Types of laryngitis in children
The mucous membrane of the nasopharynx in a child is poorly developed; viruses and microbes quickly find a nutrient medium for reproduction. Laryngitis begins in children with a cough and runny nose, gradually the voice becomes muffled and later hoarseness appears. Causes of laryngitis in children:
- colds (ARVI, flu);
- allergy;
- contaminated air;
- injuries.
It will take at least 1 week from the moment the first symptoms appear until cure.
Laryngitis occurs in two forms: acute and chronic:
- Acute laryngitis occurs more often in children, it is characterized by clear manifestations of clinical signs, and lasts from 5 to 14 days.
- The chronic form of laryngitis can develop over years, worsening at the slightest provoking factor: hypothermia, stress, vocal strain. Which symptoms will prevail depends on the form of chronic laryngitis.
According to the type of progression, at least 7 types of laryngitis are distinguished:
- catarrhal;
- stenosing;
- hypertrophic;
- atrophic;
- hemorrhagic;
- diphtheria;
- phlegmonous.
The catarrhal form of laryngitis occurs statistically most often, however, in adults. In this form, all symptoms are mild; a dry cough predominates due to a constant tickling sensation in the throat. The change in voice is not observed all the time, but after stress on the vocal cords, mainly in the evening.
The catarrhal form of laryngitis can develop into hypertrophic or phlegmonous:
- The first is one of the most dangerous forms of laryngitis, which is a precancerous condition. The patient constantly feels the presence of a foreign body in the throat, pain when the vocal cords are tense, cough, and swelling of the mucous membrane.
- The phlegmonous form of laryngitis has a pronounced clinical picture, as well as purulent discharge from the larynx.
Difficulty breathing is the most dangerous consequence of inflammation of the larynx. This outcome is possible with the stenotic form, when swelling forms in the larynx, as well as with the diphtheria form, which is extremely rare due to vaccination.
Atrophic laryngitis is a thinning of the laryngeal mucosa against the background of long-term chronic laryngitis. The mucous membrane takes on a gray-burgundy tint and may have a yellow coating and erosion. The patient constantly experiences dry throat, sore throat, and, accordingly, cough.
Hemorrhagic laryngitis is most often a consequence of toxic flu. With it, the patient suffers from a dry cough (especially in the morning), and after it becomes wet, traces of blood can be seen in the secreted mucus.
Main reasons for the phenomenon
Voice loss can occur for several reasons:
- laryngitis;
- cold;
- vocal cord tension;
- severe emotional stress;
- smoking.
Loss of voice is a common occurrence with colds and more. There are many reasons, and sometimes one can complement the other, which aggravates the patient’s situation. The most common causes include laryngitis. It manifests itself in the form of severe inflammation of the larynx, which occurs from excessive hypothermia, ingestion of toxic substances into the throat, consumption of cold or too hot, and in case of acute respiratory viral infection.
If you consult a doctor in a timely manner, laryngitis will not pose a danger, and the lost voice will quickly be restored. If the disease is neglected, the patient risks ending up on the operating table, since in the event of complications, tumors begin to appear on the vocal cords. Without surgical intervention, complete loss of voice is possible.
Smoking is another scourge that hurts human health. Hot acrid smoke burns the larynx, corroding the mucous membrane and allowing harmful bacteria to freely enter the body through the throat. Smoking is dangerous if you already have respiratory diseases, it negatively affects the voice, and with laryngitis it completely worsens the situation of the smoker.
Loss of voice is possible due to nervous strain. If a person has to remain in a state of increased nervousness for a long time, over time the hoarse voice may acquire lower tones. With severe fright, a person is at risk of losing his voice altogether.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of laryngitis begins with a history and examination of the patient. The pediatrician listens to the child’s lungs using a phonendoscope, examines the condition of the laryngeal mucosa, and palpates the lymph nodes.
In order to find out which pathogen provoked acute laryngitis in children, the doctor takes a swab from the throat to determine the culture and determine the sensitivity of the identified pathogenic microorganism to different groups of antibiotics.
The patient’s blood is also taken for a general (clinical) analysis, the leukocyte formula of which makes it possible to understand the viral or bacterial etiology of laryngitis in a particular case.
It is extremely difficult to determine laryngeal neurosis. To make an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo a thorough examination. It includes:
- Blood analysis. General and biochemistry tests are prescribed and hormonal status is examined.
- Ultrasound. An ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland, cervical spine, blood vessels of the brain and neck is performed. In the latter case, Doppler ultrasound is used.
- Radiography. The study concentrates on the respiratory tract, larynx, and cranium.
- MRI of the larynx.
To establish an accurate diagnosis, consultations with an otolaryngologist, endocrinologist, and neurologist are carried out. A visit to a psychiatrist is recommended.
Dysphagia
Dysphagia is difficulty swallowing solid and liquid foods.
This condition can develop both as a result of diseases of the esophagus, larynx, pharynx and surrounding organs, and due to diseases of a neurological nature, because it is the nervous system that regulates the entire process of eating.
Several related specialists are involved in the diagnosis and treatment of this syndrome: ENT, neurologist, gastroenterologist and oncologist. The prognosis depends on the cause that caused its development.
What it is
The act of swallowing is a rather complex process:
- First, a person chews food, bringing it to a crushed state, while each particle is moistened with saliva, creating better conditions for further swallowing. Then the tongue and cheeks push the food bolus so that it lands on the root of the tongue.
- After it hits the root of the tongue, a reflex is activated, as a result of which the food enters the pharynx. The soft palate immediately rises, which seals the pharyngeal cavity from the nasal cavity (it will fall as soon as the food reaches a certain level), the muscles that lift the larynx contract (so that food does not fall into it and further into the trachea).
- The esophagus opens only when a certain pressure is created in the throat. Food is pushed through the esophagus by its circular muscles towards the stomach. This act is facilitated by a “wave” of reduced tone of the esophagus, which, ahead of the food bolus, creates an area of low pressure.
Only by the process of chewing and moving to the root of the tongue can a person consciously; the remaining phases are produced by the joint work of the nervous system and pharyngoesophageal structures.
With dysphagia, it is these involuntary stages that are disrupted, which manifests itself:
- returning food from the pharynx to the mouth;
- pain in the esophagus (in the center of the sternum);
- a feeling of “stuck”, “coma” of food in the throat or esophagus.
Classification
According to the localization of the pathological process, dysphagia can be:
- Oropharyngeal (oropharyngeal), when it is difficult for food to pass from the pharynx to the esophagus. The causes of this form are pathologies of the muscles of the pharynx, peripharyngeal structures or nervous system.
- Esophageal (esophageal), which develops as a result of either blocking the lumen of the esophagus, or disruption of the movements of its muscles. Conventionally, esophageal dysphagia will be divided into lower, middle and upper.
- Cricopharyngeal incoordination is an uncoordinated contraction of the circular fibers of the upper esophageal sphincter.
- Dysphagia that occurs as a result of compression of the esophagus by large vessels passing nearby (the aorta and its branches), which is possible with pathology of these vessels.
Degrees
There are 4 degrees of problems with swallowing food:
- It is impossible to swallow only certain types of solid foods.
- It is not possible to swallow solid food; soft and semi-liquid are swallowed without complications.
- Only liquid food can be swallowed.
- The act of swallowing becomes completely impossible.
Diseases of the esophagus accompanied by dysphagia
- spasm of the esophageal mouth;
- esophageal diverticula;
- foreign body;
- inflammation of the organ mucosa;
- reflux esophagitis;
- cancer;
- benign tumor of the esophagus;
- hernia of the opening of the diaphragm through which the esophagus passes;
- spasm of the lower esophageal sphincter;
- benign stricture;
- Plummer's syndrome;
- chemical burn of the esophagus;
- congenital narrowing of the muscle ring where the pharynx passes into the esophagus (Schatzky rings);
- scleroderma;
- acquired or congenital dissection of esophageal tissue.
What other diseases can cause dysphagia?
- Benign tumor or cancer of the pharynx. In this case, in addition to problems with swallowing, there will be discomfort in the throat, a sensation of a “lump”, swallowing will be painful, and such pain will radiate to the ear.
- The pharyngeal “pocket” is a pathology most often of a congenital nature, when the mucous membrane protrudes, forming a pocket.
In this case, there will be dysphagia and bad breath, and a protruding pouch will be visible on the neck. - Stroke. In this case, other symptoms also occur: paralysis of the limbs, facial asymmetry, impaired understanding or reproduction of speech, confusion.
- Encephalitis.
Dysphagia occurs against the background of usually impaired consciousness (inadequacy and agitation or stupor), elevated body temperature, and other symptoms of brain damage: breathing problems, decreased blood pressure. - Botulism.
In addition to difficulty swallowing, there is double vision, the inability to read text, and wide pupils that do not respond to light. Usually, with the onset of dysphagia, breathing problems also appear. Blood pressure and temperature do not change during botulism. - Myasthenia gravis will also manifest itself as weakness of the facial muscles, difficulty chewing, and weakness of the muscles of the limbs.
- Parkinson's disease. In this case, movement disorders, tremors, and mental disorders come to the fore.
- In addition to dysphagia, multiple sclerosis can manifest itself with various symptoms: paresthesia, blurred vision, speech impairment, limb weakness, and cognitive impairment.
- Guillain-Barré syndrome usually begins with a fever, then pain in the extremities. Then the range of movements in the limbs decreases up to paralysis; such paralysis rises from the legs upward - to the muscles of the abdomen and chest.
Features in children
The main causes of dysphagia in children occur with diseases of the nervous system, for example, with cerebral palsy (the risk of developing this symptom is especially increased in a child with paralysis of all four limbs).
The risk is also high in children suffering from athetosis (constant involuntary movements), which is often congenital. Dysphagia also develops with muscle diseases, spina bifida, and Arnold-Chiari malformation. The symptom can also develop with congenital malformations of the pharynx and esophagus, Rossolimo-Bekhterev syndrome.
You should suspect a problem in a child with the following symptoms:
- small amount of food eaten by the baby;
- prolonged sucking of formula or breast;
- cough or facial flushing after eating/drinking;
- placing the head and neck in an unusual position when feeding;
- cough and shortness of breath will not always be pronounced if a small volume enters the trachea during feeding;
- milk or formula appears in the nose.
If a child often suffers from pneumonia or bronchitis, has a red face after eating, or has developed asthma (but his relatives do not suffer from this disease), this may also be a sign of problems with the innervation of the esophagus.
A lump in the throat can be caused by cervical osteochondrosis. Find out all the details about this disease.
Read about vegetative-vascular dystonia here.
Nervous dysphagia
It is also called functional. It is caused by various kinds of neuroses - inorganic diseases of the nervous system. The pathology develops in children, adolescents, and adults of both sexes up to 40 years of age; after this age, the disease is practically not registered in men.
In children, neurosis can “linger” from an early age. Initially, it manifests itself in the fact that the child has a decreased appetite, regurgitation, vomiting, and poor sleep.
At school age, such children are characterized by increased pain, thinness, intolerance to transport, and poor appetite. In adults, such dysphagia develops for the first time against the background of a traumatic situation and is characterized by choking followed by difficulty in breathing, which is accompanied by a panic attack.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis can be made by swallowing liquids or solids. Next, based on research, the problem that led to the development of dysphagia is diagnosed:
- X-ray of the esophagus with contrast (barium);
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland;
- FGDS;
- examination by an ENT doctor;
- MRI of the brain.
Treatment
Therapy depends on the cause of the symptom. Thus, for reflux esophagitis, conservative treatment with Domperidone and Omeprazole is used, functional dysphagia is treated together with a psychotherapist.
In the presence of tumors, strictures, chalasia, achalasia or diverticula of the esophagus, surgical intervention is performed.
For inflammatory diseases of the pharynx, treatment consists of anti-inflammatory and antibacterial therapy.
Below is a video - the program “Live Healthy” about the causes and solution to the problem of a lump in the throat:
Source: https://www.neuroplus.ru/bolezni/simptomy-i-sindromy/disfagiya.html
How to treat laryngitis?
Laryngitis is an inflammation of the larynx that can spread throughout the throat or be localized to certain areas. Laryngitis is the main cause, if the throat is sore and hoarse, the voice has become dry. This disease can develop independently or against the background of other respiratory ailments.
How to restore a shrunken voice due to laryngitis? The patient needs to visit an ENT doctor, as only he can prescribe treatment. The patient will have to comply with the following measures:
- urgently quit smoking, at least for the duration of treatment and the rehabilitation period, which lasts about 10 days;
- avoid places where smokers may be, since passive smoking is no less dangerous for the patient;
- Avoid staying outside in wet, frosty or windy weather;
- the patient's room should be maintained at an optimal temperature with a humidity of 55%;
- carry out inhalations, make warming compresses;
- Heat compresses of the chest (mustard plasters can be used for this), compresses of the calf muscles, and hot foot baths are important.
If voice loss is detected, immediate treatment is necessary. The patient needs to take medicine; it can be purchased at the pharmacy before visiting the doctor. Anti-inflammatory drugs such as Ingalipt or Camphomen, antipyretics (Tera-flu or Coldrex) are suitable. You can buy lollipops that will help relieve pain, for example, Strepsils or Neo-angin.
How is laryngeal neurosis treated?
Treatment of pharyngeal neurosis is impossible without mastering techniques for relieving the symptom when it occurs, or at least reducing the degree of its manifestation.
- The most important thing when an attack occurs is not to panic. Panic is activated by the sympathetic part of the nervous system, which, in turn, tenses all the muscles of the body in order to attack or run away from danger. But since attacking the source of stress, as well as escaping from it, is difficult for many civil reasons, tension becomes auto-aggressive: that is, muscle tension begins to cause discomfort to one’s own body. Therefore, in order to ensure that the stress of an attack against the background of the current situation does not lead to greater spasms of the muscles of the larynx, it is important not to panic.
- The second stage of treatment for pharyngeal neurosis at home is to perform any relaxation technique:
- Breathing technique – conscious deep measured breathing, in which the exhalation time should be three times longer than the inhalation.
- Relaxation technique - gradual, “step-by-step” relaxation of all the muscles of the body, starting with the limbs; if performed correctly, at the end of the “procedure” the body should become weightless, and drowsiness may appear.
- Contemplative technique is a transfer of attention from internal sensations to the external world: you need to listen to all the sounds coming, from the point of view of an artist or photographer, examine the surrounding objects, touch the surfaces of things and try to formulate a tactile sensation. You can also connect taste buds to the technology, but this point is dangerous because you may develop the habit of “eating” stress.
- Physical exercise technique – when muscle spasms occur, a good way to relieve tension is light physical activity, such as walking. It should take place in a comfortable rhythm, and you can combine breathing and contemplative techniques with it.
You need to be able to relax so that there are no psychological problems
Therapy for laryngeal neurosis always involves complex treatment, including corrective actions by a psychotherapist, drug treatment and physiotherapy. A good effect is observed when using traditional medicine recipes.
The main task of the doctor is to find out the mental problems of neurotics, what exactly causes him stress and makes him nervous. In the future, the identified problems are solved step by step through training in the following skills:
- relaxation, avoidance of panic attacks;
- focusing attention, avoiding negativity and negative emotions;
- keeping your nerves under control, tuning into the right wave during stressful situations.
The expression “lump in the throat” is often figurative, meaning that some things, for moral or ethical reasons, do not want to be said out loud.
Sometimes this expression is used as a metaphor, meaning strong excitement, for example, before giving a speech, and this is closer to the concept of a lump in the throat during neurosis.
What is false croup
The need to provide prompt medical assistance to a child is due to the danger of a phenomenon called false croup. This is stenosis of the larynx, that is, a narrowing of its lumen, in which thick sputum secreted in large quantities obstructs the narrowed lumen, as a result of which air cannot freely enter the body.
If medical care is not provided on time, oxygen starvation (hypoxia) will develop, with a corresponding disruption of the nervous and cardiovascular systems of the body. In the terminal stage, false croup can cause death.
False croup can be recognized by three main signs:
- barking cough;
- hoarseness of voice;
- noisy breathing.
Treatment is a complex of measures consisting of the use of hormonal (glucocorticosteroids), anti-inflammatory and sedative drugs. It is useful to adjust the diet, provide air flow and give the patient more alkaline drinks.
An attack of laryngitis is a patient’s condition in which his breathing becomes difficult. Even if this symptom is mild, you should immediately call an ambulance. While waiting for the doctors to arrive, you should:
- give the child the necessary medications to alleviate his condition (antipyretics, painkillers, antispasmodics, antihistamines);
- increase air humidity using a special device or several containers of water placed around the room;
- give an alkaline drink (mineral water and a solution of 1 teaspoon of soda in a liter of water) a tablespoon every 10 minutes;
- calm the child to reduce laryngeal spasm.
Nervous disorders
When the vocal cords hurt when speaking, a person often has to raise his voice or experience nervous tension. In this case, dysphonia may develop. It affects people in such professions as teachers, artists, translators, announcers and others for whom the voice is the main working instrument.
Sometimes it happens that the voice still disappears, and sometimes it remains in an altered state for a long time. In this case, elementary stress takes place. There is a lot of stress these days, so some may periodically experience voice changes. If hoarse voice is caused by nervousness, antiviral and anti-cold tablets do not help, for treatment it is wiser to purchase natural-based sedatives, which include valerian, motherwort and other sedative herbs.
Prevention
Prevention of psychosomatic conditions also involves working with a psychologist or psychoanalyst. A specialist will help you feel confident in difficult situations, cope with your emotions without suppressing them, and see more positive aspects in life.
An important point in the prevention of future mental health conditions is to find out the cause of their occurrence. By working through difficult moments from his past with a specialist, the patient will feel relief and find an explanation for his condition.
Psychosomatic illnesses are widespread these days and need to be taken seriously. Fighting them, visiting a psychotherapist or psychologist is normal and will help you resolve your problems.
Traditional methods
Treatment of laryngitis in children is a set of actions aimed at eliminating the causative agent of the inflammatory process, improving well-being by reducing the severity of symptoms, as well as adjusting the functioning of the body’s defenses.
Typically, laryngitis in a child does not require hospital treatment. Exceptions are cases when the patient:
- predisposition to croup;
- complex form of the disease;
- the presence of serious concomitant pathologies.
But even if the patient is not hospitalized, he is prescribed strict bed rest until complete recovery. To speed up the process of voice restoration, you need to completely abandon the load on the vocal cords. If it is problematic to keep your child silent for several days, you should explain to him the need to speak exclusively in a whisper.
Air humidity has a positive effect on the speed of recovery. If possible, a special device should be installed in the patient’s room that will maintain the indoor microclimate at a humidity level of about 70% at a temperature of 18 degrees.
The diet for laryngitis has two goals:
- give the body the energy it needs to fight the disease;
- exclude mechanical damage to the inflamed mucosa.
Therefore, it is very important to completely exclude rough foods (nuts, crackers, seeds), hot dishes and drinks, spices and seasonings from the diet. It is useful to eat porridges and light broths. If you have a severe sore throat, it is recommended to puree food.
If there are no contraindications from the urinary and endocrine systems, you need to drink a large amount of fluid (2-2.5 liters per day):
- water;
- tea with lemon;
- fruit drink;
- compote.
Medicines for laryngitis in children are selected taking into account the symptomatic picture. For fever, the patient is given antipyretic tablets (except aspirin), and for a sore throat, anti-inflammatory lozenges with an anesthetic effect. Antihistamines for laryngitis in children can quickly cope with swelling of the mucous membrane in the throat. Cough is eliminated with expectorant syrups.
| Purpose | Name | Age restrictions |
| Antihistamines | Fenistil | – |
| Zyrtec | from 6 months | |
| Zodak | from 12 months | |
| Expectorants | Ambrobene | from 2 years |
| Lazolvan | – | |
| For sore throat | Strepsils | from 5 years |
| Faringosept | from 3 years | |
| Antipyretics | Nurofen | from 6 years |
| Paracetamol for children | from 3 months |
Antibiotics for illness are rarely prescribed, only when bacteria are detected during examination of a smear from the larynx, or severe intoxication against the background of fever: nausea, vomiting, chills, headache.
Inhalations
Inhalations for laryngitis provide tremendous assistance in getting rid of the unpleasant symptoms of the disease. However, you should not force your child to breathe steam from potatoes: if the mucous membrane of the throat is inflamed, the risk of tissue burns is very high.
To perform the procedure, you need an inhaler or nebulizer device, into which you need to fill a special composition:
- for thinning sputum: Lazolvan, Mukolvan;
- to soften the laryngeal mucosa: saline solution, alkaline mineral water;
- antiseptics: Furacilin, Miramistin.
Any drug is diluted with saline immediately before use. You should not use herbal infusions and essential oils for inhalation in a nebulizer; they are suitable for steam inhalation using a saucepan or kettle. However, such methods must be used with great caution, since plant components can provoke allergies, the risk of which in children is already high due to the immaturity of the immune system.
The advantage of using an inhaler over internal administration is a significant reduction in the number of side effects.
Inhalations can only be done between meals, at least an hour before a meal, or an hour after it.
Folk remedies
The most common method of alternative treatment for laryngitis is rinsing with herbal decoctions. This method is only suitable for older children, since babies do not know how to gargle properly.
To prepare solutions you can use:
- fresh beet juice;
- soda with salt dissolved in water;
- decoction of chamomile, sage, oak bark.
It is important to understand that such measures are purely symptomatic and cannot be used instead of drug treatment.
Physiotherapy
To speed up recovery, the doctor may prescribe physical therapy, which relieves the severity of symptoms, making you feel better:
- UHF therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- Ural Federal District;
- microwave therapy.
A sore throat can be treated at home using traditional methods known since ancient times. There are many recipes based on medicinal herbs, honey and other healthy products that can be used to successfully treat colds:
- If the vocal cords have been under tension for a long time, they can be helped as follows: heat milk with a high percentage of fat content, then add 1 tsp to it. butter and 1 tsp. honey All this must be mixed and drunk in small sips. This procedure should be carried out over 3-4 days.
- The voice will help to return the recipe with yolk and milk. You need to heat the full-fat milk and add 1 egg yolk to it, then drink it slowly. With this treatment, the loss of voice will disappear within a few days.
- A combination of cognac, lemon juice and honey has a healing effect. This recipe is useful for colds and as a preventive measure during the cold season. It is necessary to heat a small amount of cognac, add 3 tsp to it. honey and a few drops of lemon juice. The healing decoction should be drunk at night, slowly, allowing it to slowly pass through the sore throat.
- Gargling will help cure your throat. This is a mandatory procedure for any diseases of the larynx, especially sore throat or laryngitis. Today, aloe juice is in demand among folk remedies. You need to tear off a fleshy leaf from the plant, remove the skin from it, and put the juice and pulp separately. Using gauze, squeeze out the pulp, the output should be 3 tbsp. l. juice It is mixed with 3 tbsp. l. boiling water Once the mixture has cooled to an acceptable temperature, it can be used as a gargle.
- Beetroot juice is an excellent folk ingredient for gargling. It is necessary to grate the beets on a fine grater, squeeze the juice out of it, add 1 tbsp to it. l. apple cider vinegar and gargle several times a day.
Complete treatment requires complex therapy in combination with medications prescribed by a doctor. Only a doctor can make the correct diagnosis and identify why the loss of voice occurred. He will be able to prescribe safe medications if a similar problem arose during pregnancy or other limiting factors.
“Lump in the throat”: symptoms and treatment of pharyngeal neurosis or pharyngoneurosis
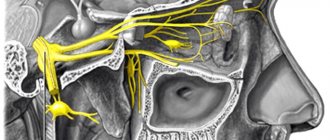
A lump in the throat during neurosis is the first signal that malfunctions are occurring in the functioning of the nervous system. Patients who have problems with swallowing and sore throat seek help from many specialists (therapist, laryngologist), but few of them associate these symptoms with psychosomatics. By “pharyngeal neurosis” or “pharyngoneurosis” is meant a pathology involving the funnel-shaped canal. It is the connecting anatomical link between the mouth and the esophagus.
General information about the disease
Laryngitis is an inflammatory process of the membranes of the larynx, into which the vocal cords become “drawn in.” It is believed that laryngitis can develop during a cold or during an infectious disease. Inflammation of the larynx is promoted by hypothermia, inhalation through the mouth, excessive tension of the larynx, if you have to scream a lot and loudly.
Laryngitis manifests itself as hoarseness; the sick person can even completely lose the ability to speak. The throat feels dry and sore. The cough is dry and unproductive, barking in nature. Swallowing becomes difficult and painful.
As part of the treatment, the patient is prescribed a regime of silence; he should speak as little as possible. Even a whisper is dangerous, since it strains the vocal cords no less than loud speech.
False croup (stenotic laryngotracheitis) occurs only in children, since their larynx is naturally narrower. In the absence of emergency qualified medical care, the child may die from asphyxia.
Treatment of a lump in the throat with neurosis
Is a lump in the throat a harmless neurosis or a harbinger of a serious illness? The rhythm of modern life and the variety of nervous situations in which we find ourselves every day lead to psycho-emotional exhaustion, severe shocks, depression and anxiety disorders. Due to a malfunction of the central nervous system, such an unpleasant symptom appears as a nervous lump in the throat, similar to the one that “gets stuck” in the larynx when you cry. The reasons for this phenomenon can also be associated with various kinds of psychogenic and somatic factors, less often - diseases of internal organs and disruptions in the functioning of life support systems.
Psychosomatic causes in adults
Psychosomatics studies the psychology of the disease and can answer the question of what factors of this kind could lead to the development of the disease. Laryngitis is not always caused solely by bacteria or viruses. Sometimes there are no visible reasons for inflammation of the larynx, but the voice disappears and swallowing becomes painful. In this case they talk about psychogenic laryngitis.
In psychosomatics, the larynx is an organ that allows a person to reproduce sounds and express his thoughts and feelings. All diseases of the larynx are a sign that a person forbids himself to express something or cannot express it out of fear. Most often, laryngitis begins in those who do not risk voicing their negative emotions: anger, irritation, resentment. These emotions and words “accumulate” and settle in the throat, which ultimately leads to an inflammatory process and swelling.
Adults and teenagers have another reason: a feeling of guilt and anger at themselves for not keeping a secret, for letting someone out about something. If this anger is strong enough, the larynx will become inflamed and the voice will disappear for a while.
Esophageal spasm and stress
Psycho-emotional overload and stress often cause an imbalance in the contractions and relaxations of the muscles of the esophagus, when pushing food to the stomach. As a result, muscle contraction prevails over the narrowing process, which causes spasm of the esophagus, which is characterized by the sensation of a lump rolling up to the throat. In addition, spasm is characterized by:
- difficulty swallowing food or liquids;
- Pain behind the sternum and between the shoulder blades, radiating to the back and shoulders.
Pharyngeal neurosis is one of many forms of psychogenic disorders that affect the functioning of internal organs. It manifests itself in changes in the sensitivity threshold of a given organ, which (depending on the type of disorder) can increase or decrease. The main sign of pharyngeal neurosis is a lump in the throat, which causes some discomfort during swallowing, breathing and (rarely) pronouncing sounds. Pharyngeal neurosis can be treated, which is prescribed by a specialist depending on its type and severity of symptoms.
- VSD is not a death sentence, neuroses are reversible
- What music helps best with obsessive thoughts and insomnia?
Unfortunately, the modern pace of life often does not allow a person to undergo a full course of treatment for neurasthenia from a specialist. And the question arises, what to do if throat neurosis finds a person in a situation where quick medical help is impossible.
1) First you need to suppress the sign of panic. In ancient times, this condition saved a person’s life, as it causes muscle activity that can help one very quickly climb a tall tree, rock, or simply run away. Since in the modern world it is impossible to relieve muscle tension caused by panic, you need to learn to ignore panic in principle so that your muscles do not cramp.
2) You need to relax, there are several ways to do this. For example, breathing exercises: on the count of “one,” a strong inhalation is taken, and the exhalation should be done long, on the count of “one, two, three.” If a panicked state leads to hyperventilation due to rapid breathing, the person may lose consciousness.
3) You can relax the muscles step by step, that is, first the legs, then the muscles of the abdomen, back, chest, shoulders, arms and then the neck.
4) Another method of relaxation is called the distraction method. It is necessary to distract from your inner state to contemplate the world around you - the flight of birds or clouds, the rustle of the wind in the foliage of trees, the murmur of water in a stream, and so on. The main thing is not to think about the reason that caused the stressful state.
5) Signs of stress and impending laryngeal spasm can be relieved by light physical activity, such as a light jog or walk.
You need to understand that fear is the cause of a neuropathic attack. And accordingly, victory over the fear of an attack will finally rid a person of it. For example, if a person is sure that he always has a special drug with him that can instantly relieve the symptoms of an attack, then he will never experience it.
But if a person, having driven far from home, discovers that he forgot to take the medicine, then a panic attack will quickly cause a throat spasm. That is, the medicine is always in a person’s head, he can always calm himself down, as well as vice versa - he can turn his psyche into a fit. All this once again suggests that a psychiatrist should treat pharyngeal neurosis.