What is neuritis
Facial nerve
Neuritis is damage to peripheral nerve endings. Translated from Latin, pathology means inflammation of the nerve.
The facial nerve is one of twelve cranial nerves. It innervates the facial muscles and is responsible for the movement of the lips and eyelids. Inflammation spreading in the facial nerve leads to partial or complete loss of muscle tissue function.
Causes
Diabetes mellitus in children
In newborns, damage to the facial nerve occurs as a result of birth trauma. This can happen both during uterine development or during the passage of the child through the birth canal.
During pregnancy, the baby's face is closely pressed against the soft tissues and bones of the mother's pelvic ring. This leads to compression of the nerve. If a woman remains in this position for a long time or stops pushing, the nerve is damaged. This is what causes damage and loss of function of muscle tissue. Often the lesion appears on only one side of the face.
In older children, the causes of neuritis are various external and internal factors:
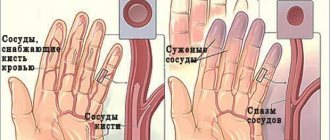
- Hypothermia and drafts. In this case, spasms of the facial muscles also occur.
- Herpes.
- Polio.
- Adenoviral infection.
- Poisoning with toxic substances.
- Tumors of a malignant or benign course.
- Dental manipulations.
- Injuries of varying degrees in the area of the skull and ears.
- Hit to the face.
- Stressful situations.
- Diabetes.
Systemic lupus, in which the pathological process affects nerve endings and blood vessels, can also provoke the appearance of symptoms of neuritis. The causes of neuritis can also be hidden in various diseases of the auricle and ear canal, for example, otitis media.
How neuralgia manifests itself and is treated in children
Acute sharp pain that prevents movement is the main symptom of neuralgia. This disease is a lesion of nerve endings, compression of them by surrounding tissues. It is believed that this can only happen in adults. But in medical practice, neuralgia is also encountered in children.
general characteristics
Infantile neuralgia is a disease of the peripheral nervous system. Most often it develops due to compression of the nerve roots by blood vessels or inflamed tissues. Sensory receptors react to pressure and transmit impulses along the nerve. This is expressed in sharp, sometimes burning pain. It can be sudden, paroxysmal or constant.
Neuralgia can develop in adolescents, preschool age or in infants. Most often, children are affected by trigeminal or intercostal neuralgia.
Recognizing pathologies is quite difficult, especially in young children. But without treatment, the consequences can be serious.
Due to the fact that the baby is in severe pain, he may experience delays in mental and mental development, speech disorders, emotional instability, and nervousness.
The child becomes whiny, irritable, and apathetic. Schoolchildren are lagging behind in their studies, hyperactive or lethargic.
Muscle atrophy, impaired development of the musculoskeletal system, and oxygen starvation due to respiratory failure may develop.
Intercostal neuralgia occurs more often in adolescents, but can occur even in infants. The ICD-10 code for this disease is G58.0. It refers to diseases of the nervous system. Characterized by damage to the peripheral nerves passing between the ribs.
It can occur for various reasons, but most often develops during a period of intensive growth during school age. The disease is dangerous because it prevents you from moving normally; the pain can intensify even with breathing.
Without treatment, this leads to developmental delays, hypoxia and other consequences.
According to ICD-10, trigeminal neuralgia also refers to damage to nerve endings, pathology code G50.0. Such neuralgia can often be observed in infants. The trigeminal or facial nerve becomes inflamed for various reasons, one of which is intrauterine developmental anomalies. Due to constant pain in the face, the baby experiences a delay in speech development and decreased appetite.
Reasons for appearance
When neuralgia is diagnosed in a newborn, the causes of the pathology are the mother’s improper behavior during pregnancy, which led to disturbances in the baby’s intrauterine development. Nerves are compressed mainly by blood vessels. This can happen for the following reasons:
- fetal hypoxia;
- smoking or drinking alcohol by a woman during pregnancy;
- decreased hemoglobin in the mother;
- severe stress or depression;
- pathological childbirth, including caesarean section;
- various birth injuries
- infectious diseases.
Sometimes neuralgia develops in the first months of a baby’s life due to parental neglect.
A pinched nerve can occur if the baby is not handled correctly, if he is exposed to drafts, or if he is overcooled. Carrying a baby in a baby carrier can also cause neuralgia.
It develops in premature infants, in the presence of various congenital anomalies in the development of blood vessels and organs.
The cause of intercostal neuralgia in adolescents can be active growth of the skeleton, incorrect posture or other diseases of the musculoskeletal system, or increased physical activity. Sitting at a computer for a long time, wearing a heavy backpack, or an uncomfortable posture during sleep - all this can lead to nerve damage.
Damage to the intercostal nerves also occurs with herpes infection or herpes zoster.
Trigeminal neuralgia can develop in the first year of a baby's life or later. The reason for this is most often drafts or severe hypothermia.
But inflammation of the facial nerve often appears with infectious diseases of the ENT organs or the oral cavity.
After all, all inflammatory processes develop very quickly in children, and the peculiarities of the anatomical structure contribute to the fact that they even affect the nerve roots.
The pathology is often caused by injuries, improper dental treatment, and chickenpox. In babies, the trigeminal nerve is located too close to the skin; even a small draft or careless touch can cause it to be pinched. Tumors or diseases of the cervical spine should not be ruled out.
How it manifests itself
It is especially difficult to recognize the symptoms of neuralgia in newborns. Its main manifestation is acute pain. A small child cannot tell or show what is bothering him, he just cries. But by the characteristics of behavior, the mother can recognize the pathology. Signs indicating neuralgia:
- sleep becomes restless;
- heavy sweating and redness of the skin;
- increased body temperature;
- the child pulls his hands to his face while crying;
- visible muscle cramps, nervous tics;
- increased salivation;
- decreased appetite.
Trigeminal neuralgia can be manifested by muscle spasms that distort one side of the face, twitching of the cheek muscles, and trembling of the lips. Children do not eat anything and may complain of a headache or earache.
The main symptoms of intercostal neuralgia in children are anxiety when changing body position. A baby may cry when picked up, turned over, or dressed. It hurts the child to raise his hands up, to sneeze or cough, or to breathe deeply. Twitching of the back muscles, numbness and weakness in the limbs may occur.
The appearance of redness and a rash around the body at the level of the ribs may be a sign of shingles.
To diagnose the disease, you must contact your local doctor. The pediatrician can make a preliminary diagnosis after examining the child and talking with the parents about the symptoms.
But the doctor also prescribes an examination to exclude other pathologies. This can be an X-ray, MRI or CT, sometimes an ECG. This is especially important for intercostal neuralgia, if the pain is localized on the left side.
After all, it is necessary to exclude heart disease.
The pathology belongs to the field of neurology, so the child is referred for treatment to a neurologist. Consultation with an ENT specialist, dentist, or surgeon is also necessary.
Symptoms
Half facial paralysis
Neuritis in newborns manifests itself in a special way. One half of the face, which is devoid of mobility, looks like a mask and is completely motionless. The difference becomes more noticeable when the baby begins to cry.
If the facial nerve is affected, parents will not be able to evoke the innate search reflex, in which the baby begins to reach out with his mouth to his fingers if the corner of his mouth is touched. With neuritis, the baby cannot fully attach to the breast while eating, and milk begins to flow out of the mouth. In severe cases, effective sucking becomes impossible. On the affected side, the child cannot completely close the eye, and lacrimation begins. In rare cases, dry mucous membranes and conjunctivitis are observed.
In older children, the symptoms of the disease are more pronounced. First of all, the asymmetry of the face is clearly visible. Changes in the cheeks, eyes, and forehead are also noticeable. The lower lip begins to droop, and the nasolabial fold begins to sag. When laughing or talking, the mouth becomes distorted and a baring effect appears. The eyes, like those of babies, do not close completely. A child cannot kiss his parents or whistle. In addition, when chewing food, food remains between the teeth; the taste of food is not felt on the damaged side.
Facial nerve paresis in newborns: symptoms, surgery and treatment at home
This article talks about the symptoms of facial paresis in newborns. Describes the causes, diagnosis, treatment (including surgery), consequences, prognosis and prevention of the disease.
One of the possible complications of the birth process for a child may be facial nerve paresis . The facial nerve moves the facial muscles and is responsible for the first search reflexes (sucking). Damage during childbirth to this nerve is caused by its passage in a narrow canal, which increases the risk of paresis due to prolonged compression of the nerve fiber.
Facial nerve paresis is characterized by immobilization of the muscles on the affected side.
Types of facial nerve paresis
Facial nerve paresis is divided into:
- Central paresis;
- Peripheral paresis;
- Congenital.
Peripheral paresis is a more common complication during childbirth due to local compression of the facial nerve itself. Peripheral paresis is also called Bell's palsy.
Manifests:
- hypotonicity ;
- asymmetry of the face (warping of the mouth, smoothing of the nasolabial fold);
- lagophthalmos (the eyeball points upward when trying to close the eye);
- pain in the area of innervation of the affected nerve, in the ear area, behind it, in the back of the head, in the eye;
- leaking from the corner of the lips;
- drying out of the oral mucosa;
- impairment ;
- disorder ;
- lacrimation or lack of eye hydration on the side of the innervation of the affected nerve.
Central paresis occurs as a consequence of more dangerous birth injuries, accompanied by brain damage, stroke and manifests itself:
- Weakening of the muscles of the lower part of the face;
- Hemiparesis not only of the face, but also of the torso;
- Both sides of the face often affected
- The upper face and eyes retain their function and are not affected by symptoms;
- No taste disturbances.
Congenital facial nerve palsy occurs when there is an abnormality of the facial nerve.
Severity
- 1st degree. It is manifested by a mild course, slight asymmetry of the face with intact closing of the eye (difficulty), frowning of the eyebrows, the corner of the mouth is lowered, the sucking process is disrupted;
- 2nd degree. Characterized by lagophthalmos. When performing functional diagnostic tests (smile, frown, close the eyes), the child does not complete them completely or does not perform them at all. These tests are carried out taking into account age, that is, the newborn does not yet understand human speech to complete the task, so they are carried out when the child is crying or sleeping and can spontaneously smile.
- 3rd degree. It manifests itself in a severe course. Symptoms increased. Severe facial asymmetry, eyes cannot close, diagnostic tests are positive (not performed), difficulty chewing and speaking (almost impossible).
Causes of facial nerve paresis
The most common reasons:
- The main cause is neuritis (inflammation) of the facial nerve;
- Compression of a branch of the facial nerve (birth injuries, childbirth using obstetric forceps, prolonged standing of the head in the pelvic cavity);
- Infectious diseases of the mother during gestation;
- Hypothermia of the newborn;
- Viral and infectious diseases of the child after birth;
- When performing surgery to eliminate another pathology;
- Inflammation of the ear (otitis media). In acute otitis media, paresis occurs as a result of infection of the nerve trunk and is explained by the development of toxic neuritis with swelling of the loose connective tissue surrounding the nerve, and its subsequent compression in the bony canal of the facial nerve;
- May occur with congenital syphilis;
- May occur with multiple complications in case of mumps, polio after birth;
- Tumors;
- A certain role in the development of neuritis is also played by progressive osteitis of perifacial cells, vascular dyscirculatory disorders in this area, as well as dehiscence in the bone wall;
- Central paresis of the facial nerve occurs with damage to the brain, strokes and other pathologies;
- Congenital paresis occurs when there are abnormalities in fetal development;
Symptoms of facial paresis
Symptoms:
- Muscle weakness (hypotonia) in the area of innervation of the facial nerve on one or both sides;
- Pain in the ear area , behind the ear;
- Tearing or drying of the mucous membrane of the eyeball;
- Impaired maternal breastfeeding;
- Leakage of milk from the mouth;
- Increased sensitivity to loud sound;
- Tearfulness;
- The eyelids are open , lagophthalmos on the side of the nerve lesion.
Symptoms develop acutely over two weeks. The subacute phase lasts for a month. And the chronic phase is diagnosed when paresis remains untreated for more than a month.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnostic methods:
- Objective studies are carried out (functional diagnostic tests: smiling, wrinkling the forehead, sucking, stretching the lips with a tube, carried out at rest or while screaming);
- Consultation with other specialists to exclude pathologies and tumors of the face and ear;
- Electromyoneurography to study the speed of nerve impulses;
- CT scan;
- Magnetic resonance imaging (to exclude brain damage);
Treatment of facial nerve paresis
Treatment of damage (paresis) of the facial nerve in a newborn is a gradual process.
Parents need to be patient and follow all the specialist’s recommendations:
- Immediately after birth, the newborn is given special therapy.
- It is also recommended to avoid noise and strong sounds (do not use rattles in games, do not talk loudly), and cover the sore side with a diaper during walks.
- Treatment of concomitant diseases (if any);
- Preparations to relieve swelling of affected tissues;
- Vitamin therapy (B vitamins are prescribed);
- Drugs that stimulate and improve blood circulation (dibazol, lidase, vazonit, sermion and others);
- Corticosteroid drugs to quickly relieve swelling (prescribed for severe disease and with very careful administration and constant monitoring);
- Symptomatic treatment:
- Instillation into the eyes (artificial tears, antibacterial drops (floxal, tobrex, albucid and others) in case of dryness and impossibility of closing the eye);
- Painkillers (ketamine, efferalgan, paracetamol, ibuprofen and others);
- Local treatment:
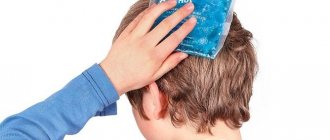
- Applications of paraffin , ozokerite;
- Dry heat (for a newborn, it is enough to heat a soft cloth made from natural substances to body temperature or slightly higher (38 degrees) and apply it to the affected area during sleep, but always under supervision);
- The use of ultrasound in the area of innervation of the affected nerve;
- Physiotherapy:
- Gymnastics should be carried out immediately after diagnosis; it is characterized by innate reflexes aimed at moving the facial muscles.
- For example, when pressing fingers to a child’s lips, the lips are pulled into a tube, and a proboscis reflex occurs; when the skin of the cheek near the lips is touched, the baby begins to look for the chest with his lips, thereby causing motor activity of the muscles; when you press the center of the baby’s palm, he opens mouth.
- Also a positive effect is the use of a pacifier.
- It is carried out symmetrically on both sides of the face.
- The massage should be performed by a specialist.
- massage technique is to prevent atrophy of the facial muscles due to the temporary impossibility of their movement.
- Begin the massage by kneading the neck muscles. At the same time, they tilt their heads in different directions.
- All massaging movements are performed symmetrically and along the outflow of the lymphatic system, but the lymph nodes are not exposed to the massage area.
- If the child begins to be capricious, this indicates pain in the pressure area. In this case, the massage should be carried out using light and superficial techniques.
Treatment at home
Treatment of facial nerve paresis at home is possible only after therapy and prescribed treatment by a specialist.
At home, they recommend:
- learn light but regular massage techniques;
- carry out daily therapeutic physical exercises;
- give medications prescribed by a neurologist.
Read more about the treatment of facial neuritis with folk remedies.
Surgical interventions
Surgical treatment of facial nerve paresis in newborns is carried out for:
- Congenital anomalies of the facial nerve, its exit opening, skull bones and other anomalies;
- Neoplasms that resulted from the occurrence of paresis;
- Complete nerve rupture.
The operation helps restore facial expressions . It is carried out during the first months of the child’s life so that the muscles do not atrophy and the nerve can move them.
When a nerve is ruptured, it is sutured. And in case of congenital pathologies, autotransplantation . That is, a healthy nerve is taken from the child’s leg and sewn into the affected area of the facial nerve. The unaffected branches of the facial nerve are connected to it. In this case, only one facial nerve controls the muscles.
After surgery, it is almost impossible to notice a previous disease. The movement of the muscles of the entire face is restored, and only the scar behind the ear can remind you of surgical intervention.
With early detection and removal of the tumor, the compressed nerve resumes its function completely.
If there is a severe facial defect, cosmetic surgery .
Diagnostics
The main method of diagnosing neuropathy is examination and medical history. The doctor determines the area of damage and the possible cause of the development of facial neuritis. The branches of the nerve pass through the facial muscles, in the area of a special bone located inside the ear, salivary glands and taste fibers. In order to clarify the location of the damage, electroneuromyography is prescribed.
Laboratory tests of blood, urine, stool, cultures to detect microbes and analysis for the presence of viral infections are also prescribed. Based on the results obtained, the degree of damage is determined and a treatment regimen is determined.
Treatment methods
Facial massage for children
When diagnosing neuritis of the facial nerve in a child, treatment is carried out with the help of medications, massage and therapeutic exercises. The goals of therapy are to relieve symptoms and restore facial symmetry.
Drug therapy
If the cause of the development of neuritis has been established, treatment begins with eliminating the underlying pathology. In cases where a cold has caused loss of sensitivity in one part of the face, it is recommended to take anti-inflammatory drugs and means to strengthen blood vessels.
If the cause of damage to the nervous system is a bacterial infection, therapy begins with the prescription of antibiotics. To combat the display virus, take Acyclovir or Interferon. The effectiveness of antiviral drugs for neuritis of the facial nerve in children has been proven. Children are also prescribed corticosteroids such as Prednisolone or Dexamethasone. They help relieve swelling and pain. To strengthen the immune system and improve microcirculation, taking multivitamins is indicated.
Massage
If pronounced facial asymmetry appears, a course of massage is prescribed. The procedure is carried out only after one week after the onset of the disease. This is due to the fact that the impact on the damaged nerve can make the change process irreversible. This is why you should not engage in self-massage. And contact an experienced massage therapist.
10-12 days after the onset of neuritis development, patients are allowed to perform the procedures independently. In this case, it is strictly forbidden to touch the lymph nodes, and movements should be light and superficial. Correct implementation of the procedure, strictly according to the recommendations of doctors, will help to avoid negative consequences.
Gymnastics
Therapeutic exercises after diagnosing neuritis of the facial nerve should be performed daily, twice a day. The duration of the procedure should not exceed 15 minutes.
The occurrence of facial nerve paresis in a newborn
In medicine, complications such as paresis of the facial nerve in a newborn are often encountered. As a result, the muscle tissue on the side where the lesion occurred is immobilized. The facial nerve passes through a narrow canal, so there is a high risk of compression.
Classification
Facial nerve paresis in newborns is divided into the following types:
- Central.
- Congenital.
- Peripheral.
Most often, children experience peripheral paresis. Sometimes local compression of the nerve fibers on the face occurs. Doctors call this condition Bell's palsy.
Peripheral paresis is characterized by:
- Hypotonicity of muscle tissue.
- Asymmetrical facial appearance.
- When you try to close your eye, the pupil points upward.
- Saliva flows from the mouth.
- The place where the nerve is pinched hurts.
- Dry mouth.
- Hearing problems.
- The voice is distorted.
- The eye is poorly moisturized and lacrimation increases.
Central paresis occurs as a result of birth injuries, and a brain disorder or stroke is diagnosed.
Additional signs:
- The muscles on the face weaken.
- Hemiparesis.
- Often both sides of the face become clogged.
- The functionality of the muscles on the upper part of the face is preserved.
- No taste disturbance is observed.
- Congenital paresis occurs when there are defects in the formation of the facial nerve.
Classification by severity:
- Slight asymmetry, the eye closes normally, the eyebrows are slightly frowned, the sucking reflex is difficult to reproduce, the corner of the mouth is directed downward.
- The baby cannot perform the actions necessary for functional diagnostic testing. Such procedures are performed taking into account the age category, since children do not understand human speech. Therefore, such diagnostics are carried out in a state when the baby is crying or is able to smile on his own in his sleep.
- The last degree has a complex course, the symptoms worsen. The eyes do not close, asymmetry is clearly visible, diagnostics reveals the presence of defects and problems with chewing function.
Causes
Let's list the main ones:
- Neuritis or inflammatory process.
- Compression of a nerve branch after an injury.
- Infection.
- Hypothermia.
- Virus.
- Surgery to combat other disorders.
- Otitis.
- Sometimes paresis occurs after infection in the nerve tissue.
- Congenital syphilis.
- New education.
- Mumps.
- Polio.
- Osteitis is a disorder of sebaceous cells, problems with blood vessels or bone tissue.
- Central paresis occurs when the brain is damaged.
The congenital form occurs with various developmental defects of the child.
Diagnostics
We list the common methods:
- Primary testing is for the ability to smile, wince, sucking function, use of lips in a calm state or during a cry.
- Consultation with other doctors is carried out in order to exclude the development of neoplasms and various pathologies.
- Electromyography allows you to determine the speed of passage of a nerve signal.
- CT scan.
- An MRI helps rule out possible brain damage.
What are the complications?
If the child is treated correctly, the prognosis will be positive. Sometimes it is difficult to restore the functioning of the facial muscles, and involuntary contraction may occur.
Sometimes vision problems arise because a baby suffering from facial nerve paresis is unable to close his eyes, the mucous membrane dries out and peels off over time. As a result, the child loses his vision.
Treatment recommendations
To cope with such paresis, you need to contact a specialist as soon as possible. The doctor will conduct an accurate diagnosis, give some advice, and help cope with the symptoms.
Here are the recommendations:
- It is necessary to protect damaged areas under the influence of input. There should be no draft in the room where the baby is. During walks you will have to cover your face with a cloth.
- The room where the child is located should not be noisy. It is not advisable to use rattles or shout during entertainment.
- If the cause of the cut is some kind of pathology, you need to treat it.
Drug therapy
We list the medicine that is used to eliminate signs of paresis:
- An anti-inflammatory agent that helps relieve swelling.
- Vitamins.
- Blood thinning medications.
- Hormonal drugs.
- Corticosteroids.
- Moisturizing eye drops.
- Anesthetics.
Physiotherapy
To combat such disorders, a warming procedure is used. Hot paraffin may be involved. Sometimes a simple cloth is used, which is preheated.
It should be soft and natural material. If you use low-quality fabric, allergic reactions and skin rashes may occur. Ultrasound therapy is used to eliminate precision and pain symptoms.
Massage procedures gymnastics
Specially developed massage techniques make it possible to strengthen the muscles on the face and increase their tone. You can press your finger on the baby's lips when he pulls them into a tube. If you touch the cheeks near the mouth, the baby will begin to move his lips to feel the mother's breast. Thus, the muscle tissue will be strengthened.
Massage procedures help increase tone and improve the conductivity of nerve fibers. It is necessary that all manipulations are carried out with moderate force, the direction of massage should correspond to the treatment of lymph, the location of the lymph nodes has an undesirable effect on the skin. It is necessary to stroke the neck muscles without touching the spine.
Having entrusted such manipulations to a specialist, after some time you can carry out a massage at home, following all the instructions. To get the desired result, massage must be performed regularly at least once a day.
Surgical intervention
What procedures are carried out in the most difficult situations in order to prevent a decrease in muscle tone on the face:
- If the nerve fibers are completely torn, surgery is performed to repair them.
- Autotransplantation, in which a normal one is sutured instead of a congenital effective nerve.
- Removal of the tumor compressing the fibers.
- Plastic surgery.
Helping a child at home
When parents have become familiar with all the features of the course of therapy, they can send the child home and engage in treatment at home. You need to do some physical exercise every day.
Medicines must be taken regularly. The neurologist prescribes the necessary medications, dosage, and determines the duration of the course of treatment.
Forecast
In newborns, the disease develops favorably, and there are no complications if treated in a timely manner. Mild paresis is eliminated without intervention. To avoid the occurrence of contractures, after diagnosis you need to engage in therapy and follow all the doctor’s instructions.
Caring for a newborn contributes to his recovery, improving the functionality of the muscle responsible for facial expressions. Developing disease is rarely diagnosed. Isolation and tension of the tissues, in which the corner of the mouth is directed downward, indicates the presence of pathology.
Prevention
It is necessary to register with the antenatal clinic to determine possible circumstances and the nature of the destruction. If there is a possibility of complications, you can prepare and reduce the risk of negative consequences. Prevention is carried out even during childbirth, if it occurs through natural channels.
The girl needs to avoid the effects of infections on the body; after the birth of the baby, she needs to pay a lot of attention to them, to prevent hypothermia or inflammation. A child develops otitis media; the disease must be diagnosed and treated in time.
If you follow all preventive recommendations, the likelihood of developing paresis will be reduced. The possibility of illness must be prevented after childbirth. When the first signs appear, you need to go to the doctor; if you try to help the child on your own, health problems may arise.
Parents are not able to determine the disease based on external symptoms. To accurately make a diagnosis, you need to conduct several examinations using special medical equipment. Doctors often make a diagnosis after childbirth if paresis occurs due to abnormal formation of nerve fibers. Even with an external examination, it is possible to identify diseases. In some situations, electroneuromyography is performed.
Source: //nevrology.net/sindromy-i-zabolevaniya/perifericheskoj-nervnoj-sistemy/parez-litsevogo-nerva-u-novorozhdennogo.html
Prevention
To prevent re-inflammation of nerve endings, it is necessary to follow a number of rules. First of all, doctors advise protecting the child from stress and hypothermia. Also, in order to prevent inflammation of the facial nerve, you should:
- Make sure your baby is eating properly.
- Give vitamins regularly, especially in the spring and autumn seasons.
- Temper the child.
To improve immunity, doctors recommend taking children once a year to a sanatorium or dispensary, to the sea or a river.
A change of environment, swimming in open water, exposure to the sun and a large amount of vitamins in fruits and vegetables will help strengthen the immune system.