What is a cranial MRI?
Magnetic resonance imaging of the skull is a non-invasive test designed to create a clear, detailed image of the skull and brain. This is done with the help of computer equipment and specially developed software, which is supplied with information about the impulses that arise when a person is exposed to a magnetic field.
Of all the diagnostic methods, MRI is considered the safest, as it does not involve the use of X-rays. This diagnostic method provides high-quality visualization of the patient’s skull; the result can be studied in detail on a monitor or printed on paper.
Using MRI of the skull, you can assess the condition of bones, brain nerves and tissues, and identify vascular pathology.
Types of hypertension
If jumps in blood pressure become regular, then doctors begin to talk about hypertension. It comes in two types: essential, or primary, and symptomatic (also known as secondary). In the first case, the disease develops due to the influence of external factors: a sedentary lifestyle, smoking and alcoholism, lack of potassium and magnesium, constant stress. Symptomatic hypertension is caused by pathological processes in the body.
What should an MRI be done for high blood pressure? If a doctor is looking for the cause of hypertension in a young person, he may refer the patient for a magnetic resonance imaging examination of the kidneys or pituitary gland. If the disease is quite long-lasting, then it is more advisable to analyze brain activity. Perhaps this is the reason.
CT scan of the skull with 3D effect
Despite the fact that CT requires the use of ionizing radiation, it is also often used because it is effective for examining the facial skeleton. What brought him to the level of MRI was the ability to create a three-dimensional image (3D).
Compared with magnetic tomography, computed tomography can more thoroughly and in detail evaluate bone pathologies of the skull in the cranio-orbital and craniobasal region. Three-dimensional reconstruction allows the treating specialist to examine the facial skeleton in volume and model the necessary implants for it with suitable sizes.
The full name of this procedure is “multislice computed tomography with 3D reconstruction” (MSCT).
MRI for hypertension
Hypertension, or hypertension, or in other words, high blood pressure, is observed in a huge number of people on the Earth, and older people are especially susceptible to this disease. A surge in pressure never goes away without leaving a trace: the heart rate may increase, the head may become dizzy, nausea and even vomiting may appear, and in some cases the person loses consciousness.
If you periodically suffer from high blood pressure, then the first thing you should do is visit a doctor: in addition to tests and ultrasound, the specialist will definitely prescribe an MRI, which will show what treatment tactics need to be applied.
When is it necessary to undergo an MRI?
The sooner the doctor refers you to the procedure, the better it will be, especially in cases where pressure surges are already regular. If symptomatic hypertension is suspected, delay is not acceptable at all, as it can significantly worsen the current situation.
Causes of high blood pressure
Hypertension can appear seemingly out of nowhere. However, if you dig deeper, you can always find the reason that made you feel not the best. This can be constant stress experienced both at work and at home, chronic fatigue, regular lack of sleep. All these minor factors greatly influence cellular nutrition. As a result, the flow of oxygen decreases, blood pressure increases - the body seems to be trying to cope with the existing problem.
#!MRTseredina!#
Indications and contraindications for MRI of the skull
MRI is mainly necessary to assess the general condition of the skull and find pathology. There is a standard list of diseases for the detection of which such an examination is used:
- pathology of the vascular system of the brain (hemorrhages, ischemia);
- traumatic brain injuries and bruises;
- GM tumors;
- loss or impairment of hearing, vision, speech;
- frequent headaches;
- deviations or disturbances in the development of blood vessels in the head;
- changes in the base of the skull;
- HIV;
- diseases of the nervous system;
- changes in the chiasmal-sellar region;
- stroke;
- multiple sclerosis;
- paroxysmal disorders;
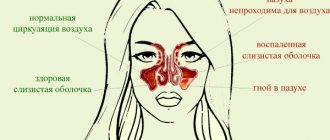
- sinusitis;
- death of GM cells;
- intracranial pressure.
Despite the large number of indications, MRI cannot always be used. There is a list of factors in the presence of which the use of such an examination without special preparation of the patient is prohibited:
- pregnancy less than 4 months;
- heart failure syndrome;
- panic attacks while being placed in the apparatus tunnel (claustrophobia);
- presence of insulin pumps;
- artificial heart valves;
- the patient's serious condition associated with the disease;
- inadequacy, alcohol or drug intoxication.
Also, special preparation is required for a patient who has tattoos in the head or neck area made with paint with metal connections. An exception to this rule are tattoos with titanium compounds.
Do not forget about the factors under which magnetic resonance imaging studies are completely prohibited:
- the presence of a pacemaker and other electronic devices installed in the body;
- middle ear implants (electronic or ferromagnetic);
Complete contraindications also include diseases associated with accelerated destruction of red blood cells.
Features of treatment
Therapy for the pathology should be comprehensive and include the elimination of possible factors that provoke internal cerebral pressure. To do this, medications are used that will help eliminate vascular spasm and restore the outflow of venous blood. Neuroprotectors and nootropics are also indicated to prevent the effects of neuronal hypoxia.
At home, you can use traditional medicine. This treatment is harmless and widely available; most often, medicinal herbs are used for therapy. Therapeutic gymnastics helps a lot with cranial pressure. It will normalize vascular tone in the head and reduce blood stagnation in the brain. If these methods of conservative therapy do not bring the desired result, it is necessary to undergo surgery with the installation of a shunt that will discharge cerebrospinal fluid from the cerebral ventricles.
Lumbar puncture will help to urgently eliminate high ICP.
Drug therapy
To eliminate this condition, the patient may be prescribed Veroshpiron.
Taking medications can help quickly reduce pressure inside the brain. The most effective among them are potassium-sparing diuretics: Furosemide and Veroshpiron. When a pathological condition has developed as a result of injury, nootropics, neuroprotectors and vitamin-mineral complexes are used. Antispasmodics will help relieve headaches. You can drink "Drotaverine" or "No-shpu". It is important to get rid of compression of the neurovascular plexus in case of cervical osteochondrosis. To do this, you need to take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or use them in the form of ointments. If the patient has severe pain in the eyes, then it can be removed through the use of glucocorticosteroids.
Impact with folk remedies
To quickly lower ICP, it is recommended to take a decoction of medicinal herbs. The collection includes chamomile, sage, valerian and St. John's wort. An alcohol tincture based on clover flowers is also used. It should be drunk before each meal, this will ensure the removal of excess fluid from the body. Treatment with herbs and other folk remedies is harmless and widely available, so it is often used among people to relieve cranial pressure.
Exercises
With this pathology, sudden movements during the execution of the complex are prohibited.
Therapeutic exercises will help relieve intracranial pressure. A set of exercises is selected individually for each patient by a qualified rehabilitation therapist. Movements should not provoke pain; sudden turns of the head and forceful loads are also prohibited. Gymnastics can improve the tone of cerebral vessels and reduce muscle spasm in the neck, which will improve venous blood flow and reduce internal cerebral pressure.
Surgery: when is it really required?
If relieving intracranial pressure by conservative methods is ineffective, then surgical manipulation is used. It consists of installing a drainage that pumps cerebrospinal fluid from the brain into the abdominal cavity. Thanks to drainage, fast and effective therapy for the pathological condition of nerve tissue is guaranteed. In addition, you can immediately reduce the ICP level by performing a lumbar puncture. The immediate indication for surgery is the presence of a formation in the head or severe hydrocephalus, which manifests itself in the compression of neurons by cerebrospinal fluid.
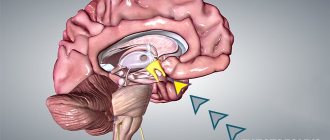
Intracranial pressure
As for determining intracranial pressure (ICP), it is quite possible. To determine the ICP stimulus, magnetic resonance imaging is used. MRI can show the effects of prolonged intracranial pressure on the brain in the form of changes in the structure of certain areas of the brain. Typically, ICP is indicated by dilated fluid cavities in the brain and spreading of the brain matter around the ventricles of the brain, as well as internal hydrocephalus.
Using a tomograph, data is read from hydrogen nuclei in human cells that respond to the influence of a magnetic field. The received impulses are transformed into an accurate image with the detected pathology. The operating principle of the device is based on the phenomenon of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR).
It will take about 30 minutes to identify the causes of intracranial pressure using the NMR phenomenon without contrast.
Causes
There are several groups of factors that can provoke increased intracranial pressure:
- Congenital abnormalities. This is hydrocephalus, which often occurs in newborns, as well as changes in the venous vessels. Due to an increase in the amount of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), the ventricles become larger in size. They begin to put pressure on the structure of the brain, the size of the head increases, and gaps appear between the bones of the skull.
- Infectious diseases of the central nervous system. During diseases such as encephalitis, meningitis, neurosyphilis, swelling of the brain occurs, its tissues become larger in size. The accumulation of plasma from the blood vessels increases, resulting in more cerebrospinal fluid.
- Hematomas and tumors. These processes, as well as the occurrence of cysts and abscesses, cause an increase in the secretion of cerebrospinal fluid and disturbances in its circulation. Tumors put pressure on the ventricles of the brain, their cavities become larger and compress the tissues located nearby.
- Brain damage. Various types of skull injuries, surgical operations and strokes also contribute to an increase in ICP and the occurrence of severe headaches, since during such injuries blood accumulates between the membranes of the brain, which prevents the proper circulation of cerebrospinal fluid.
- Problems with the endocrine system. Metabolic disorders in the body often cause increased blood pressure; the absorption of cerebrospinal fluid is impaired due to increased pressure on the walls of blood vessels. Many experts agree that the reason for this is high levels of estrogen.
- Incorrect course of pregnancy. If a woman experiences severe toxicosis, labor lasts a long time, the fetus is entangled in the umbilical cord, compensation mechanisms begin to work in the body to prevent a critical lack of oxygen, and the secretion of cerebrospinal fluid increases.
- Some infectious diseases. Some diseases, for example, otitis media, bronchitis, malaria, gastritis, can provoke an increase in blood pressure, as a result of which the body increases the production of cerebrospinal fluid and disrupts its absorption process.
- Medications. Drugs such as tetracycline antibiotics, some contraceptives, Biseptol, and corticosteroids can, when used, cause a syndrome of benign increase in ICP. This condition is accompanied by swelling of the brain and impaired circulation of cerebrospinal fluid.
Preparing for an MRI
Usually the examination takes place without special preparation. In some cases, by decision of the doctor, the specialist may ask you to abstain from food or any drinks (coffee, tea) in the morning . Already in the laboratory, before the procedure itself, it is necessary to remove all gold or silver jewelry, otherwise they will interfere with the magnetic fields from doing their job.
You may also need to change to a special surgical shirt. The need for this is determined by how many metal parts there are on the clothing and how spacious it is.
Female representatives must inform their doctor about their pregnancy, even at the earliest stage. Until now, there has not been a single case where MRI has negatively affected the body of the mother or the unborn child, but doctors are not 100% confident in the complete safety of the study.
First, the radiologist must review the patient’s medical history, operations and find out whether the patient has artificially implanted implants.
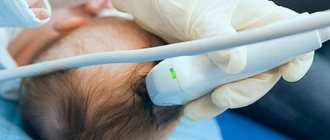
The process of performing an MRI of the skull
The MRI equipment itself is a cylindrical machine with a tunnel in the middle, which is surrounded by a magnet. A table slides into this tunnel and the patient lies on it.
- To perform an MRI of the skull, the patient is placed on a table and secured to it with special belts and ties. For convenience and immobility, there are bolsters that secure the body.
- After fastening, the head is prepared for examination. Wired sensors that conduct and receive radiomagnetic waves are attached to it. It is these signals that provide information to the computer, which is then processed by the program and shows all sorts of pathologies and causes of intracranial pressure.
- Contrast-enhanced MRI uses contrast material that is injected through a catheter into a vein in the arm. In order to avoid clogging of the veins, which interferes with the passage of the substance, saline solution is poured in front of it.
- After preliminary preparation, the patient is placed on the table in the apparatus tunnel, and all medical staff must leave the room.
- The results of the study are given to the patient immediately after the procedure. If the examination is unsuccessful, the device may produce a blurred image, and a similar examination is carried out. When finished, the doctor removes the catheter.
The standard examination time is 45 minutes. At this time, several pictures are taken (one image - 5–8 minutes).
When scanning the head, magnetic resonance imaging has its own characteristics. In the process, blocks of sections of head tissue are made in layers. One level is 5 mm thick, and in one photo scan information is read from approximately 20 levels.
The accuracy of the survey results is determined by the magnetic field induction (measured in Tesla).
Remember! While the image is being taken, the patient must lie still and do everything the doctor says.
Consequences of cranial MRI examination
Patients usually tolerate this procedure without pain or consequences. But there are some exceptions. During the examination, the patient may feel discomfort. It has to do with immobility. There are manifestations of attacks of claustrophobia even in trained people. In this case, the patient needs to take a sedative.
Additionally, the temperature of the head may increase, which is considered normal.
When using contrast material, you may feel a rush of blood and coolness, this is also considered normal. The process of inserting and removing the catheter may cause some discomfort and may cause irritation. Pain or nausea may occur. Due to the use of contrast agents after the examination, intracranial pressure or ocular itching may occur.
Doctors' recommendations
Also, during the treatment process, doctors recommend following the following points:
- control the amount of fluid consumed per day;
- brew and drink decoctions and teas that have a diuretic effect;
- do therapeutic exercises;
- eat right, limit the consumption of salty and fatty foods;
- choose a comfortable pillow for sleeping, it should be high;
- visit the pool a couple of times a week, since swimming helps reduce and normalize intracranial pressure;
- massage the cervical spine;
- consume foods containing potassium.