Headaches, changes in blood pressure and sudden redness of the face do not always indicate the presence of a serious illness. In some cases, these are signs of vegetative-vascular dystonia (VSD). A large number of people face a similar diagnosis. Most often, the first signs of pathology appear in childhood or adolescence. The disease rarely progresses and, with the right lifestyle, does not bother a person for many years. However, an exacerbation of VSD is possible at any time. Often, the symptoms of the disease are provoked by various factors. Among them are stress, climate change, and hormonal changes.
The concept of vegetative-vascular dystonia
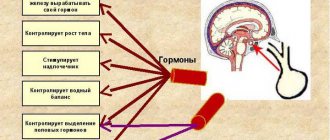
VSD syndrome consists of periodic changes in vascular tone of the autonomic nervous system. As a result of such disorders, patients may experience various pathological reactions that are functional in nature. Changes in vascular tone lead to problems with the innervation of almost all organs. Depending on which area the dysregulation predominates, the clinical picture may differ. Vegetative-vascular dystonia is not a fatal disease, but functional disorders are quite dangerous if an exacerbation develops. The most common symptoms of VSD include pressure surges, dizziness, cardialgia and indigestion.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia can make itself felt quite often or not manifest itself for a long time. This depends on the individual characteristics of the body, as well as on the presence of background pathologies and provoking factors. Despite the fact that this disorder is not classified as a serious disease, it has its own code in ICD-10. Vegetative-vascular dystonia is designated by the letter G. The numerical value in the encoding depends on the clinical manifestations of the pathology, so it ranges from 90 to 99.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia in men: causes, symptoms, treatment methods
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is a disruption of the autonomic nervous system, which is involved in the innervation of all vital systems of the human body. Adolescents and women are susceptible to VSD; in men, the syndrome is observed less frequently, since they often do not attach importance to the external manifestations of the disease. Typically, male representatives turn to a specialist only when the disease takes a serious turn.
- 1. Causes of VSD in men
- 2. Signs of autonomic dysfunction 2.1. Attack of VSD
According to doctors, vegetative-vascular dystonia (vegetative dysfunction syndrome, neurocirculatory dystonia) is a borderline state between illness and health. Autonomic dysfunction syndrome includes symptoms that are similar to the clinical picture of various diseases, but they develop in the absence of the disease itself.
Reasons for the development of VSD in males:
- heredity;
- congenital diseases of the cardiovascular and nervous system;
- lack of physical activity, physical inactivity;
- violation of the work and rest schedule;
- long periods of time in front of a computer or TV;
- mental and physical fatigue;
- sleep disorder (drowsiness, insomnia);
- work in hazardous industries;
- stress;
- bad habits (smoking, alcohol, overeating);
- chronic diseases;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- frequent changes in climate zones;
- excess weight;
- surgeries on the brain and spinal cord;
- taking psychotropic drugs.
The very first manifestations of autonomic dysfunction in men can appear already in infancy, later under the influence of hormones - in adolescence, the full clinical picture unfolds after 40 years.
Symptoms of VSD may differ for each person, it depends on the individual physiological characteristics of the patient. General signs of VSD, which are typical for all age groups, include:
- temperature increase;
- vasospasm;
- sleep disturbance;
- increased or decreased heart rate;
- lethargy;
- fatigue;
- dyspnea;
- migraine;
- pain in muscles and joints;
The clinical picture of VSD in men is in many ways similar to that in women and adolescents, but there are some differences. The symptom complex of the pathology includes the following disorders:
| Violations | Description |
| The cardiovascular system | Changes in heart rate, chest pain, tachycardia, bradycardia, decreased or increased blood pressure |
| Respiratory system | Shortness of breath, “lump” in the throat, attacks of suffocation, compression of the chest, lack of air, dry cough, wheezing, hoarse voice |
| Gastrointestinal system | Heartburn, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, constipation, pain in the stomach and intestines, flatulence, bloating, lack of appetite |
| Psyche | Aggression, apathy, nervousness, panic attacks, mood swings, irritability, anxiety, phobic disorders |
| Genitourinary system | Frequent urge to go to the toilet, increased amount of urine excreted (nuctria), decreased sexual desire, sexual weakness |
| Thermoregulation system | Increased work of the sweat glands, chills, increased body temperature to 37-38 degrees |
| Musculoskeletal system | Pain in joints and bones, muscle pain, myositis, exacerbation of arthritis, osteochondrosis |
Neurological symptoms may also be observed - tinnitus, stuttering, redness or paleness of the face, migraines, goosebumps, numbness of the limbs.
The manifestations of autonomic dysfunction alternate between states of well-being and crisis. The latter are preceded by long-term emotional experiences associated with certain events in a person’s life (death of loved ones, problems at work, financial difficulties, etc.). During such a crisis, an attack occurs that lasts from a few seconds to an hour.
Attacks of exacerbation of autonomic dysfunction begin abruptly, as evidenced by the appearance of the stress hormone cortisol in the blood, its volume reaches a critical level. At the time of such exacerbation, the following is observed:
- increase or decrease in blood pressure;
- increased heart rate;
- chest pain;
- suffocation (possible fainting);
- convulsions, tremors;
- hyperemia or pallor of the skin.
In this case, a person may experience panic attacks and fear of death. Sometimes the attacks go away on their own, but in some cases medical attention is required.
Diagnosing the disease in adults is difficult, since the syndrome combines a whole complex of symptoms. Therefore, it is necessary to undergo a full examination, collecting anamnestic information and passing the necessary tests. The examination includes consultations with narrow specialists:
- neurologist;
- cardiologist;
- endocrinologist;
- gastroenterologist;
- therapist;
- psychiatrist.
The patient is prescribed examinations: ECG, MRI, OAM, OAC, ultrasound of internal organs, Dopplerography of blood vessels, rheovasography, etc. Another method of research for the syndrome is measuring pressure in order to determine the additional one - for this, the indicators of the usual daytime pressure are compared and its indicators during time to wake up. Additionally, a “cold” test method is used, during which changes in blood pressure and heart rate are recorded. Based on the results of the studies, the type of VSD is determined and an individual treatment regimen is developed.
Clinical forms of VSD
There are 3 types of vegetative-vascular dystonia. They differ in clinical manifestations. An exacerbation of each of these forms of the disease is accompanied by a sharp deterioration in the condition and possible complications. The following types of dystonia are distinguished:
- VSD of the hypertensive type. This type of pathology is characterized by a tendency to increase blood pressure. Typical symptoms are: hypertension, dizziness and tachycardia. Blood pressure rises to a slight level (140/90 mm Hg). However, it can decrease on its own, without taking antihypertensive drugs. The danger of this condition is that it often develops into hypertension. An exacerbation of this type of pathology is a sympathoadrenal (vagoinsular) crisis.
- VSD of hypotonic type. This form of dystonia is characterized by a tendency to decrease blood pressure and is accompanied by attacks of weakness, dizziness, and lack of performance. Patients complain of periodic nausea, lack of air, and a tendency to constipation. Such a diagnosis is difficult to establish, since it has similarities with the signs of many pathologies.
- Another type of dystonia is VSD of the mixed type. It includes signs of both forms of pathology. With an exacerbation of vegetative-vascular dystonia, drops in blood pressure, headache and changes in skin color may be observed. This clinical form is the most difficult to diagnose.
What is the cause of exacerbation of VSD?
Exacerbation of dystonia rarely occurs spontaneously. This is usually preceded by various circumstances. Factors that can provoke an exacerbation of VSD include:
- Stressful situations.
- Impaired cerebral circulation resulting from cervical osteochondrosis.
- Head injuries.
- Exacerbation of chronic diseases.
- Poisoning and bad habits.
- Hormonal changes.
- Emotional turmoil.
Most often, there is an exacerbation of VSD after stress. Symptoms of dystonia can be triggered by overwork at work, lack of sleep, and problems in relationships with loved ones. In addition, stress factors for the body include: pregnancy, the postpartum period, menopause, adolescence, premenstrual syndrome, etc.
In most cases, the exacerbation of dystonia is influenced by the time of year. Symptoms of pathology can be associated with any changes in weather conditions. However, most often the manifestations of the disease intensify in the spring. Exacerbation of VSD during this period occurs as a result of activation of the nervous system, namely subconscious reflexes. The main symptoms of the disease include depression, anxiety, tachycardia and headache.
Reasons for development
In men, disruptions in the autonomic system are usually associated with age. The first signs of VSD begin to appear at the age of 40–45 years.
The reasons for the development of the disease include the following factors:
- hereditary predisposition;
- abuse of alcoholic beverages and other harmful substances (tobacco, drugs);
- changes in hormonal levels;
- lack of rest, overwork;
- emotional overload, “psychological burnout,” constant stress;
- constant mental stress;
- infectious diseases.
VSD is not an independent disease. It manifests itself only as a result of certain disorders of the body, failures in its functioning. More often due to constant stress, overwork, lack of rest, and neuroses. It affects the entire body and depresses it. Therefore, when starting treatment, it is worth fighting its root causes, and not the symptoms.
Return to contents
The mechanism of development of signs of VSD
Despite the fact that vegetative-vascular dystonia does not relate to organic pathologies, exacerbations can be accompanied by severe symptoms from the cardiovascular system. This occurs as a result of nervous exhaustion. Under the influence of stress, the body begins to react in a specific way: vascular tone is disrupted. In the hypertensive form, the muscle layer of the arterioles contracts too much, leading to increased pressure. Often this is facilitated by stress, emotional background and changes in weather conditions. The hypotonic form develops against the background of vascular relaxation. This type of dystonia occurs in adolescents due to increased growth of the body. Hormonal changes also contribute to the exacerbation of VSD. As a result of a violation of the vascular system, insufficiency of the autonomic nervous system occurs, affecting the functions of the entire organism.
ethnoscience
Despite the fact that hospitals offer an extensive list of medications and methods for treating vegetative-vascular dystonia, many people prefer traditional methods. So, for example, healers recommend treating VSD with clay. To do this, you need to drink a solution of one teaspoon of clay in warm water every day. Reduce the amount of clay over time. This will help remove waste and toxins from the body. It is useful to mix beetroot, carrot and cucumber juices in a ratio of 1:3:1. Traditional healers advise using decoctions of herbs and roots for therapy. Herbs that are more suitable for men are St. John's wort, mistletoe, rose hips, licorice roots, valerian, Leuzea extract, angelica and Rhodiola. To do this, dried roots and herbs need to be ground in a coffee grinder. Then pour 2 tablespoons of the resulting powder into 0.5 liters of boiling water. Take in small portions after settling.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=M3l6avEsyZQ
etodavlenie.ru
Symptoms of exacerbation of the disease
The autonomic nervous system regulates almost all organs and systems. Therefore, if vascular tone is disturbed, various symptoms may be observed. Among them are pressure surges, heart pain, dizziness, etc. Depending on the predominance of certain symptoms of exacerbation, the following types of disorders are distinguished:
- Vagoinsular crisis. This form is characterized by a decrease in blood pressure. Vagoinsular crisis occurs with VSD of the hypotonic or mixed type. Symptoms of an exacerbation include: increased sweating, sudden weakness and loss of strength, pale skin and decreased body temperature. Patients complain of difficulty breathing and severe headaches.
- Sympathoadrenal crisis. This form accompanies dystonia of the hypertensive type and develops with exacerbation of VSD. The following symptoms are observed: increased blood pressure, heart pain, tachycardia. During the period of exacerbation, a person feels fear and anxiety. Due to nervous overstrain, a temporary deterioration in visual acuity and shortness of breath may occur.
With VSD of mixed type, symptoms of both vagoinsular and sympathoadrenal crisis occur. In addition to the listed signs of pathology, dystonia is accompanied by asthenic syndrome. It is characterized by emotional lability, apathy, fatigue and irritability.
Treatment of VSD
Vegetative-vascular dystonia and its symptoms respond well to treatment in men once the causes of the development of the main clinical syndrome are determined. The clinical picture manifests itself when the central regulation of autonomic functions is disrupted.
The center of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system is located in the structures of the midbrain and medulla oblongata. Therefore, centrally acting drugs become the drugs of choice for drug therapy.
The following drugs are used to treat VSD:
- antidepressants;
- drugs of the tranquilizer group.
Depending on the type of clinical syndrome, the duration of the course of therapy is determined. Antidepressants are used for up to a year or more. But long-term use of tranquilizers is prescribed with caution, as addiction to them quickly develops.
The clinical effectiveness of treatment depends on the frequency and manifestation of panic attacks. Attacks of VSD require immediate symptomatic treatment. The following groups of drugs are mainly used:
- adrenergic blockers for the development of hypertensive syndrome;
- antispasmodic drugs for severe spastic processes;
- nootropic agents to improve the functioning of brain cells;
- drugs that improve trophism and blood supply to tissues;
- herbal sedatives are used to relieve stress;
- analgesics are prescribed for severe pain, for example, for cardialgia;
- antioxidants – to improve tissue regeneration;
- for hypotension, herbal tonics are used;
- for spastic constipation, it is advisable to prescribe laxatives in combination with antispasmodics.
Treatment of VSD should be comprehensive and long-term. For a positive outcome of the disease, drug therapy is combined with other non-traditional methods. These include:
- psychotherapy method - helps people cope with panic attacks through self-control or self-hypnosis;
- acupuncture – aimed at relaxing the body;
- physiotherapeutic techniques allow you to cope with clinical syndromes;
- physical therapy keeps the body in good physical shape;
- therapeutic and preventive massage normalizes the tone of the body muscles and leads to their relaxation.
There are many more methods for treating and preventing attacks of VSD. All of them are aimed at developing the body’s ability to relax and control itself. Running, swimming or simple walking help.
Relieving attacks of VSD returns patients to their usual way of life, they forget about unpleasant symptoms. But it is worth remembering that under the influence of unfavorable factors, clinical dystonia syndromes can develop again.
Recurrences of VSD can be minimized with proper treatment and compliance with preventive measures. To do this, make a healthy lifestyle a priority and minimize the impact of stress factors.
distonija.ru
Crisis severity
Exacerbation of dystonia consists in the development of symptoms of crisis. Often the clinical picture of one of the forms of the disease predominates. Crisis conditions differ not only in type, but also in severity. According to the generally accepted classification, there are 3 types of exacerbations. A mild crisis is characterized by severe symptoms. The patient's condition sharply worsens and several symptoms of dystonia are observed at once. Such violations last no more than half an hour. In most cases, symptoms go away on their own.
With moderate severity, signs of a crisis are observed from 30 minutes to 1 hour. During this period, the clinical picture is clearly expressed. Unlike mild cases, signs of exacerbation disappear gradually. Symptoms such as headache, loss of energy and anxiety may bother a person for another day.
In a severe crisis, signs of pathology last more than 1 hour. In addition to changes in blood pressure, cardialgia and breathing problems, convulsive syndrome may develop. Symptoms of exacerbation disappear gradually. They are replaced by asthenic syndrome, which lasts several days.
Diagnosis of vegetative-vascular dystonia
One of the exclusion diagnoses is vegetative-vascular dystonia. ICD-10 (codes G90-G99) includes several nosologies for which VSD is determined. The doctor has the right to indicate the code of this disease only after excluding other pathological conditions. Therefore, when symptoms of dystonia appear, a comprehensive examination is carried out. It includes a general and neurological examination. You should also check your thyroid hormone levels, as most signs of VSD resemble endocrine disorders. Instrumental diagnostic methods include ECG, EEG and EchoCS. In some cases, consultation with a psychologist is required. Only after excluding diseases of the nervous, endocrine and cardiovascular systems is a diagnosis of “vegetative-vascular dystonia” made.
Treatment of VSD in adults and children
The main aspect in the treatment of VSD is emotional peace. To this end, you should minimize stressful situations in your life, give up bad habits and normalize your work and rest schedule. Treatment of VSD in adults consists of acupuncture, magnetic therapy, and taking soothing herbal decoctions. Teas with the addition of chamomile, hawthorn, and sage are recommended. Alcoholic drinks and caffeine should be excluded from the diet. The same recommendations apply to teenagers. Children suffering from VSD should not engage in strenuous sports.
Vegetovascular dystonia - treatment for children and adults
Before treating vegetative disease in children or adults, you need to understand the causes of the disease. External causes must be eliminated. Having determined the type of VSD, the doctor will prescribe a course of treatment.
A neurologist will treat a characteristic disorder in the body’s functioning. If vegetative-vascular dystonia is associated with an internal organ disease, the doctor will prescribe treatment with pills or other therapy.
If the use of folk remedies is sufficient to treat VSD, tablets can be excluded.
How to treat women and men
The psychological reasons for women and men may differ, but the essence of the problem and treatment are carried out in one direction - relaxation. Causes associated with internal organs may differ between women and men by gender, and there are differences in treatment.
Treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia in women can consist of auto-training, a course of massage, and physical therapy.
The doctor may prescribe:
- drugs;
- physiotherapy;
- visiting a psychiatrist.
In women, if the main cause of VSD is hormonal imbalance, treatment will consist of hormonal drugs.
Treatment of VSD in men consists of normalizing the mode of existence. You need to determine the time for sleep and rest, follow a diet, and eliminate bad habits.
Diagnostics will allow you to prescribe a course of treatment depending on the malfunctions in the body. It is possible to treat arrhythmia, insomnia, and pain. To get rid of vegetative-vascular dystonia, you can contact a psychologist for relaxation.
Treatment of children
Vegetative vascular dystonia in children is not determined by examination. Symptoms of VSD in children are a reason for diagnosis and testing. Based on the examination, the doctor will prescribe treatment.
Most of the reasons for the development of VSD are emotional. To choose treatment methods, you need to evaluate the symptoms and identify the causes. If the reasons are external, they need to be eliminated. Children need to create an atmosphere of love, warmth and comfort.
Treatment of adolescents and children can be carried out by different means:
- drugs, medicines, folk remedies;
- psychological impact;
You can treat children and adolescents without taking medications using:
- performing a strict regime;
- physical education classes with permitted load;
- eating a balanced diet;
- conducting a course of physiotherapy: electrophoresis, massage;
- herbal medicine applications;
- taking vitamins;
- course with a psychologist.
Methods of treatment with folk remedies
Treatment with folk remedies for VSD is carried out at home, but after the diagnosis has been established. A disorder in the body in an adult or in children must be restored without causing harm or wasting time.
If vegetative disease is associated with a mental disorder, it is useful:
- drink decoctions, herbal infusions and tinctures that have a calming effect (motherwort, valerian, hawthorn);
- take relaxing baths;
- perform aromatherapy;
- cleanse the body of waste and toxins;
- soothing clay masks
- Tinctures of valerian and motherwort will soothe and relieve pain in the heart area.
- Treatment with freshly squeezed juices or various teas is possible.
In order for a lasting result to appear, you need to be treated with folk remedies for a long time and follow the principle of regularity.
How to get rid of vegetative vascular dystonia forever
You can get rid of vegetative-vascular dystonia forever at home if you really want to. Having identified the symptoms and found out the cause, you need to treat the affected organ or restore the psyche. In parallel with the course, you need to switch to a healthy lifestyle.
The drugs in combination with the right way will give a positive result, the body will recover gradually.
If treatment for an adult or child is completed, do not forget about:
- physical activity;
- proper nutrition;
- balanced work and rest regime;
- elimination of bad habits and stressful situations;
- healthy sleep;
- walks in the open air.
Emergency care during an exacerbation
The development of the crisis requires the adoption of urgent measures. If blood pressure increases, antihypertensive drugs are prescribed for single use. These include medications "Captopril", "Nifedipine". For the hypotonic form of VSD, the drugs “Caffeine” or “Citramon” are used. During a crisis, you should take the person out into the fresh air and try to calm him down. A warm bath, a decoction of valerian or motherwort will help cope with nervous tension.