Signs of apnea
As a rule, adults associate the baby’s restless sleep, frequent waking up and whims with hunger, indigestion, intestinal colic and other reasons. However, when observing a sleeping baby, in some cases a condition is noted that is described as “as if the child forgets to breathe.” A short breath hold lasting more than 10-15 seconds is the main symptom of apnea.
If the duration of stops is less than the threshold value, but they are repeated frequently, this should be reported to the pediatrician. Severe cases of prolonged apnea can cause the baby to turn blue and have difficulty breathing. In these circumstances, hospitalization is possible.
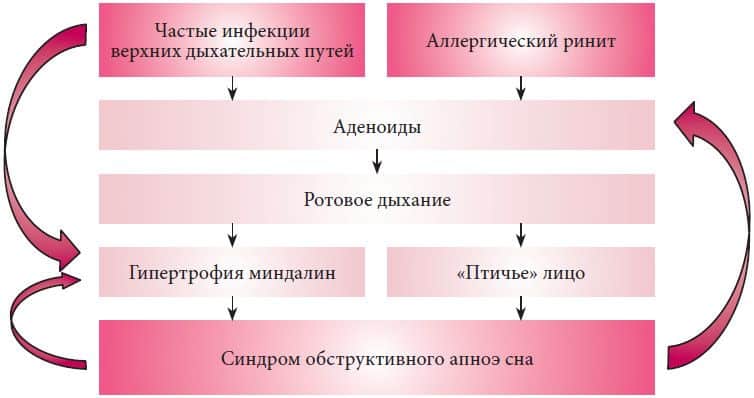
Children with signs of apnea often toss and turn at night, sleep with their mouths wide open and their necks outstretched, and breathing is complicated by snoring. At a more mature age, children may experience enuresis. Respiratory dysfunction is also accompanied by internal disorders: the heart rate slows down and the level of oxygen in the blood decreases.
Systematization of apnea: causes of occurrence
Based on the severity, mechanism of formation, and causes of occurrence, three main types of sleep apnea are distinguished and described.
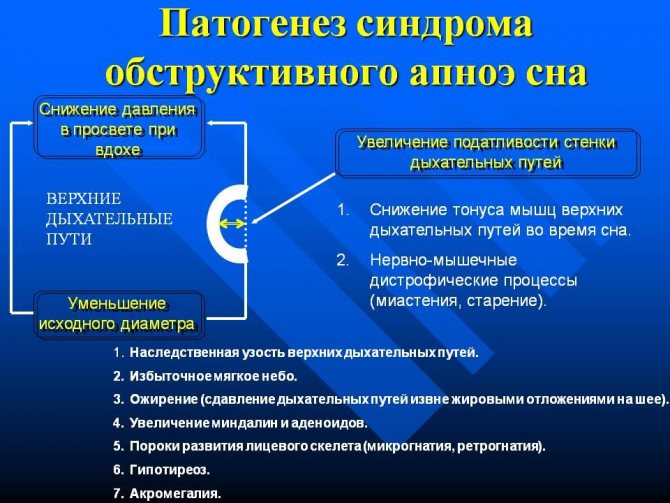
Obstructive apnea
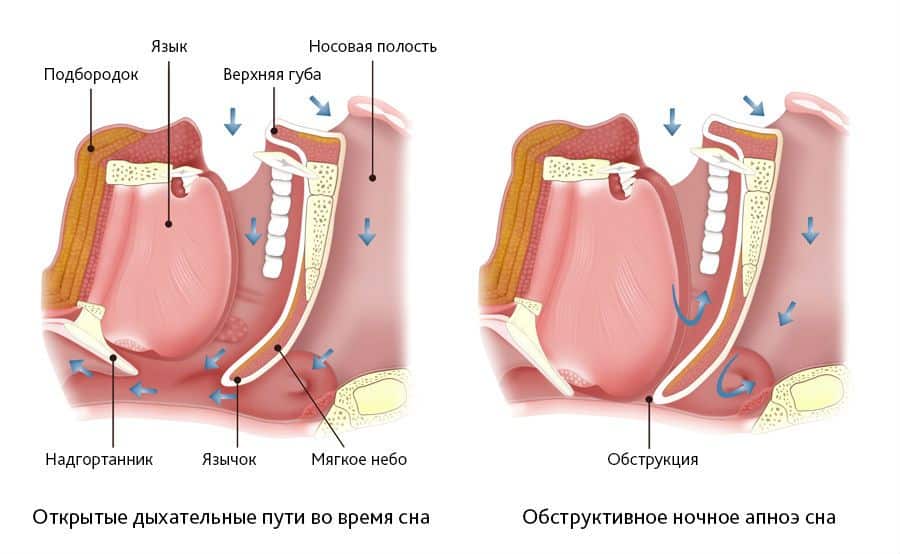
Episodes of breath holding occur due to narrowing of the respiratory passages. Lack of oxygen leads to sudden snoring with a rise in the chest and the possible awakening of the baby. Attacks may occur several times during the night.
The reasons why a child holds his breath during sleep with obstructive apnea are predominantly anatomical in nature:
- Congenital pathology of the tongue is macroglossia, accompanied by abnormal enlargement of the organ.
- Overlapping of ligamentous gaps due to attacks of laryngospasm - a sharp contraction of the muscles of the larynx.
- A cleft along the upper edge of the mouth is called a “cleft lip.”
- Pathology of the development of bones, cartilage, including the base of the skull - achondroplasia.
- Laryngeal muscle dysfunction.
- Increased size of the tonsils and pharyngeal tonsil.
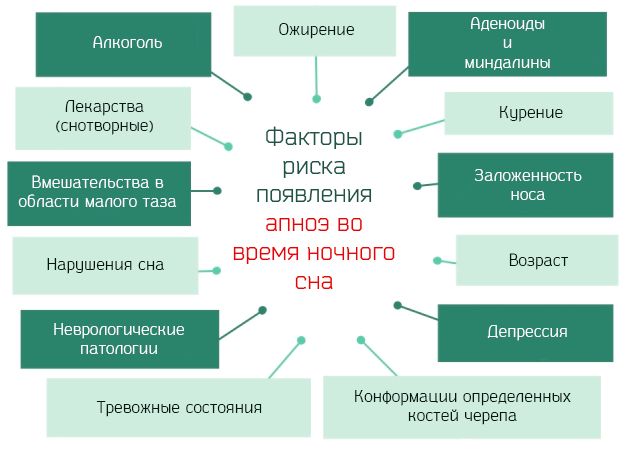
- Excess weight to obesity.
- Stridor (translated from Latin as “hissing”) is an abnormal narrowing of the larynx.
- Pierre Robin syndrome or anomaly is a congenital malformation of the maxillofacial bones.
The described type of apnea is observed in any age group, but the peak of the disease occurs in children of the primary preschool category - from 2 to 6-7 years.
Apnea central
This type of apnea is characterized as breathing consisting exclusively of exhalations; inhalation seems to be skipped. It occurs as a result of a malfunction of the respiratory center located in the lower part of the brain. Lack of control from the brain center leads to decreased activity of the respiratory muscles.
As a result, the child holds his breath during sleep for quite a long time, which leads to disturbances in the activity of the cardiac system and brain hypoxia.
The reasons are both congenital and acquired:
- Immaturity of the central nervous system due to prematurity. Delivery at 34 weeks or less, weight less than 2.5 kg.
- Birth injuries of the central nervous system.
- Hypoglycemic syndrome is a decrease in blood glucose concentration to a critical level.
- Alveolar hypoventilation is a violation of gas exchange in the lungs.
- Convulsive attacks in epilepsy.
- Infectious diseases of viral and bacterial origin.
- Low hemoglobin levels (anemia).
- Cardiac arrhythmia.
- Damage to the bronchi and lungs in premature infants due to artificial ventilation is bronchopulmonary dysplasia.
- Increased levels of bilirubin in the blood.
- Violation of electrolyte and acid-base balance in the body.
- Blood poisoning - sepsis.
- Maternal smoking during pregnancy.
Central type apnea occurs in approximately 60% of premature babies; infants from birth to one year of age are more likely to suffer.
Mixed type of apnea
The terminology “mixed apnea” speaks of a mixture of symptoms of obstructive and central types of apnea, with the latter manifesting itself first, flowing into airway obstruction.
Children at risk include:
- with metabolic disorders, and, as a result, having excess body weight;
- frequently regurgitating;
- with imbalance of body thermoregulation;
- with disturbances in the calcium-sodium balance in the body.
This type of respiratory obstruction is rare and difficult to diagnose.
Premature babies with a low body mass index or children with cerebral palsy or Down syndrome are most susceptible to sleep apnea syndrome.
Causes of apnea in children aged 1 year
Apnea in children under one year of age poses a serious danger associated with all kinds of complications, even involving a risk to life.
The reasons why a newborn baby holds his breath while exhaling may be the following:
- immaturity of organs and systems, including the respiratory system, in premature infants;
- infectious ENT diseases;
- birth asphyxia and other injuries received during the perinatal period;
- the use of drugs that block the activity of the respiratory center;
- inflammation of the intestinal mucosa – necrotizing enterocolitis.
Intermittent, inconsistent breathing during sleep in a child, with delays of more than 15 seconds, threatens the accumulation of carbon dioxide in the blood due to insufficient oxygen supply. For newborns, the outcome may be loss of consciousness, partial destruction of the brain with subsequent development of dementia, and in especially severe cases, death.
Treatment options for apnea
Treatment of the pathology in question begins with eliminating the root cause that provoked this dangerous condition. For these purposes, the following methods are used:
- if the problem is a malocclusion, it will need to be corrected through surgical correction;
- if you are obese, you need to consult a nutritionist and gradually reduce body weight;
- in the case when nighttime respiratory arrests are dependent. In other words, apnea occurs when the child takes a certain sleeping position; you need to wean the baby from sleeping in this position.
Important: If the culprit is excess soft tissue mass, it must be partially excised. In the case where apnea is caused by a defect in the nasal septum, it is impossible to correct the problem in childhood.
In this case, maintenance therapy will be required until the little patient reaches adulthood.
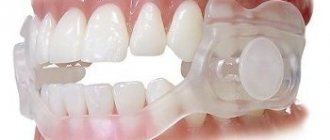
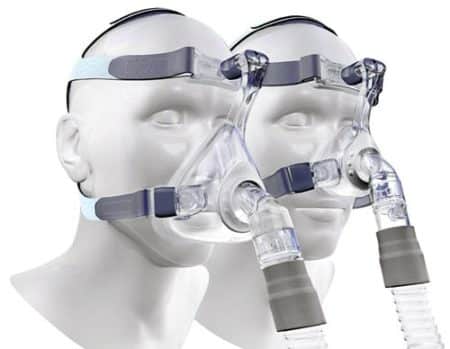
In some cases, surgery is contraindicated. Therefore, the doctor may recommend CPAP therapy. This method allows you to block interruption of breathing through artificial ventilation. CPAP therapy eliminates the possibility of hypoxia and creates optimal conditions for normal oxygen supply to the brain.
Operationally
Treating apnea with surgery is indicated when the cause of the pathology is the presence of acquired or congenital defects of the respiratory tract. In such conditions, the following types of manipulations are indicated:
- in case of abnormal development of the tonsils, tonsillectomy is recommended;
- if shortness of breath is caused by adenoids, adenoidectomy is prescribed;
- To eliminate the curvature of the nasal septum, surgical correction is indicated;
- less often, but tracheostomy may be recommended if the culprit of apnea is obstructive pathology or abnormal development of the airways;
- and the last method, which is also used in rare cases, is uvulotomy, excision of the uvula.
In general, the effectiveness of surgical intervention reaches 100%. However, a month after the manipulation, a re-examination of breathing will be required.
CPAP therapy
As mentioned above, this method is used when surgical intervention is contraindicated for some reason. With this type of treatment, a mask with a hose is put on the baby before going to bed, through which the air produced by the device flows.
Using this method, inhalation and exhalation becomes uniform and deep. However, it is worth emphasizing that the device must work continuously both during the day and at night.
Unfortunately, CPAP therapy has a short-term effect. Once you stop using the delay equipment, uneven breathing returns. There are also positive aspects to this. By resorting to this method of treatment, parents have the opportunity to block hypoxia until the facial skeleton is fully formed.
Of course, treating a child with this method takes a long time, however, reviews say that with the help of CPAP therapy you can forget about apnea forever, provided that the facial skeleton is fully formed.
Symptoms of childhood apnea
The appearance of the first signs of breath holding should not go unnoticed by adults. The following conditions indicate the presence of sleep apnea syndrome in a child:
- The child's breathing is uneven and intermittent; in his sleep he snores, grunts, and coughs.
- At night, the baby constantly sweats profusely, which indicates discomfort in sleep.
- When inhaling, the chest remains motionless.
- Breathing through the mouth prevails, not only during sleep, but also during wakefulness. This indicates oxygen starvation, which the baby is trying to compensate for.
- Difficulty swallowing food indicates an obstruction in the airway.
- The child takes unnatural positions, falling asleep, he tries to settle in such a position so that the larynx remains as open as possible.
- Nocturnal enuresis additionally indicates malfunctions of the central nervous system.
Apnea, unknowingly, can be confused with periodic breathing, which is the norm for infants up to six months of age. The main difference is the duration of breath holding: periodic is characterized by a pause of less than 10 seconds, while the child himself controls the process of inhalation and exhalation.
Treatment of pathology in children of different ages
Sleep disordered breathing is a serious pathology; sleep apnea is especially dangerous if it occurs in children under one year of age. During this period, the child’s body is actively growing, the brain is developing, skills and abilities are acquired daily. With a constant lack of oxygen, hypoxia occurs, which leads to the death of neurons.
Treatment of apnea begins after examination by an otolaryngologist and surgeon, a thorough diagnosis of the functioning of the central nervous system. Depending on the type of syndrome, conservative therapy using drops, sprays, tablets or surgery is prescribed.
A child with sleep apnea should be under parental supervision at all times. Temporary episodes can develop into complete interruption of breathing. In this case, it is necessary to urgently provide first aid and call an ambulance team. Alarming symptoms of deterioration:
- pallor, cyanosis of the skin and mucous membranes;
- epileptic seizure, convulsions;
- pulse rate less than 90 beats per minute;
- unnatural posture;
- lack of reaction to what is happening.
To prevent such a serious condition and death, consult a doctor in a timely manner. Short-term cessation of breathing should not exceed 10 seconds in duration; the episode itself does not repeat more than 2-3 times per night.
When breathing stops completely, brain cells die after 6 minutes. These damages are irreversible, and in the absence of emergency assistance, death occurs. Therefore, if alarming symptoms appear, immediately call a team of doctors. Before their arrival, the following manipulations must be done:
- Try to wake up and bring the child to his senses.
- Spray your forehead, arms and legs with cold water.
- Give artificial respiration. Tilt your baby's head back, close his nose and gently inhale mouth to mouth. The procedure should last no more than 2 seconds, since a child’s lungs are much smaller than those of an adult.
As a last resort, before the ambulance arrives, a closed heart massage is performed. During these procedures, be sure to open the child’s mouth and hold his tongue so that the baby does not choke.
Many techniques have been developed to treat apnea. Their main task is to remove pathological symptoms and restore breathing as soon as possible. Depending on the cause of sleep disturbance, the following therapy is prescribed:
- Taking medications. If the cause of uneven breathing is respiratory diseases, antiviral drugs are prescribed. To increase the tone of the palate and uvula, and eliminate complete closure of the walls of the larynx, antispasmodics are taken. To reduce allergic swelling - antiallergenic drugs. With the help of medications, apnea is treated, caused by disruption of the central nervous system.
- Physiotherapy. For the obstructive type of apnea, inhalations and treatment with special devices that regulate the flow, pressure, and humidity of the air are prescribed. For newborns, stimulation of the respiratory center or artificial ventilation is performed.
- Surgical intervention. Prescribed for enlarged adenoids, tonsils, the presence of polyps in the nasal passages, congenital or acquired pathologies of the skull.
Dangerous consequences of apnea in children
Periodic pauses in breathing threaten the child’s health. The most severe case is sudden infant death syndrome. Lack of oxygen leads to pathological changes in the baby’s body and negatively affects its development and behavioral reactions. The following consequences are likely:
- Syndrome of disobedience and hyperactivity. The child has a reduced concentration of attention and memory, his actions are impulsive, his behavior shows nervousness, tearfulness, and whims for no reason.
- Deterioration of the cardiac system with periodic surges in blood pressure. The body, trying to compensate for oxygen starvation, activates reserve mechanisms that increase blood circulation. The heart rhythm is disturbed, and over time this can result in heart failure syndrome.
- Failure of heart rate in the future threatens to result in atrial fibrillation.
- Night sleep disorder leads to drowsiness, lethargy and apathy during the daytime, as if the child falls asleep on the go.
Due to the severity of the pathology, episodes of apnea at night are recorded at intervals from 5 to 100 times, that is, the total time period is almost 4 hours. It is no wonder that the baby, suffocating in his sleep, sleeps restlessly and intermittently.
The danger of nocturnal respiratory arrest in children of different age categories
If your child holds his breath during sleep, sleeps with his mouth open, and often wakes up, it is recommended to visit an otolaryngologist and neurologist. Apnea is most dangerous for children born prematurely or weighing less than 2 kilograms. Consequences of prolonged episodes of sleep apnea at night:
- increased excitability, the child often cries and is capricious;
- headache;
- attention deficit disorder;
- heart failure;
- hypoxia;
- pulse disturbance;
- epilepsy;
- physical and emotional developmental delays;
- diabetes.
Nocturnal attacks of breath holding for an infant are often fatal. At one point, a baby may forget how to breathe. Therefore, parents are recommended to pay attention to the nature of breathing: extraneous sounds, duration of inhalation and exhalation, the number of episodes of apnea per night.
Medical (polysomnographic) examination and accurate diagnosis
An important role in detecting signs of childhood apnea is played by parents' observations of the behavior of a sleeping child. But for an accurate diagnosis of the disease, it is better to be examined in a hospital setting. The modern level of medical equipment makes it possible to identify the functioning of all systems and organs online.
Using electrodes and CCTV cameras with infrared illumination, the following indicators are recorded:
- electrical processes in brain neurons;
- activity of the cardiac system;
- duration of the rapid eye movement phase;
- electrical activity of the masticatory muscles;
- determination of the degree of blood oxygen saturation - pulse oximetry;
- pneumography – recording the activity of the respiratory flow;
- control of the frequency of inhalations and exhalations.
The entire examination is carried out under the constant supervision of medical personnel. In addition, the child must be examined by an otolaryngologist, neurologist and endocrinologist.
Expert advice and popular experience in the treatment of childhood apnea
To care for premature babies, they are placed in an incubator - a pressure chamber, where over time the babies reach typical heights and weights. Neonatologists monitor these children around the clock and, if symptoms of apnea are detected, provide treatment. The newborn is given emergency care.
- Activation of the respiratory center. The initial degree of apnea is amenable to tactile stimulation - rather weak tapping or slaps on the baby’s body.
- Severe disease requires external oxygen supply. Artificial ventilation is used.
- In case of pronounced hypoxia, an oxygen therapy procedure is carried out - an oxygen cocktail is inhaled into the baby’s lungs.
- If it is difficult to diagnose apnea, vasodilating pharmacological drugs are prescribed.
As a child diagnosed with sleep apnea grows, he or she undergoes regular polysomnography testing. With the formation of the skull bones, the laryngeal gap increases, and the pathology resolves naturally. If the measures taken do not provide the desired result, further treatment is carried out, which depends on the severity of the disease.

Surgical route
The radical method is surgery. The following operations are carried out:
- removal of the tonsils - tonsillectomy;
- cutting off adenoids;
- correction of the nasal septum;
- in the most extreme and severe cases, tracheostomy is practiced - opening the trachea for external communication;
- correction of the contours of the uvula or its complete cutting off - the operation is indicated in exceptional cases.
Surgery shows a fairly high cure rate, from 80 to 100%. A month and a half after the operation, the child is examined again and changes in breathing are assessed.
Non-surgical method
If there are no indications for surgical treatment of apnea, CPAP therapy is used. The child wears a mask while sleeping. Compressed air is compressed through special hoses. Thus, constant pressure is maintained in the walls of the respiratory vessels; they do not vibrate, remaining in good shape.
The device must be used until the child’s facial skeleton is fully formed. The sensors in the device are set and adjusted by the doctor depending on the weight and age of the baby and the severity of apnea. The duration of treatment varies from person to person; you may have to use the device throughout your life.
Alternative medicine methods
Traditional methods of getting rid of apnea are applicable for older children, since many procedures are unattainable for infants.
- Moisten your sinuses before bed with a salt water solution. This will get rid of accumulated mucus and clear the airways. It is better to use sea salt (a teaspoon per 200 ml of warm water).
- Before bed, drink a glass of freshly squeezed cabbage juice with a dissolved teaspoon of honey. Recommended course – 1 month.
- The bactericidal and wound-healing effect of sea buckthorn oil has been known since ancient times. Tip: place 3-5 drops in each nostril before going to bed.
- Yoga exercises are effective. Stick your tongue as far forward as possible and lower it to your chin. Hold it in this position for 2-3 seconds. The following exercise is aimed at strengthening the jaw muscles: grab your chin with your hand and move it, counteracting the resistance of your palm.
It is important to remember that traditional methods are only an auxiliary way to alleviate the symptoms of the disease; in severe cases of apnea, the help of a specialist is required.
TREATMENT OF THE DISEASE
The causes of sleep apnea in a child may vary depending on the age of the child.
Accordingly, the treatment of nocturnal disorders should also be selected taking into account the age characteristics of children with problems with breath holding during sleep.
In newborns
Premature babies are placed in pressure chambers. Here, doctors constantly monitor the breathing of newborns and provide assistance in emergency situations.
The initial phase of treatment is the use of tactile stimulation. The doctor taps and slaps the baby's body, activating his breathing.
If the attacks are prolonged and repeated frequently, pulmonary stimulation is used on the newborn.
When the attacks are reduced and no complications are observed, the child is discharged. Doctor's supervision continues at home.
In preschoolers
When a child from 2 to 5-6 years old holds his breath during sleep often and for a long time, CPAP therapy is applied to him.
The procedure helps support the walls of the airways by accumulating air under high pressure.
Before going to bed, a mask is placed on the little patient’s face with a hose running from it to supply air. The process is controlled by a doctor. CPAP therapy can last for months or even years.
When the disease is complicated by additional pathologies, doctors recommend surgical correction of the problem. In such cases, the following types of operations are relevant:
- correction of the uvula;
- removal of adenoids;
- correction of the shape of the nasal septum;
- elimination of respiratory tract pathologies.
Operations are effective in 80-100% of cases. The next check of the little patient is carried out after 1-2 months.
In school-age children
If sleep apnea occurs suddenly in adolescents, it should be seen by a doctor to determine the cause of the respiratory system disorder.
After diagnosis, the same treatment methods are used for schoolchildren as for preschoolers: drug or CPAP therapy, surgical intervention.
To help young mothers: preventing apnea and providing first aid if a child stops breathing
Preventive measures on the advice of Komarovsky are aimed at preventing attacks of apnea and reducing the frequency of their manifestations. The measures are simple but effective:
- walk with your child more often;
- ventilate the room before going to bed;
- clean the spout with cotton swabs soaked in salt water or oil
- practice sleeping on your side;
- do not overheat or overcool the child;
- sleep on an orthopedic mattress, preferably without a pillow.
If breathing is interrupted for a long time or cyanosis appears, you should immediately call emergency help. While waiting for the ambulance to arrive, mothers need to wake up the baby, move the head back, and perform artificial respiration.
- Cover the child's nose and mouth with your lips and make 2 blows at half the volume.
- If a pulse appears, do not interrupt the procedure until the baby begins to breathe.
- It is important to be able to do indirect cardiac massage - it is necessary in the absence of a pulse.
The offer of hospitalization in severe cases of apnea should never be refused. With this, parents will help their children cure a dangerous illness and eliminate further negative consequences.
Sleep-disordered breathing: symptoms in children
Healthy sleep is the key to the proper development of a child. Prolonged and frequent pauses in breathing during sleep affect well-being, growth and can cause death. It is important to be able to distinguish the signs of apnea from minor breath holds.
Symptoms in children can be noticed both during sleep and during the day. A sleeping child should be alert to the following manifestations:
- frequent intermittent breathing;
- poor sleep;
- restless movements, muscle twitching;
- snore;
- lack of movement of the chest and abdomen for more than 10 seconds.
In severe cases, there is also cyanosis (cyanosis) of the skin, usually starting from the nasolabial triangle, slow pulse, and loss of consciousness.
With such symptoms, it is necessary to wake up the child, check whether the airways are free of foreign objects, vomit, mucus, massage the arms and legs, restoring blood circulation. In a difficult situation, you must immediately start artificial respiration, chest compressions and call an ambulance.
With sleep apnea, the following symptoms may appear during the day:
- drowsiness;
- restless, sometimes aggressive behavior;
- delayed growth and weight gain;
- slowdown in mental development.
Even infrequent apnea events that do not lead to a serious condition negatively affect the health and development of the child. Therefore, it is necessary to note deviations in the sleep process and report them to doctors in a timely manner.