The main thing about the syndrome
This is a rare, poorly studied disease. It is detected in one in 30,000 newborns. It was first described in the 19th century and has since been systematically studied, but the causes of the disease have not yet been fully identified.
In addition, even in the 21st century, the pathology is difficult to treat, even if it is started in a timely manner. A child with such a disease looks emotionless - due to improper development of the cranial nerves, he is incapable of facial reactions.
He expresses his feelings with sound, for example, crying, but without a characteristic grimace. Such crying (or laughter, in case of pleasure) sounds unnatural, because it is difficult for the baby to control the vocal apparatus.
Today, the cause of the disease is usually listed as paralysis of the facial nerves, although it can also be associated with other processes in the body, such as a lack of oxygen inside the womb.
Congenital anomalies
Children with Mobius syndrome often suffer from congenital malformations. These may include:
Supporting
Bone and muscle abnormalities of the arms and legs. Club feet, missing fingers, short fingers or even a split hand. Club feet, where the feet turn inward at the ankles, are one of the most common bone deformities.
The breasts on one side of the body may be underdeveloped. Muscle tone is weak.
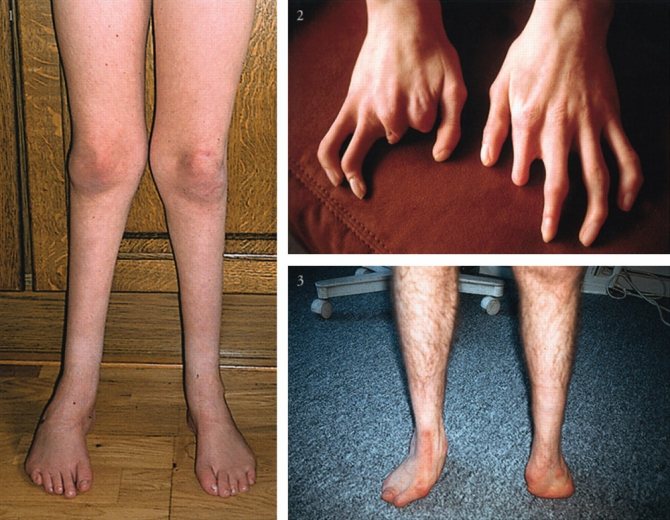
Facial
A child may have a small chin, a condition called micrognathia. Teeth may be missing or misaligned. The mouth is small with a short or unusually shaped tongue. The palate is high, arched or cleft.
These features add problems with speech development and feeding. The outer ear may be absent or underdeveloped. Hearing loss occurs if the VIII nerve is affected.
Signs and treatment of Mobius syndrome in children
Mobius syndrome is a condition that affects the development of cranial nerves VI and VII, either on one or both sides of the head.
It is named after neurologist P. J. Mobius, who studied the condition in 1888. It is estimated to affect about 1 in 50,000 to 1 in 500,000 births. Men and women are affected equally.
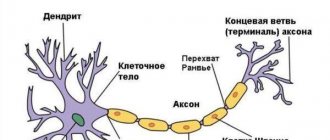
Anatomy of cranial nerves
There are twelve pairs of cranial nerves, of which the first two arise from the brain, the rest from the trunk. Nerves are either sensory, that is, they carry sensations to the brain.
Motor – control muscle movements, or mixed, both sensory and motor.
They innervate the head and neck region, with the exception of the tenth (vagus) nerve and several fibers of the 11th, which supply the chest and abdomen.
The VI cranial nerve is a motor nerve and innervates the lateral rectus muscle, which causes the eyeball to move laterally, that is, to the outer corners of the eyes. VII - mixed nerve, carries both sensory and motor impulses.
The sensory part carries taste sensations from the outer 2/3 of the tongue, the soft and hard palate, which form the roof of the mouth, to the brain. The motor portion of the facial nerve controls the muscles of the face.
When the facial muscles contract, various emotions are visible on the face, such as a smile or forehead wrinkles. In addition, the facial nerve carries parasympathetic nerve fibers that control the secretion of saliva, mucous glands of the mouth and nose, and the secretion of the lacrimal gland.
Based on the extent of the disease, the disorder can be classified as:
- Moebius syndrome in children - VII and VI nerves are completely paralyzed on both sides;
- Incomplete syndrome - here some movements are present on one side of the face;
- Mobius-like forms - one side of the face is paralyzed, other cranial nerves are working.
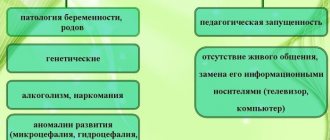
Genetic factors
Changes in chromosomes 3, 10, 13 may be the cause. However, family history cannot be identified in most cases.
Environmental factors
Environmental factors, such as certain medications or drugs used during pregnancy, can lead to a child with the disorder. They cause changes in blood flow to the brain, where cranial nerves arise, thereby affecting their development.
Cause an embryonic defect in the brain, leading to the condition.
Symptoms
Features of Mobius syndrome are present from birth. These include the following:
Facial paresis or paralysis
Weakness or paralysis of the facial muscles is the main feature. As a result, the child:
- Has difficulty breastfeeding. It is necessary to feed with a special bottle. You can notice throttling at the corners of the mouth. The mouth usually remains open. Speech affected.
- Disadvantages of facial expressions. The child is unable to smile or frown, resulting in a mask-like face.
These two features interfere with the interaction between mother and child in the initial period after birth.
The muscles of the eyelids and around the eyes are also affected. Older children cannot raise their eyebrows. Incomplete closure of the eyelids leads to dry eyes , damage to the cornea due to overexposure.
Lack of facial expressions interferes with social communication.
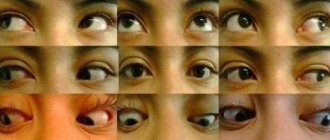
Eye movement problems
Due to paralysis of the lateral muscle, the eyes do not turn outward. As a result, the child must move his head while reading or following the movements of objects. Squint may be present. Vertical eye movements are not affected.
Involvement of other cranial nerves
Symptoms due to involvement of other cranial nerves may be present: 5, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12.
Intelligence is usually normal, although developmental delays occur around 1 year. Children tend to catch up with their peers by age 5.
Congenital anomalies
Children with Mobius syndrome often suffer from congenital malformations. These may include:
Supporting
Bone and muscle abnormalities of the arms and legs. Club feet, missing fingers, short fingers or even a split hand. Club feet, where the feet turn inward at the ankles, are one of the most common bone deformities.
The breasts on one side of the body may be underdeveloped. Muscle tone is weak.
Facial
A child may have a small chin, a condition called micrognathia. Teeth may be missing or misaligned. The mouth is small with a short or unusually shaped tongue. The palate is high, arched or cleft.
These features add problems with speech development and feeding. The outer ear may be absent or underdeveloped. Hearing loss occurs if the VIII nerve is affected.
Surgery
Severe cases require surgery. Surgical treatments for facial paralysis include the following:
- "Smile surgery" where a thigh muscle called the gracilis is transferred to the face and connected to the nerves supplying the muscles. Facial massage is necessary so that it can function. This surgery is currently considered the best option for the condition.
- Temporal tendon transfer. The temporalis facial muscle is transferred to the corners of the mouth, a “cross-facial nerve graft” is done in cases of unilateral paralysis.
Other deformities, such as deformities of the limbs and jaw, may require surgical treatment.
More severe cases require surgical intervention in the form of transplantation without muscle mass innervated by motor nerves.
Can it be cured?
Mobius syndrome cannot be completely cured. However, symptoms and complications are easily controlled and treated with supportive measures.
Does it get worse as you get older?
No. It is not a progressive disorder and does not get worse as you get older. However, the patient may suffer from complications that require treatment. These include:
- Poor nutrition due to difficulty swallowing;
- Aspiration pneumonia due to aspiration of stomach contents into the lungs;
- Corneal ulceration due to overexposure;
- Moderate ear infection due to facial deformities.
How to prevent
Since most cases have no family history, genetic counseling may not be very helpful. Avoiding exposure to off-label medications, illicit drugs, and toxins during pregnancy helps reduce the incidence of Mobius syndrome and other congenital anomalies.
Risk of heart disease
Children with Mobius syndrome rarely suffer from heart disease. Sometimes there is dextrocardia (the heart is located on the right side of the heart instead of the left), a ventricular septal defect, or abnormal attachments of large blood vessels to the heart (great vessel transfer or complete anomalous pulmonary venous connection).
Source: https://ovp1.ru/nevrologicheskie/mebiusa
Symptoms and diagnosis
The most characteristic symptom of Mobius syndrome is the absence of facial expressions.
Other symptoms that help clarify the diagnosis include:
- abnormalities of body structure;
- complete or partial dysphagia (inability to swallow), difficulty sucking;
- Often, reduced intelligence is added to the symptoms; however, intelligence in patients with Mobius syndrome may be normal.
Babies with the syndrome are difficult to feed and care for, since their wishes often have to be guessed. They require additional care in a hospital setting until the symptoms of the disease are eliminated.
The disorder is diagnosed, as a rule, within a short time after birth. The diagnosis can only be made by a doctor based on available data on the symptoms of the disease. Usually no additional procedures are required to make a diagnosis.
Department of Endocrinology
Treatment of endocrine diseases. Endolymphatic therapy
Whatsapp phone
Diagnosis of Möbius syndrome in a newborn
Timely diagnosis of the disease is very important, as this will allow timely detection of various forms of developmental deviations, but will also reveal the psychological and clinical mechanisms of the disorders.
Complications
The prognosis for newborns with Mobius syndrome is favorable. Surgical intervention will partially restore the functions of the facial nerves and give the child the opportunity to adapt in the future among his peers.
Most children with Mobius syndrome today have the opportunity to lead a normal and fulfilling life on an equal basis with other children.
What can you do
Since the causes of this disease are not fully understood, it is not possible to completely get rid of the pathology today.
It is for this reason that doctors are trying to help not only such children, but also their parents.
In this matter, psychological assistance to parents is very important, which in turn will help support the normal functioning of the child at every stage of his development and maturation.
Such children need the help of qualified specialists who can provide certain symptomatic assistance - correction of gait, speech, strabismus, etc.
Pathogenesis
Genetic determination and unfavorable antenatal conditions potentiate various disorders, delaying the formation of nuclei and roots of cranial nerves at the level of the brain stem. The facial and abducens nerves are primarily affected. Amymia occurs due to a disturbance in the innervation of the facial muscles. Denervation of the muscle that rotates the eyeball outward causes convergent strabismus. Often Mobius syndrome involves underdevelopment of other cranial nerves located in the trunk. Hypoplasia of the glossopharyngeal, vagus, and hypoglossal nerves leads to disorders of sucking, swallowing, voice production, and articulation. When the VIII pair is underdeveloped, hearing loss is detected, while the V pair is characterized by a lack of sensitivity of the facial skin.
Symptoms of Mobius syndrome
The symptoms of Mobius syndrome depend on which nerves are affected.
Whatever symptoms a person has experienced since birth. In most cases, the sixth and seventh cranial nerves are absent, although other cranial nerves may be affected. Common Symptoms The most common signs of Mobius syndrome include:
- Facial paralysis
- Lack of facial expressions; children with Möbius syndrome cannot smile or frown (the face is often described as "mask-like")
- Infants with Moebius syndrome cannot move their eyes to track an object. Instead, they will need to turn their head completely to follow the object.
- Eyelids that don't close completely, even while sleeping
- Dry and irritated eyes
- Small chin and mouth; many people with Mobius syndrome cannot close their mouth completely
- Dental problems associated with a small jaw, misaligned teeth, or open-mouth effect (increased risk of tooth decay)
- Drooling, feeding problems, poor sucking in infancy
- Cleft palate
- Head tilt back when swallowing
- Syndactyly
- Strabismus
- Short tongue
- Weak muscle tone (hypotonia)
- Abnormal curvature of the spine (scoliosis)
- Respiratory disorders
- Sleep problems
- Weakness of the upper body, which can lead to delayed motor function
- Ear abnormalities that may lead to frequent or persistent ear infections (otitis media)
- Hearing loss (due to damage to certain cranial nerves)
- Skeletal abnormalities of the arms, legs and limbs (clubfoot)
- Other speech, swallowing and vision disorders
- Underdeveloped chest wall muscles (which may also include breast tissue)
Causes
The exact cause of Mobius syndrome is unknown. There are genetic and environmental factors.
Genetic factors
Changes in chromosomes 3, 10, 13 may be the cause. However, family history cannot be identified in most cases.
Environmental factors
Environmental factors, such as certain medications or drugs used during pregnancy, can lead to a child with the disorder. They cause changes in blood flow to the brain, where cranial nerves arise, thereby affecting their development.
Find out more Causes of flatulence
Cause an embryonic defect in the brain, leading to the condition.
Complications
The prognosis for the life of children with Mobius syndrome is favorable. Most of these children lead a normal life, but modern society creates incredible difficulties for such children, preventing them from adapting among their peers. Constant ridicule and bullying from peers, especially in adolescence, undermines such children's self-confidence and makes them social outcasts.
This attitude towards them from others interferes with normal communication and development of the child. Often such children choose loneliness at a certain stage of their lives, which subsequently does not prevent them from starting a family, having friends and adapting to society.
Possible complications
Swallowing disorders are dangerous due to food entering the respiratory tract with asphyxia. The accumulation of food debris in the oral cavity creates favorable conditions for the development of caries and other dental diseases. Due to disturbances in the structure and functioning of the upper respiratory tract (nasopharynx, larynx), respiratory infections often occur, which can be complicated by pneumonia. The presence of structural features of the ear causes frequent otitis media in children. A complication of lagophthalmos is increased dryness of the eye (xerophthalmia) and associated inflammatory processes (conjunctivitis, keratitis). Facial paralysis and speech difficulties sharply limit the patient’s ability to express his emotions, and difficulties in communication and acquisition of social skills are observed. As a result, patients are prone to depression and have learning difficulties. Dysarthria and hearing loss lead to the formation of general speech underdevelopment; without proper correction, they become the cause of mental retardation. Dysplastic changes in the limbs cause certain restrictions in the motor sphere; if left untreated, joint contractures develop.
Additional facts
Moebius syndrome is a congenital anomaly of the facial nerve (VII pair) in combination with pathology of the abducens (VI), glossopharyngeal (IX), sublingual (XII), less commonly, trigeminal (V), vestibulocochlear (VIII) nerves. First described by the German neurologist P. Mobius in 1888. In the modern literature on neurology, the following synonymous names are found: “facial diplegia”, “congenital oculofascial palsy”. The prevalence of the pathology is 1 case per 150 thousand. Newborns, boys and girls get sick equally often. Hereditary and sporadic cases of the disease are known.
Moebius syndrome - which doctors can help a child?
People with Moebius syndrome are unable to express emotions. The disease completely deprives a person of facial expressions, and he cannot demonstrate his condition - laugh, cry or even blink. For the first time in 1888, the disease was studied by the neurologist P. J. Mobius, after whom the disease was named. The causes of congenital pathology are still not fully understood, and treatment options are limited.
Mobius syndrome - what is it?
Many patients, when faced with pathology, wonder what Moebius syndrome is. This is a rare congenital anomaly in which a person is completely deprived of the ability to demonstrate facial reactions to others.
The patients' face resembles a mask - they cannot use not only their facial muscles, they cannot even swallow. In such people, the 6th abducens and 7th facial nerves are often affected.
With a complex course of the disease, other cranial nerves are also affected.
Why is Mobius syndrome called this?
The absence of facial expressions in people was first studied and described by the German neurologist P. J. Mobius in 1888 and gave the disease his name.
In modern reference books on neurology there are such synonymous names as: “facial diplegia”, “facial diplegia”, “oculofascial paralysis”.
The pathology does not select gender and affects both boys and girls equally. The prevalence of the disease is 1 case per 150,000 infants.
Mobius syndrome - pathogenesis
Facial diplegia (Moebius syndrome) is a rare pathology that occurs in newborns. Diagnosing the disease is difficult because it has not been fully studied, and it is much easier to diagnose cerebral palsy, deafness or blindness. This makes it very difficult to treat Moebius syndrome, which means that the chances of getting rid of the disease are reduced.
The disease is neurological and has a number of characteristic symptoms:
- visual dysfunction;
- inability to move your eyes while watching the movement of an object;
- violation of the swallowing reflex and tongue function;
- incorrect anatomical structure;
- sensory response disorders;
- lack of facial expressions;
- problems with the sucking reflex;
- difficulty producing or lack of tears;
- problems in the functioning of the vestibular apparatus.
Mobius syndrome - causes
The causes of Moebius syndrome have not yet been thoroughly studied, but scientists put forward 3 common theories in this regard:
- The disease develops due to improper formation and development of cranial nerves.
- Mobius syndrome in children occurs as a result of insufficient oxygen supply to the fetus during its prenatal period.
How to check for Mobius syndrome?
Facial amyia is diagnosed during a detailed examination, which necessarily includes the following points:
- Appointment with a neurologist for examination.
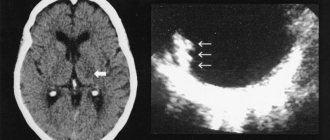
If the disease is present, the doctor diagnoses facial paralysis, swallowing dysfunction and tongue atrophy. If there is a pathology of the trigeminal nerve, then hypoesthesia of the skin on the face is added to the list. Disturbances are observed on both parts of the face. - Möbius syndrome in adults requires an MRI of the brain.
Using this diagnosis, the presence of hypoplasia of the cranial nerves is revealed. MRI allows you to exclude or confirm the presence of congenital cysts, tumors, malformations of the meninges and hematomas. The procedure is not recommended for children. - Neuropsychological examination.
In young children, visual reactions and psychomotor function are checked for compliance with age standards. Appropriate tests are carried out with older children. - Appointment with a geneticist.
Moebius syndrome (the photo shows deviations from the norm) is clearly visualized during the examination, but it is important to consult a geneticist to draw up a detailed picture of the disease. The specialist draws up a family tree and identifies the type of inheritance of the disease.
Answering the question - how to treat Mobius syndrome is not so simple. There is no definitive system suitable for all patients.
Treatment of this disease involves complex therapy involving many highly qualified specialists.
Therapy corrects disorders of a certain type that a particular patient has, depending on his individual picture of the disease.
Mobius syndrome requires the involvement of the following specialists:
- neurologist;
- pediatrician;
- otolaryngologist;
- orthopedist;
- dentist;
- speech therapist;
- plastic surgeon;
- audiologist;
- ophthalmologist.
The list can be continued indefinitely, because each case requires the involvement of a larger number of specialists, or a selective one of one direction or another.
The pathology is so unique and unpredictable that it is possible to give a definite direction of treatment only after a detailed study of the medical history.
Moebius syndrome is treated in various ways, including surgery, but mainly involves accompanying constant monitoring.
Mobius syndrome - prognosis
People with Mobius syndrome live with a mask on their face, and their life is not as simple as it seems from the outside. There are no cures for this type of congenital pathology.
However, people with this disease can live for many years. Success in this matter is determined by correctly selected accompanying treatment and proper care.
By showing care and understanding, you can provide the patient with a good standard of living.
| Alalia in children - causes and signs of all types of pathology Alalia in children is a developmental disorder characterized by a complete absence of speech. The disease develops due to damage to the cortical speech centers of the brain, which are damaged in utero or in the first 3 years of the baby’s life. | Ectopia of the heart - causes, types of anomalies, life prognosis Ectopia of the heart is a severe developmental anomaly in which the main “motor” of the body is carried outside the body or occupies an unusual position among other organs of the abdominal cavity. The pathology is treated surgically, but the chances of survival are low. |
| Sleepwalking in children - is it dangerous, and what should parents do? Sleepwalking in children is common, which causes parents to panic and fear for the child’s mental health. Sleepwalking is not a dangerous condition or even a disease; you just need to help your child comfortably outgrow this temporary problem. | Krabbe disease - can the pathology be cured? Krabbe disease is a rare genetic pathology. The disease manifests itself in early infancy. Due to the similarity of symptoms, it is mistaken for cerebral palsy, but with a comprehensive examination it is possible to establish the true cause. |
Source: https://womanadvice.ru/sindrom-mebiusa-kakie-vrachi-sposobny-pomoch-rebenku
Symptoms and diagnosis
The most characteristic symptom of Mobius syndrome is the absence of facial expressions.
Other symptoms that help clarify the diagnosis include:
- abnormalities of body structure;
- complete or partial dysphagia (inability to swallow), difficulty sucking;
- Often, reduced intelligence is added to the symptoms; however, intelligence in patients with Mobius syndrome may be normal.
Babies with the syndrome are difficult to feed and care for, since their wishes often have to be guessed. They require additional care in a hospital setting until the symptoms of the disease are eliminated.
The disorder is diagnosed, as a rule, within a short time after birth. The diagnosis can only be made by a doctor based on available data on the symptoms of the disease. Usually no additional procedures are required to make a diagnosis.
What can modern medicine do?
The disease is difficult to treat and cannot be completely cured, since even now its mechanism has not been studied in sufficient detail. Nevertheless, in the conditions of modern healthcare, it is possible to partially reduce the symptoms and greatly alleviate the fate of the patient.
Both symptomatic treatment of Moebius syndrome and surgical intervention are carried out. To reduce the severity of symptoms, correction of strabismus is used, speech therapy is carried out to improve pronunciation.
Article on the topic: Pancreatitis - causes, symptoms and treatment methods
Surgery helps to significantly reduce the severity of the pathology. For treatment, the patient's muscles are taken (usually the thigh muscles) and transplanted to the face. After such an operation, the patient is able to partially express his emotions through facial expressions and completely close his lips.
With the support of charitable organizations, treatment is provided free of charge.
Related diseases and their treatment
Descriptions of diseases
Robin's syndrome Pierre-Robin's syndrome Apert's syndrome Pfeiffer's syndrome Asherson's syndrome Oculocerebrocutaneous syndrome
National treatment guidelines
Congenital anomalies of the bones of the skull and face, congenital musculoskeletal deformities of the head and face Hematuria in children
Medical standards help
STANDARD of medical care for patients with craniofacial dysostosis, syndromes of congenital anomalies affecting mainly the appearance of the face
Other symptoms of Mobius syndrome
In some cases, underdeveloped chest muscles are associated with another condition called Poland syndrome (or Poland anomaly).
People with Polish syndrome are missing part of one of the large muscles of the chest (the pectoralis major). This abnormal development can give the breasts a concave appearance and typically causes upper body weakness and sometimes chest wall abnormalities. These missing muscles typically only affect appearance, and people with this condition do not experience any health problems directly related to the condition. However, people who also have Mobius syndrome may have other symptoms that affect movement. Some studies report that up to 20-30% of children with Möbius syndrome have also been diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder, although this association may be overestimated. Because people with Möbius syndrome are physically unable to demonstrate facial expression and may struggle to look people in the eye, these features may be interpreted as autistic behavior even if they are due to physical limitations.
Some children with Mobius syndrome may have motor, speech, or other delays. Most people with this condition do not have an intellectual disability, although assumptions may be made due to their physical struggle with speech and unique facial features.
Symptoms
The first clinical manifestations of the syndrome are facial amyia, strabismus, sucking and swallowing disorders. The lack of facial expressions in the newborn is noteworthy. The appearance of the child is characteristic: the face is motionless, the corners of the mouth are drooping, the mouth is slightly open, lagophthalmos is observed (incomplete closure of the eyelids). There is no crying, smiling, or lacrimation. Moebius syndrome is often combined with other congenital defects of various structures of the head: cleft hard palate, micrognathia, dental anomalies, auricular dysplasia, microphthalmia. 50% of patients have congenital anomalies of the limbs: syndactyly, polydactyly, clubfoot, foot deformities. Poland syndrome is common: aplasia of the pectoralis major muscle, mammary gland and nipple, rib dysplasia, brachydactyly.
Description
Mobius syndrome.
Congenital combined underdevelopment of the nuclei of the V, VI, IX, XII pairs of cranial nerves, which is predominantly bilateral. It is manifested from birth by the absence of facial expressions, incomplete closure of the eyes, impaired sucking, swallowing, and articulation. In most cases it is combined with anomalies of the facial skull and limbs. Diagnostics includes neurological, neuropsychological examination, cerebral MRI, ENMG, genetic counseling. Conservative and surgical treatment is aimed at correcting congenital defects, restoring speech, and social adaptation of patients.
Moebius syndrome treatment | Saratov, Russia
Treatment of Mobius syndrome is aimed at restoring lost functions.
Treatment of the facial nerve
Sign up for a consultation. There are contraindications. Specialist consultation is required.
Photo (©) Fxquadro | Dreamstime.com \ Dreamstock.ru The people depicted in the photo are models, do not suffer from the diseases described and/or all similarities are excluded.
Related posts:
Accentuation of character in adolescents, types, test, methodology, correction in Saratov
Nocturnal enuresis, urinary incontinence, children's enuresis, treatment
Human brain, child brain, sections, structure, brain treatment
I'm afraid to speak, logophobia: treatment of logophobia for stuttering, the child is afraid to speak
Kogan syndrome: treatment, how to treat Kogan, oculomotor apraxia
Comments ()
Treatment of Mobius syndrome
In relation to the disease, complex therapy is carried out, aimed at correcting existing congenital anomalies, maintaining the functioning of the brain, musculoskeletal system, and psychological support for the patient and his loved ones. Nutrition is provided using a special syringe, through a tube, and, if necessary, parenterally. The child is consulted by a pediatrician, a pediatric surgeon, a plastic surgeon, an ophthalmologist, a psychologist, and an orthodontist. Treatment includes the following components:
- Neurological.
Supportive neurotropic pharmacotherapy with amino acids, nootropic, vascular, and vitamin preparations is carried out. Correction of amymia is performed surgically; the operation involves transplanting a muscle graft from the thigh to the face. - Ophthalmological
. In order to prevent complications of xerophthalmia, moisturizing eye drops are constantly instilled. If inflammation develops, antibacterial drops are prescribed. To protect the cornea, partial tarsorrhaphy is indicated - suturing the edges of the eyelids. Strabismus requires surgical treatment. - Orthopedic
. Involves surgical correction of malformations of the extremities: separation of the fingers in case of syndactyly, elimination of clubfoot, operations on the bones and joints of the foot. It is recommended to wear orthopedic shoes, regular exercise therapy, physiotherapy, and massage. - Dental
. Closing of the cleft palate, orthodontic treatment of malocclusions, and straightening of the dentition are carried out. In severe cases, treatment is carried out using maxillofacial surgery. - Speech therapy.
Articulation gymnastics and speech therapy massage are used. Regular classes with a speech therapist are prescribed to correct dysarthria, OHP. - Psychological.
Of great importance in complex treatment are the child’s sessions with a psychologist, child psychotherapy, art therapy, and psychological counseling of parents. For the purpose of social adaptation, older children take part in group psychological trainings.
Sources
- https://NeuroDoc.ru/bolezni/drugie/sindrom-myobiusa.html
- https://ovp1.ru/nevrologicheskie/mebiusa
- https://kiberis.ru/?p=34206
- https://DetStrana.ru/service/disease/children/sindrom-myobiusa/
- https://www.krasotaimedicina.ru/diseases/zabolevanija_neurology/Mobius-syndrome
[collapse]
Mobius syndrome: photos, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
It is difficult to imagine a person who cannot laugh, cry or express any emotions. However, there are such people, and they have been given a terrible diagnosis - Moebius syndrome. Photos of such people at first glance may seem quite normal, but during live communication you realize that their face is completely immobilized.
This is a congenital anomaly that develops for the main reason due to the abnormal structure of the cranial nerves. Facial paralysis is one of the most terrible defects of the human body. It is characterized by the absence of facial expressions, the face seems frozen and like a mask.
Historical reference
The syndrome was first described in medicine in 1892 by the German neurologist and psychiatrist Paul Mobius. This anomaly is extremely rare, a maximum of 10-20 times per 1 million children born.
German physician Paul Julius Mobius was born in 1853 in Germany and lived there all his life. The scientist studied the clinical development of progressive paralysis and neuropsychic abnormalities in thyrotoxicosis. He made a description of ophthalmoplegic migraine, calling it Möbius disease.
Alleged reasons for development
The most severe form of pathology is considered to be Moebius syndrome, the causes of which are still unknown to medicine. The opinions of researchers and specialists are divided.
- The first believe that the reason is improper development of the cranial nerves.
- The latter are confident that this is the harmful influence of destructive processes that develop as a result of oxygen starvation of the child in the womb.
- Still others point to the abnormal development of the facial motor center as the main cause of the disease.
Mobius syndrome is a rather old and very mysterious disease. This is a congenital anomaly of the facial muscles, due to which facial expressions are completely absent. Paralysis can be unilateral or bilateral. The person does not react in any way to external stimuli, does not smile, does not frown, and is completely devoid of emotions.
Children have a poorly developed sucking reflex; they cannot swallow food and water on their own due to weakened tongue function. The disease often affects several family members.
Symptoms of the disease
Mobius syndrome is a congenital neurological disorder that is quite rare. People with this pathology lack the ability to move their facial muscles and eyes from side to side. This disease entails serious disturbances in the functioning of the musculoskeletal system and deformation of the feet.
The main clinical manifestation of the syndrome is limited mobility, but there are other, pronounced symptoms that confirm that this is Moebius syndrome:
- anatomical abnormalities;
- deformed foot;
- difficulty swallowing and sucking;
- sensory perception disorders;
- weakening of language functions;
- visual impairment.
There is also a violation of vestibular excitability and lack of tear secretion. The skin of a sick person's face is tense, without wrinkles even when laughing or crying. It does not move in relation to the subcutaneous tissue; the corners of the mouth are always lowered.
The defect is accompanied by limb anomalies such as syndactyly, clubfoot, brachydactyly and extra digits. With partial paralysis, the process mainly involves the muscles of the upper part of the face; the tissues do not sag as much as with an acquired disease.
Diagnosis of pathology
An anomaly such as Moebius syndrome is quite rare. Diagnosis is therefore difficult, especially in young children, and often leads to misdiagnosis, which is more dangerous and requires surgical treatment, for example:
- cerebral paralysis;
- blindness;
- deafness.
Examination and further therapy are being conducted in this direction.
Modern medicine cannot yet fully study the cause of this disease, therefore, it is also not possible to cure it completely. Research and study of the genetic material of patients at the chromosome level is being conducted in search of cell mutations.
Today, doctors set themselves the task of helping parents of children suffering from this syndrome in maintaining normal functioning at every stage of life. This is possible when correcting speech, strabismus, and gait.
Timely diagnosis is necessary not only to detect various forms of developmental disorders, but also to assess the degree of development of mental functions and identify psychological and clinical mechanisms of disorders.
The diagnosis of abnormal development includes psychological, pedagogical and clinical genetic research. It is carried out to determine the level of delay in emotional, behavioral, intellectual and speech development. It also influences the establishment of a connection between the underlying disease and other pathological manifestations, age and neurological condition of the patient.
Treatment of Mobius syndrome
Only surgical treatment can help get rid of such an insidious disease as Mobius syndrome.
It is impossible to completely cure the disease; in addition to cosmetic deformity, impaired swallowing functions and other body problems that the defect entails, patients experience severe psychological stress throughout their lives. This condition can only be alleviated through surgery.
With the help of plastic surgery, it is possible to create artificial facial expressions, which means that the patient will be able to lift the corners of his mouth, experiencing a feeling of joy.
The rest of the face will remain immobilized and expressionless. There are cases that after such procedures, patients are disappointed with the results.
Therefore, before the operation, the patient is fully informed about the consequences and possible complications.
Psychology of social relations
This operation is quite complex from a technical point of view; its duration is rarely less than 8 hours. After this, patients are rehabilitated in the intensive care ward for two days. Fortunately, most people suffering from this defect lead normal lives, work, start a family, and have children.
However, facial expressions are very important for communication and social adaptation. The patient cannot fully develop. Due to the fact that a person is deprived of the ability to smile and has pronounced squint, he is unfairly perceived as an intellectually retarded person. Although mental retardation is observed in only 10% of patients.
It is very difficult for interlocutors to understand what reaction their words evoke and what a person is experiencing at that moment. All this interferes with normal communication, making patients with Moebius syndrome outsiders.
Young children tend to express different emotions and quite often, so a child suffering from Mobius syndrome is immediately visible. He does not react in any way to external stimuli, does not cry, does not laugh, and even blinks with difficulty. Only by sounds can you vaguely understand what the baby needs.
From birth, such children have a motionless face, a clear asymmetry, a slightly open mouth, the eyes do not close well, and the child can only follow objects by moving his head. Retardation of mental development is rarely observed; the patient requires massage not only of the face, but also of the tongue, developing articulation classes.
Symptoms in a newborn
Moebius syndrome is a hereditary pathology, the type of inheritance is autosomal recessive or, less commonly, dominant. With the syndrome, while still in the maternity hospital, the mother notices that the child’s facial expressions are unnatural, he does not cry or close his eyes, sometimes even at night. Such children also have abnormal defects:
- absence or fusion of fingers;
- deformation of the ears;
- epicanthus.
Although the specific causes of the disease have not yet been established, doctors suggest that taking medications and drugs during pregnancy increases the risk of pathology. Mobius syndrome in children cannot be completely cured, although its manifestations become milder with age.
Trainings to improve communication skills
Thanks to special trainings organized by Danish professors, people suffering from Mobius syndrome improve their social communication skills. The goal of the training is to activate paralinguistic means of communication using intonation and various gestures.
The effectiveness of the classes has been repeatedly proven by experiments and observations; during the dialogue, patients stop feeling nervous, do not fuss and become more relaxed. According to the results of the patients themselves, many do not feel any improvement.
The project's co-author is Kathleen Bogar, who was diagnosed with Mobius syndrome. Having built a career and become a successful doctor, her main goal in her work is to develop a program that will help people suffering from Mobius syndrome adapt to society.
Source: https://FB.ru/article/249310/sindrom-mebiusa-foto-simptomyi-diagnostika-lechenie