What is regulation of body functions
The human body has a very complex structure. From cells to organ systems, it is an interconnected system, for the normal functioning of which a clear regulatory mechanism must be created. It is carried out in two ways. The first method is the fastest. It's called neural regulation. This process is implemented by the system of the same name. There is a misconception that humoral regulation is carried out with the help of nerve impulses. However, this is not at all true. Humoral regulation is carried out with the help of hormones that enter the body fluids.
Differences
Despite the obvious interrelation between the mechanisms of nervous and humoral regulation, they have differences at the level of biological and morphofunctional units. For the most part, they are divided according to their properties:
- nervous regulation, in contrast to humoral regulation, is goal-directed - the impulse moves to a strictly designated area,
- humoral signal - spreads throughout the body with the bloodstream, and the tissue reaction depends on the presence of molecular receptors,
- the speed of signals is higher along the nerve fiber, and not in the liquid media of the body,
- the signal retention time in the nervous system is short, therefore the reaction of the controlled organ is rapid, while the concentration of hormones remains for a long period,
- the study of nervous regulation is better, since it can be recorded by instrumental devices, and the study of humoral functions is complicated by the vastness of the subordinate tissues.
The result of both differences and similarities in humoral and nervous mechanisms for controlling the activity of internal organs is the integrity of a person as a biological unit. The advantages of one system compensate for the possible shortcomings of the other, however, the leading role still belongs to higher nervous regulation.
Features of nervous regulation
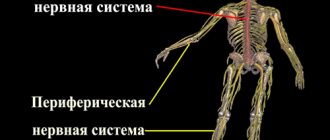
This system includes a central and peripheral section. If the humoral regulation of body functions is carried out with the help of chemicals, then this method represents a “transport highway” connecting the body into a single whole. This process happens quite quickly. Just imagine that you touched a hot iron with your hand or stepped out into the snow barefoot in winter. The body's reaction will be almost instantaneous. This is of utmost protective importance and promotes both adaptation and survival in various conditions. The nervous system underlies the innate and acquired reactions of the body. The first are unconditioned reflexes. These include breathing, sucking, and blinking. And over time, a person develops acquired reactions. These are unconditioned reflexes.
Automaticity of the heart
Note 1
Automaticity of the heart is caused by the occurrence of periodic excitation in certain cells of the heart.
The cardiac center of automatism is a cluster of certain cells located in the walls of the right atrium. These cells are capable of independently excitation with a frequency of 60-75 r/s. The ventricles of the heart do not contract together with the atrium, but with some delay.
Excitation occurs in the centers of the cells, which is transmitted throughout all muscle cells, causing contraction. When the center of automaticity fails, cardiac arrest occurs.
Features of humoral regulation
Humoral regulation of function is carried out with the help of specialized organs. They are called glands and are combined into a separate system called the endocrine system. These organs are formed by a special type of epithelial tissue and are capable of regeneration. The effect of hormones is long-term and continues throughout a person’s life.
What are hormones
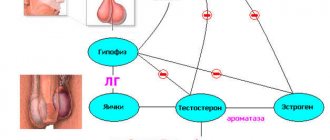
The glands secrete hormones. Due to their special structure, these substances accelerate or normalize various physiological processes in the body. For example, at the base of the brain is the pituitary gland. It produces growth hormone, as a result of which the human body increases in size for more than twenty years.
Glands: features of structure and functioning
So, humoral regulation in the body is carried out with the help of special organs - glands. They ensure the constancy of the internal environment, or homeostasis. Their action is in the nature of feedback. For example, such an important indicator for the body as blood sugar level is regulated by the hormone insulin at the upper limit and glucagon at the lower limit. This is the mechanism of action of the endocrine system.
Pathologies
A person feels the influence of the close relationship between nervous regulation and humoral control best in unusual conditions - when more effort is required to complete assigned tasks. For example, in the event of a fire with high air pollution, the load on the respiratory and cardiovascular systems increases. When the concentration of carbon dioxide increases, the body tries to compensate for it. If this fails, diseases such as bronchitis, asthma, and chronic pharyngitis appear.
Pathological conditions in the heart muscle are often the result of a malfunction in the secretion of adrenal hormones, adrenaline and norepinephrine. When they fluctuate in the bloodstream, various cardiac arrhythmias, tachycardias, and then heart failure occur. Nervous regulation does not always cope with the protective function, because hormones can maintain their influence on the heart for a long time.
Pathologies of the thyroid gland have been well studied. They lead to changes in metabolic processes. Oxygen consumption by tissues directly depends on their concentration. If there are a lot of them, then the body temperature rises, the absorption of nutrients accelerates, and body growth increases. All these symptoms are characteristic of hyperthyroidism. Whereas when the supply of hormones slows down, myxedema occurs - increased weight, body weight, apathy, decreased metabolic processes and temperature.
Pathologies of the reproductive system are difficult if they are based on hormonal imbalances. For example, the nature of the hairline, physique, voice modulation, and ability to reproduce change.
The prognosis for diseases of a humoral nature will largely be determined by the timeliness of a person seeking medical help and the correct selection of hormonal therapy. In most cases, doctors manage to achieve positive results in the fight to restore adequate regulation of internal organs.
Exocrine glands
Humoral regulation is carried out with the help of glands. However, depending on the structural features, these organs are combined into three groups: external (exocrine), internal (endocrine) and mixed secretion. Examples of the first group are salivary, sebaceous and lacrimal. They are characterized by the presence of their own excretory ducts. Exocrine glands secrete biologically active substances onto the surface of the skin or into the body cavity.
Hypo- and hyperfunction of the endocrine glands
The activity of each endocrine gland has “two sides of the coin.” Let's look at this with specific examples. If the pituitary gland secretes an excess amount of growth hormone, gigantism develops, and if there is a deficiency of this substance, dwarfism occurs. Both are deviations from normal development.
The thyroid gland secretes several hormones at once. These are thyroxine, calcitonin and triiodothyronine. When their quantity is insufficient, infants develop cretinism, which manifests itself in mental retardation. If hypofunction manifests itself in adulthood, it is accompanied by swelling of the mucous membrane and subcutaneous tissue, hair loss and drowsiness. If the amount of hormones in this gland exceeds the normal limit, a person may develop Graves' disease. It manifests itself in increased excitability of the nervous system, trembling of the limbs, and causeless anxiety. All this inevitably leads to emaciation and loss of vitality.
The endocrine glands also include the parathyroid, thymus and adrenal glands. The latter glands secrete the hormone adrenaline during a stressful situation. Its presence in the blood ensures the mobilization of all vital forces and the ability to adapt and survive in non-standard conditions for the body. First of all, this is expressed in providing the muscular system with the necessary amount of energy. The reverse-acting hormone, which is also secreted by the adrenal glands, is called norepinephrine. It is also of utmost importance for the body, since it protects it from excessive excitability, loss of strength, energy, and rapid wear and tear. This is another example of the reverse action of the human endocrine system.
Nervous breakdown: symptoms
A nervous breakdown can be characterized by various manifestations, which in particular depend on the specific type of symptomatology. Thus, the symptoms of a nervous breakdown can be physical, behavioral and emotional in their type of manifestation.
Physical symptoms:
- sleep disorders, which can consist of both a long period of insomnia and a long period of sleep;
- constipation, diarrhea;
- symptoms that determine the difficulty of breathing in one or another manifestation;
- migraines, frequent headaches;
- memory loss;
- decreased libido;
- disorders associated with the menstrual cycle;
- constant fatigue, extreme exhaustion of the body;
- state of anxiety, stable;
- pronounced changes in appetite.
Behavioral symptoms:
- behavior that is strange to others;
- pronounced mood swings;
- sudden manifestations of anger, desire to commit violence.
Emotional symptoms (these symptoms are peculiar harbingers of a future nervous breakdown):
- depression, which acts not only as a symptom that determines the possibility of a nervous breakdown, but also is the cause of its possible occurrence;
- anxiety;
- indecision;
- feeling of anxiety;
- guilt;
- decreased self-esteem;
- thoughts of paranoid content;
- tearfulness;
- loss of interest in work and social life;
- increased dependence on drugs and alcohol;
- the emergence of thoughts about one’s own invincibility and greatness;
- the appearance of thoughts about death.
Now let's look in more detail at the manifestations of some symptoms associated directly with a nervous breakdown.
Sleep and appetite disturbances, depressed emotional state, weakening of social contacts in one area or another of life, irritability and aggressiveness - all these are the main symptoms characteristic of a nervous breakdown. A person has a feeling of being cornered, in which he, accordingly, finds himself in a state of depression.
Attempts to provide help from loved ones in such a situation, as a rule, lead to aggression and rudeness towards them, which also implies a logical refusal of any help in such a state. A nervous breakdown also borders on symptoms indicating overwork, which consist of apathy and lack of strength, in addition to this, a loss of interest in everything that is happening and the environment.
As noted above regarding the main points, a nervous breakdown consists not only of changes associated with a person’s psycho-emotional state, but is also directly related to his physical state. In particular, disorders associated with the activity of the autonomic nervous system become relevant; they include excessive sweating, panic attacks, dry mouth, etc. Further, after damage to the nervous system, damage occurs to the cardiovascular system, as well as the gastrointestinal tract.
In the first case, the most common changes manifest themselves in the form of hypertension and tachycardia (increased heart rate), pain in the heart also appears, which is defined, respectively, as angina pectoris. These symptoms require medical attention, otherwise the condition in question can simply lead to a stroke or heart attack.
As for the damage to the digestive system during a nervous breakdown, it consists of a change in appetite (it either decreases or disappears altogether), and attacks of nausea. The patient's stool is also subject to certain disorders in the form of constipation or diarrhea. These conditions also determine the need for a certain correction, and not a medicinal correction aimed at treating the gastrointestinal tract, but a correction aimed at eliminating the nervous breakdown directly, which is the primary condition affecting the listed manifestations.
Thus, with an adequate and effective determination of therapy for a nervous breakdown, the result will provide relief from concomitant symptoms from the gastrointestinal tract and other systems.
Glands of mixed secretion
These include the pancreas and gonads. The principle of their operation is twofold. The pancreas produces two types of hormones at once. These are insulin and glucagon. They, accordingly, lower and increase blood glucose levels. In a healthy human body, this regulation goes unnoticed. However, when this function is disrupted, a serious disease occurs, which is called diabetes mellitus. People with this diagnosis need artificial insulin administration. As an exocrine gland, the pancreas secretes digestive juice. This substance is secreted into the first section of the small intestine - the duodenum. Under its influence, the process of splitting complex biopolymers into simple ones occurs there. It is in this section that proteins and lipids are broken down into their component parts.
The gonads also secrete various hormones. These are male testosterone and female estrogen. These substances begin to act during the embryonic period. During embryonic development, sex hormones influence the formation of sex, and then form certain sexual characteristics. As exocrine glands, they form gametes. Man, like all mammals, is a dioecious organism. Its reproductive system has a general structural plan and is represented by the gonads, their ducts and the cells themselves. In women, these are paired ovaries with their ducts and eggs. In men, the reproductive system consists of testes, excretory ducts and sperm cells. In this case, these glands act as exocrine glands.
Nervous and humoral regulation are closely interconnected. They work as a single mechanism. Humoral is more ancient in origin, has a long-term effect and affects the entire body, since hormones are carried by the blood and reach every cell. And the nervous system works pointwise, at a specific time and in a certain place, according to the “here and now” principle. Once the conditions change, it will cease to apply.
So, the humoral regulation of physiological processes is carried out using the endocrine system. These organs are capable of releasing special biologically active substances called hormones into liquid environments.
general description
As a result of a nervous breakdown, there is a feeling of lack of control over one’s own feelings and actions, in which, accordingly, the person completely succumbs to the states of stress, worry or anxiety that dominate him during this period.
A nervous breakdown, despite the general picture of its manifestation in many cases, is, however, a positive reaction on the part of the body, and in particular a protective reaction. Other similar reactions include, for example, tears, as well as acquired immunity, which occurs against the background of mental stress in combination with intense and prolonged mental stress.
When a person reaches a critical state for the psyche, a nervous breakdown acts as a kind of lever, due to the activation of which the accumulated nervous tension is released. Any event can be identified as the cause of a nervous breakdown, be it large-scale and intense in its impact or, conversely, insignificant, but “long-term undermining.”
It is extremely important to know the symptoms of a nervous breakdown in order to take the necessary measures in a timely manner, because we are actually talking about an extremely serious disorder in which the development of events can occur in a variety of ways, from subsequent admission to the cardiology department and ending with a neuropsychiatric dispensary.