Dyscirculatory encephalopathy of mixed origin is one of the types of pathological process in the brain, which is characterized by impaired functioning of organ tissues at the cellular level. In all aspects of its consideration, this disease is extremely dangerous for humans, and therefore requires early detection and high-quality therapy.
With any delay in the treatment of encephalopathy, serious consequences, often irreversible, should be expected. Today we’ll talk about how to prevent this and what dyscirculatory encephalopathy of mixed origin is. Interesting? Then be sure to read the article below to the end.
General description and mechanism of pathology development
Encephalopathy of any kind is a dangerous brain disease that requires competent and timely treatment. The mechanism of its development is hypoxia, which is expressed in some oxygen starvation of organ tissues.
A hypoxic state provokes dystrophic disorders in the brain, as a result of which nerve cells continuously die. The result of encephalopathy is the development of the most dangerous disorders for humans, some of which are incompatible with life.
The complex genesis of the pathology indicates the presence of several reasons for its development or the impossibility of identifying them. Surprisingly, even modern medicine does not always allow us to diagnose the root cause of encephalopathy. The occurrence of the disease is associated with the adverse effects of certain factors on brain tissue. Most often, encephalopathy develops due to:
- cranial injuries
- toxic damage to the body (poisoning with alcohol, drugs, etc.)
- exposure
- past infection with bacterial toxins
- metabolic disorders
- problems with water-salt balance
- vascular lesions of the brain
- taking certain medications incorrectly
If there is one cause for the development of a disease, it is classified in a specific way. For example, in case of vascular problems with the brain and developed hypoxia, discirculatory encephalopathy is observed, in case of poisoning of the body - toxic, and so on.
The type of pathology considered today is distinguished either by the presence of several causes, or by the impossibility of accurately diagnosing them. This feature of encephalopathy with a complex genesis makes the treatment of the pathology extremely difficult, since it is necessary to act on several factors provoking hypoxia at once or act blindly, which is even worse. Otherwise, this type of disease is no different from the others and poses a great danger to the patient.
Medicinal and traditional methods of therapy
Treatment depends on the cause and extent of brain damage
Treatment of dyscirculatory encephalopathy is organized with the mandatory participation of two specialists:
- A cardiologist necessary to eliminate the root causes of pathology.
- A neurologist who organizes relief of brain damage.
That is, pathology therapy is organized in two main directions:
- Elimination of the root causes of its development.
- Fighting the manifestations of the disease, expressed in damage to brain tissue and the corresponding symptoms.
Depending on the nature of the course and severity of encephalopathy, patients are prescribed different treatment methods. In general, they come down to either surgery or conservative therapy. In modern medical practice, the second one is predominantly found.
Conservative treatment of dyscirculatory encephalopathy involves taking specialized medications. Often their list includes:
- antihypertensive drugs (Hartil, Concor)
- cholesterol-lowering medications (Atorvastatin, Rosuvastin)
- diuretics (Lasix, Diacarb)
- vascular drugs (Cinnarizine, Cavinton)
If there are specialized prescriptions for a particular patient, the presented list may well be supplemented with other medications.
The form of the latter is determined for each patient individually, however, tablet preparations are usually used, less often - injections.
Dosages and duration of therapy for dyscirculatory encephalopathy are also strictly individual concepts. Depending on the severity of the existing illness, the patient can be treated for several weeks, several months, or years.
As for folk methods of combating dyscirculatory encephalopathy, there are no really effective means. The following measures can improve the general condition of the patient:
- Increased intake of fiber, vegetables, fruits, grains and dried fruits.
- Organization of fractional meals based on “healthy principles”.
- Reducing the consumption of sugar, flour dishes and fatty foods.
- Drinking herbal and berry teas (for example, with black elderberry and birch leaves).
- Periodic intake of herbal decoctions and infusions.
Otherwise, during drug treatment of dyscirculatory encephalopathy, one should adhere to all the recommendations of the treating specialists and not deviate from the treatment tactics they prescribed. Only this approach will be most effective in the fight against such a serious illness.
Surgical treatment of the disease
Surgical intervention is indicated for vascular damage by atherosclerotic plaques
Surgical treatment of encephalopathy is not used so often. The main purposes for the operation are:
- Development of intracranial complications (for example, hemorrhagic stroke).
- Extensive damage to brain tissue.
- Serious disturbances in the functioning of the vascular structure of the organ.
Surgical intervention for dyscirculatory encephalopathy is aimed at high-quality and rapid elimination of the manifestations of pathology. As a rule, operations are carried out by cardiologists and are carried out with the aim of improving vascular patency. Less commonly, craniotomy is required to eliminate cerebral edema and similar conditions.
In most cases, surgery for dyscirculatory encephalopathy gives the desired result, as a result of which the patient experiences significant improvements, and the risks to his life disappear altogether.
When recovering in the postoperative period, it is extremely important to adhere to all the doctor’s recommendations and periodically conduct a comprehensive examination of the body in order to exclude the development of complications.
Otherwise, there are no special features in the surgical treatment of encephalopathy. After it is completed, the implementation of a medicinal course of therapy often begins to consolidate the results obtained.
Forms of encephalopathy
There are many classifications of encephalopathy in medicine. In situations with a complex genesis of pathology, several types are diagnosed at once. The most common forms are:
- Discirculatory encephalopathies complicated by diabetes mellitus. They develop due to atherosclerotic or hypertensive disorders in the vascular system and diabetes that occurs together with them. Such encephalopathy has a complex genesis and is of a discirculatory-metabolic nature.
Other forms of encephalopathy - radiation, toxic-infectious, drug-induced and others - can also form specific combinations with each other. However, in cases with pathology of complex genesis, such combinations occur infrequently, so we will not consider them in detail.
Treatment of brain diseases should be carried out only with a professional doctor and after a comprehensive diagnosis in a medical institution. The information presented in this article should be used for informational purposes only. Don't forget this.
What medications are prescribed for this disease?
In order to improve tissue nutrition, vascular medications are prescribed as part of treatment.
These can be drugs from the group of nootropics, for example, Nootropil, Piracetam and other drugs. In addition, medications are also used to help strengthen the walls of cerebral vessels, we are talking about Cavinton and Cinnarizine. Among other things, antioxidants are used, for example, tocopherol acetate along with vitamin C and Solcoseryl.
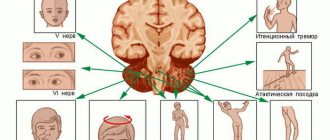
Signs of brain damage
The symptoms of encephalopathy with complex genesis are determined by several factors:
- severity of pathology
- the root causes of its development
- general condition of the patient and his age
Depending on the specifics of a particular case, signs of pathology may include the following manifestations:
- problems in the implementation of mental activity (difficulty with concentration, decreased intellectual abilities, etc.)
- memory impairment
The noted symptoms are typical for encephalopathy. As a rule, it occurs in all patients with such a terrible disease. Sometimes the noted symptoms may be supplemented by:
- impaired function of the limbs
- problems with the vestibular system
- attacks of heart and vascular diseases
- tremors of certain areas of the body
- local or general paralysis
- speech dysfunction
- nausea and vomiting
- increased body temperature
An accurate diagnosis of encephalopathy based on the symptoms shown is impossible. If at least a few of the considered signs appear, it is better not to take risks and seek help from professionals.
It is important to remember that timely diagnosis is the key to successful treatment of any disease. Encephalopathy of complex origin is no exception.
Stages of the disease
Encephalopathy of complex origin always develops in several stages. Depending on the period of development of the disease, its danger to the patient and the nature of its manifestations depend. Medical professionals distinguish 3 stages of encephalopathy:
- Stage 1 – moderately expressed or compensated course. The mildest stage of the disease, expressed in the appearance of minor disorders. Often, at the 1st stage of encephalopathy, mild memory problems, increased stress or depression, increased irritability, frequent dizziness and sleep problems appear. There are no neurological or other symptoms at this stage of the disease.
The neglect of encephalopathy with complex genesis largely determines the prognosis of its therapy. Complete cure is possible only in the 1st stage of the disease. At the 2nd stage there is a chance of partial recovery, but at the 3rd stage the chances of saving the patient are small. Unfortunately, advanced encephalopathy almost always leads to death or coma of the patient.
Diagnosis and treatment
Treatment of encephalopathy with complex genesis is a real puzzle for doctors. The presence of several causes of illness or their complete absence always causes problems for doctors. It is unacceptable to ignore such a serious pathology, so its treatment is organized in any case.
For proper treatment of the disease, the moment of examining the person is important. High-quality diagnostics includes:
- analyzes of all biomaterials (blood, saliva, urine, etc.)
- ECG of all types
- EEG
- REG
- Ultrasound of the sternum and head
- MRI and CT of the brain
Comprehensive diagnostics allows:
- To identify the fact of the course of encephalopathy.
- Determine the cause of its development (not always, but in about 80% of cases).
- Organize a further course of therapy.
Pathology treatment is implemented for each patient individually. Depending on the characteristics of a particular case, the following are prescribed:
- medication course (almost always)
- surgical treatment (for serious brain damage)
- lifestyle adjustments
No doctor can guarantee a complete cure for encephalopathy, even stage 1. As practice shows, the absence of delays in treatment and a competent approach to its organization allows you to avoid dangerous complications of the disease or even completely recover from it. In any case, the pathology of the brain is individual for each patient, so it is necessary to talk with a doctor regarding the prognosis for its treatment.
As you can see, encephalopathy of complex origin is a rather dangerous disease that requires high-quality and timely treatment. It is unacceptable to ignore the course of the disease or treat it condescendingly. The danger of encephalopathy is high, so treatment of the pathology is inevitable and requires immediate implementation. We hope that the presented material helped all readers of our resource understand this.
In the vast majority of cases, the diagnosis of encephalopathy of complex genesis is made only when its development has reached the second stage.
At the same time, the wording itself often frightens patients, since behind this name lies something incomprehensible for them, but, in their opinion, a strong threat to their health. But in reality, everything is not so scary: it is assumed that the patient has signs of several forms of the disease and/or its causes are simply not fully identified.
Since such a diagnosis in the vast majority of cases is accompanied by a number of other complications, the doctor should be as careful as possible both when diagnosing and when prescribing therapy.
- All information on the site is for informational purposes only and is NOT a guide to action!
- can give you an ACCURATE DIAGNOSIS !
- We kindly ask you NOT to self-medicate, but to make an appointment with a specialist !
- Health to you and your loved ones!
Modern medicine works with several varieties of this disease - venous form, post-traumatic, discirculatory and some others. If any of these forms is not diagnosed in a timely manner and treated, it progresses to the second, and often to the third degree.
Unfortunately, simultaneously with growth, many other changes occur in the human body: new lesions appear, the number of dysfunctions increases, symptoms worsen and their number increases. Thus, if encephalopathy was not identified and treated at the first stage of its development, if the second stage is present, we can already talk about a complex genesis.
This situation will be more understandable using a specific example: the patient developed a post-traumatic form of encephalopathy, for which he consulted a doctor too late. At the time of treatment, he already had asthenoneurotic syndrome, as well as a moderate degree of various cognitive disorders.
In addition, in the vast majority of cases, this condition will be accompanied by cephalgia in the chronic phase, which often provokes hypertension of the third and higher stages. Concomitant diseases are possible - atherosclerosis, stenosis or even diabetes mellitus. Of course, the diagnosis for such a patient will be “encephalopathy of complex origin.”
As for the signs that manifest this form of pathology, they, in fact, are not much different from the symptoms of the classical course of the disease. Thus, the early stage makes itself felt by periodic mood changes, frequent headaches, which are difficult to respond to drug therapy.
Problems with memory and spatial orientation are also common. The patient cannot maintain the thread of a conversation, the interlocutor constantly seems to be distracted by something, and intellectual abilities are significantly reduced.
It is quite clear that such symptoms rarely make anyone wary and suspect a dangerous disease, and therefore at the first stage it is almost never diagnosed, gradually developing into the second. At this stage, the symptoms remain the same, their intensity simply increases greatly and the ability to cope with them significantly decreases.
Psycho-emotional disorders are added to the symptoms listed above. A person may have a tendency to hysterics and manic behavior. During the day, without any compelling reasons, the patient’s mood can change dramatically in any direction.
If measures were not taken in this case, the next stage develops, in which mental disorders no longer allow the patient to lead full life activities, working capacity is lost, and restrictions on motor functions may occur. All this leads to gradual, but inevitable, disability of the patient.
Be sure to read the information about Reye's syndrome in children.
There are three stages of the disease in question, each of which is characterized by certain features and symptoms:
- At this stage, the supply of nutrients to the human brain stops. Since the disease is not yet very advanced, only certain fragments of the brain are affected, but in general the human body is still quite capable of coping with all the problems and does not allow the disease to manifest itself fully.
- As a rule, at this stage, many patients complain of problems with sleep: it is weak, often interrupted, and there is no feeling of rest after it. The patients themselves notice that they can be enraged by any little thing, even one that does not deserve attention.
- All symptoms increase progressively, the patient himself is constantly lethargic and apathetic, the thought of the possibility of a serious illness and the need for its treatment does not even occur to him.
- Psycho-emotional disorders are accompanied by physical symptoms: tinnitus, deterioration of joint mobility, trembling of the limbs. Possible disturbances in the visual system.
- Characterized by severe damage, often irreversible. Basically, all disorders are associated with a mental state, while internal changes become noticeable on MRI.
- If the disease is accompanied by an acute circulatory disorder, attacks of loss of consciousness and even a coma cannot be ruled out in the second or third stages.
Disability in cerebral encephalopathy: criteria for assigning a group
Brain pathology is encephalopathy of complex origin, which appears as a consequence of circulatory disorders and insufficient oxygen supply to brain tissue. As a result, a disruption of the trophic process appears. Often situations lead to serious deviations, and a person is assigned a disability due to cerebral encephalopathy.
How does encephalopathy appear?
The disease appears due to diffuse changes in brain tissue. Chronic or recurrent problems with the supply of nutrients lead to the appearance of the disease. Insufficient blood supply to tissues leads to the development of pathology.
The appearance of the disease is provoked by:
- Hypokinesia (lack of physical activity).
- Overweight.
- Psycho-emotional stress.
- Alcohol abuse.
- Concomitant somatic pathologies.
- Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine with vertebral artery syndrome.
The appearance of encephalopathy is caused by various inflammations of the walls of blood vessels, intoxication of the body, and blood clots in the arteries through which the brain tissue is nourished.
A common cause of pathology is the existence of several diseases: hypertension + atherosclerosis or another combination. This combination often provokes disruption of normal blood circulation and leads to the appearance of encephalopathy of brain tissue.
At risk are active smokers and people who are often under stress. Pathology can be inherited.
In the initial stage of the disease, patients ignore symptoms. The diagnosis of “encephalopathy” is made at a later stage in the development of the pathology. Patients' health deteriorates so much that it is difficult for a person to perform basic household manipulations. The question of disability arises reasonably.
Stages of encephalopathy
Doctors call 3 stages of development of the disease, each of which has its own characteristics.
Stage 1
The patient experiences a feeling of slight discomfort: dizziness, headache, sleep problems, anxiety, noise in the head, minor memory problems, fatigue, decreased performance.
If the patient suffers from hypertension, blood pressure may increase. After rest, the symptoms disappear, so they do not pay attention to them. and problems with oculomotor ability appear Intelligence begins to decline.
Stage 2
The patient's symptoms intensify: memory problems appear more often, severe dizziness, poor coordination of movements - walking becomes unstable, narrowing of the arteries and dilation of the fundus veins.
The patient may have a mini-stroke. Often, when the second stage of the disease is detected, a disability is assigned.
Stage 3
The patient loses the ability to self-care. The patient's condition worsens and is accompanied by: fainting, epileptic seizures, memory loss, significant impairment of motor coordination, and significant intellectual impairment.
A person feels severe dizziness, sleep is disturbed, and noise in the head increases. Possible paralysis. The patient is not able to realistically assess his condition. Recovery of a patient at the third stage of pathology development is impossible.
In this situation, the question arises of the inability to perform work functions and everyone is assigned a disability.
Who makes the decision to assign disability?
A medical and social examination (MSE) examines the patient’s medical history and condition and assigns a specific disability group. The decision to assign disability is made by a medical commission. This eliminates the possibility of false and biased conclusions.
The basis for disability is a chronic disease that has caused the development of encephalopathy, as well as the person’s ability to perform certain actions. Encephalopathy as a pathology is not a basis for assigning disability. Depending on the stage of development of the disease and health status, a group is assigned.
III disability group
The disability group is working. Having such an examination, a person can perform simple actions. A person receives this disability group for encephalopathy if he has:
- mild deviations in motor activity;
- epileptic seizures recorded by doctors;
- partial loss of ability to work;
- the development of chronic pathologies that cause the development of cerebral encephalopathy.
In the event of such indications and the assignment of disability, the person is transferred to lighter work, his qualifications are changed while maintaining partial earnings.
II disability group
The category does not provide for professional employment. In order for the commission to assign group II, a person must have:
- stable and severe mental disorders;
- severe asthenic condition;
- data on severe paraparesis (limitation of motor activity) and widespread hyperkinesis (involuntary muscle contraction) are indicated;
- symptoms indicate the patient’s inability to engage in work;
- the illness that provoked the appearance of encephalopathy manifests itself clearly and clearly.
I disability group
Appointed by a commission if a person has:
- severe mental disorders;
- severe movement disorders;
- epileptic seizures;
- extensive hyperkinesis;
- the sick person cannot independently perform basic self-care activities.
Prohibited types of work
If the patient is diagnosed with encephalopathy, there are contraindications for work:
- in a hot shop;
- associated with significant neuropsychic and physical stress;
- at night time;
- in conditions associated with the influence of toxic substances;
- with the likelihood of stressful situations;
- requiring precise coordination of movements;
- associated with long walking.
Indications for assigning a group and mandatory examinations
ITU pass if:
- the pathology progresses rapidly;
- certain types of activities and working conditions are contraindicated;
- against the background of repeated strokes (acute cerebrovascular accidents), it is impossible to perform work manipulations.
Before passing the commission, a person undergoes examinations:
- ECG;
- X-ray of the skull and cervical spine;
- CT scan of head tissue;
- rheoencephalogram;
- Dopplerography of the arteries and veins of the brain;
- examination by a therapist, ophthalmologist, psychiatrist;
- tests for glucose, blood lipids and cholesterol.
The commission is provided with data from all examinations and medical reports.
Preventive measures
Doctors have developed 3 types of preventive measures to avoid disability due to cerebral encephalopathy.
Primary measures . They provide for taking into account the initial risk factors for the appearance of vascular diseases, and the correct treatment of patients with NPCI (initial manifestations of cerebrovascular insufficiency). Completion of disease therapy.
Secondary level . Detection of early pathology and treatment of cerebral encephalopathy, especially at an early stage. Elimination of causes that provoke the development of the disease. Quarterly clinical examination to examine and monitor the patient’s health status. For patients who have suffered a stroke, complete rehabilitation.
Tertiary prevention measures . Timely examination for group 3 and appropriate employment. Carrying out other measures for the purpose of social protection of the patient.
To reduce the risk of disease, you should avoid head injuries and various types of poisoning - alcohol, toxic substances, infectious.
Regular and medical examinations will help you avoid an unpleasant situation. The slightest deviations in health cannot be ignored, especially if they relate to brain functions.
Source: https://nevrology.net/sindromy-i-zabolevaniya/entsefalopatiya/invalidnosti-pri-golovnogo-mozga.html
Diagnostics
Even a person who does not have a medical education should understand that the earlier a disease is detected, the greater the chances of successfully getting rid of it, and encephalopathy of complex origin in this case is no exception.
Unfortunately, only three out of 10 patients with the pathology in question are diagnosed at the first stage of development.
The development of the second stage rarely goes unnoticed. If the patient has the above symptoms, he is prescribed modern informative methods for diagnosing this disease: computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging.
Both of these methods are capable of visualizing all the changes that encephalopathy provokes in the body.
In addition to CT and MRI, other methods of diagnosing the disease can be used: Ultrasound examination or laboratory diagnostics.
The final choice of diagnostic method remains with the doctor; it will depend on what contraindications are present in a particular patient and how clearly the symptoms manifest themselves.
Treatment of encephalopathy of complex origin
Treatment of this disease should be carried out exclusively by qualified specialists. Under no circumstances should you use someone else's therapeutic regimen, even if it had a positive effect on someone.
Treatment will depend on the stage at which the disease is detected and what complications it is accompanied by.
The medications used to treat this disease include many groups of drugs, the choice of which directly depends on the damaged organ or system.
The main drugs are:
Diseases of the cerebral vessels that have a chronic course are classified as cerebral pathologies according to the ICD. However, in some cases, vascular lesions can be caused by various reasons, so treatment of such pathologies should be carried out not only on the basis of the diagnosis, but also taking into account the causes that caused the pathology. In this regard, a difficulty may be dyscirculatory encephalopathy, which according to the ICD is not classified in any category. However, it is dyscirculatory encephalopathy that most often correlates with the concept of encephalopathy of complex genesis. Speaking about this disease, it is worth noting that the causes of the disease lie in focal or diffuse damage to the brain matter. The reasons why encephalopathy of complex genesis occurs can be different - these are cerebral atherosclerosis, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and vertebrobasilar disorders.
Symptoms of the disease
The dyscirculatory form of the disease at an early stage of its development rarely does not produce pronounced symptoms if the patient has activated compensatory mechanisms that restrain the manifestation of the disease. With significant damage to the medulla and the addition of other pathological signs, the symptoms of the disease become noticeable in all patients. Sometimes patients consult a doctor about cardiovascular problems, and after consultation with a neurologist they receive another unpleasant diagnosis - dyscirculatory encephalopathy of a certain degree. It is worth noting that when neurologists interview patients, they already receive complaints of constant or recurrent headaches and mental disabilities of varying degrees.
Symptoms of pathology can be divided into several groups. Mnestic symptoms of the disease include a decrease in the level of mental abilities, affective symptoms include the appearance of psychosis, falling into depression, and paranoid symptoms include the emergence of obsessive ideas, inventing problems that the patient wants to solve, a heightened sense of justice, and the occurrence of unfounded grievances against others.
In addition to these specific symptoms, which appear in varying degrees of the disease, discirculatory complex encephalopathy has other classic signs of the disease that occur during the development of the disease. Such signs include severe headache, mood swings, blues, and tearfulness. A little later, patients begin to suffer from forgetfulness, impaired concentration, noise in the head and dizziness, spatial disorders, a feeling of intoxication, and visual disturbances. It becomes more and more difficult to communicate with the patient - he cannot concentrate on the conversation, vaguely describes his problems, and cannot assess his well-being. Basically, such symptoms occur in the first stage of development of the disease, but then the situation only worsens.
The manifestations of the pathology of the next degree include movement disorders - patients cannot walk as before, drag their feet and shuffle, and are unstable when turning. As the disease progresses, they cannot move without the help of others. Patients suffer from convulsions and paresis of the limbs. In this case, you can apply for disability.
With the third degree of development of the disease, control over excretory acts - urination and defecation - is lost. As neurological abnormalities increase, one can notice how speech defects become more and more noticeable in patients, and they have difficulty swallowing. Often patients begin to laugh or cry forcefully, although the environment was not conducive to this. Patients also suffer from light and sound intolerance and have problems sleeping. This contributes to the emergence of fears and causeless panic.
At this point, the disease reaches the third stage, when pathological processes have so destroyed the brain that the patient generally loses interest in what is happening, and some patients have thoughts of suicide. Note that the implementation of such invented suicidal ideas is quite often carried out by such patients. At the last degree of the disease, complete degradation of the personality occurs.
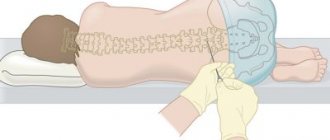
Diagnosis of pathology
To make a diagnosis, a thorough examination of attention, memory and intelligence is necessary. At the same time, other studies are carried out - magnetic resonance imaging, ultrasound examination of cerebral vessels, angiography with a contrast agent, electroencephalogram, blood test. If necessary, an additional examination by an ophthalmologist may be prescribed. Since the symptoms of the disease are similar to other diseases, differential diagnosis is carried out with Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and other neurodegenerative disorders.
Diagnostic methods
The diagnosis can be confirmed using an MRI of the brain.
In the diagnosis of dyscirculatory encephalopathy of mixed origin, the greatest emphasis is placed on studying the patient’s cardiovascular system, since one of the main manifestations of the pathology is damage to the vascular structure of the brain.
In addition to examining the patient, analyzing his condition and studying the medical history, the doctor prescribes a whole list of instrumental diagnostics.
If dyscirculatory encephalopathy is suspected, the following types of examinations are most often prescribed:
- general blood and urine test
- extended blood test
- electrocardiography (ECG) of different formations
- electroencephalography (EEG)
- Resoencephalography (REG)
- duplex ultrasound of the vascular system of the upper body (sternum and head)
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) of the brain, less often of the cervical spine
Based on the results of a comprehensive diagnosis, the doctor, who is usually a neurologist, determines:
- The presence or absence of dyscirculatory encephalopathy and other brain pathologies.
- If present, the severity, degree of neglect and pathogenesis of the disease(s).
- Further vector of therapy for a specific patient.
Due to the specificity and severity of encephalopathy of any type, the diagnostics discussed above are mandatory. In the absence of an examination, it will be impossible to confirm the fact of the disease, determine its severity, or choose the most effective treatment tactics. Taking this into account, at the slightest suspicion of encephalopathy, you should immediately visit the clinic and organize diagnostic and therapeutic measures with the participation of a professional doctor.
Treatment of the disease
The disease responds well to treatment in the first stage, until more serious abnormalities have developed and caused disability. With the help of medicine, it is possible to compensate for impaired brain functions and restore the patient’s health to a significant extent. The basis for treating the disease is nootropic drugs that have a vasodilating effect. These are Cerebrolysin, Ceraxon, Piracetam, Encephabol. Cognitive impairment is corrected by Gliatilin, Amiridin, Remanil, and antioxidant therapy is carried out by Bilobil, Actovegin, Mexidol. Disorders of the vestibular apparatus are treated with Betaserc, Belloid. Rehabilitation measures include acupuncture, balneotherapy, and massage. From time to time, such patients are placed in sanatoriums.
Discirculatory encephalopathy (ICD code 10 - G93.4 - encephalopathy unspecified) is a form of chronic cerebrovascular disease with further slow progression. This disease is a consequence of various diseases, common in which is damage to small arteries and arterioles.
The disease is characterized by a complication of impaired cognitive and mental functions, which interacts with motor and sensory disorders. The conclusion is made by a neurologist after examination, as well as studies completed.
To eliminate hypertension
Dyscirculatory leukoencephalopathy of the brain often develops against the background of hypertension with pressure readings of 160/100 mm Hg. Art. and higher. In this case, antihypertensive drugs are prescribed for treatment:
| Group of drugs | Examples of funds | Action |
| Beta blockers |
|
|
| ACE inhibitors |
| They block the angiotensin-converting enzyme, which converts angiotensin to renin. This helps to dilate blood vessels. |
| Diuretics |
| Increase the amount of fluid excreted in the urine. As a result, the swelling of the blood vessels decreases, their lumen increases, and the pressure decreases. |
| Calcium antagonists |
| They prevent calcium from passing through the vascular walls, thereby reducing blood pressure. Additionally, they increase exercise tolerance. |
- How to pack flowers
- How to open a DMG file. Which program opens files with the DMG extension in Windows
- How to lose weight with activated carbon: recipes and reviews
Degrees of the disease
Discirculatory encephalopathy is divided into 4 degrees, each of them corresponds to certain symptoms:
- Stage I – characterized by minor organic abnormalities of the brain. Most often occurs in children or young people. It can be confused with signs of other diseases and complications. The first degree of dyscirculatory encephalopathy is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Fast fatiguability;
- Irritability;
- Bad mood;
- Headache;
- Memory impairment;
- Noises in the head;
- Dizziness;
- Anxious sleep;
- Migraine;
- Memory impairment. The causes of DEP of the 1st degree are:
- Inadequate sleep;
- Poor nutrition;
- Minimal physical activity;
- Bad ecology.
- Stage II is a neurological disease that is very common among older people. The disease progresses quite slowly, but if its development is ignored, it can lead to a stroke and disability, but the patient will still be able to care for himself. The main difference between grade 2 DEP and grade 1 are well-defined symptoms. The second stage of dyscirculatory encephalopathy is clearly expressed by the following signs: Absent-mindedness;
- Poor memory, even to the point of lapses in it;
- Inability to control your actions;
- Frequent irritability;
- A state of depression and antipathy to everything;
- Lethargy;
- Decreased activity;
- Loss of interest in life;
- Emotional and mental problems;
- Sclerosis;
- Inattention.
In what cases is a person assigned a disability?
Often relatives of the patient are interested in the question of whether a disability group is assigned for such a disease? The answer to this can be unequivocal: “Yes.” To obtain a group, the patient is sent for an MSE (medical and social examination), according to the results of which he is either assigned the status of a disabled person or is rejected without finding any grounds for this.
The basis for issuing disability is a confirmed diagnosis of “encephalopathy” or the pathologies that caused it. The presence of symptoms and complications is an absolute indication for a positive verdict from the commission.
Disability is assigned for dyscirculatory encephalopathy at 2 and 3 degrees of development. At these stages of the pathology, a person loses the ability to independently care for himself and perform his professional duties.
Children often experience residual encephalopathy, which occurs when there is organic damage to an organ in the perinatal period. Post-traumatic organ pathology that arose during childbirth, as well as brain disease caused by hypoxia, intrauterine infection, and heredity, are often diagnosed. A child's disability group is assigned according to the same parameters as for adults.
Features of DEP 2nd degree
- Most often, dyscirculatory encephalopathy of the second degree affects people who are from 35 to 60 years old, but who are not yet pensioners.
- This disease especially develops in the population whose work is closely related to active brain activity.
- Very often , people who suffer from alcohol addiction, diabetes, and diseases of the neurological system are prone to this disease.
- It is discirculatory encephalopathy of the 2nd degree that is a fairly common disease of mixed origin, which occurs in 75% of all cases of the disease.
- DEP of the 2nd degree of complex genesis is a form of the disease that has several causes of occurrence. It often occurs when the oxygen content in the atmosphere decreases.
Characterized by symptoms such as:
- Headache;
- Dizziness;
- Memory loss;
- Increased pressure.
DEP 2nd degree - classification
DEP of the 2nd degree is classified into the following types, which have their own clinical picture and specificity of progression:
- Discirculatory encephalopathy of the hypertensive type often appears in young people, the disease passes quickly and is quite acute. This type is characterized by frequent attacks of hypertensive crisis. The main symptoms are:
- Violation of neuropsychological processes;
- Slow reaction;
- Frequent mood changes.
- The first group is associated with deviations that arose at birth. Most often, the blood supply to the brain is disrupted;
The main syndromes of grade 2 DEP are noted:
- Cephalgic syndrome . Often manifests itself in headaches, vomiting, and tinnitus. This type includes all unpleasant sensations that are associated with the head;
- Astheno-neurotic syndrome is characterized by frequent mood swings, dizziness, and constant pain in the head. With this type of illness, a person becomes very tearful, apathetic to everything, and also has a bad mood;
- Vestibular-coordination disorders include frequent dizziness, problems with coordination, instability when walking;
- Dissomnia syndrome is characterized by disruption of adequate sleep;
- Cognitive syndrome includes significant memory impairment, as well as absent-mindedness and concentration.
Preventive measures
Doctors have developed 3 types of preventive measures to avoid disability due to cerebral encephalopathy.
Primary measures . They provide for taking into account the initial risk factors for the appearance of vascular diseases, and the correct treatment of patients with NPCI (initial manifestations of cerebrovascular insufficiency). Completion of disease therapy.
Secondary level . Detection of early pathology and treatment of cerebral encephalopathy, especially at an early stage. Elimination of causes that provoke the development of the disease. Quarterly clinical examination to examine and monitor the patient’s health status. For patients who have suffered a stroke, complete rehabilitation.

Tertiary prevention measures . Timely examination for group 3 and appropriate employment. Carrying out other measures for the purpose of social protection of the patient.
To reduce the risk of disease, you should avoid head injuries and various types of poisoning - alcohol, toxic substances, infectious.
Regular and medical examinations will help you avoid an unpleasant situation. The slightest deviations in health cannot be ignored, especially if they relate to brain functions.
Symptoms of dyscirculatory encephalopathy
Stage 2 DEP is characterized by the following symptoms::
- Changes in memory for the worse;
- Lethargy;
- Apathy towards the environment;
- Decreased activity;
- Frequent headaches;
- Dizziness;
- Problems with perceiving larger amounts of information;
- Difficulty in performing mental work;
- Poor reference in time and location;
- Frequent irritability;
- Insomnia;
- Nausea;
- Weakness in the body;
- Impairment of an efficient function;
- Impaired cognitive function;
- Violation of social adaptation.
Causes of dyscirculatory encephalopathy
And also the causes of dyscirculatory encephalopathy of the 2nd degree are:
- Inflammation of blood vessels;
- Vein thrombosis;
- Intoxication of the body;
- High pressure;
- Atherosclerosis of blood vessels and arteries;
- Constant stress;
- Emotional stress and disorders;
- Pinched blood vessels;
- Blood diseases.
All these reasons lead to impaired blood circulation in the vessels of the brain. This favors the development of oxygen starvation, as well as the development of heart attacks.
REVIEW FROM OUR READER!
I recently read an article that talks about PhytoLife for treating heart disease. With this tea you can FOREVER cure arrhythmia, heart failure, atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction and many other diseases of the heart and blood vessels at home. I’m not used to trusting any information, but I decided to check and ordered a bag. I noticed changes within a week: the constant pain and tingling in my heart that had tormented me before receded, and after 2 weeks disappeared completely. Try it too, and if anyone is interested, below is the link to the article. Read more "
Encephalopathy disability
Advice from lawyers:
1. I am interested in the question: is neonatal encephalopathy a disability?
1.1. Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of February 20, 2006 N 95 (as amended on November 14, 2019) “On the procedure and conditions for recognizing a person as disabled”
Read more >>>
Did the answer help you?YesNo
Consultation on your issue
8
Calls from landlines and mobiles are free throughout Russia
2. Is it possible to get disability for the disease encephalopathy hydrocephalus.
2.1. Write an application for examination.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
3. Diagnosis of post-traumatic encephalopathy with cognitive and behavioral impairments. Do they give disability with this diagnosis?
3.1. —Hello, dear visitor, the determination or refusal of a disability group is decided ONLY by ITU doctors,
To establish the disability group (or strengthen it), you need to contact your attending physician and ask to fill out a mailing list on the ITU form Form No. 080/u. You receive this sheet and visit all the doctors listed on it, and then go through the ITU, in accordance with the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 95 of February 20, 2006 (as amended on March 22, 2019) “On the procedure and conditions for recognizing a person as disabled.” And in case of refusal to establish a disability group, or its reduction. Appeal the refusal in court. The court will appoint a commission examination and make its decision. Good luck to you and all the best.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
4. My husband had pancreatic necrosis. He has been in the hospital since September 25, 2019. 4 months in intensive care. Now he is diagnosed with toxic encephalopathy. As I understand it, 02/25/20 is the deadline for registration of disability. And they are not trying to discharge him from the hospital. My husband doesn’t walk, doesn’t maintain the networks, disorientation in time and space, part of his intestine was removed, he has an ileustomy. Tell me whether the hospital should independently issue documents for disability or whether I have to do this myself. Discharged to your home.
4.1. You need to do the registration. But do not forget that it is necessary to issue a power of attorney from your husband in order to perform actions on his behalf and in his interests.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
5. I have bronchial asthma of moderate severity that is not under control, angina pectoris, dyssurkilatory encephalopathy of the 2nd degree. MSEC did not accept the documents, they said that they give me a disability diagnosis, what should I do?
5.1. It is within the bounds of the law to take advantage of this provision. Rules for recognizing a person as disabled (approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of February 20, 2006 N 95) 19. If a medical organization, a body providing pensions, or a social protection body refuses to send a citizen a referral for a medical and social examination, he is issued a certificate on the basis of which a citizen (his legal or authorized representative) has the right to contact the bureau independently. The bureau's specialists conduct an examination of the citizen and, based on its results, draw up a program for additional examination of the citizen and carrying out rehabilitation or rehabilitation measures, after which they consider the question of whether he has any disabilities.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
6. Conclusion MRI of the brain: Focal encephalopathy of mixed origin, post-traumatic vascular. Focal leukoaraiosis. Moderate uneven expansion of the subarachnoid convexital liquor space. Which disability group corresponds to me?
6.1. Diagnosis alone does not determine disability. The actual condition and degree of disability are taken into account. With encephalopathy, all three groups are possible, depending on the severity and consequences.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
7. Discharged from neurology with a diagnosis of dyscirculatory encephalopathy of 2-3 degrees, syndrome of severe cognitive impairment, cerebral and technical syndrome. Decompensation. Is it possible to apply for disability? The clinic said that three months after discharge, now is the rehabilitation period.
7.1. Elena, the assignment of a disability group does not depend on the disease, but on the physical ability of the person, his ability or inability to care for himself, etc.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
8. I have AD of mixed origin. The diagnosis was made a month ago. I also have grade 2 cephalgia, vestibulopathy, stage 2 encephalopathy, hypertension. Am I entitled to disability?
8.1. Only the commission will tell you for sure.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
9. I had a stroke in 2020. MRI showed encephalopathy, ischemia and atrophy and a cyst. Can I be given disability?
9.1. Ask for a referral to ITU.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
10. My husband had an open head injury on 06/04/19. Craniotomy, encephalopathy. Was not officially employed. After what time can I apply for a disability group?
10.1. These are questions for your attending physician, not for lawyers. Also consult a neurosurgeon.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
11. My child was diagnosed with residual encephalopathy and SPD. The pediatrician does not want to send us to ITU because... I don't think it's that serious. At the same time, in neurology we are told to register a disability. Is our pediatrician right or can I count on disability?
11.1. It is unknown that the status of disability is determined by doctors, not lawyers. And not by diseases (surgeries, injuries), but by their consequences. Rules for recognizing a person as a disabled person (approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of February 20, 2006 N 95) 5. The conditions for recognizing a citizen as a disabled person are: a) impairment of health with a persistent disorder of body functions caused by diseases, consequences of injuries or defects; b) limitation of life activity (complete or partial loss by a citizen of the ability or ability to carry out self-service, move independently, navigate, communicate, control one’s behavior, study or engage in work); c) the need for social protection measures, including rehabilitation and rehabilitation. 6. The presence of one of the conditions specified in paragraph 5 of these Rules is not a sufficient basis for recognizing a citizen as disabled. 7. Depending on the severity of persistent disorders of body functions resulting from diseases, consequences of injuries or defects, a citizen recognized as disabled is assigned disability group I, II or III, and a citizen under the age of 18 is assigned the category “disabled child.” .
Did the answer help you?YesNo
12. I have been diagnosed with severe encephalopathy of complex origin, will I be given a disability pension?
12.1. Again a purely medical question. These questions are not for lawyers! And to medical experts. Even a simple doctor cannot answer this question for you. Only MSEC expert specialists.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
13. I am disabled group 2 indefinitely. Registered with the PND for epilepsy and encephalopathy. Collectors constantly bother me. One loan from the bailiffs. Can I somehow get rid of the collectors and resolve the issue with the loan from the bailiffs? They won't hire me. Disability 8000 rub. And I have a dependent child and a disabled mother who is bedridden. We have no property, no real estate, we have nothing, we are threatened by collectors and a visit from bailiffs. Sincerely, Julia.
13.1. Hello. You have the right to write a refusal to interact. Then the collectors will only have the right to write letters to you by mail, but then they will not be able to call, send SMS or meet with you. Such a refusal must be sent by letter with notification to both the collectors and the bank (or microfinance organization). How to write such a refusal, see here More details >>>. Before this, suggest collectors to go to court. If you have no property, then bailiffs can also remove up to 50% from your disability pension. But you have the right to apply to the court for a reduction in payments due to your difficult financial situation.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
Consultation on your issue
8
Calls from landlines and mobiles are free throughout Russia
14. Can I be given a disability group with a diagnosis of Stage 2 Encephalopathy of mixed origin?
14.1. Most likely yes. This is decided by the MSEC commission.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
15. My child is 1.5 years old. We were examined at a regional hospital. They diagnose cerebral palsy and early epileptic encephalopathy. Please tell me if he is entitled to disability and where he needs to apply. Thank you.
15.1. Yes it is, ask for a referral to MAS from your attending physician.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
16. 1997 severe head injury with a fracture of the base of the skull, moderate contusion. Today: encephalopathy grade 2, ataxia grade 1, bilateral sensorineural hearing loss grade 3 on the left and grade 1 on the right, osteoarthritis affecting large and small joints, necrosis of the lunate bone, rheumatoid arthritis, polyarthritis grade 1-2, osteochondrosis. Can I count on disability, thank you.
16.1. This question is of a medical nature. The decision to establish disability is strictly within the competence of the ITU.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
17. What disability group will I be assigned at MSEC with a diagnosis of: Stage 3 dyscirculatory encephalopathy on the background of hypertension, cerebral atherosclerosis, atrial fibrillation with decreased cognitive functions. NOSE: paroxysmal form of atrial fibrillation. Hypertension stage 3, risk 4 (very high). CHF 2 A. FC 2.
17.1. We are lawyers here and lawyers, we are not doctors, this is decided by the ITU.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
18. I have asthma of mixed genesis atopic, infection-dependent severe exacerbation, respiratory failure of 2-3 degrees, chronic gastritis, chronic calculous cholecystitis, chronic viral hepatitis C toxic encephalopathy, am I entitled to disability?
18.1. Hello Nellie! The conditions for recognizing a citizen as disabled are: a) impairment of health with a persistent disorder of body functions caused by diseases, consequences of injuries or defects; b) limitation of life activity (complete or partial loss by a citizen of the ability or ability to carry out self-service, move independently, navigate, communicate, control one’s behavior, study or engage in work); c) the need for social protection measures, including rehabilitation and rehabilitation. To establish disability, it is necessary to undergo a medical and social examination (MSE) at the ITU bureau. To do this, you need to receive a referral for medical examination from a medical organization - after carrying out the necessary diagnostic, therapeutic and rehabilitative measures or rehabilitation measures if there is data confirming a persistent impairment of body functions caused by diseases, consequences of injuries or defects; - in the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation or in the social protection authority - in the presence of medical documents confirming impairment of body functions due to diseases, consequences of injuries or defects. If you have severe asthma, you can apply for disability. If you have any questions, write.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
19. My child has been on disability since she was 2.5 years old, now she is 6 years old, the disability has been removed because there is no reason for this. Diagnosis of encephalopathy, unspecified and from a psychiatrist F 067
19.1. Svetlana, what is the essence of your question?
Did the answer help you?YesNo
20. I have toxic encephalopathy hepatitis C for 18 years, stage 2 liver fibrosis, can I get disability.
20.1. —on establishment or refusal, in the disability group, ONLY ITU doctors decide
, to establish the disability group (or strengthen it), you need to contact your attending physician and ask to fill out a mailing list on the ITU form Form No. 080/u. You receive this sheet and visit all the doctors listed on it, and then go through the ITU, in accordance with the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 95 of February 20, 2006 “On the procedure and conditions for recognizing a person as disabled.” Form No. 080/u-06 is signed by the head of the department, as the chairman of the Medical Commission. And if you refuse to establish a disability group, you will appeal the refusal in court within 3 months from the date of receipt. The court will appoint a commission examination and make its decision. Good luck to you and all the best.
Did the answer help you?YesNo
I have hepatitis C, HIV, right-sided pyramidal insufficiency, HIV-associated encephalopathy, I have been on therapy for 6 years, is it worth collecting documents for disability?
Hello, I have postnatal hypoxic post-traumatic encephalopathy.
Situation: after an attack of encephalopathy, my legs stopped working a year ago. I can’t go to an examination (fluorography, ENT, ophthalmologist, etc.) - I move in a wheelchair.
How long does disability for Wernicke encephalopathy last for a 63-year-old predominantly bedridden patient with induced strabismus?
I have been seeing an epileptologist since 2013. DZ: symptomatic epilepsy with secondary generalized seizures.
I am interested in what disability group will be given for the diagnosis of a malignant neoplasm of the body of the stomach T1N0M0 1st degree.
I want to know if they can register it. I'm ill. Encephalopathy did not give me a disability. They said they would give it if there were complications and continue treatment. But for what? And How?
I am interested in what disability group will be given for the diagnosis of a malignant neoplasm of the body of the stomach T1N0M0 1st degree.
Declared unfit for military service due to military trauma - organic personality disorder and behavior of mixed origin - post-traumatic,
For 2 years I had 1 disability group, then a year 2, now it’s not fair that they give 3,
At first I had 1 gram for 2 years. disability, then they gave 2, after a year now they give 3,
Diagnosis of DEP stage 2
In order to diagnose a disease, one must first have symptoms of various relevant clinical findings.
In order to make a correct diagnosis, the doctor must note changes in the patient’s condition, based on the following criteria:
- Neurological disorders and their intensification;
- Study of the patient’s neuropsychic state;
- Changes that were identified during computed tomography;
- Changes that were identified when studying the patient's blood.
- Rheoencephalography - what is it? This is one of the methods for diagnosing DEP and includes a study of the condition of the brain vessels, which provides information about their tone, as well as how saturated they are with blood. This method is absolutely painless and is performed by a neuropathologist or neurologist.
- Computed tomography is a painless research method that provides information about the presence of atrophic processes in the brain.
- Assessment of neurological manifestations of the disease . This method is characterized by having a neurologist examine the patient and check his reflexes. But it is important to take into account that in order to make a diagnosis of DEP, one must rely not only on the manifestations of neurological diseases, but also on various signs.
- Doppler ultrasound of cerebral vessels is a method of ultrasound examination of cerebral vessels, which allows an objective assessment of the speed of blood flow through the vessels.
- Neuropsychological examination is a method for diagnosing the patient’s mental state. This method determines various damage to higher mental functions.
Criteria for assessing the patient’s condition and assigning him a disability group
The disability group for encephalopathy is determined by the following criteria:
— Third disability group. The patient has low-grade motor impairment. This may be flaccid paresis of the limbs or hyperkinesis of a localized form. A history of epileptic seizures recorded by a medical institution. The aggravation of chronic diseases that cause encephalopathy is considered. If the general condition physically prevents the performance of work manipulations, there is an obvious partial loss of ability to work, the commission assigns the 3rd disability group. This provides grounds and requirements for transferring the patient to lighter work or changing qualifications, which will preserve the possibility of limited earnings.
— Second group of disability due to encephalopathy. The patient's medical history contains information about widespread hyperkinesis and severe paraparesis. Mental disorders are persistent and intense, asthenic conditions are severe. Severe symptoms of the underlying disease that interfere with work activity. This group is not working.
— First group of disability due to encephalopathy. Prescribed to patients with severe motor impairment, dementia, and profound mental disorders, in which patients completely lose the ability to self-care and work. Epilepsy attacks, multiple and extensive hyperkinesis are also grounds for transferring the patient to this disability group.
Encephalopathy often results in disability, but this is largely influenced by the underlying disease. For example, the post-stroke period, cerebral circulatory disorders and other diagnoses that can provoke the emergence of severe conditions that interfere with the patient’s performance of work duties.
Of course, disability due to encephalopathy is not a good thing. Moreover, this directly indicates the severity of the patient’s condition. To prevent such developments, you should contact the specialists of our medical center at the first symptoms of the disease. If there are chronic pathologies in the anamnesis, it is necessary to promptly monitor their dynamics.
Here you can conduct diagnostics of the whole body and receive competent advice from medical specialists. Come to our center, do not wait for the disease to overcome you or your loved ones.
4 minutes Irina Smirnova 157
Encephalopathy is a brain disease that develops as a result of disruption of trophic processes in this area caused by oxygen starvation or circulatory pathology. As a rule, the disease is diagnosed already at the 2nd stage, when clearly expressed symptoms occur. Due to a significant deterioration in general condition and the rapid progression of pathology, a person cannot lead a normal lifestyle. In this case, we can talk about assigning a disability group to the patient.
Treatment of DEP
The most effective treatment method is direct treatment in combination with drugs of various groups.
Treatment for DEP also includes drug therapy, physical therapy and a healthy lifestyle. It should be aimed at compensating for the disease that already exists, as well as optimizing microcirculation.
A popular method in the treatment of dyscirculatory encephalopathy is etiotropic therapy. It is characterized by individual selection of antihypertensive drugs, as well as drugs that lower blood sugar.
The basis of treatment for DEP consists of various medications that improve cerebral hemodynamics.
Such means are:
- Calcium channel blockers: flunarizine, nimodipine;
- Phosphodiesterase inhibitors: pentoxifylline;
- Antagonists: nicergoline.
- Clonidine;
- Pentamin;
- Octadine;
- Vitamins;
- Medicines of animal origin.
Surgery is also one of the treatment methods for DEP. It is carried out on the walls of the great vessels, at a time when medications are no longer able to cope with vascular problems.
During treatment, it is necessary to change the quality of normal life:
- You definitely need to leave out various types of work that involve lifting weights.
- Get away from stressful situations.
- Walk a lot, often be in the fresh air.
- Regularly engage in light exercise and exercise.
- It is necessary to do gymnastics every day. If dizziness is present, the exercises must be performed while sitting.
Traditional methods of treating DEP
Folk remedies can also be very useful in the treatment of dyscirculatory encephalopathy. Herbs and decoctions significantly alleviate the patient's condition.
Effective infusions are:
- Clover infusion;
- Propolis tincture;
- Hawthorn infusion;
- Herbal infusions with valerian, chamomile, hop cones, rose hips, mint, lemon balm;
- Onion tincture.
- Young garlic and onions help very well in treatment.
Herbs are not universal for everyone, but in combination with drug treatment they give a much more effective effect. The main thing is a positive and serious attitude towards fighting the disease.