The concept of “blown head” is not medical. Nevertheless, it exists and includes a whole range of symptoms that are dangerous to the body.
A bloated head is a reflex reaction of the body to cold, which is expressed in spasm and inflammation of blood vessels and muscles and can lead to inflammation of nerve endings.
The symptoms of hypothermia depend on which part of the skull is affected, which organs and nerves are affected by the inflammatory process. Symptoms that bother the patient:
- headache;
- heat;
- chills;
- changes in blood pressure;
- noise in ears;
- dizziness.
If you have a cold in your head, not only it, but your entire body will suffer. The first sign of hypothermia is a cold: the patient’s temperature rises, a runny nose, cough, weakness, and headache appear.
A more serious problem may arise, for example, an inflamed nerve in the head. In severe cases, the trigeminal nerve is involved in the pathological process, the branches of which pass in the forehead, cheeks, nose, and chin. The condition manifests itself as short-term but sharp pain in the facial area.
What caused your head to blow?
If your head felt a bit drizzly, most likely you were in a draft. The main reasons why hypothermia occurs are presented below.
Air conditioner
Even in the summer heat, you can feel the air on the left or right side of your head. If you work in an office or are in a house with the air conditioner on all the time, you should not be surprised when painful symptoms occur on the side of your face and head where it is located.
Wet hair and strong wind
We are constantly in a hurry and, having washed our hair in the morning without drying it properly, we rush to work or run errands. We rushed out into the street, and this is the result - our wet head was blown by the wind.
Unpleasant symptoms appear: temperature 37 and above, shooting in one ear, pain in the left or right side of the skull and ear. All this is due to the fact that it blew.
Open doors and windows
Are you used to ventilating a room by opening doors and windows at the same time? The result will not be long in coming. If you add cold drinks and ice cream to such conditions, you may not be surprised that both parts of your skull are blown out. The back of the head and neck may also be affected.
To avoid chilling the nerve on your head, leave the room during ventilation.
Draft in the car
A common cause of a painful condition is that the head was blown in the car. This is a consequence of opening all the windows in the car at once.
It is wise not to open all the windows at the same time, but to lower the glass only on one side, and only halfway. And don't lean out of the window while driving.
Neuritis of the facial nerve in a child
The causes of damage to the facial nerve in a child can be as many as in an adult: hypothermia;
- inflammation of the middle ear;
- damage to the facial nerve itself.
A reliable symptom of the development of the disease is the skewing of the mouth in the healthy direction when trying to bare teeth. Treatment of the disease in younger patients depends on its etiology, but usually recovery occurs within 2-3 weeks. In some cases (when the cause is a serious illness), more time is required.
During therapy for fever, antipyretics are prescribed. In the acute phase of neuritis, anti-inflammatory and vasoactive medications are also prescribed. During the remission phase, exercises may be prescribed, which the child performs first with a doctor and then with a parent.
Consequences for the human body
A cold threatens with a number of unpleasant and even dangerous complications. Even after a slight draft that blows through the back of your head, you can get:
- neuritis, in particular, neuritis of the facial nerve;
- tendonitis (tenosynovitis, tendobursitis), arthritis;
- inflammatory processes in the maxillary and frontal sinuses (sinusitis, sinusitis);
- otitis, meningitis;
- arachnoiditis;
- conjunctivitis;
- lymphadenitis (inflammation of the lymph nodes);
- infectious brain abscess.
All of these diseases are serious, require difficult and long treatment, sometimes threaten irreversible complications, and require referral to different specialists.
Neuritis of the facial (trigeminal) nerve
If the left side of the head or the right is blown, there may be inflammation of the nerve innervating the facial muscles on one side of the face. As a result, their weakness (paresis) and even complete paralysis of facial movements develops.
People with an anatomically narrow bone canal are more prone to inflammation of the trigeminal nerve. Due to deterioration of blood supply and pinched nerve, tunnel syndrome is observed.
Pathology occurs due to the fact that the head is blown by the wind or blown by a fan. People sitting near air conditioning or constantly exposed to drafts are at high risk.
Meningitis
Meninitis does not occur from hypothermia; it is infectious or bacterial in nature. However, if an adult or child constantly has a cold head, this indicates a decrease in immunity. This means that the body is especially susceptible to various viruses and bacteria.
Meningitis is a very dangerous disease, so if, after blowing through the right or left side of the head, you experience pale skin, weakness, lethargy, anxiety, drowsiness, or severe headache, you should urgently consult a doctor who will prescribe medication treatment.
Otitis
Otitis is a group of inflammatory diseases of the ear, which manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- pain when opening the mouth;
- pain in the ear;
- swelling and redness of the ear;
- pus from the ear;
- increased body temperature;
- itching and congestion in the ear.
If all these symptoms occur after the back of the head or neck has been blown, you should urgently consult an otolaryngologist.
Infectious brain abscess
This is the name of the purulent-inflammatory process that occurs in the brain tissue. Most often, this complication affects people who have a cold, have a weakened immune system, or have a history of severe chronic diseases.
Often the cause of an abscess is untreated purulent otitis media - also a consequence of a frozen head.
The disease is accompanied by:
- high temperature;
- chills;
- weakness and pallor;
- blood leukocytosis and increased ESR;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- nausea and vomiting.
How can you get a cold on the facial nerve?
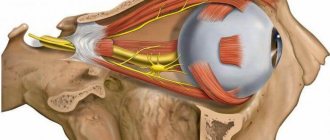
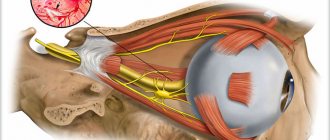
The anatomical location of the facial nerve is quite confusing. It passes through the facial canal of the temporal bone and exits into the auditory canal. At this point it intersects with the intermediate nerve.
It is quite easy to get colds in the maxillofacial area. However, this disease is similar in symptoms to others. It is important not to self-medicate, but to consult a specialist in time.
The nervous system is complex. The skin and muscles are equipped with nerves that intersect with each other. When viruses damage the facial muscles of the face, neuritis or neuropathy of the facial nerve develops. Neuritis is inflammation of a nerve. Neuropathy is a disease that causes unilateral paralysis of the facial muscles.
My ear and the right side of my head hurt – what’s there?
When the right side of your head is blown and your ear hurts, what could it be? One might suspect:
- neuritis and trigeminal neuralgia;
- tunnel syndrome;
- neuralgia of the glossopharyngeal nerve;
- purulent otitis media and internal otitis;
- arthritis of the temporomandibular joint, including purulent;
- acute sinusitis.
Diagnostics
If you notice symptoms of sciatica, you should seek help from a therapist or neurologist. Specialists are able to determine inflammation by external manifestations. There are other pathological conditions that successfully disguise themselves as signs of the disease being described, therefore, at the first examination, the doctor carefully collects an anamnesis, enters it into the treatment protocol, and then begins to examine the patient: he performs deep palpation along the sciatic nerve and determines the main pain points. Additionally, the doctor conducts a number of simple tests.
- The patient is placed on the couch and asked to raise his straight leg. With sciatica, a lumbago occurs in this position, which subsides as soon as the person returns the limb to its original state.
- The patient's nose and mouth are covered and he is asked to create forced breathing. It increases pressure in the chest and abdominal cavity. The pain in this condition should completely disappear, but if there is sciatica, other neurological symptoms will appear: loss of sensitivity in the calf area, weakening of the knee reflex (detected by tapping the hammer), impaired motor functions of the foot and toes.
- The person is asked to stand, bend their knees slightly, lean their torso forward, and carefully try to straighten their legs. If the sciatic nerve is inflamed, severe pain will occur in this position.
- If you try to tilt your head forward while standing, the affected limb will reflexively bend at the knee.
To determine the causes of illness, the extent of inflammation, and the involvement of surrounding tissues in the process, instrumental examination methods are used.
Be sure to prescribe:
- electroneuromyography - it is used to evaluate the speed of transmission of nerve impulses;
- X-ray - allows you to confirm or exclude the presence of a compression tunnel;
- Ultrasound - helps to assess the condition of surrounding tissues;
- CT or MRI - used to determine the localization of the inflammatory process and the extent of its spread.
The transcript results provide a complete picture of the etiology and pathogenesis of the disease.
Causes of headaches
A severe headache is just one of the symptoms of hypothermia. Usually it is accompanied by a number of other signs on the basis of which one or another disease can be suspected:
- if the condition is accompanied by a runny nose and nasal congestion, a headache may be a sign of sinusitis, sinusitis, or sinusitis;
- if shooting in the ear, purulent discharge is observed, we are talking about purulent otitis media;
- if your head starts to throb. There is twitching on one side, accompanied by weakness and a desire to put on something warm, indicating nerve damage;
- severe pain in the head, accompanied by dizziness, nausea, vomiting, loss of balance - a sign of inflammation of the brain and its membrane (meningitis, encephalitis);
- if the temple shoots, more often on the right side, when it hurts to touch, this does not indicate that the face is blown, but about more serious problems;
- if there is aching in the temple, the pain manifests itself in peaks (increases and subsides), radiates to the shoulders and back - this is osteochondrosis of the cervical spine;
- a lumbago in the back of the head is a sign that there is air conditioning or a draft. If the pain appears in the morning, it may simply indicate sleeping in an uncomfortable position;
- Increasing pain in a lying position indicates a diseased tooth. You're on your way to the dentist.
Symptoms of facial nerve disease
If a person has a cold on the facial nerve, symptoms of the lesion appear in the form of unilateral or bilateral lesions. Often the affected part of the face (cheek, ear, chin) may become painful or numb. In 90 percent of cases, paresis is unilateral. The reason for this is that the temporal portion of the facial nerve is the most vulnerable.
Paresis (prosoparesis) is a decrease in voluntary movements of facial muscles. It has significant differences from paralysis. Paresis involves only partial impairment of muscle function.
The problem in diagnosing the disease is that paresis is not easy to notice (especially in mild forms of the disease). It only appears when a person speaks.
Paresis is divided into mild and severe. The mild form is characterized by minor changes in facial expressions in conversation. Severe paresis is a very indicative symptom of the disease. Such a defeat is expressed in the fact that the face turns into a mask. It is difficult for the victim to puff out his cheeks and close his eyes. Also, these movements are accompanied by pain.
Pathological synkinesis is divided into eyelid-labial and eyelid-frontal. In the first case, when the eyelid lowers, the corner of the mouth rises. In the second, when the eyelid droops, the forehead wrinkles.
The causes of paresis are:
- Fiber compression.
- Nerve damage.
Paralysis is also observed in the following:
- it is difficult for a person to speak;
- the victim has difficulty swallowing;
- the patient experiences lacrimation and salivation;
- there is a lack of sensation of taste of food;
- there are painful sensations in the face that are shooting in nature;
- the corners of the mouth and eyebrows (on the right or left side of the face) are lowered;
- difficulty closing your eyes;
- the victim feels pain in the ear, jaw;
- asymmetry of the facial muscles occurs;
- it is difficult for a person to whistle and puff out his cheeks;
- Sometimes the patient experiences eye twitching.
Thus, the main symptoms are expressed in high or reduced skin sensitivity; facial pain; malfunction of the salivary and lacrimal glands; numbness; pain inside the face (usually aching or dull); problems with facial expressions (reflected on the part that is cold).
Signs of the disease also differ depending on the phase. In the acute course of the disease, the lesion can be very visible, in this case the degree of facial distortion is very large.
How to treat a cold head at home?
What to do if you have a cold? Which doctor should I contact, how to understand how to treat the ailment?
- if your ear, throat, or nose hurt, see an otolaryngologist;
- in case of nerve damage, a neurologist will help;
- the treatment of acute respiratory viral infections is carried out by a therapist;
- For conjunctivitis, an ophthalmologist is recommended.
The right decision would be to first contact a therapist, who, after examining and listening to complaints, will refer the patient to specialized specialists.
First aid
If your head is cold and it hurts, some advice from doctors that can be easily implemented at home will help:
- provide yourself with bed rest for several days;
- limit the consumption of fatty, fried, salty, smoked foods;
- do not smoke or drink alcohol;
- At the first sign of a cold, you should drink tea with lemon, honey, and raspberries. A flock of rose hips, fruit and berry juices, and natural juices help well;
- provide dry warmth to the head (tie it with a down scarf, apply hot salt or semolina).
Treatment methods
Self-medication is unacceptable here. When the doctor discovers that the facial nerve is cold, treatment usually begins without delay. For greater effectiveness, it is comprehensive.
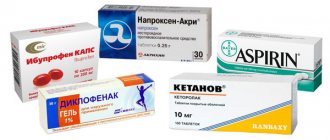
Usually the doctor prescribes medications, including:
- Pharmaceuticals.
- Decongestant medications (they relieve swelling).
- Diuretics (remove excess moisture, dilate coronary vessels).
- Drugs that increase the sensitivity of nerve tissue.
- Substances to maintain muscle tissue in tone (preventing infection).
- Vasodilators (allow you to saturate the tissues with oxygen).
- Painkillers (relieve pain).
Usually, not only drug treatment is prescribed, but also special gymnastics, as well as physiotherapy. If necessary, antibiotics may be prescribed as part of complex therapy.
Important: therapeutic exercises are performed on the side that is not affected. In this case, relaxation and tension of the facial muscles alternate. Gymnastics is aimed at simulating the expression of various emotions (anger, laughter, joy, crying).
Articulatory sounds come to help in the training process.
It should be remembered that physiotherapy may have contraindications. Therefore, they are prescribed after a special examination.
Traditional medicine can also be used in complex therapy:
- Goat milk with honey before bed (the drink should be warmed before drinking).
- Flax seeds are steamed and applied to the painful area.
- Rubbing fir oil into the affected area.
- Rose tea (a drink made from red rose petals). The drink calms the central nervous system.
Many people are interested in the question of whether it is possible to heat the skin in the area of inflammation of the facial nerve. To combat the disease, you can use not only medications and therapeutic exercises. Dry heat can also be a way to relieve pain. But this method is controversial; it is better to use such treatment with the permission of a doctor.
What to do to avoid hypothermia?
In order to get a cold as little as possible, without looking for someone to turn to and how to treat the ailment, follow simple prevention methods:
- Never go out into the cold in winter without a hat to prevent frostbite on your head.
- Avoid drafts to avoid overcooling your head.
- Toughen up.
- Exercise to strengthen your immune system.
- Practice good hygiene and wash your hands frequently to avoid bacterial infections.
- Drink more vitamin drinks and eat healthy foods.
If, after all, a cold has caught up with you, you should not treat a cold at home and swallow everything. Visit your doctor and follow his treatment recommendations to avoid unpleasant complications.
Visits: 70,525
The main causes of coldness of the sciatic trunk
Usually a cold is a consequence of a negligent attitude towards one’s own health. It can be triggered by:
- driving fast with the window down;
- wearing clothes that are not appropriate for the weather;
- constant drafts;
- swimming in cold water;
- prolonged exposure to the cold.
Hypothermia is the main cause of the disease, it contributes to inflammation of the nerves or surrounding muscles. To understand the scale of possible complications, you need to know the anatomy of the ischial column.
The nerve begins in the lumbar region, branches into two parts, each covering almost all parts of the lower extremities: a branch from the sacral joint enters the pelvis, through the infrapiriform foramen goes under the gluteal muscle, branches into smaller processes and covers the femoral and calf muscles.
The sciatic nerve is involved in the innervation of all joints of the lower extremities, the skin of the lower leg and foot, and the muscles that move the legs. If the trunk gets cold and inflamed, impulse transmission is disrupted. This leads to the development of a characteristic clinical picture.
Therapy
To treat colds of the sciatic nerve, a set of procedures is used that relieve symptoms.
Self-medication for this disease is dangerous, because the resulting complications can only be cured in an inpatient setting. Several treatment regimens have been developed.
- The patient is turned over on his stomach, placed on a flat bed, there should be a pillow or a folded thin blanket under the chest. Cover, but only so that there is no pressure on the body.
- Under no circumstances should you heat damaged parts of the body, because this will not relieve the pain, but will intensify it and lead to swelling.
- Treatment should be carried out by a neurologist or general practitioner; in case of severe pain, it is recommended to call an ambulance. Pain medication may be used when transporting the patient to the hospital to establish an accurate diagnosis and treatment.
You cannot do any form of treatment on your own. This can aggravate the situation, cause allergies and other side symptoms, including burns or swelling of the damaged part of the body.
Only a neurologist can correctly assess a person’s condition and prescribe the necessary medications and procedures. He conducts diagnostics and collects anamnesis.
The main goal of therapy for a cold of the sciatic nerve is to relieve pain, eliminate physical activity, and ensure peace. This reduces the load on the nerve and prevents the development of edema.