Insomnia is considered one of the most common pathologies, especially in old age, but it occurs in children and adolescents, and pregnant women.
It is not easy to accurately determine the cause of the disease, because it is caused by many factors and has different symptoms.
Sleep disturbances are dangerous not only for health, but also for human life, because it is at this time that the body restores the energy resources spent during the day.
Almost a quarter of all people in the world suffer from constant or periodic insomnia.
Etiological factor
The most common causes of logoneurosis are:
Children and adolescents develop this condition more often than adults. There are separate reasons for each age. In young children who are just learning to speak, logoneurosis may be a normal stage in the formation of the speech apparatus.
Stuttering with logoneurosis does not appear arbitrarily, but only in stressful situations. The triggering factor can be any emotional stress, quarrel, all sorts of strong positive or negative emotions.
The patient's mental state also changes. He becomes more vulnerable and begins to acutely feel his own inferiority. Many patients complain of lack of appetite and sleep disturbances (insomnia or nightmares). The level of anxiety increases significantly, and unmotivated fears may appear. This state of mind, in turn, provokes the emergence of new attacks of neurological stuttering.
What to do: treatment
As in the treatment of any disease, and in the treatment of insomnia, the doctor must not only eliminate the symptoms, but also find out the cause of the pathological condition.
Therefore, using sleeping pills alone will not solve the problem.
In the treatment of insomnia, it is important to adhere to the principles relating not only to the treatment of neurological and mental diseases, but also to eliminating the situation that caused the disease and normalizing sleep and wakefulness.
The most popular drugs prescribed by a doctor:
- barbiturates (antidepressants);
- Phenobarbital;
- drugs that improve cerebral circulation;
- Phenazepam;
- adaptogenic agents;
- antihistamines;
- benzodiazepines.
In addition to taking medications, it is necessary to maintain a daily routine, avoid overeating, and exercise.
You should not take tonics shortly before bedtime, but just before bedtime, you can take a relaxing bath and drink a glass of warm milk. You cannot take medications without a doctor's prescription.
Principles of diagnosis and therapy
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to determine the cause of stuttering. To determine organic brain lesions, it is necessary to do an MRI or CT scan. A psychologist or psychotherapist helps establish the presence of a traumatic agent in the past.
Logoneurosis is a multicomponent disease that requires an integrated approach to treatment. Each patient requires an individual approach and the development of a whole range of measures aimed at eliminating the disease and its consequences.
Classes with a speech therapist help the child get rid of stiffness and learn to pronounce all sounds correctly. Children develop clear and competent articulation of all sounds, which allows them to feel more relaxed in the next stages of treatment. The doctor helps you master the technique of proper breathing and speech. With its help, the patient learns to fully control his own voice and speech apparatus. For this, Harutyunyan’s techniques or Strelnikova’s breathing exercises are used.
Diagnosis of the disease
The main criteria for diagnosing the disease are the complaints of the patient himself.
Based on the history and clinical picture of the disease, the doctor can make a preliminary diagnosis and prescribe additional examinations.
The main criteria for the development of insomnia:
- long time to fall asleep;
- daytime lethargy, drowsiness and weakness;
- irritability, bad mood;
- regular night awakenings;
- getting up early;
- disturbance of the emotional background, mood swings.
If the patient experiences such sensations regularly over the course of a month, then it is worth seriously considering further treatment.
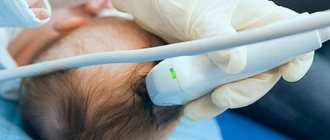
One of the main diagnostic measures is polysomnography. It is carried out only when a person is sleeping, using an electroencephalogram and a special monitor.
The method allows you to accurately determine the duration and ratio of sleep phases, electrical activity of the brain, blood oxygen saturation, and eye movement.
Simultaneously with such a study, a cardiogram of the heart is performed, but signals to the monitor come from all parts of the body.
After which, the information received is converted into a complex graph (hypnogram), which is deciphered by a qualified somnologist. Based on this study and accompanying symptoms, the patient is diagnosed with insomnia.
Logoneurosis
Logoneurosis is a speech disorder that is manifested by repetition of the same words, utterance of individual sounds, conversational pauses and interrupted speech. Logoneurosis according to ICD-10 has code F98.5 - this is stuttering/stammering. Logoneurosis and stuttering are synonymous concepts, but to understand the difference between them, it is worth paying attention to the causes of stuttering. If stuttering is neurotic in nature, then it is logoneurosis. In addition, there is also neurosis-like or organic stuttering associated with physiological reasons. Below we will talk specifically about neurotic stuttering. Logoneurosis prevents a person from living fully, so you need to start fighting it in childhood and as early as possible. The earlier a violation is identified, the easier it is to correct it and the fewer associated problems there are (self-doubt, low self-esteem, anxiety, fear of speaking - logophobia). Before you begin speech correction, you need to identify the causes of logoneurosis. According to statistics, logoneurosis appears in preschool age. Boys are three times more likely to stutter than girls. If logoneurosis is not cured, the person will continue to stutter into adulthood.
Classification of dementia codes in ICD 10
As indicated, any dementia syndrome is included in class F and is additionally coded with a digital designation from 00 to 03. Their systematization and distinctive features are presented in more detail in the table.
Basic codes for dementia in ICD-10
| Name of the disease | Code in the ICD 10 classification | Distinctive features |
| Dementia associated with Alzheimer's disease | F00 | The disease is based on a severe degenerative disorder with specific neurochemical manifestations. |
| Vascular dementia | F01 | Appears due to disruption of the blood vessels in the brain, which in turn cause a heart attack. |
| Dementia developing against the background of other diseases | F02 | The basis of the problem is diseases originally classified in other ICD categories. Accordingly, dementia always appears secondarily. |
| Dementia of unspecified origin | F03 | The causes of the disease are not entirely clear. This ICD 10 group includes many forms of dementia. |
Important! Regardless of which form of the disorder is diagnosed, they are united by two features: the disease always progresses slowly and cannot be cured.
Some forms of dementia in the ICD-10 classification have additional coding because they have exceptional features during the course of the disease, its symptoms or other aspects.
Vascular dementia in ICD-10
Vascular dementia code according to ICD 10 is F01, but this group includes not one, but several separate forms. They are all connected by a common reason - they develop against the background of vascular dysfunction. The time of manifestation of the disease also usually coincides - it occurs at a late age - after 70 years.
Moreover, there are people who are initially predisposed to the development of this form of pathology (diabetics, people suffering from arterial hypertension, smokers). Additional codes are applied due to existing differences:
- F0 - used to designate acute onset dementia as a result of multiple strokes, hemorrhage or cerebral infarction.
- F1 – denotes dementia caused by constantly recurring heart attacks. Most often, this disease affects the cortical structures.
- F2 – intended for cases of dementia originating in subcortical structures.
- F3 – used to designate mixed dementia, developing in both cortical and subcortical structures.
- F8 and F01.9 are vascular dementias, which are based on other problems, often not specified.
The type of vascular dementia and the ICD code are determined as a result of examinations, although they do not have fundamentally different treatment.
Dementia in other diseases
Coding F02 in ICD 10 refers to dementia, the cause of which was various neurological diseases not associated with Alzheimer's or vascular disorders. Their peculiarity is that the age range of manifestations of dementia is much wider, moreover, they are mainly diagnosed at a fairly young age. The group includes:
- F0 – appears as a secondary problem of Pick's disease.
- F1 – dementia based on Creutzveld-Jakob disease. One of the fastest growing forms of the disorder, in which death occurs within a couple of years.
- F2 – dementia in Huntington's disease. It is characterized by extensive degeneration of the brain, and the disease is considered one of the youngest, since it appears already in the third decade.
- F3 – dementia based on Parkinson's disease. It is distinguished by the predominance of motor disorders.
- F4 – is caused by HIV, and therefore always has a complex clinical picture.
- F8 – dementia that begins due to any other diagnosed diseases, if their relationship is proven.
At the same time, the ICD 10 code for dementia in Alzheimer's disease differs from all those listed. It stands out as a separate group, since the disease is most common compared to other forms of disorders.
Alzheimer's dementia
The disorder associated with Alzheimer's disease is also divided into several separate subtypes in ICD 10. They are mainly associated with the period of development of the disease, but there are other nuances that stand out separately:
- F0 – dementia in early Alzheimer's disease. It appears before the age of 65 and develops quite progressively.
- F1 – late-onset Alzheimer's dementia. Often the ICD 10 code for senile dementia coincides with this type.
- F2 – atypical dementia or dementia of mixed type, which arose against the background of Alzheimer's disease.
- F9 – unspecified Alzheimer's dementia.
Strictly speaking, in the realities of Russian medicine, additional clarification of the diagnosis coding for confirmed Alzheimer’s disease is rarely assigned. They do not differ in treatment methods. Is that the speed of development is faster in some places, slower in others.
Dementia unspecified according to ICD 10 is allocated in a separate section. This happens if the patient has not undergone enough research to establish the exact basis of the disease or they have not shown a clear clinical picture. The mixed dementia code according to ICD 10, as well as the senile dementia code according to ICD 10, do not have their own code. In the classification, such disorders join other groups, often with dementia, the exact causes of which are not established.
The wide variety of types and forms of this mental disorder has not led to the creation of unique treatment methods and, by and large, the list of drugs used is the same in all cases. The fact is that in this case, individual elimination of symptoms is much more effective; medications are selected taking them into account.
But this does not mean that you can resort to self-medication. The doctor leading the patient plays a major role in obtaining a positive result. Therefore, whatever the basis of the pathological process and at whatever stage it is detected, it is necessary to immediately contact a specialist who can select medications.
Causes of logoneurosis
Currently, the exact causes of logoneurosis are unknown. Possible reasons include:
- Underdevelopment of the articulatory apparatus;
- When learning conversational speech, the child’s brain was subjected to a heavy load, so a failure occurred, leading to the appearance of a speech defect.
- Imitation. If a child communicates with a relative who stutters, he copies this manner of communication.
- Early development of child speech. The vocal muscles do not have time to cope with a large vocabulary if their formation has not been completed.
- Unhealthy family atmosphere, lack of attention. Children stutter, subconsciously wanting to attract the attention of their loved ones.
- Strictness in education and reprimand (punishment) for pranks.
- Early child language teaching. Due to oversaturation, the children's brain does not have time to absorb information.
- Memorizing huge and complex poems. The speech apparatus cannot withstand heavy loads. If this fact is not taken into account, logoneurosis may develop.
- Retraining a left-handed person to become right-handed, which causes the child a lot of stress.
- Resulting in severe stress or fear.
Correction and treatment of logoneurosis
The diagnosis of Logoneurosis is usually made in childhood or adolescence. If your child develops logoneurosis, treatment must be started immediately. Having discovered speech defects in a child, parents should show him to competent specialists. When stuttering, doctors mainly prescribe the use of medications. The use of medications alone without psychotherapy does not lead to the expected result, because full speech correction is possible only with classes with a speech therapist and psychologist. Also, you should not self-medicate, but rather consult a specialist, as the problem can worsen.
Specialists correct logoneurosis in children without prescribing medications. Specially developed techniques are used to help children and adults get rid of stuttering forever. Activities carried out by specialists before the start of classes:
Parents play an important role in the correction of logoneurosis in children. Their task:
It is more difficult to treat an adult than a child, since the child’s psyche and speech are more plastic, children have a higher potential for compensating for defects. With adults, correction of logoneurosis is more difficult and takes longer. But if the client wishes and exercises regularly, logoneurosis in adults is also eliminated. To correct logoneurosis, the client must strictly follow the recommendations prescribed by the specialist. In some cases, you will need to remain silent for several days and perform special exercises.
Symptoms and signs
With hypersthenic neurasthenia, patients suffer from increased excitability and irritability, loss of emotional and physical strength, increased sensitivity to bright colors, loud sounds, and strong odors.
For example, short-term inhalation of an irritating but harmless aroma or a neon sign of the “wrong shade” can trigger a migraine or a rage attack .
Many neurasthenics experience the development of weather sensitivity, increased sweating, and disturbances in cardiac activity.
As the disease moves into the second stage, patients gradually lose interest in the life around them, become passive, and constantly feel physically exhausted .
“Bells” indicating neurasthenia as the cause of loss of general tone:
- I often suffer from headaches, protracted and pronounced migraines with “prizes” in the form of dizziness, severe nausea from any strong smell. From time to time, the manifestation of a “neurasthenic cap or helmet” is possible: the patient has the feeling of wearing a tight cap, which brings severe discomfort.
- Problems with sleep: it is difficult to fall asleep, rest does not bring relief and vigor, getting up in the morning requires significant volitional efforts. With frequent insomnia, a natural daytime reaction follows in the form of drowsiness, lethargy and depressed mood.
- Emotional imbalance: even the smallest errors in the behavior of others cause irritation.
- Memory fails, the process of memorizing new things takes more time than usual and the result is not pleased with the quality.
- For no apparent reason, the temperature stays several degrees below or above normal.
- The pressure is acting up .
- Interest in sexual life fades to the point of impotence in men and frigidity in women .
- Frequent attacks of dizziness .
- Unstable bowel function , lack of appetite, flatulence for no apparent reason.
- The head often feels unusually heavy.
Where to go?
Over the course of six years of work, specialists have successfully relieved their clients (adults and children) from logoneurosis. Correction of logoneurosis should be carried out by competent specialists. Contact us - our specialists will save you or your loved ones from logoneurosis forever. If necessary, professionals conduct classes at home, in an environment that is comfortable and familiar to the child.
Make an initial appointment for the correction of logoneurosis by phone or fill out the form on the right.
emberint.ru
What is logoneurosis in adults
Nervous speech disorder implies the inability to speak smoothly, with a relaxed speech apparatus, while the patient has no organic reasons for this condition. A person may repeat syllables and words many times, experience throat spasms, nervous twitching of facial muscles, and sudden shortness of breath. In connection with these symptoms, logophobia arises - the fear of speaking. In ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision), logoneurosis has code F98.5.
Stuttering in adults can be explained by the difficulty of self-expression, self-doubt, fear of humiliation, public “shame,” excessive thoughts about how a person looks from the outside and how people perceive him. Often a person does not consider himself worthy to communicate on equal terms, to express himself freely and boldly, he sees himself as uninteresting and “worse than others.” Like all existing neuroses, logoneurosis almost always occurs in sensitive people with high demands on themselves and complexes.
If stuttering haunts an adult throughout his life, one can add to the prerequisites demanding and authoritarian parents, often neurotic, who cut off the child’s attempts to express his individuality.
conclusions
Let's try to draw a few conclusions from the above...
- In the overwhelming majority of cases, neurosis is exactly the same psychosis, but not as tragic and sometimes is reversible.
- Even if we are talking about psychosomatic diseases, then the primacy is still with the psyche, with what it can do to a person.
- Passion for neurology often interferes with medical practice. Thus, effective methods of getting rid of panic attacks appeared only after the syndrome began to be considered a separate mental disorder and treated with psychotherapy.
In fact, the understanding that some condition has exclusively mental roots should inspire optimism, not despondency. For example, if a person has cancerophobia and for a long time he was afraid that he had cancer, and now he understands, has received confirmation, and is sure that these are all just fears in the mind, then he needs to dance with happiness.
Neurosis is in many ways similar to psychosis, but not as tragic
You don’t have to take any antidepressants or antipsychotics. No cancer! All this was just tormenting constructions of consciousness. That’s it, there’s nothing to be afraid of anymore... It’s unlikely that this happiness would overwhelm a person if it turned out that he actually had cancer.
Causes of stuttering
There are several causes of speech disorders:
- Organic brain damage due to strokes, injuries, contusions, as well as due to the development of tumors and infectious diseases of the central nervous system. In this case, it is not logoneurosis; stuttering is treated together with the underlying disease.
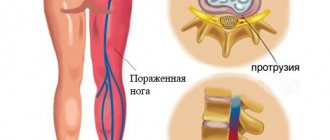
- Cervical osteochondrosis and pinched cervical nerve, subluxations of the vertebrae of the cervical spine.
- The development of neurosis after a strong psychological shock, emotional shock. For example, stuttering may appear after a sudden traumatic event - an attack, a hostage situation, etc. Or develop in connection with the loss of a loved one. Stuttering is not associated with physiological reasons, and occurs periodically, for example, when it is necessary to speak in front of an audience, or in the presence of a certain type of people - for example, women.
- Fear or anger. Temporary stuttering caused by anger or fear goes away with time and does not require treatment. Neurosis with such causes is called reactive or stressful. Despite its unexpressed form, it requires timely diagnosis and treatment, as there is a risk of perpetuating the disorders. Stress stuttering is usually accompanied by twitching or spasms of the facial muscles. It is the unpleasant experiences of one’s speech “inferiority” that can lead to the transition of stress stuttering into habitual stuttering.
- Genetic reasons. Sometimes stuttering develops in people whose parents also suffered from speech neuroses. In this case, the person cannot remember when he spoke without stuttering - the disturbances appeared in childhood, along with the first attempts to speak.
The second and third set of causes relate to logoneurosis. Treatment is carried out in accordance with the identified cause, and is fundamentally different in each case listed above. Correction of neurotic speech disorders in adults is impossible without psychotherapy.
Which doctor should I contact?
Who treats neurasthenia?
Effective therapy for the disorder consists of influencing physical and mental health, therefore, after the patient contacts a therapist, it is necessary to visit a psychotherapist .
Specialists will need to not only correct the patient’s current unstable condition, but also try to find the main emotional cause of the imbalance that has begun in his body in order to prevent a relapse of the disease.
You should not ignore the recommendation to undergo examination and treatment by a psychotherapist. The statement, the essence of which is that most human diseases develop due to problems with the nervous system, is not just a catchy, loud phrase.
Life is full of examples when it was the fortitude of spirit that helped a person overcome unimaginable physical and emotional overloads, which became the last frontier in life for people with a less stable psyche.
And, unfortunately, the “chest” with statistics is no less in volume, when worries about one single fact drove a person to insanity or death.
How does adult stuttering differ from childhood stuttering?
If stuttering began after a shock, quick help in the form of sedatives can prevent the speech defect from becoming permanent. For example, you can offer a person hot tea, a mild sedative, sit him in a quiet place, and cover him with a blanket. However, if the defect appears once, you need to carefully monitor your condition - stuttering may appear in the next stressful situation, and then you will need to treat logoneurosis with a neurologist and psychologist.
Irina, a medical university student, says:
I started stuttering when I got my first C in my life on an exam. This put me under terrible stress, I cried all day, couldn’t eat or sleep, and during the next oral exam I noticed that I was stuttering. Fortunately, I soon got rid of this problem without doing anything special. The stress just went away. It was the penultimate exam of the winter session, and I had the opportunity to recover.
Psychologists note: logoneurosis in adults differs from childhood stuttering in that a person is able to speak normally in a calm state, but in a situation of stress begins to stutter. In addition, children often have repetition of syllables even in their thoughts, while in adults, internal speech remains free. The onset of stuttering in adulthood is much less common than in childhood. It is believed that “adult” stuttering is more treatable. But self-medication - self-prescription of drugs such as Pantogam or others - rarely contributes to a final cure.
Externally, logoneurosis in children and adults looks exactly the same. Spasms of the palate, lips, tongue, larynx, as well as respiratory spasms with a feeling of lack of air may be present. But at the mental level in adults, speech disorders often coexist with other neurotic symptoms - anxiety, unreasonable fear, a feeling of melancholy, a feeling of inferiority, poor sleep, sweating, appetite disturbances.
Symptoms
With bronchial obstruction, there is wheezing, difficulty breathing, whistling when exhaling, and a persistent, unproductive cough may occur. In general, the symptoms of this disorder largely depend on the cause of its development and the rate at which the obstruction increases.
Along the way, 4 forms of this syndrome are distinguished in children and adults:
- spicy;
- protracted;
- recurrent;
- continuous.
Acute broncho-obstructive syndrome is one of the most severe forms of pathology. In some cases, symptoms increase very quickly and cause severe respiratory failure. In other cases, a specific clinical picture is observed within one week.
Prolonged broncho-obstructive syndrome is a pathological condition of bronchial obstruction, the symptoms of which persist for a week and a half or longer. Broncho-obstructive syndrome is called recurrent, occurring in an acute form and exacerbating three times a year. As a rule, this form of pathology is associated with a seasonal allergic reaction or exacerbations of bronchial asthma.
Continuous broncho-obstructive syndrome is a dangerous pathology, manifested by very frequent relapses with short remission between attacks.
Symptoms in children
A child with broncho-obstructive syndrome will feel severe lethargy and weakness
In general, the general symptoms are the same for children and adults, the difference is only in the general well-being of the patient. Children experience difficulty breathing hoarsely with a characteristic whistle when exhaling. General health depends on two factors – the cause of the biofeedback and the severity of the symptoms of the disorder. With a mild form of broncho-obstructive syndrome, the patient generally feels well, but if the obstruction is associated with infectious diseases, the patient's condition will depend on the severity of the underlying disease. At the same time, body temperature may increase, and in some cases symptoms of general intoxication appear.
With broncho-obstructive syndrome of moderate severity, the child feels constant fatigue, but at the same time becomes moody. Against the background of pulmonary obstruction, severe weakness, refusal to eat, lethargy and apathy are observed. Children develop a dry cough, sleep deteriorates, and nightmares are possible.
In case of severe broncho-obstructive syndrome, the patient needs urgent help. This condition is manifested by the following symptoms:
- severe wheezing when inhaling, which can be heard over a long distance;
- constant shortness of breath;
- dizziness;
- inability to take a deep breath;
- cyanosis of the skin.
The child feels severe weakness, dizziness, and “spots” may appear before the eyes. If such symptoms appear, it is necessary to call a doctor at home as soon as possible; with severe manifestations of broncho-obstructive syndrome, emergency care is needed.
Symptoms in adults
Manifestations of broncho-obstructive syndrome in adults are generally the same as in children. Typical signs of this disorder:
- wheezing in breathing;
- whistling exhalation;
- dyspnea;
- severe weakness;
- prostration;
- apathy;
- cyanosis of the skin.
The severity of broncho-obstructive syndrome can be determined by the intensity of symptoms. Thus, mild manifestations of obstruction are wheezing breathing, in which it is difficult to take a deep breath. The skin may be slightly paler than usual, but there is no obvious cyanosis.
Broncho-obstructive syndrome of moderate severity in adults is characterized by shortness of breath that appears on exertion, general weakness, and breathing problems. The bluishness of the skin is moderate.
A severe form of the pathology is accompanied by severe shortness of breath at rest, lack of air, and severe wheezing when inhaling. Cyanosis is pronounced, the patient feels severe weakness, accompanied by dizziness and darkening of the eyes. Such symptoms indicate developing hypoxia and are very dangerous.
Treatment of logoneurosis in adults
Let's talk about how to treat stuttering. First of all, the disease is treated by restoring the harmony of the nervous system through effects on the body. This goal can be achieved by a variety of methods - reflexology, physiotherapy, herbal medicine and the prescription of a medicine such as glycine or novopassit. The direction of treatment is chosen by the neurologist after examining the patient. Often several treatment methods are prescribed - for example, taking sedative herbs and acupuncture, or osteopathy and acupressure, or physiotherapy and manual therapy.
With the help of these methods, the emotional background is leveled, the transmission of nerve impulses is improved, the body's stability is increased, the excitation of the autonomic nervous system is reduced, and, as a result, symptoms are alleviated. In addition, quality sleep returns, mood becomes good, the overall tone of the body increases, and depressive states disappear.
Typically, integral therapy methods are prescribed in combination with speech therapy treatment. A speech therapist helps a person get rid of fear and constraint by repeatedly pronouncing problematic sounds. A speech therapist can also teach the patient breathing exercises and proper breathing. With mild forms of logoneurosis, patients completely get rid of unpleasant symptoms and regain the joy of communication.
If the problem goes away only temporarily or not completely, more serious treatment for logoneurosis is needed. This means that the reasons are deeper than a simple “nerve disorder” from fatigue and overexertion. A psychotherapist teaches a person auto-training and relaxation techniques, analyzes the causes of stuttering, helps eliminate the fear of speaking and increase self-confidence. We are also working with psychological trauma. Psychologists use the following techniques:
In some cases, the psychotherapist prescribes nootropic drugs - for example, piracetam, phenotropil, gopantam, anvifen, noofen, phenibut or pantogam. The most popular nootropics are the last two, they are prescribed most often. Pantogam has an anticonvulsant effect. Both phenibut and pantogam contain hopantenic acid, which stimulates brain function, reduces its sensitivity to stress factors and has a mild sedative effect. Which drug is better? Only your doctor can answer this question.
In the video, an adult man tells his story - how hard it was for him to study at school, what a torment literature classes were for him, and how often stuttering interfered with his life. The problem followed him even after school. What helped the hero of the video get rid of his illness was the need to overcome fear and anxiety when communicating with a stranger.
Living with a stutter is difficult, because success in society, self-esteem, personal life, and career advancement depend on the ability to communicate. If the symptoms of logoneurosis are combined with other neurotic manifestations, it is necessary to find out the causes and cure it.
psihodoc.ru
Classification
The disorder has been the subject of close study by representatives of the scientific world since the 19th century.
In 1869, the complex of symptoms was given a term that is still used today.
And only after more than 30 years, the disease was identified as a separate disease , justifying its differences from the signs of schizophrenia and other mental disorders.
Mental health specialists distinguish two main types of neurasthenia: hypersthenic and hyposthenic. In some cases, the second is a consequence of the lack of adequate therapy for the first.
Symptoms of logoneurosis and specific treatment of the disease
Logoneurosis (lalonervoz, speech neurosis) is a form of stuttering that appears as a symptom of neurosis. According to ICD 10, logoneurosis refers to mental disorders and behavioral disorders and is not a separate nosological entity. Logoneurosis can occur in both children and adults.
Logoneurosis or speech neurosis can develop as a reaction to a strong stress factor or be a consequence of organic brain damage.
- Brain injuries, infectious diseases in which the infectious agent is tropic to the nervous tissue, cerebral palsy, tumor neoplasms, disorders of brain trophism, strokes;
In adolescents, the cause of neurotic stuttering is mental instability, increased emotional excitability, a tendency to dramatize and excessive impressionability.
Speech disorders appear as a response to family troubles and frequent conflicts. If the situation in the house is tense, there are constant conflicts, then a child, and especially a teenager, may react to this with speech problems.
Causes of insomnia
The development of insomnia has its own characteristics and occurs differently in children, the elderly, and pregnant women.
Not only the causes and symptoms, but also treatment methods depend on this.
Causes of sleep disturbance in adult men and women:
- prolonged stress;
- binge eating;
- drinking strong coffee (tea) at night;
- chronic diseases;
- jet lag;
- overwork;
- alcohol abuse;
- depression;
- poor sleep hygiene;
- taking certain medications;
- emotional experiences;
- change of usual environment.
In addition, asthma, cancer, and diabetes can cause insomnia. Psychological phobias and physiological changes are considered no less dangerous.
Unfortunately, children of preschool age often suffer from problems falling asleep, but this disorder is not uncommon among adolescents.
It is the child’s body that insomnia causes the greatest harm, because during rest the child produces the hormone somatropin, which directly affects the full mental and physical development.
Most often, the disorder occurs in children under 3 years of age, and the cause can be teething, certain diseases, or external factors.
Insomnia in adolescents is often provoked by emotional experiences, increased stress at school, problems in the family, and excessive physical activity.
It happens that sleep problems are caused by malfunctions of the endocrine or nervous system, vascular diseases, and heart diseases. In the first case, the situation will be corrected by strict adherence to the daily routine, rationing of exercise and light soothing decoctions, and in the second, immediate consultation with a doctor.
Almost 98% of pregnant women suffer from insomnia, especially in the last trimester of pregnancy.
It occurs both due to physical inconveniences, such as pushing the baby, lower back pain, cramps, and an emotionally unstable state before childbirth.
During this period, it is important not to use any sedatives so as not to harm the child. On the advice of a doctor, you can drink motherwort or valerian decoctions at night, but in limited quantities.
Very often you can hear complaints of insomnia from older people, and the reason for this is deep stress after retirement, a change in the usual routine, and impaired cerebral circulation.
In old age, many chronic diseases worsen, hypertension and heart failure develop.
These factors lead to unnecessary emotional shocks that interfere with a good night's rest.