Neurosis - what is it?
Neurosis is a collective term that refers to certain types of neurotic disorders. It can develop in both women and men. At risk are people who are in a certain phase of physiological changes: aging of the body or puberty. However, neurosis can occur at absolutely any age. In children, it usually goes away on its own, without treatment, and does not lead to any mental disorders. In adulthood, neurosis can greatly affect health - both physical and psychological. Often, neurotic disorders in adults cause pathologies of internal organs.
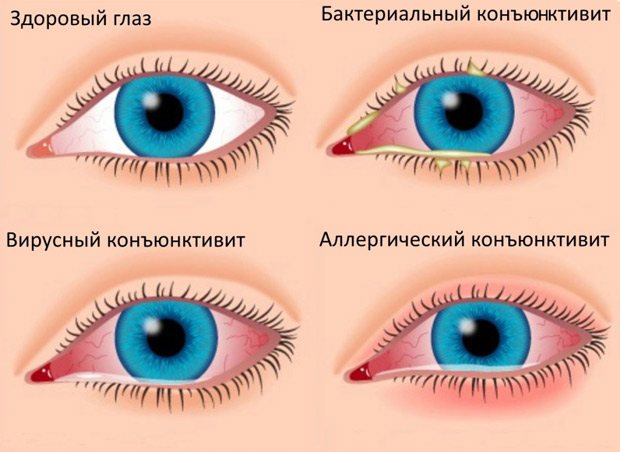
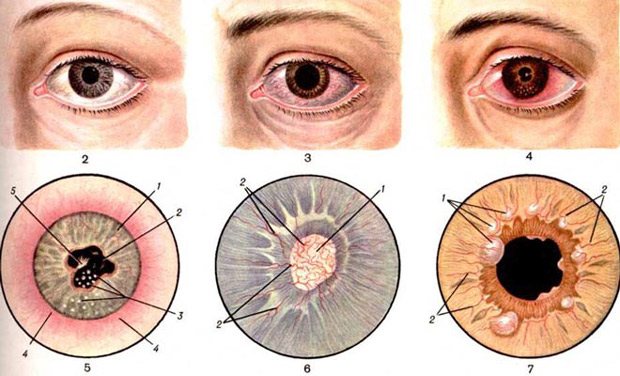
Conjunctivitis
Allergic conjunctivitis is a seasonal disease that manifests itself in the spring as a reaction to pollen from flowering plants. In addition to excessive production of tear secretion, it is characterized by unbearable itching, burning in the eyes, swelling and hyperemia of the eyelids, and photophobia. Shortness of breath, sore throat, and nasal congestion are often associated.
The infectious type of conjunctivitis is characterized by the appearance of purulent discharge and excessive production of tears.
Causes of neurosis
There are several theories, each of which suggests considering certain factors that provoke neurotic disorders. So, from the physiological point of view, neurosis is a pathology of the body, the cause of which is a malfunction in the nervous system. Excessive mental activity, accompanied by a large number of nervous processes, can contribute to the destabilization of the psychological state.
There is another theory, according to which the cause of neurosis is a combination of an irritant and personality characteristics. For example, there is a stressful situation. People may perceive it differently. Some may treat it indifferently or with great patience, others are not always able to adequately respond to various stimuli.

General health is also important. People who do not take care of their health, smoke, eat poorly, abuse alcohol, do not have a clear regime and daily routine, often get sick, are constantly overworked physically and mentally, and are more susceptible to neuroses. In the event of a stressful situation, they are especially vulnerable. At the same time, not only negative factors can provoke a disorder. Even positive emotions can lead to the development of neurosis. The sharp and constant alternation of positive and negative factors has an even worse effect on the psyche. Thus, in childhood, a neurotic disorder can be the result of a “carrot and stick” type of upbringing.
There is also a psychoanalytic theory. Neurosis, according to its postulates, is the result of an internal conflict that arose due to the dissatisfaction of a basic need. Moreover, the foundations of conflict can be laid at any age. Subsequently, they manifest themselves in the form of an unstable psychological state.
In general, the causes of neurosis in certain cases are the following factors:
- isolation of a person from society;
- conflict between instinctual drives and moral standards;
- strong pressure and control from others;
- a person's strong need for protection or recognition;
- a thirst for power, glory that cannot be satisfied;
- striving for ideality, perfectionism;
- inability to rest, uncontrolled workaholism;
- lack of life experience and skills to adequately perceive stressful situations.
These are psychological reasons. Physiological diseases include diseases of infectious or inflammatory etiology, addictions, including alcoholism and smoking. These factors reduce immunity, and therefore the body’s resistance to the external environment. How does a neurotic disorder manifest itself? Is it possible for vision to deteriorate with neurosis?
Iridocyclitis
With inflammation of the iris and ciliary body, at the first stage a sharp pain syndrome appears, which intensifies and radiates to the head area when touching the eyeball. As the disease progresses, the first signs include lacrimation, fear of bright light, blepharospasm, constriction of the pupil, and changes in the shade of the iris.
Symptoms of neurosis
There are two large groups of signs of neurosis: psychological and physical. The first include:
- emotional instability, frequent and causeless mood swings;
- lack of initiative, indecision;
- inadequate self-esteem: overestimation or underestimation of one’s own abilities;
- obsessive thoughts, uncontrollable fears;
- irritability, aggressiveness;
- constant feeling of anxiety, restlessness;
- a cynical attitude towards others, a desire to criticize everyone and for any reason;
- inconsistency of desires and needs;
- tearfulness, vulnerability, excessive impressionability, touchiness, suspiciousness.

A person in a state of neurosis concentrates heavily on traumatic events. In other words, this or that situation does not let the patient go; he constantly thinks about it, considers himself guilty, even if there is no reason for this. It’s almost impossible to focus on work or positive life moments. In this state, it is impossible to perform the amount of work that is normal for a healthy person. Labor productivity is falling. Because of this, a conflict situation at work may arise. This will worsen your mental state.
The most common symptom of neurosis is insomnia. It becomes increasingly difficult for a person to fall asleep at the usual time. If he does fall asleep, he has nightmares and wakes up in a cold sweat. In the morning you feel very tired, and drowsiness persists throughout the day.

Sometimes neurosis is accompanied by increased sensitivity to sounds. Loud voices and music irritate the patient. Photophobia and meteosensitivity develop. These factors are associated with the physical manifestations of neurosis. Among them:
- headache that hardly goes away, dizziness;
- discomfort in the heart area;
- digestive problems;
- increased blood pressure;
- weakness and trembling of hands;
- decreased appetite;
- excessive sweating;
- frequent need to urinate;
- changes in the menstrual cycle;
- decreased sex drive;
- the appearance of “floaters” before the eyes, blurring of vision, and a decrease in its acuity.
Keratitis
Symptoms of inflammation of the cornea are constantly watery eyes, the sensation of a foreign body in the eyeball, intolerance to bright light, and closing of the eyelids. Keratitis requires immediate contact with an ophthalmologist, since advanced infection can damage the cornea and spread deep into the eyeball.

Deterioration of vision due to neurosis
Neurosis and vision: can they be connected? As mentioned earlier, neurotic disorder occurs for various reasons, including as a result of infectious diseases. Moreover, the consequences of these disorders are also varied. Deterioration of vision due to neurosis is a fairly common picture observed by doctors.
Psychogenic manifestations of an unstable mental state include: narrowing of visual fields and a decrease in its acuity. Patients come to the ophthalmologist with complaints that they see poorly or see almost nothing. In this case, the patient is well oriented in space, does not bump into objects, and can even drive a car. Upon examination, it turns out that there are no visible reasons for the decrease in visual functions. This is due to the fact that the main factor leading to vision deterioration is a person’s reluctance to “see the problem.”

Narrowing of the visual fields is characteristic of hysterical neurosis. Usually it is also accompanied by increased photosensitivity and various signs of asthenopia - rapid eye fatigue. The behavior of patients also changes. It can be partly called strange. On the one hand, a person complains of decreased visual function, and sometimes partial or complete blindness. On the other hand, such a condition does not cause him great anxiety, as it does in people who suddenly become blind. In other words, vision loss is not so painful if there are no pathological reasons behind it. They are not detected during examination. When the ophthalmologist has ruled out all hypothetical ailments that could explain the deterioration of vision, we are talking about psychological factors.
When a person is very frightened, he develops anxiety, a desire to hide, he instinctively closes his eyes so as not to physically see the problem. This is how a person protects himself with the help of various functions of his body. Psychological protection will manifest itself in the appearance of a veil before the eyes, narrowing of the visual fields and other ophthalmological symptoms.
Why is stress dangerous?
Emotional stress contributes to nervous tension and negatively affects the eye muscles. Chronic overload of the muscular system of the eye is the main cause of deterioration in the functioning of the visual organs, which results in the development of such diseases:
- Farsightedness is a disorder of the visual organ, in which a person sees close-up images unclearly, while recognizing distant objects perfectly.
- Myopia is a defect that causes distant objects to appear blurry.
- Astigmatism is a change in the structure of the eye, in which the image quality may deteriorate.
Long-term exposure to stress leads to irreversible processes, as a result of which a person’s vision may decline. With constant nervous tension, its complete loss is possible.
Visual impairment due to neurosis - how to treat it?

Neuroses are treated by a neurologist or psychotherapist. It is carried out in several stages:
- reduction of emotional tension;
- elimination of symptoms of neurotic disorder;
- social adaptation of the patient, psychotherapy.
In some cases, medications are used, including sedatives and sleeping pills. There are many types of neuroses, as well as its causes and symptoms. Treatment is always individual. It is important to establish the factors that led to the neurotic disorder.
Ocular neurosis should not be confused with optic neuritis, which is inflammation that occurs as a result of an infection in the eye, as well as due to injury or a cold. Such diseases are treated by an ophthalmologist, not a neurologist.
To avoid neurosis, you need to lead a healthy lifestyle, organize your work day correctly, try to communicate more with people, get enough sleep, and treat all illnesses on time. However, no one is immune from a stressful situation. If you realize that you have become irritable, get tired quickly, or overreact to problems that usually do not cause much concern, consult a doctor. Perhaps you just need to rest a little, change your usual daily routine, change your surroundings. Almost all neuroses are reversible if you do not neglect them and take responsibility for your health, physical and mental.

By the way
In order for the text to cause minimal “harm” to the eyes, the distance from the eyes to the paper with a straight back should be about 30 cm, and it is better if the book or notebook is located at a right angle to the gaze, that is, the surface of the table should be slightly inclined, like a desk.
Work and rest, severe emotional shock can contribute to weight loss, but, as a rule, we are talking about two to three kilograms, which are soon restored. But if we are talking about something significant without obvious reasons, then it is necessary to find out why a person is doing this, because it can be caused by serious diseases.
The reason to see a doctor is the loss of 4.5-5 kilograms in 6 months.
Diagnostics
To determine what caused the tearing, the ophthalmologist carries out a number of diagnostic measures. He carefully collects anamnesis, finds out the nature and duration of clinical signs, and the presence of diseases in the patient that can provoke such symptoms.
A physical examination of the visual organs and adjacent areas is carried out: the ophthalmologist examines the cornea and conjunctiva for damage, palpates the lacrimal sac area to determine swelling and pain, assesses the symmetry of the facial muscles, and, if necessary, conducts a biomicroscopic examination.
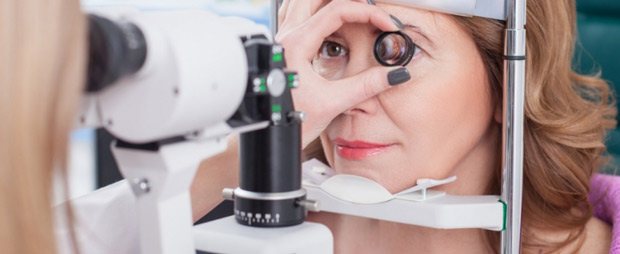
In some cases, the doctor takes a so-called Schirmer test, which allows you to determine the level of secretion production. If this value exceeds 25 mm, they speak of dry eyes due to increased evaporation. If fluid production is below 5.5 mm, this indicates insufficient secretion production.
As an auxiliary diagnostic method, probing and flushing of the lacrimal drainage system with a special saline solution with or without staining is used. Based on the diagnostic results, the doctor selects a comprehensive treatment.
Treatment Options
Watery eyes are a symptom, so you can get rid of it only by treating the underlying pathology. Depending on the cause of excess tears, your doctor may prescribe antiviral, antibacterial, antifungal, antihistamine, or anti-inflammatory medications.

Complex therapy includes folk remedies that have an anti-inflammatory effect (decoctions of chamomile, calendula). Most often they are used in the form of compresses and rinses. Such products must be used strictly as prescribed by a doctor.
For dry eye syndrome, effective treatment is the use of drops with the function of artificial tears and the reduction of intense visual loads.
If tearing is caused by wearing contact lenses, following recommendations for their use and hygiene will help.