Who is at risk? ↑
Over the past decades, the number of cases of dyscirculatory encephalopathy has increased significantly, amounting to about 6% on the entire planet.
Most often, DEP is diagnosed in people who have not reached retirement age, after 45 years, but there are cases of earlier development of the pathology and even cases of the disease in children cannot be excluded. Despite the fact that DEP occurs more often in able-bodied people, the risk of developing the pathology is also high in old age. The reason for this is diseases that often occur at retirement age and contribute to the development of DEP, for example, diabetes mellitus or arterial hypertension. It is dyscirculatory encephalopathy that is one of the main causes leading to the development of senile dementia.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tbqO2FNYU9Y
An interesting fact is that people who are engaged in intellectual activity, that is, mental work, as well as creative individuals are more susceptible to the disease. All this is due to the fact that their brain is forced to work actively, without proper rest, and such people do not have enough physical activity.
Degree of severity of dep ↑
Depending on the clinical manifestations, it is customary to distinguish three degrees of severity of this disease:
- 1st degree. In the initial stage of the disease, subjective sensations appear. The patient notes decreased performance, mood swings, sleep disturbances, decreased memory, and increased fatigue. In most cases, there are no objective signs.
- 2nd degree. It is characterized by more obvious manifestations of the disease. Neurological disorders are noted. Upon examination, a neurologist can detect deviations from the norm in the psychological and emotional sphere.
- 3rd degree. The last stage of DEP is characterized by serious neurological changes. The patient's mental state becomes unstable, there may be attacks of aggression, and coordination is impaired. In some patients, the functions of the visual and sensory systems are impaired. Mental abnormalities, lethargy, and periodic fainting are observed.
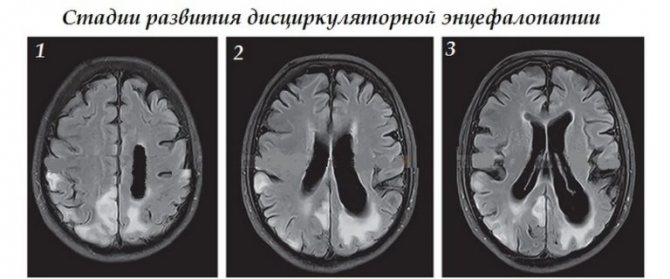
Dyscirculatory encephalopathy has three stages of severity. Depending on which of them the pathology was detected, the further prognosis largely depends.
DEP refers to chronic pathologies that gradually progress. It is interesting that the transition from one degree to another can take more than five years, or it can occur quickly and in just a few years you can move from the first stage to the third.
In total, there are three degrees of severity:
- Discirculatory encephalopathy of the 1st degree, as a rule, has no objective symptoms. All that the patient or his relatives can notice is a partial decrease in memory, and this is often attributed to age, increased fatigue, and mood swings. That is, all the symptoms that cannot accurately indicate a particular disease;
- DEP of the second degree has more obvious manifestations of the disease. Here neurological disorders may already appear, as well as psycho-emotional deviations;
- discirculatory encephalopathy of the 3rd degree is the last and most difficult stage. The main goal of treating DEP is to prevent the development of this degree of severity and the course of the pathology. In this case, the clinical picture is pronounced, there are uncontrolled mental disorders and neurological symptoms. The patient becomes uncontrollable, he may experience attacks of aggression, memory loss, problems with coordination and movement in general, and much more.
Symptoms of prostate hyperplasia 3 degrees
The symptoms of this disease progress gradually and reach their greatest severity by the third stage. The patient may experience:
- severe difficulty in the outflow of urine;
- an increase in the volume of residual urine in the bladder to 150-200 ml;
- stretching of the walls of the bladder, loss of their ability to contract. The contours of the organ look like a neoplasm, their borders can reach the navel;
- involuntary drip of urine both at night and during the day;
- general weakness, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite and weight loss, constipation, thirst, dry mucous membranes, hoarse voice. This set of signs indicates a critical decrease in kidney functionality and general intoxication of the body with waste products;
- the smell of urine from the mouth is considered one of the correct diagnostic symptoms of BPH grade 3;
- psycho-emotional disorders - depression, apathy, anxiety, insomnia.
Intensification of symptoms can be caused by low mobility, hypothermia, attempts to hold urination for a long time, as well as the use of alcohol and certain medications, such as painkillers.
What causes dep? ↑
In addition to intellectual work and a sedentary lifestyle, there are a number of reasons that can lead to the development of pathology. The main ones:
- arterial hypertension. This disease is the scourge of the 21st century. At first glance, nothing supernatural, just high blood pressure. But not everything is so simple, it is pressure surges and high levels that lead to disruption of the integrity of the vessels of the brain; they can, for example, burst from the strong pressure of the blood flow, as a result of which plasma and blood enter the cavity of the ventricles of the brain, which leads to hypoxia and death of neurons. It is for this reason that heart attacks most often occur, so people suffering from hypertension should control their blood pressure;
- hypotension, that is, low blood pressure, also negatively affects brain function. In this case, the situation looks different. Due to insufficient pressure, the blood flow is weak and critically little oxygen is delivered to the brain tissue, which also leads to hypoxia;
- atherosclerosis is a disease of old people, as well as lovers of fatty and fried foods. Atherosclerotic plaques are fatty clots of cholesterol that wander along with the blood flow through the vessels. They arise as a result of high cholesterol, and the latter, in turn, is formed due to poor nutrition. These plaques, “travelling” through the vessels, can enter the arteries of the brain, where they attach to these walls, reducing the lumen and preventing the flow of oxygen. At one point, the vessel may be completely blocked, which will lead to severe hypoxia. Atherosclerosis is one of the main causes of ischemic stroke;
- osteochondrosis. Lack of movement, a sedentary lifestyle, and working in one position all lead to deformation of the cartilage tissue of the vertebrae. The most common is cervical osteochondrosis, and as a result, the cartilage, being deformed, compresses the vessels leading to the brain, thereby also causing a lack of oxygen;
- traumatic brain injuries. After an injury, a hematoma can form in the brain, which compresses the surrounding capillaries and vessels.
This is not a complete list of possible causes of DEP, but they are the most common in history.
Causes of pathology and its varieties
Before starting treatment for DEP, you need to understand the causes of its occurrence and the types of this disease. Pathology often develops as a result of the patient’s poor lifestyle in combination with the effects of other diseases on the body. Severe pathologies that have not been completely cured also affect blood vessels.
In the presence of exposure to additional unfavorable factors, dangerous changes begin to develop in cerebral vascular tissues, which is the trigger for the occurrence of dyscirculatory encephalopathy.
Sometimes a single pathology leads to this disease, but very often there are several of these pathologies, and because of them, different vessels are damaged. In this case, they say that the disease is of mixed origin. Among the main reasons that provoke the development of DEP are:
- Hypertension. Due to frequent cases of increased pressure, the vessels lose their elasticity, and cracks form on their walls, through which blood enters the brain tissue. This leads to the development of pathologies.
Hypotension. It causes insufficient cerebral blood supply, resulting in oxygen starvation.- Atherosclerosis. With this pathology, cholesterol deposits form in the vessels, blocking the blood path to various organs, including the brain.
- Excessive thickness of blood. This feature increases the risk of blood clots.
- Deviations in the functioning of the endocrine system. Because of them, the production of certain useful substances stops or decreases. This causes destruction of the walls of blood vessels. This feature is the cause of the development of DEP in women during menopause.
All these and some other pathologies can cause problems with cerebral vessels. Therefore, patients with such diseases should be especially careful. The development of DEP can be accelerated by harmful external influences and dangerous habits of the patient himself. This means that it is necessary to give up bad habits and poor nutrition, rest more often, play sports, etc.
Features of stage 3
The development of vascular dementia is observed. All symptoms progress and become more pronounced.
Seizures similar to epileptic ones appear, and intelligence decreases.
A person becomes unable to care for himself; he requires constant attention and care. His fate depends entirely on those around him.
Urinary incontinence is observed, walking is impaired, and dementia develops. The patient loses the ability to learn new skills.
Ultimately, grade 3 dyscirculatory encephalopathy ends in disability, and in especially severe cases, death.
The transition from mild to severe forms can sometimes exceed 5 years, but there are cases when the stages of DEP change rapidly, in less than 2 years.
The last stage of discirculatory encephalopathy (DEP) is characterized by serious disorders.
The psyche of a person affected by this disease becomes unstable, he has problems with coordination, and attacks of aggression occur.
In some cases, the patient's sensory system is disrupted. Seizures that are very similar to epileptic ones appear, intelligence deteriorates, and elderly patients are at risk of developing dementia.
A person becomes unadapted to life and requires round-the-clock attention and constant care.
The first stage goes unnoticed, and the symptoms can be confused with other diseases or the consequences of injuries.
Characteristic:
- Noise in the head.
- Dizziness.
- Headache.
- Sleep disturbances, insomnia, dysania (weakness, feeling unwell when waking up, difficulty getting out of bed).
- Memory impairment, absent-mindedness.
- Decreased cognitive activity.
- The appearance of instability when walking, stiffness of movements.
Causes of dyscirculatory encephalopathy
A mass of vascular disorders can cause a diagnosis of “grade 3 dyscirculatory encephalopathy.” The prognosis is extremely disappointing. It is very important to prevent its onset.
- Arterial hypertension is an increase in blood pressure.
- Atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels is a disorder of the functioning of the arteries.
- Simultaneous presence of atherosclerosis and arterial hypertension.
- Inflammatory processes – vasculitis of various origins.
Contribute to the progression of the disease: alcoholism, advanced osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, chronic stress and overexertion.
The development of DEP is a consequence of capillary pathology, which is why nutrients do not enter the brain in the required quantities.
The reasons for this may be the following:
- hypotension;
- hypertension;
- atherosclerosis;
- osteochondrosis;
- increased blood viscosity;
- patient smoking;
- congenital anomalies (angiodysplasia);
- hematomas;
- pathologies of blood vessels and blood (thrombophlebitis, vegetative-vascular dystonia);
- hormonal imbalance.
The transition to the third degree of DEP is facilitated by frequent stress, smoking and drinking alcohol, and osteochondrosis.
Discirculatory encephalopathy develops due to the pathology of the capillaries, as a result of which they cannot fully supply the brain matter with nutrients and oxygen.
This happens for the following reasons:
- Hypertension causes damage to the integrity of blood vessels. They overlap and burst, causing brain matter to absorb plasma or blood. Harmful substances can also enter when the walls of blood vessels lose elasticity.
- Hypotension. The capillaries are weakly filled with blood, it slowly flows through them.
- In atherosclerosis, cholesterol plaques clog blood vessels. Due to improper metabolism, fats accumulate on the walls, gradually the lumen decreases and is completely blocked. Under such conditions, blood does not reach all parts of the brain.
- Osteochondrosis of one of the spine sections. With this pathology, the brain receives less blood than it should due to compression by spasmed muscles and bone processes of the vertebral artery.
- Impaired blood circulation can be caused by increased blood viscosity, which causes platelets to stick together and form clots or thrombi. They block the vessel, and the part of the brain that it supplied gradually dies.
- Nicotine addiction leads to a decrease in the lumen of capillaries, this is especially pronounced in the brain. With prolonged smoking, this condition becomes irreversible.
- Pathology of blood vessels and blood reduces the speed of movement of the latter throughout the body. Such diseases include thrombophlebitis and vegetative-vascular dystonia.
- Disturbances in the functioning of blood vessels are observed with congenital anomalies (pathological development of veins and arteries, angiodysplasia).
- Hematomas formed due to brain or spinal injuries. They put pressure on the capillaries, compress them, and impair the access of oxygen and nutrients to the nerve cells.
- Hormonal imbalance. Endocrine glands produce hormones that regulate the state of the lumens of blood vessels in the brain. With their pathology, the production of hormones is disrupted. A hormonal imbalance often causes the development of dyscirculatory encephalopathy in women during menopause.
The transition of the disease to stage 3 is facilitated by stress, emotional stress, smoking, alcoholism, and osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.
You can study what autonomic dysfunction is and how it manifests itself in our article.
Inability to coordinate movements, spinocerebellar ataxia - features of symptoms and treatment of the disorder.
- Hypertension causes damage to the integrity of blood vessels. They overlap and burst, causing brain matter to absorb plasma or blood. Harmful substances can also enter when the walls of blood vessels lose elasticity.
- Hypotension. The capillaries are weakly filled with blood, it slowly flows through them.
- In atherosclerosis, cholesterol plaques clog blood vessels. Due to improper metabolism, fats accumulate on the walls, gradually the lumen decreases and is completely blocked. Under such conditions, blood does not reach all parts of the brain.
- Osteochondrosis of one of the spine sections. With this pathology, the brain receives less blood than it should due to compression by spasmed muscles and bone processes of the vertebral artery.
- Impaired blood circulation can be caused by increased blood viscosity, which causes platelets to stick together and form clots or thrombi. They block the vessel, and the part of the brain that it supplied gradually dies.
- Nicotine addiction leads to a decrease in the lumen of capillaries, this is especially pronounced in the brain. With prolonged smoking, this condition becomes irreversible.
- Pathology of blood vessels and blood reduces the speed of movement of the latter throughout the body. Such diseases include thrombophlebitis and vegetative-vascular dystonia.
- Disturbances in the functioning of blood vessels are observed with congenital anomalies (pathological development of veins and arteries, angiodysplasia).
- Hematomas. formed due to brain or spinal injuries. They put pressure on the capillaries, compress them, and impair the access of oxygen and nutrients to the nerve cells.
- Hormonal imbalance. Endocrine glands produce hormones that regulate the state of the lumens of blood vessels in the brain. With their pathology, the production of hormones is disrupted. A hormonal imbalance often causes the development of dyscirculatory encephalopathy in women during menopause.
You can study what autonomic dysfunction is and how it manifests itself in our article.
Inability to coordinate movements, spinocerebellar ataxia - features of symptoms and treatment of the disorder.
First stage of the disease
Interesting fact! The diagnosis of first-degree depression is more often made in children and adolescents; in adulthood, as a rule, the second degree is diagnosed immediately.
At any age, it is very difficult to determine DEP at the first stage, since the disease at this stage does not have any specific signs. Thus, the patient may experience some of the following symptoms:
- dizziness;
- headache;
- increased feelings of fear and nervousness;
- sleep problems;
- increased fatigue;
- surge pressure;
- noise in the head.
As you can see, all the symptoms are quite ordinary and are often simply attributed to overwork or diagnosed with another, less serious disease, without reaching the truth.
How does the disease manifest itself?
Symptoms of discirculatory encephalopathy fully manifest themselves at stage 2. The patient's mental state changes, problems with vision and hearing arise, and emotional instability is observed. At the last stage, pathological changes become irreversible, they progress rapidly, and the symptoms of the disease become pronounced. The clinical picture of grade 3 encephalopathy includes the following manifestations:
- change in character (the patient becomes aggressive, irritable, conflict-ridden);
- deterioration of vision and hearing up to complete blindness and hearing loss;
- problems with coordination of movements (gait becomes unsteady, holding objects in hands becomes impossible);
- apathy, lethargy, lack of interest in what is happening around (the patient reacts inadequately to events);
- speech impairment (spoken words become slurred, voice volume decreases);
- deterioration of intellectual abilities (at stage 3 of the disease, the patient cannot solve simple problems, his ability to remember and assimilate new information decreases);
- inability to control physiological processes (urinary and fecal incontinence, problems with swallowing and breathing);
- memory impairment, loss of writing and reading skills;
- trembling of the limbs, paralysis and paresis, convulsive seizures.
In case of stage 3 discirculatory encephalopathy, the patient is assigned disability group 1. A person cannot live a normal life, perform professional tasks and daily activities. The patient himself is not aware of the problem and does not complain about deterioration in health.
Stage 3 DEP is characterized by serious impairment of vital functions.
The patient experiences severe headaches, tinnitus, disturbed sleep, sudden mood swings, increased fatigue, and a significant decrease in performance.
Such changes occur due to damage to the subcortex of the brain, where information centers are located. They control sleep and are responsible for the functioning of the body’s sensory systems (hearing, vision).
When the integrity of the capillaries is disrupted, a microstroke develops. As a result, the mental center suffers.
It becomes difficult for the patient to focus on specific things, memory decreases, and it is difficult for him to imagine the final result of his actions.
If the medulla of the frontal lobe is affected, emotional instability, depression, indifference, attacks of aggression, hysterics, and apathy are noted.
The process of transmitting information from nerve cells to organs is disrupted.
It becomes difficult for the patient to coordinate movements, walking changes, it becomes unsteady. On examination, the tendons and muscles are in spasm.
The patient loses the ability to perform the simplest tasks of self-care.
He needs care, the constant presence of a person who will help him.
When the occipital lobe is damaged, vision is affected. Sometimes symptoms of oral automatism are observed: a nasal voice, opening of the mouth when some part of the body is irritated, difficulty swallowing.
This disease is characterized by disturbances in the vital functions of the body.

Symptoms of grade 3 dyscirculatory encephalopathy at the beginning of the development of the disease are manifested by pain in the head, tinnitus, the patient complains of insomnia, increased fatigue.
A person’s performance sharply decreases, and causeless mood swings appear. The reason for this is damage to the subcortex of the brain, where the areas responsible for sleep and vision and hearing are located.
After a violation of the integrity of the capillaries, a micro-stroke may develop, due to which the patient cannot concentrate on something specific and his memory decreases.
When the frontal lobe is damaged, emotional instability, apathy, depression, and attacks of aggression appear. When the occipital lobe is damaged, vision problems appear, the patient's voice becomes nasal, and breathing becomes difficult. If the transmission of information from nerve cells to organs is disrupted, the patient has problems with walking and coordination of movements, and urinary incontinence appears.
The patient loses the ability to care for himself independently; he needs round-the-clock help from another person and constant attention.
The patient loses the ability to perform the simplest tasks of self-care.
Clinical picture of the second degree dep ↑
At this stage, the symptoms become more obvious, and DEP is most often identified during this period. Clinical picture characteristic of second degree depression:
- the first degree symptoms described above;
- nausea and vomiting not associated with food intake;
- problems with coordination of movements, gait becomes uncertain and shaky. The patient often loses his balance and may fall out of the blue; problems with speech, it becomes slow, diction is slurred. the patient finds it difficult and takes a long time to find words to express his thoughts;
- deterioration of memory, thinking, concentration and other cognitive changes develops;
- mental and emotional disorders. The patient becomes more aggressive, experiences depression, anxiety and even panic;
- The clinical picture of multiple sclerosis develops. Encephalopathy is one of the main causes of multiple sclerosis.
For the second degree of DEP, the risk of developing disability is high; patients are often assigned a third disability group; in some cases, group 2 may be assigned.
Treatment approach
The process of treating third-degree dyscirculatory encephalopathy contains many difficulties along the way. For complete recovery, strict adherence to all prescribed recommendations is necessary.
You need to start with nutrition - the patient is prescribed a special diet with limited salt and fat. It is imperative to take vitamins.
Psychotherapy also plays an important role - the patient will recover more easily if certain goals are set for him to achieve.
This will help the patient understand that there is a chance to get rid of the disease, and he can do it. To get rid of this disease, both drug treatment and surgical intervention will help.
In addition to medication and surgery, some methods of physiotherapy are also used to treat grade 3 DEP: hirudotherapy, massage, acupuncture, cryotherapy, etc.
Medication
To get rid of stage 3 DEP through medication, medications are prescribed that help restore blood flow, renew nerve cells, and remove the cause of the disease itself.
The following groups of drugs are used:
- diuretics;
- antihypertensive drugs;
- vasodilators;
- anticonvulsants;
- neuroprotectors;
- psychotropic drugs.
Surgical
Surgery is used when prescribed medications are no longer able to cope with the problems.
Most operations are performed on the walls of great vessels. For the operation, you can use local anesthesia.
After anesthesia, an introducer is inserted into the artery, with which you can insert the instruments necessary for the operation. With the help of these instruments, the narrowed vessel expands to the desired size.
The goal of therapeutic measures is to treat the underlying pathology, eliminate lesions and restore brain function, protecting it from oxygen starvation.
Treatment of grade 3 dyscirculatory encephalopathy is complex.
To eliminate the pathology and restore the condition of the brain cells, you need to strictly follow all the recommendations.
A diet with limited salt and fat is prescribed. The use of vitamins is mandatory.
It is important to engage in psychotherapy.
The patient will recover more easily if he is occupied with certain tasks that he can perform. This approach will help him realize that there is a chance for recovery.
Several drugs are prescribed at once to ensure normal blood flow, restore nerve cells and eliminate the cause.
The following drugs are used:
- Lisinopril is a drug to lower blood pressure if hypertension has led to the development of DEP.
- Acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) – thins the blood, prevents platelets from sticking together and blocking blood vessels.
- Curantil - helps to increase the lumen of capillaries, strengthens their walls.
- Nimodipine - blocks the supply of calcium to the muscles, which leads to their relaxation and improved blood flow. As a result, movements improve and the ability to think sensibly is restored.
- Atenolol - removes excess fluid from the body, normalizes heart function, increases blood flow, reduces heart rate and blood pressure.
- Vasobral - protects brain cells from oxygen starvation, prevents the formation of blood clots, improves metabolic processes in the subcortex, and restores functions.
- Ginseng tincture is a natural remedy. It helps increase productivity, improves brain function, cardiovascular system, reduces the amount of cholesterol in the blood, and fights increased fatigue. However, the use of ginseng tincture for hypertension is contraindicated.
Physiotherapeutic methods are also used in the treatment of grade 3 DEP: electric sleep, massage, galvanotherapy, baths, laser and UHF therapy.
This method is used if drug treatment does not give the desired results. Surgery is performed on the great vessels.
Treatment of the disease
Discirculatory encephalopathy of the 3rd degree is difficult to treat, but the patient’s condition can be corrected. The goal of therapy is to normalize blood pressure, improve blood circulation and restore cell metabolism. Otherwise, the remedies are selected individually depending on the symptoms and severity of the disease. Diuretics and analgesics are often used, as well as venotonics if the patient suffers from cephalgic attacks.
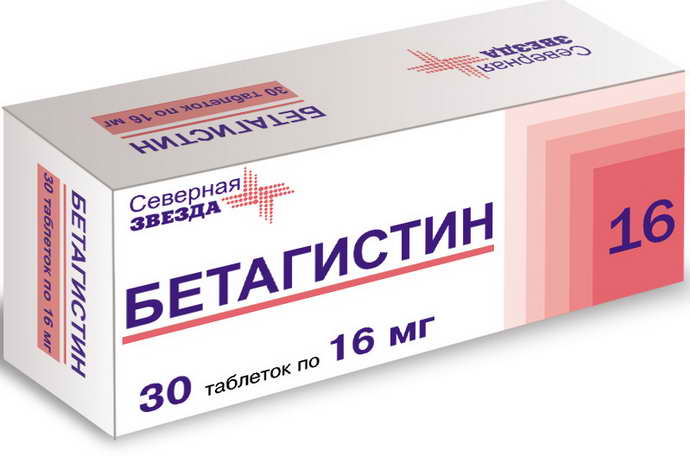
For dizziness and other vestibular disorders, the drugs chosen for the treatment of discirculatory encephalopathy are betahistine and daedalone. If the patient develops nervous or dyssomnic syndromes, drugs with a mild sedative effect are used.
Important! Cognitive disorders can be corrected with nootropics and herbal remedies (pantogam, tanakan, piracetam).

During treatment for grade 3 encephalopathy, it is important to follow an organic diet with a minimum of salt and unhealthy fats. It is recommended to take vitamin C and substances that reduce cholesterol concentrations. Hormones are also prescribed. Treatment methods, dosages and duration are prescribed by the doctor.
Stage 3 discirculatory encephalopathy is a complex neurological disease, the prognosis for which is unfavorable in 80% of cases. Especially when the pathology is detected in people of retirement age. The only thing that can be done to make the patient feel better is to provide him with all possible assistance, use medications to eliminate symptoms and take care of peace of mind.
Signs of third degree dep ↑
Encephalopathy grade 3 is extremely difficult. As a rule, the patient is assigned the first disability group. In addition to all the previously listed symptoms:
- epileptic seizures;
- development of dementia against the background of decreased intelligence;
- development of vascular dementia;
- urinary incontinence occurs;
- the ability to move is lost.
The patient is no longer able to take care of himself independently; the basic skills that he used previously disappear.
Diagnostics
Nowadays, diagnosing osteoporosis is quite easy. The following methods are used for diagnosis:
- Radiography.
- Ultrasound densitometry.
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
An x-ray allows you to see changes in bone tissue. In the image, the bone structure has a blurred appearance; areas of clearing are noticeable, which reflect reduced mineralization.
With grade 3 osteoporosis, the bone marrow cavity expands, which also becomes noticeable on an x-ray.
The shape of the vertebrae changes: they become flattened, thickened and take on a concave appearance.
X-ray will not give informative results at stages 1 and 2 of osteoporosis; it allows you to see changes only after stage 3. Therefore, at the initial stages of the disease, other methods are used.
It is mandatory to carry out general and biochemical blood tests, a blood test for hormone levels and ionized calcium levels.
Possible consequences
Third degree DEP can lead to complications such as ischemic stroke, cardiovascular collapse and myocardial infarction. In older patients, this disease can cause senile dementia. Discirculatory encephalopathy of the 3rd degree often causes disability of varying severity.
Discirculatory encephalopathy can be called one of the main diseases in the world, leading to death.
DEP of the 3rd degree of mixed origin leads to the development of the following complications:
- stroke (necrosis of brain tissue caused by cerebrovascular accident);
- cardiovascular collapse (heart failure develops as a result of a decrease in vascular tone, it is accompanied by a decrease in circulating blood volume and the rapid progression of encephalopathy);
- dementia (a condition characterized by a pronounced decrease in intelligence, in which the patient becomes unable to self-care).
Classification of pathology
Several types of DEP are classified, which are based on the causes of the pathology:
- atherosclerotic – the most common type of pathology that causes disruption of the main vessels of the brain;
- venous – the functioning of the venous system is disrupted, the outflow becomes difficult or slows down. This leads to stagnation, which provokes swelling of the brain tissue, which further aggravates the situation;
- hypertensive is a type of pathology that can affect quite young people who experience surges in blood pressure. When the indicators increase, the condition worsens; when the indicators decrease, brain activity returns to normal. But this is only in the initial stages of the disease, since constant full compensation of functions is impossible a priori;
- mixed - a type of pathology that is the worst amenable to any kind of treatment. Both arteries and veins are affected. In this case, the condition is aggravated by constant surges in blood pressure. With this type of disease, grade 3 DEP gives very unfavorable life prognosis, since neurological disorders become dominant.
Discirculatory encephalopathy from the first to the third stage can reach either several months or several years. Sometimes the disease does not progress for a long time, stopping at a certain stage. But this often happens in cases where the correct diagnosis is made at the very beginning of the development of the pathology and adequate treatment is carried out to stop the process. Unfortunately, it is not possible to cure this disease.
Dyscirculatory encephalopathy grade 3 - dangers of the disease
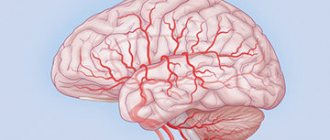
Dyscirculatory encephalopathy (DEP) is a serious brain disease that affects blood vessels. As a result, some areas of the brain matter do not receive oxygen and nutrients.
This leads to oxygen starvation of the nervous tissue, swelling, dysfunction and destruction.
The disease develops due to the pathology of small and large vessels. Affects approximately 5–6% of the total population.
Most cases occur in older people, but are often found among the working population.
DEP grade 3 is a severe pathology in which brain functions are significantly impaired, leading to serious abnormalities.
Causes
Discirculatory encephalopathy occurs as a result of a long-term chronic course of somatic ailments:
- atherosclerosis – damage to the elastic arteries of the brain;
- hypertension - persistent arterial hypertension;
- venous hyperemia – difficulty in venous outflow due to narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels;
- vegetative dystonia syndrome;
- angiodystonic crises due to disruption of systemic hemodynamics;
- diseases of the circulatory system;
- inflammatory lesions of the walls of blood vessels - vasculitis.
Chances of recovery are slim
An optimistic prognosis for the patient’s recovery can be made when the disease is in the first stage.
Unfortunately, with grade 3 dyscirculatory encephalopathy the prognosis is disappointing - the chances of recovery can be called minimal.
Complete restoration of lost body functions is impossible, and social and self-care skills can actually be considered lost forever. The method of drug therapy in this case is aimed at treating symptoms.
With dyscirculatory encephalopathy of the 3rd degree, the prognosis is unfavorable.
It is impossible to restore completely lost functions. The patient, even after treatment, is unable to perform basic self-care skills.
Drug therapy is aimed at eliminating symptoms.
Forecast
If grade 3 dyscirculatory encephalopathy has been diagnosed, then doctors give an unfavorable prognosis. It is no longer possible to restore brain function, and it will be extremely difficult to restore a person’s health. You can only try to extend his life and make it as comfortable as possible. At the same time, do not forget about taking medications, which help well with this pathology.
Relatives often wonder how long they can live with dyscirculatory encephalopathy at stage 3. It is impossible to give a definite answer, because everything depends on the quality of care, the correctness and timeliness of treatment, and even luck. Some people live as long as possible for this condition, but there are others who quickly die. The second option is possible when complications of encephalopathy occur. It is for this reason that it is important to consult a doctor on time.
Many diseases are easier to treat in the initial stages, because later they become advanced. As a result, irreversible changes occur that are incompatible with life. Already when the first negative signs appear, a person is recommended to immediately undergo diagnostics.