help him recover from a fainting state. To do this, you can use whatever is at hand.
- This could be splashing with cool water, lightly wiping the head, or slapping the cheeks. Be sure to give the victim access to oxygen. It is advisable to remove clothes from the neck (scarf, headbands), unbutton the jacket, shirt.
- If you have ammonia, you can moisten a rag with it and bring it to your nose. Sometimes all it takes is opening the bottle.
- Manifestations of loss of consciousness.
Despite the fact that this condition is sudden, people still experience sensations preceding fainting:
- Dizziness, spontaneous pain in the head.
- The appearance of "floaters" before the eyes.
- There is a noise in my ears.
- Uncontrollable yawning.
- Pallor.
- Trembling, “cold” sweat.
- Vomiting.
- Muscle trembling.
Children should be treated with extreme caution. If there is a temperature of 38-39 degrees, children may experience muscle cramps. In such cases, call an ambulance immediately!
The general picture of fainting with spasms is reminiscent of epilepsy. Alcohol abusers feel similarly after a binge. This is caused by excessive intoxication of nerve tissue and a critical decrease in potassium. Involuntary contractions occur when the victim is unconscious.
Sequence of occurrence of seizures:
- There are three types of cramps.
- During loss of consciousness.
- To the point of fainting.
- After waking up.
Often when you faint, the spasms stop. Convulsions in the second option act as a precursor to fainting. It happens that the victim lies unconscious for a long time. Due to a lack of oxygen, the brain itself causes convulsions during hypoxia through a signal.
Consequences
After the incident, it is necessary to figure out what caused the fainting. Find out whether this has happened before and whether this condition occurs regularly. With a single attack, it can be assumed that the condition was caused by external conditions.
But if this is not an isolated incident, a doctor’s consultation is necessary. After undergoing a full examination, the cause will be determined. If found, treatment will be provided. Don't put off questions about your health until later.
If you do not pay attention to fainting, to the main cause, new complications of the underlying disease may appear. First of all, brain activity suffers.
Lack of oxygen is harmful to brain cells. The person becomes very irritable. Household abilities suffer. There may also be complications in the form of impaired coordination of movements, deterioration of hearing and speech.
Mental illnesses are also common in this context.
Who should I contact? You need to start by visiting: a therapist, a neurologist, a specialist in manual therapy.
Fainting accompanied by convulsions
When a person loses consciousness, the brain does not have enough oxygen. When convulsions appear, the victim’s condition cannot be called normal; the situation becomes much more serious. Brain cells become irritated, causing seizures. This is dangerous because the muscles may contract incorrectly.
Symptoms
There are a number of symptoms for this disease:
- I feel dizzy and have a severe headache.
- Vision deteriorates, dark spots appear before the eyes.
- The person begins to yawn frequently.
- There is noise in the ears, different sounds can be heard.
- Pale skin.
- Nausea begins and vomiting appears.
- Contraction and relaxation of muscles.
- Cold sweat appears.
- The heartbeat is disturbed.
In children, the body tenses, the gaze becomes glassy, after which the muscles begin to contract involuntarily . In alcoholics, mainly after heavy drinking, seizures are similar to epilepsy. This is due to the fact that there is a lack of potassium in the blood and alcohol poisoning of the brain occurs. Convulsions appear when the victim is unconscious and last for a very long time.
Convulsions begin during an attack and end when the person has passed out. There is another option: the victim has passed out and does not return to normal for a long time. The nervous system, suffering from a lack of oxygen, sends an impulse to the muscles, causing cramps to begin.
Rules for providing first aid during an attack
In this case, you need to proceed as follows:
- Place the person so that his legs are higher than his head. This is necessary to restore blood circulation in the brain.
- It is necessary for the person to lie on his side, the tongue should not sink in, and vomit should not enter the respiratory tract.
- You have to keep your head up because he can hurt himself due to his uncontrolled behavior.
- Open the window, unbutton his clothes so that air can flow to the patient.
Spray with cold water or wipe your face with something damp, a napkin, handkerchief, towel, pat on the cheeks, if anyone present has ammonia, give the victim a sniff.
Causes of fainting with convulsions, signs of convulsive loss of consciousness in epilepsy
Convulsive fainting is one of the most common pathological conditions. As a rule, it occurs due to a sharp decrease in blood supply to the brain. The approximate duration of loss of consciousness varies from 5-10 seconds to a quarter of an hour. At the same time, a person’s prolonged stay in this state can be life-threatening.
Convulsive syncope in children
A person can lose consciousness at any age. Convulsive fainting occurs in children from 7 months. The predisposition to the occurrence of such a condition in childhood depends directly on the degree of development of the nervous system. However, this is not the only factor that can lead to this form of loss of consciousness; they also highlight:
- a sharp increase temperature ;
- traumatic brain and birth injuries.
At the age of 7 months to 2 years, a similar phenomenon can occur as a reaction of the body to fear, acute pain or strong negative emotions. Since it is at this age that the nervous system is formed and is characterized by increased excitability.
Frequently, convulsive fainting occurs in adolescence due to rapid body growth, problems with blood vessels occur, as a consequence of the development of vegetative-vascular dystonia and frequent loss of consciousness.
This type of fainting is very common in childhood, which is why it is so important to strengthen the immune and nervous system of the child’s body.
Pregnancy and loss of consciousness with seizures
During pregnancy, women often experience dizziness and various types of ailments. However, if convulsive fainting occurs in this case, this is evidence of the occurrence of serious complications.
In some cases, such loss of consciousness ends in a state close to comatose. In addition, the risk of premature birth increases sharply, creating a danger to the health and life of the child.
In case of convulsive loss of consciousness, a woman needs to consult a specialist, since frequent repetitions of this condition can lead to death.
Features
In some cases, convulsive syncope is confused with an epileptic seizure. However, both conditions have their own characteristic features:
- Before losing consciousness, a person feels dizziness and weakness throughout the body, and tinnitus. A minor epileptic seizure begins abruptly and asymptomatically.
- When fainting, the convulsions are clonic in nature, in which the muscles relax, contract variably and extremely quickly. In the case of epilepsy, they are tonic-clonic in nature. The muscles become stiff for a period of 3 to 10 minutes, after which clonic contractions occur.
- An epileptic seizure may not stop for 30 minutes . With convulsive fainting, consciousness returns to the person after a few seconds, less often after a few minutes.
- Loss of consciousness extremely rarely occurs in a supine position; epilepsy often begins even when a person is sleeping.
According to theory, it is almost impossible to confuse convulsive fainting and an epileptic attack, but in practice it is extremely difficult to distinguish between these conditions.
Convulsive fainting is a common pathological condition, which in most cases is associated with disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system, insufficient blood circulation to the brain and prolonged stressful situations. To avoid such situations, it is important to monitor your body and consult a doctor in a timely manner.
Source: https://nevralgia.ru/obmoroki/s-sudorogami-prichiny/
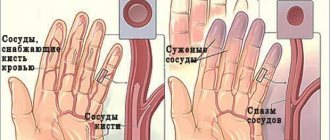
Relieve spasm of cerebral vessels
Only a specialist can prescribe a complete comprehensive treatment for this problem. However, vascular spasm can be temporarily relieved using traditional medicine or medications. There are several ways to eliminate vasospasm:
- With the help of anise, valerian, yarrow and motherwort. In this capacity, you can also use a tincture of any of these herbs.
- With frequent spasms, decoctions of nettle, rose hips, St. John's wort and hawthorn will help reduce the likelihood of their recurrence.
- The incipient spasm can be relieved by immersing your feet in cold water for 3-4 minutes, and then rubbing them thoroughly.
- An infusion of common agrimony or lesser periwinkle helps relieve cerebral vascular spasm.
- Simply washing with cold water has the same effect.
- When experiencing severe headaches, it is advisable to lie down with a pillow under your head.
- It is useful for spasms to massage the area of the back of the head and temples with light movements.
- Severe pain can be relieved with a tablet of aspirin, ibuprofen, analgin, spasgan, nurofen or other similar drugs.
- If the pain is prolonged and does not go away with the above remedies, then you should seek medical help.
How to relieve spasm of cerebral vessels
Drugs
Several groups of medications are used to relieve cerebral vascular spasm:
- Agents that promote vasodilation. These include aminophylline, lipofor, mefacor, atromidine, atomax.
- Antispasmodics. Drugs in this group are considered the most effective for vascular spasms. These are spasmolgon, papaverine, cinnarizine, bendazone and others.
- Drugs that improve blood flow to the brain. This group includes piracetam, nootropil, calcium antagonists, which include diltiazem, cordafen, finoptin, isoptin, diltiazem and others.
- Blood thinners. A typical representative of such drugs is trental.
- Drugs that improve brain metabolic processes. These are sermion, piracetam and others.
Only a doctor can determine which drug will be most optimal in a particular situation, taking into account all the existing symptoms and the patient’s condition. For mild spasms, there is no need to resort to medications to relieve vasospasm; good rest and folk remedies are sufficient.
Folk remedies
Many recipes offered by traditional medicine help cope with vasospasm no worse than medications. Of the folk remedies for vasospasm, the following are the most effective:
- infusion of St. John's wort, birch leaves, nettle, rose hips. The selected medicinal plant is brewed in boiling water, based on the proportion of a large spoon per 200 ml of water, and then infused for 2-3 hours;
- Regular lemons and garlic will help restore the elasticity of the walls of blood vessels. To prepare the product, you need to grate 4-5 lemons and the same number of garlic heads. After this, pour half a liter of honey into the resulting mixture. The product should be infused for 5-7 days, after which it can be taken one spoon per day;
- There is another recipe based on garlic. To do this, the head of this plant is ground to a pulp and mixed with a glass of vegetable oil. After a day of infusion, add a spoonful of lemon juice. The course of treatment with this remedy is 3 months, during which you should take a spoonful of the medicine every morning;
- three large spoons of thyme are poured into a liter of cold water and brought to a boil, then the product is left to infuse for an hour. A spoonful of juice squeezed from the golden mustache is added to this infusion. Drink 100 ml of the product every day for two weeks.
Convulsive syndrome without loss of consciousness
With a sharp outflow of blood from the brain, a short-term loss of consciousness is possible. In this case, fainting with convulsions can last from a few seconds to 10-12 minutes, and the longer it is, the more dangerous and serious its consequences.
At this time, patients are unable to adequately assess the surrounding situation and take any action, so it is extremely important that there are close people nearby who can provide first aid in case of a convulsive attack.
Causes of convulsive fainting
As a rule, for the development of such a condition, there are predisposing factors that have a direct impact on the human body.
The most common factors that may be accompanied by seizures are:
- physical and mental trauma;
- pain attack, fear, prolonged stay in a stuffy room;
- sudden change in body position (from horizontal to vertical);
- drop or increase in blood pressure;
- heart attack, arrhythmia;
- in some cases, an attack occurs due to a malfunction of internal organs (cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, central nervous system disorder, vascular problems, etc.).
Quite often, loss of consciousness, accompanied by convulsive syndrome, occurs as a result of tumor-like neoplasms in the brain and epilepsy.
The etiology of a neuroepileptic attack is not fully understood, but, as a rule, this condition is accompanied by stroke, anoxia (hypoxia) of the meninges, which leads to loss of consciousness.
Types of fainting and their consequences
Spontaneous loss of consciousness can be short-term and persistent. As is correct, short-term fainting does not pose a threat to life and lasts no more than a few minutes.
Short-term fainting can occur with the following diseases:
- state of hypoglycemia (sharp decrease in blood glucose);
- epilepsy;
- ONMK;
- a sharp change in blood pressure;
- minor brain injuries (concussions, bruises).
Persistent loss of consciousness is accompanied by more dangerous consequences, and even if timely assistance is provided, a threat to the patient’s life remains. The development of persistent fainting is possible as a result of the following factors:
- extensive strokes and cerebral hemorrhages;
- cardiac arrest and arrhythmia;
- subarachnoid hemorrhages resulting from aortic ruptures;
- various states of shock;
- severe TBI;
- acute poisoning of the body;
- heavy bleeding due to damage to internal organs.
In addition, the pathological condition may be the result of asphyxia with prolonged oxygen starvation.
Factors influencing the development of the disease
Loss of consciousness depends on the cause of its occurrence:
Hyperthermia
Quite often, the cause of seizures, which are accompanied by loss of consciousness, is high body temperature. Most often, hyperthermia with convulsions occurs in childhood.
For adult patients, the temperature limit is 40 degrees. In children, convulsions can occur at a temperature of 38-39 degrees. In this case, the symptoms of the pathological condition appear suddenly.
The child tenses, his head is thrown back, and his gaze is fixed at one point, then a convulsive attack occurs.
Pregnancy
Loss of consciousness, accompanied by convulsions in pregnant women, is considered one of the most dangerous complications, the result of which can be premature birth, disturbances in intrauterine development of the fetus, etc. This condition reminds us of coma and with frequent fainting, there is a possibility of death for the woman.
Alcohol intoxication
This condition does not appear very often, but is considered a rather serious problem in medicine. This situation is accompanied by sudden pallor of the patient, he loses consciousness with the onset of a convulsive attack. Loss of consciousness can be sudden, and after the attacks the patient can sleep soundly for 6-7 hours.
Quite often, alcohol intoxication takes on a chronic form, recurring regularly. Uncontrolled consumption of alcohol can provoke the development of irreversible processes in the brain, which cause fainting, accompanied by convulsions, even in the absence of alcohol intake.
Development of convulsive syndrome in children
Sudden fainting in children, accompanied by convulsions, requires mandatory medical intervention, since the consequences of such symptoms can be unpredictable.
Often the cause of this condition is traumatic brain injury. Brief loss of consciousness is complicated by sudden bleeding from the ears and mouth.
In this case, emergency hospitalization of the child is necessary to clarify the diagnosis and further treatment.
In children under 2 years of age, convulsive fainting is possible with increased excitability of the nervous system.
In this case, an external stimulus can be a loud cry, which is accompanied by cessation of breathing during inspiration, cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle and hypoxia, which ultimately leads to loss of consciousness.
However, it is important to consider that in some cases the opposite effect is possible when fainting is preceded by a seizure, which is most often provoked by hyperthermia. In addition, children have a hereditary predisposition to developing seizures, which can occur with normal fainting.
Differences between epilepsy and convulsive syncope
When diagnosing, it is necessary to differentiate epilepsy from convulsive syncope, since both of these conditions are accompanied by changes in blood pressure and pupil dilation. As a rule, after loss of consciousness has occurred, the patient cannot remember what preceded such a state.
However, there are differences between an epileptic seizure and a convulsive seizure:
- loss of consciousness may be accompanied by warning signs such as dizziness, ringing in the ears, headache and weakness. However, this condition never occurs during sleep, unlike epilepsy, the attack of which occurs completely unexpectedly. It can occur during movement, even at night when a person is sleeping;
- if the patient loses consciousness as a result of psychological and physical influences, he is able to subsequently talk about them, in contrast to an epileptic attack, the cause of which patients cannot explain. An epileptic attack is always accompanied by involuntary urination, in contrast to ordinary fainting;
- convulsive manifestations vary in form: with the development of fainting, convulsions can be clonic. Muscle contraction and relaxation occurs very quickly. Epileptic fainting is characterized by the development of generalized tonic-clonic forms, in which the muscle group is constrained by a spasm for 3-5 minutes, followed by a transition to the clonic phase.
Most often, fainting is short-lived. In this case, the patient’s consciousness returns within a few seconds, but retardation remains.
First aid
In the case when the patient's unconscious state is accompanied by a seizure, it is recommended to immediately begin providing first aid:
- First of all, you should call a medical team;
- if there is a clear cause of loss of consciousness, measures should be taken to eliminate it;
- The patient should be placed on a horizontal surface with his legs elevated using a pillow or bolster. This position will ensure blood flow to the head and normalize the general condition of the patient;
- to prevent the tongue from sinking and biting, it is necessary to wrap a wooden spoon or any available item in a napkin or thick cloth and place it between the victim’s teeth;
- It is important to ensure that vomiting does not occur, which can lead to asphyxia. To prevent this, you need to put the patient on his side, holding his head.
Source: https://gribkovnet.ru/varikoz/sudorozhnyj-sindrom-bez-poteri-soznanija.html
Prevention of cerebral vascular spasms
Proper nutrition plays an important role in the prevention of cerebral vascular spasms. The diet of a person prone to this pathology should include more fresh fruits and raw vegetables. It is advisable to have breakfast with whole grain cereals with the addition of nuts and dried fruits. You should regularly consume a variety of seafood, legumes and lean meats. Be sure to monitor the fat content of dairy and other products.
Other preventive measures include:
- Quitting drinking alcohol and smoking.
- Controlling stressful situations and the ability to relax.
- Avoiding overstrain and overwork.
- Regular exercise.
- Timely detection and treatment of diseases of the nervous and cardiovascular systems.
- Drinking enough liquid per day.