Marden-Walker syndrome is a rare connective tissue disorder that is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. Patients with this disorder typically have a distinct facial expression, a cleft lip or high arched palate, a small jaw, joints in a fixed position, delayed growth, and limited control in muscle movements. Marden-Walker syndrome develops more often in men than in women.
McDuffie syndrome
MacDaffie syndrome is an allergic hypocomplementary vasculitis that occurs mainly in young women. It is believed that the pathogenesis of the disease is based on chronic necrotizing vasculitis associated with the deposition of immune complexes in the vascular wall. A possible connection between the pathology and carriage of the HLA-B51 antigen is assumed. Typical manifestations of the disease include chronic recurrent urticaria, arthralgia or arthritis, fever, and abdominal pain. Transient neurological disorders and changes in the liver are also possible. An acute onset of the disease is characteristic. Initially, it manifests itself as sudden swelling of the face (Quincke's edema) or extremities, less commonly arthralgia or arthritis. The level of complement in the blood is reduced, in particular its Cx component. However, cryoglobulins and laboratory signs of systemic lupus erythematosus are absent. A histological examination of the skin reveals signs of necrotizing leukocytoclastic vasculitis with infiltration of the vascular wall with pyknotic altered polynuclear cells and circulating immune complexes. When making a differential diagnosis, it should be borne in mind that chronic urticaria, combined with arthritis, can be observed with systemic lupus erythematosus, mixed cryoglobulinemia, drug-induced disease, congenital deficiencies of the C2- and C^-components of the complement system or a Cj-esterase inhibitor.
Marden-Walker syndrome
Marden-Walker syndrome is a complex of hereditary anomalies (autosomal recessive type of inheritance), manifested by contractures of the joints of the limbs, arachnodactyly, kyphoscoliosis, “chicken breast”, blepharospasm, micrognathia, frozen facial expression, polycystic kidney disease. Marie-Lery syndrome is a chronic polyarthritis with severe neurotrophic lesions of bones and soft tissues. Extensive symmetrical disintegration in the area of the wrist and ankle joints and bone curvature are observed. Due to massive osteolysis of the carpals, metatarsals and phalanges of the fingers, the limbs are shortened. In this case, the “extra” skin forms folds over the fingers and toes. In addition, scoliosis, extra and wedge-shaped vertebrae, spina bifida, meningocele, areflexia, cataracts, anisocoria and other anomalies are common. The history often reveals psoriasis, urticaria, eczema, iritis, as well as recurrent joint lesions.
Marden-Walker syndrome. Symptoms and manifestations
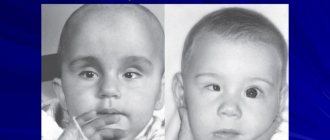
Patients with Marden-Walker syndrome have a variety of facial features, including abnormalities in the jaw, drooping eyelids, a flat bridge of the nose, low ears, and a fixed facial expression. Other manifestations of this disorder include curvature of the spine resulting in a hump, joint contractures, cleft or high arched palate, delayed growth and slow muscle movement. Other symptoms of Marden-Walker syndrome may include a small head circumference, heart abnormalities, abnormalities in the urinary system, decreased bone mass, abnormally small eyes, a short neck, a small mouth, and/or a low hairline. A small number of patients with this condition may also have additional tissue causing small intestinal obstruction, a narrowing of the ring separating the stomach from the first part of the small intestine that causes a blockage in the flow of partially digested food (pyloric stenosis); and/or loss of appetite, inability of the body to absorb nutrients properly, stomach pain and weight loss.
Maroteaux-Lamy syndrome
Maroteaux-Lamy syndrome is a hereditary disease from the group of mucopolysaccharidoses, the first signs of which appear as early as 2-5 years. Initially, limited upward movements of the arms and stunted growth are noted. Later, contractures of other joints occur. A typical symptom is dwarfism, with the limbs and spine developing proportionately. The head is of normal size, but the face is puffy, the eyes are widely spaced, the lips are thick, and the lower jaw is underdeveloped. The neck is short, the chest is barrel-shaped with the sternum protruded forward and raised shoulder girdles. Movements in the spine are not limited. The arms are in a flexed position and do not fully extend at the elbow joints. The movements of the fingers in the interphalangeal joints are limited (active clench of the fingers into a fist is impossible), supination and movements in the wrist joints, rotation and abduction in the hip joints, flexion and extension in the knee joints. The brushes are increased in size and elongated. The gap between the 1st and 2nd toes is widened. Umbilical and inguinal hernias, enlarged liver and spleen, corneal dystrophy, hearing loss, dysplasia and hemangioma of the auricles, and cleft palate are often detected. On the radiograph, the acetabulums are small, oblique, the femoral heads are small, deformed in the form of a triangle, the femoral necks are valgus straightened and thinned. The epiphyses of the bones forming the knee joint are reduced in size, and the epiphysis of the tibia is flattened. The vertebral bodies are cuboid in shape. Characteristic is depression of the posterior end plate of the lumbar vertebrae. There is an increased content of chondroitin sulfate B in the urine.
Marden-Walker syndrome. Photo
A child with manifestations of Marden-Walker syndrome
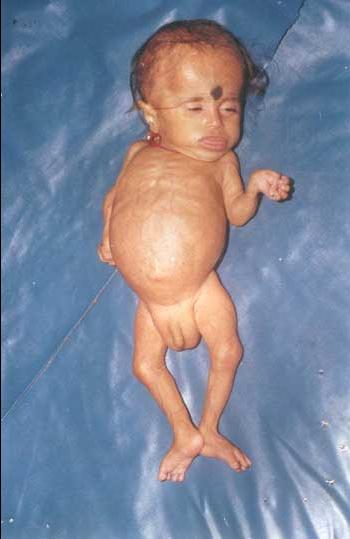
A nine-month-old boy with Marden-Walker syndrome. Severe somatic and psychomotor development, weight 2.5 kg, height 55 cm, head circumference 43 cm, hypotonia, protruding tongue, half-open eyes, joint contractures, arachnodactyly and bilateral inguinal hernias
Marfan syndrome
Marfan syndrome is a complex of hereditary abnormalities (autosomal dominant inheritance), including the following developmental defects.
- Changes in the musculoskeletal system - abnormally long upper and lower limbs, elongated and bizarrely curved fingers (arachnodactyly, “spider fingers”), “chicken” or funnel-shaped chest, spinal arches, flat feet, valgus deviation of the first toe, underdevelopment of the chin and large nose (“bird face”), senile appearance of the face in children, underdevelopment and weakness of skeletal muscles and poor development of subcutaneous fat, excessive elasticity of the capsular ligamentous apparatus of the joints, promoting hyperextension and subluxation of the joints. Generalized joint hypermobility is manifested by the following symptoms:
- passive hyperextension of the little fingers more than 90°;
bringing the thumbs across the side and back until they touch the forearm (the patient can touch the thumb to the forearm with the wrist joint bent);
- hyperextension of the knee and (or) elbow joints by more than 10°;
- the ability to touch the floor with your palms when bending forward from a standing position, without bending your legs at the knee joints.
- Changes in internal organs - mitral valve prolapse, aortic valve insufficiency, dilation of the aortic root (sometimes its aneurysm, including dissecting), varicose veins of the lower extremities, hernias, reduction of segments and lobes of the lungs, intestinal hypoplasia or hyperplasia.
- Changes in the central nervous system - diabetes insipidus, autonomic disorders, hydrocephalus, mental disorders.
- Characteristic changes in the eyes are congenital ectopia (dislocation) of the lenses, mobile lenses, blue sclera, anisocoria, iritis, glaucoma, absence of eyelashes, pathology of the eye muscles, lack of response to light, nystagmus.
There is a predisposition to the development of arthralgia, synovitis, damage to ligaments, tendons and menisci, as well as bone fractures. It is believed that joint hypermobility leads to the development of early osteoarthritis.
Diagnostics
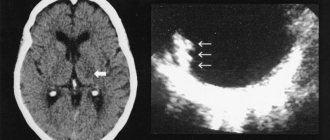
Diagnosing Dandy-Walker syndrome at the present stage of development of neuroimaging research techniques is not very difficult. An MRI or MSCT myelography is performed using a contrast agent, which is administered by puncturing the cerebrospinal fluid spaces.
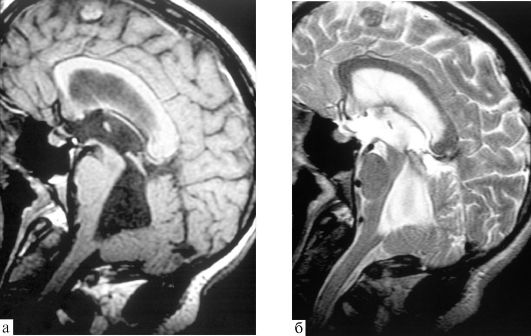
MRI examination allows even intrauterine diagnosis during pregnancy if a screening ultrasound examination reveals an expansion of the fetal skull.
In children, echoencephalography can be considered a screening method. In some cases, it is necessary to differentiate the diagnosis from retrocerebellar cysts and other cystic changes in the brain, especially in older age.
Morquio syndrome
Morquio syndrome is a hereditary disease that belongs to the group of mucopolysaccharidoses and occurs predominantly in men. Patients have disproportionate growth retardation: the torso is short, and therefore the limbs appear long. With age, the decrease in height is most pronounced. Dwarfism depends primarily on the flattening of the vertebral bodies. The head is large, the facial features are rough, the nose is wide, the lower jaw is enlarged, the mouth is slightly open, the teeth are large and sparse. The neck is short, so it seems that the head “sits on the shoulders.” The chest is wide, the sternum protrudes forward, the shoulder blades are located high, and kyphosis of the thoracic and lumbar spine is pronounced. Movement in the shoulder and elbow joints is limited. The hands are deformed as if they were clubbed. There is valgus alignment of the knee joints and flat feet. The skin is loose, hearing is reduced, vision is impaired due to clouding of the cornea. There are no mental disorders. Increased urinary excretion of keratan sulfate. X-ray examination reveals tongue-shaped deformation of the lower thoracic and upper lumbar vertebrae. In the hip joints, the acetabulums are wide, flat, pressed into the small pelvis, the femoral necks are wide, valgus curved, the femoral heads are sharply flattened. Fragmentation of the greater trochanters and femoral heads is also observed. Changes in the knee joints are characteristic: the epiphyses of the bones forming the knee joint are fragmented and have a rectangular shape; the most intense flattening is observed along the outer surface of the epiphyses of the femur and tibia. In addition, fragmentation of the patella occurs. The valgus deformity of the knee joint gradually increases up to the medial subluxation of the tibia. The phalanges of the fingers and metacarpal bones are thickened and shortened, ossification nuclei are detected late, and have an irregular jagged shape. The epiphyses of the tibia in the distal section are beveled, and the trochlea of the talus is deformed. The feet are deformed similarly to the hands.
Dandy Walker syndrome in dogs
This anomaly in the development of the child can be seen using ultrasound in the first months of pregnancy. In particular, all the symptoms of this disease are visible already at 20 weeks. The main evidence of the development of pathology are various signs of brain damage: cysts in the cranial fossa are clearly visible, a poorly developed cerebellum, the fourth ventricle is too dilated. In this case, ultrasound signs become more distinct as the fetus develops.
Over time, clefts appear on the hard palate and lip, abnormal development of the kidneys, and syndactyly. If for some reason an ultrasound was not performed during pregnancy, then the symptoms of the disease become clearly visible immediately after the birth of the child. Due to high pressure inside the skull, such children can be very restless. They develop hydrocephalus with muscle spasms and nystagmus. In some cases, there may be no signs of hydrocephalus.
[12], [13]
First signs
- Atresia of the foramina of Magendie and Luschka (fusion or congenital absence).
- The posterior part of the cranial fossa increases in size.
- Atrophy of the cerebellar hemispheres.
- Cystic formations appear, including fistulas.
- Hydrocephalus of varying degrees.
All these first signs are clearly visible during an ultrasound of the fetus. This is why it is so important for pregnant women to undergo all tests and studies on time.
[14], [15], [16]
Dandy-Walker syndrome in children
A priori, Dandy-Walker syndrome is considered a childhood disease. Fortunately, it is quite rare (only one case in 25,000 newborn babies). Its symptoms can be seen in the womb, but if for some reason this was not done, then children with this disease develop quite strong and severe complications with age.
Over time, noticeable cerebellar symptoms appear. In older children, coordination of movements begins to be impaired, so it is quite difficult for them to move and walk (sometimes even impossible). The main symptom is severe mental retardation, which is practically impossible to cure. Associated problems also appear: kidney disease, heart disease, abnormal development of fingers, face, hands, poor vision.
[17], [18], [19]
Dandy-Walker syndrome in adults
Dandy-Walker syndrome is an anatomical and clinical variant of vicious hydrocephalus. This disease is characterized by atresia of the orifices in the brain, as well as dilatation of the ventricles (third and fourth).
Despite the fact that this pathology is considered congenital, in very rare cases its first signs begin to appear in early childhood (four years of age) or even later. For a long time, there are no symptoms of this congenital defect. Decompensation sometimes occurs only in school-age children or adolescents. Exceptional cases are when the first symptoms of Dandy-Walker syndrome appear in adults.
Among the main symptoms of the disease in adults are:
- The size of the head gradually increases.
- The bones of the back of the head begin to protrude: they seem to protrude.
- Coordination of movements is greatly impaired, fuzzy and sweeping movements appear.
- Nystagmus develops, which manifests itself in oscillatory movements of the eyes from side to side.
- Frequent seizures with convulsions.
- Muscle tone increases greatly (sometimes to the point of spasticity). The muscles are in constant tension.
- The development of mental disability, which manifests itself in the fact that a person does not recognize relatives, has difficulty reading and distinguishing letters, and cannot write.
[20], [21], [22], [23], [24], [25]
Source: ilive.com.ua
Among live-born children, the frequency of Dandy-Walker syndrome is low - from 1: 5000 to 1: 25,000; Boys are more often affected. Meanwhile, among children with congenital hydrocephalus, the incidence of the syndrome ranges from 3.5 to 12%. If the syndrome is not associated with a genetic pathology, then the risk of recurrence during repeated pregnancy is 1 - 5%, with autosomal recessive inheritance - 25%.
► Dandy-Walker syndrome is a malformation of the brain, which is characterized by a triad of signs:
- ■ hypoplasia of the vermis (and hemispheres) of the cerebellum; ■ expansion of the third ventricle to the formation of a cyst of the posterior cranial fossa due to its enlargement associated with upward displacement of the lateral sinuses and cerebellar tentorium); ■ internal hydrocephalus.
Prenatal functional diagnostics specialists distinguish complete and incomplete, as well as closed and open forms of Dandy-Walker syndrome. The full form is characterized by agenesis of the cerebellar vermis and the presence of obvious communication between the fourth ventricle and the cyst in the region of the cistern magna. The incomplete form is partial agenesis of the lower part of the cerebellar vermis, and therefore communication of the fourth ventricle with the cisterna magna cyst is not traced throughout the entire length of the vermis. The open and closed forms differ in the presence or absence of occlusion of the foramina of Luschke and Magendie and the connection of the ventricle with the subarachnoid space.
[
anatomical diagram of Dandy-Walker syndrome
] In 1989, AJ Barkovich et al. proposed a classification of cerebrospinal fluid accumulations in the posterior cranial fossa based on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data. According to this classification, they describe the concept of the “Dandy-Walker complex,” which includes four types of anomaly:
ADU (classical) - characterized by an enlargement of the posterior cranial fossa with cystic dilatation of the fourth ventricle; it is typically characterized by a high position of the tentorium.
date of birth;
Dandy-Walker variant - characterized by less severe structural changes: hypoplasia of the lower part of the cerebellar vermis and communication of the fourth ventricle with the occipital cistern through a perforated membrane covering the exit from the fourth ventricle; the location of the tentorium cerebellum and the size of the posterior cranial fossa are not changed; the brain stem is not compressed, hydrocephalus is rare;
Blake's pouch cyst - distinctive features of a Blake's pouch cyst: tetraventricular hydrocephalus, infra- or retrocerebellar localization of the cyst, relatively well-developed cerebellar vermis, cystic dilation of the fourth ventricle without communicating with the cistern magna; in embryogenesis, Blake's pouch is a transitional finger-like projection of the posterior membrane space of the roof of the fourth ventricle;
mega cisterna magna (focal increase in the subarachnoid space in the lower and posterior parts of the posterior cranial fossa) - there is an increase in the size of the large occipital cistern; in this case, the cistern communicates freely with the fourth ventricle and with adjacent parts of the subarachnoid space; the enlarged cistern reaches the straight sinus from above and to the level CI-CII from below.
Cerebral abnormalities associated with Dandy-Walker syndrome may include dysplasia (neuronal heterotopia, schizencephaly, dysgenesis of the corpus callosum, holoprosencephaly, and stenosis of the Sylvian aqueduct; sometimes the cerebellar vermis may be completely absent). Now these findings are generally regarded as a variant of Dandy-Walker syndrome.
According to modern concepts, the etiology of Dandy-Walker syndrome is extremely heterogeneous, since various factors are involved in its occurrence: hereditary (chromosomal and gene) and exogenous - teratogens (it is assumed that factors such as viral infection [CMV, rubella] also play a certain role , alcohol, diabetes during pregnancy). In 1/3 - 1/2 of cases, Dandy-Walker syndrome is combined with various congenital syndromes (see table).
Among the main hypotheses for the occurrence of Dandy-Walker syndrome, the following can be identified: arrest of embryonic development in the process of formation of the rhombencephalon, atresia of the outlet from the fourth ventricle with delayed opening of the foramen of Magendie, the appearance of the choroid plexus of the fourth ventricle in the middle of the thin roof of the rhombencephalon.
Dandy-Walker syndrome is characterized by pronounced clinical polymorphism: from almost normal postnatal development (there is evidence that normal cognitive development is recorded in 50% of children with Dandy-Walker syndrome; cases of Dandy-Walker syndrome being detected in adults during routine examination have been described) to severe disability and even death of the child (as a rule, the postnatal development of children has a more serious deviation in their neurological status). Perinatal outcomes largely depend on the depth of damage to the central nervous system (increasing hydrocephalus), as well as on the presence of concomitant pathology, which accompanies this syndrome in 60 - 75% of cases. According to the literature, postnatal morbidity and mortality rates are higher in situations where the syndrome is diagnosed in the prenatal period.
In the case of serious deviations in the neurological status and the child has a Dandy-Walker, the clinical picture will include symptoms of hydrocephalus in the form of an increase in head circumference and bulging of a large fontanelle. The newborn exhibits increased excitability (including hyperreflexia), ocular symptoms (spontaneous nystagmus, strabismus), episodes of apnea, and facial nerve paresis.
However, in this early period of life it is not possible to detect cerebellar symptoms. Neurological dysfunctions are usually caused by compression of brain structures. The skull of newborns increases in size faster in the occipital than in the frontal region. Also, children with Dandy-Walker syndrome are characterized by rapid growth in head circumference during the first 2 months of life and divergence of cranial sutures more in the back or in front (thinning of the skull bones occurs in the same sequence).
Despite the gross deficiency of tissue in the vermis and cerebellar hemispheres, pronounced signs of ataxia are not at all obligatory for the Dandy-Walker anomaly (observed in only a third of cases). More often, insufficiency of higher mental functions is detected, which, in particular, includes not only known cognitive impairments, but also general motor awkwardness detected in patients. Of greatest interest is the combination of cerebellar vermis hypoplasia with various autistic manifestations, which are observed in approximately 25% of cases of Dandy-Walker anomaly. In the literature of the last 15–20 years, attempts have been made to connect childhood autism directly with the pathology of the cerebellum itself and its connections with the associative areas of the cerebral cortex.
Changes characteristic of Dandy-Walker syndrome can be detected by neurosonography (ultrasound of the brain) as part of prenatal screening. Despite the improvement of prenatal ultrasound diagnostics, which makes it possible to detect Dandy-Walker syndrome as early as 15-16 weeks of gestation (according to some authors, the earliest prenatal diagnosis of Dandy-Walker anomaly was carried out with transvaginal echography at 12-14 weeks of pregnancy), in In a number of cases, the authors note the objective difficulties of visualizing the fine structures of the brain in the early stages of pregnancy.
In particular, the size of the IV ventricle does not exceed 1 mm (!) up to 22 weeks of pregnancy and only by full-term pregnancy it increases to 3 - 4 mm.
To make a timely diagnosis of Dandy-Walker syndrome (anomaly), the following examination plan for the child is recommended:
- ■ conducting magnetic resonance imaging of the brain with a sagittal and axillary view of the fourth ventricle; ■ search for other abnormalities of brain development; ■ ophthalmological examination; ■ echocardiography; ■ karyotyping in the presence of other developmental defects; ■ consultation with a neurosurgeon.
Treatment. In the absence of hydrocephalus and signs of intracranial hypertension, follow-up with a pediatrician and neurologist (! if necessary, a neurosurgeon). If there are symptoms of intracranial hypertension, shunt surgery is performed. Since 1983, attempts have been made at intrauterine shunting (installation of a ventriculo-amniotic shunt).
Source: laesus-de-liro.livejournal.com
Dandy-Walker syndrome is a complex of heterogeneous developmental defects characterized by: 1) cystic dilatation of the fourth cerebral ventricle; 2) hypoplasia of the cerebellar vermis; 3) hydrocephalus; 4) large posterior cranial fossa; 5) atresia of the foramen of Luschka and Magendie. [1,3,5] Dandy-Walker malformation is considered a violation of the fusion of the dorsal median structures of the primitive neural tube. Also at the basis of this syndrome is a violation of the development of the median part of the cerebellum with subsequent expansion of the posterior cranial fossa, an abnormally high location of the tentorium of the cerebellum and elevation of the transverse sinuses. The syndrome may also be associated with syringomyelia and agenesis of the corpus callosum. (CH Vite, 2004)
A similar disease has been found in several dog breeds such as Beagle, Australian Silky Terrier, Chow Chow, Boston Terrier, Briard, Labrador Retriever, Bull Terrier, Dachshund and domestic short-haired kittens. This disease can manifest itself both at two weeks of age and at 3-4 months of age. There have also been cases of clinical symptoms appearing in adult dogs. (CH Vite, 2004) Dandy and Blackfen in 1914 reported a group of congenital malformations of the central nervous system that eventually became known as Dandy-Walker syndrome. Dandy and Blackfan believed that atresia of the foramen of Luschka and Magendie was the main cause of cystic dilatation of the fourth cerebral ventricle, cerebellar malformation and hydrocephalus. This theory was confirmed by Walker and Taggart. The term Dandy-Walker syndrome was coined by Benda in 1954. (Howard H. Kaufman, 1998)
Dandy-Walker syndrome is characterized by aplasia or hypoplasia of the cerebellar vermis, fluid-filled cysts (fistulas) located in the posterior fossa, and cystic dilation of the fourth ventricle. [1,2] Hydrocephalus is often present (CH Vite, 2004). In humans, this disease is the cause of 5-10% of all hydrocephalus (B. Goldberg etc., 1996). In addition, parts of the cerebellar hemispheres and the flocculus may be affected. (CH Vite, 2004)
Microscopic changes include focal or diffuse chromatolysis and atrophy of Purkinje cells, scattering of deep cerebellar nuclei, axonal spheroids, and reduction of granule cells in the cerebellar cortex. Retrograde transsynaptic neuronal degeneration, such as chromatolysis or neuronal vacuolization, can be noted in brainstem nuclei. This degeneration is reflected in the cerebellum, which includes the oval, lateral reticular, lateral cuneus and vestibular nuclei. The wall of a posterior fossa cyst may be lined by the pia-arachnoid membrane, neuropil, and an inner layer of flattened ependymal cells, or by ependymal cells only. The lateral foramina through which the fourth cerebral ventricle communicates with the subarachnoid space should be microscopically normal in dogs. Likewise, there is no evidence of foraminal atresia in affected kittens. Hydromyelia is not a common sign, but occurred in two adult dogs. (CH Vite, 2004)
The pathogenesis has not been definitively established. A study was conducted on mice in which hydrocephalus and cerebellar agenesis were artificially created, during which it was revealed that hydrocephalus and a posterior fossa cyst occur before the cerebellar malformation. Primary pathology is believed to occur at the "roof" of the fourth ventricle, which develops further into the preceding and subsequent meninges. (DA Pass etc., 1981)
A comparison of the pathological features observed in animals with Dandy-Walker syndrome and Chiari I malformation is shown in Table. 1. (CH Vite, 2004)
Clinical symptoms.
A hopping rabbit gait was observed in one 12 month old Beagle. (CH Vite, 2004)
Clinical signs are usually not progressive, so surgery may not be necessary. (Curtis W. Dewey, 2008)
Source: neurovet.ru
I have a terrible situation in my life, just like everyone else here. She gave birth to her third child. He is 7 months old now. There are two more older ones, 3 and 5 years old. The third pregnancy was unexpected, while taking approx. But we thought (or rather, I did. I still had the last word) and decided that it was a terrible sin to refuse the gift of God. How funny and sad I feel now from those thoughts and decisions (((All the screenings, 7 ultrasounds - perfect. I did so many ultrasounds because I had an ARVI with a fever at 31 weeks. But all the doctors reassured me and assured me that everything was fine is progressing. As a result, premature rapid labor at 36 weeks, greenish waters, vui, hypoxia, ischemia of the central nervous system. From the maternity hospital they transferred to the Speransky hospital, where a greatly expanded occipital space was found on the nsg. Immediately suspicion of DU, God only knows what hell I’m going through passed there, even thoughts ran through my husband and I to abandon the child there with a positive remote control. They did an MRI for us, the result: rejoice, mommy, you just have a mega cistern magna, everything will be fine. No one was happier than us! Then within two months the child was strange, I have experience, I know what kind of children should be. The baby could often lie “in one point”, hypodynamism, no fixation of the eyes, no humming, there was no talk of holding the head, add to this the impossibility of sucking the breast , I was eating poorly, I was starving, I tried pumping, and the Medela central nervous system system, syringes, cups, special spoons, all to no avail, I ate for an hour as fast as I could. I switched to formula after struggling with pumping. It turned out that he had a rather high palate and a short frenulum, which we trimmed, but there was no improvement with special feeding. She reassured herself that she was premature, but she felt in her guts that something was wrong. I ran for an expert ultrasound to the luminary Voevodin, I said, look for Dandy. He looked at me and reassured me, and said that the increased submental space is your development option. I went to see a good neurologist, they did an NSG, he says I’m probably underweight. Dial and come back in a couple of months, at 4 months. In general, what I mean: they did an ultrasound after birth 6-7 times and no one saw the remote control. What the hell is this?!!! Twice we were treated for rheumatology in hospital No. 32, however, we also had obstructive bronchitis and lost a month in development (would it have happened though???) We started studying with Pykhtina, worked for a week and had a fever in my teeth. A 7-month-old child only turns over on a roll well, does not like to be on his stomach, rests on his stomach on his elbows, there is no support on his straight arms, he holds everything to his chest. Holds his head. Emotionally, everything is not bad, although not as active as in healthy people, there is a buzz, but it’s also not so great, poor. I couldn’t stand it and went to Solntsevo for an MRI. Constriction is like a death sentence, Hypoplasia of the lower parts of the cerebellar vermis, thinning of the corpus callosum, enlarged posterior cranial cavity, cyst in the cerebral cortex, moderate external anterior hydrocephalus. We are shocked. To say that they were killed is to say nothing. I understand even without doctors that this is a disabled child, he won’t walk normally, it’s 50:50, he might get a plus and an epi and all that follows. I hate all the blind ultrasound doctors who didn’t see anything during pregnancy. The slightest doubt that there is any defect or syndrome - without thinking about abortion. I think this is more humane for everyone. For the baby, so that he doesn’t suffer, never becoming a full-fledged member of society, for my family, for my healthy two children, who, by the way, almost no longer see their mother jumping around all the hospitals in Moscow with their brother. And in general, I’m a perfectionist by nature, I seem to have gotten my life together, I have a good husband, good kids, average income - it’s a sin to complain. Now all this is collapsing before our eyes. I am not one of those who are ready to leave older children and move from rehabilitation to rehabilitation, live in hospitals, spend all their money on the youngest, depriving two healthy good paid classes, sections and vacations at sea. There were and are thoughts of sending the child to an orphanage, but as I look at him, in this angelic face, tears flow like a hail, my heart breaks, as I imagine him alone in a strange place. I’m writing and crying(((But it’s impossible to continue like this. My heart hurts, I can’t eat or sleep, I’ve lost almost 40 kg, I’m scared of what will happen next. I can’t come to terms with the fact that the child is disabled((( I can’t come to terms with the fact that his elders will be ashamed of him, they will quickly run away from home if possible, this atmosphere of a crypt at home... I don’t want to put my life and health on the eternal rehabilitation of a child who, neither in mind nor in physics, will become even close to healthy. Yes, I’m selfish (((But also my mind and heart I am at odds. I have no strength anymore((((
Source: forum.detiangeli.ru
All articles about vascular disease and treatment:
Pfoundler-Hurler syndrome
Pfoundler-Hurler syndrome (gargoilism) is a hereditary disease belonging to the group of mucopolysaccharidoses. In patients, enchondral bone growth is impaired. All patients are similar to each other: dwarf stature due to disproportionately short limbs with normal body size. First of all, the proximal parts of the limbs are shortened - the hips and shoulders, and to a lesser extent - the legs, forearms, metatarsals and metacarpals. The patient's hands are characteristic: the fingers are shortened and identical in size (isodactyly), fan-shaped. A hydrocephalic skull with a steep forehead, flat face, sunken nose, thick lips. The neck is short - the head seems to “sit on the shoulders.” Kyphosis is noted at the junction of the thoracic and lumbar spine, lordosis in the lower lumbar spine with protrusion of the abdomen anteriorly and the buttocks posteriorly. The psyche is normal. Large amounts of chondroitin sulfate B and heparin sulfate are excreted in the urine.
Stickler syndrome
Stickler syndrome is a complex of hereditary abnormalities of the eyes and joints (autosomal dominant type of inheritance). The first symptoms appear in childhood: congenital severe myopia, degenerative changes in the retina, often blindness; cataracts, secondary glaucoma, chronic uveitis, keratopathy, and wrinkling of the eyeball develop in the blind eye. In some cases, cleft jaws are noted, and mesotympanitis is common. Changes in the inner ear lead to hearing loss or complete deafness. In later stages (3rd-4th decade of life), severe arthropathy appears, mainly in the large joints of the lower extremities (hip, knee and ankle). A biopsy of the synovial membrane of the joints and a biochemical blood test showed no abnormalities. Sometimes flattening of the vertebrae, kyphosis occurs, and less commonly, kyphoscoliosis.
Teuchlander syndrome
Teutschlander syndrome (tumor calcification) is a type of hereditary lipoidthesaurismosis. The disease occurs only before the age of 20 years and is characterized by the formation of focal calcifications in the muscles and capsules of large joints; a fluctuating tumor is usually located in the center of the lesion. Deposition of lipoids is detected in the muscular fascia and serous membranes, and around them there are giant cell granulomas. Muscular dystrophy, scleroderma, and osteoporosis are often observed. During the formation of a fluctuating tumor, fever and deterioration in health are noted. In the blood - hypercholesterolemia.
Winchester syndrome
Winchester syndrome is a complex of hereditary anomalies (autosomal recessive type of inheritance), characterized by dwarf growth, facial anomaly, contractures of the extremities, corneal opacities, osteoporosis, resorption of the carpal and tarsal bones, destruction of intra- and periarticular structures, simulating rheumatoid arthritis. Histological examination of the skin reveals extensive proliferation of fibroblasts, and electron microscopic examination reveals swelling and degeneration of mitochondria.
Marden-Walker syndrome. Similar disorders
- Trisomy 13
- Trisomy 18
- Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome
- Spinal cord injuries
- Infantile spinal muscular atrophy
- Mobius syndrome
- Van den Ende-Gupta syndrome
- Freeman-Sheldon syndrome
- Schwartz-Jampel syndrome
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (generalized fibrodysplasia) is a rare hereditary disease (autosomal dominant inheritance) caused by a primary defect in collagen synthesis, causing increased elasticity of connective tissue. The disease is characterized mainly by changes in the musculoskeletal system and hyperelasticity of the skin. Patients experience looseness (hypermobility) of the joints, abnormal mobility of the fingers in the interphalangeal and metatarsophalangeal joints in the dorsal direction. Other typical clinical signs include arachnodactyly, kyphoscoliosis, spina bifida, flat feet or cavus foot. Habitual dislocations and subluxations of the shoulder joints, head of the radius, patella, and sternoclavicular joint are described. The gait of patients resembles that of tabes dorsalis. Sometimes effusion is detected in the cavity of the knee joints, due to their looseness and constant injury. The skin has a velvety appearance, shiny (reminiscent of wet suede), thinned, and easily vulnerable. Hyperpigmentation of the skin in the area of the knee and elbow joints and chin was noted. Characterized by the rapid appearance of bruises and hematomas, poor healing of skin wounds, and the formation of keloid scars. Patients also experience dental deformation, frequent hernias, sometimes congenital heart defects, emphysema, pneumothorax, eye symptoms (ectopic lenses, blue sclera).
Exostotic chondrodysplasia
Exostotic chondrodysplasia (multiple juvenile osteochondral exostoses, exostotic disease) is a malformation of the epiphyseal growth cartilage, expressed in the pathological proliferation of cartilaginous tissue in the area of growth zones. The disease develops during the period of skeletal formation - from 6 to 18 years. In approximately 8-10% of cases the disease is hereditary. Excessive production of cartilage tissue does not occur strictly along the axis of the bone, but sideways, which leads to the appearance and growth of exostoses - cartilaginous spines, which later calcify. Sometimes exostosis cartilage looks like cauliflower forks. Exostoses are formed from epiphyseal cartilage and, possibly, also from congenital defects of the periosteum, especially at the sites of tendon attachment. The growth of exostoses especially increases during puberty and stops with the cessation of skeletal formation. The process is usually symmetrical and multiple. The number of exostoses can range from a few to hundreds. Most often, exostoses are localized in the area of the knee joints: the proximal metaphysis of the tibia or the distal metaphysis of the femur. Somewhat less frequently, exostoses form in the area of the proximal ends of the humerus, distal ends of the bones of the forearms, trochanters of the femurs, iliac bones, shoulder blades, clavicles, and ribs. Sometimes there is underdevelopment and curvature of the bones of the forearms (Madelung deformity). Mucous bursae may form over the tips of the exostoses. Compression of nerve branches by exostoses causes pain. Thus, exostos, located in the area of the medial surface of the proximal metaphysis of the tibia near the p. saphenus, causes pain when wearing high boots. When palpating the joints, dense swellings (bone protrusions) are determined. Injury to soft tissue in the area of exostosis, especially during movement, can lead to the development of tendinitis and bursitis. With large growths in the area of the knee joints, limited movements and lameness are observed.
Calendar for Today
Birthdays: Nata A. (38) Lacoste (41) Actrice (38) Haritoshka (35) lelik2 (36) INNIK (53) Radi (34) BABOCHKA 42) Lyudmila-mila (49) pulochek (37) Alizi (37 ) sasha-12 (38) anjey (38) Epoch (42) Funny (49) Nataliya86 (34) Andrei-D (41) Ryzhulya (41) irish1980 (40) Avdeev (35) Inspector (48) ninela (9) alieva (33) natanya79 Vega (45) Zhmenya (34) Olga Dankova (33) FAIRY (37) [email protected] _Tim (50) malyava (37) sashurka (35) Lyulyaka (36) ylius87 (33) mamasasa (41) alexandermos (31) BruceGonza (31) mira79 (41) @mouse@ (31) Lelik.123 (35) koondiikks (31) Luidok.83 (127) AlugAcceddy (34) Broofefetette (33) modnizhaasa (31) TOCharles (35) soreHiliarota (35) hefedulge (31) NsolevssGlissia (33) Ekaterina the sun (37) Antoninochka (33) Hedgehog-Katka (36) Eroha (31) kyrima (35) nupbainee (35) tanya1494 (11) Indins (48) Physlette (50) sirlDeefs (34) Faith82 (38) viwerhsad (49) remikelmiser (48) Priecitty (32) Encazycinunny (45) lieklysix (34) EXCILDDIT (42) vertu-ozzz (40) Slorporarlopy (40) IamStarpr (45) Useffeemn (43) AmourseRoom (36) pcsoft (33) Gavrila (43) jonathanpose (42) snocialioboca (47) drierfatt 36) AbubbiniogVob (34) obliskgog ) PertyrorFem (39) nacyjohy (39) Unobia (43) SteetLiailm (45) Elena Petrovna (34) fuergeunurf (32) NeebpapJele (35) EnammaSlinna (42) tarappaienk (45) abuntenda (45) reaggitiefs (33) Cheakarbereiz (42) apaceala (43) D_Lena (37) Jailmerma (32) Judas_kiss (31) envemable (33 ) Dupquitte (44) janaubf (45) Morsagosila (34) FlanceEarnelD (41) Misdisss ( 43) JerTycleral expargosworse (43) sleestypeMest 32 Sweeseeengirl ) SettyAredywek (32) SaikewWrara (44) Flilfeledooda (42) Preltfrultpem (44) pedpreeta (42) Cmepnvvllj (39) Iri$ka (28) Buihoomyboamy (32) Zexspuaser (34) PseubssuenTab (42) paper.stankosaurus (38) lukArrime (44) Injupejen (44) Enebariarrorm (43) AllochkaP (32 ) naitteSer (33) DyncStaxytymn (34) Morirremo (32) Mypefeesini (32) aidelryplails (32) flavelsbroolf (32) cActuadia (32) Etenuemep (32) ginuarmoronna (32) unupleWoolf (32) Emormatet (32) majinsild (36) NaisteCreassy (32) Atfshspsks (37) Joyloaplierry (32) crutuargy (44) Bleaceria (32) TreatmentChina (33) Sinquenddonee (32) Driervima (32) attarkabs (32) brabodoCeaxia (32) sochiache (32) zorwayDyday (32) RizDilivere (32 ) HarfPabsral (32) Staind (45) arcatrise (36) FliefeTix (43) Haimbile (44) Bivyenved (44) SineNeind (43) capnereevag (44) Delpallopsy (43) rouptRooriPoP ) bolshbutre (33) Smefupennania (45) WhinnyInfully (42) shooguils (43) Brandon (35) offilfure (38) testersgamess (40) granconz ) starsesco (45) Ribekka (42) sadovod (45) AssaumPlash (43) Johndenves (37) anaemaneege (42) BlopleRes (45) ) dretyuo (39) russiando (40) GrinkWememing (43) bltimes (44) reoneypelow (33) OccawnVaw (42) [email protected] @@2 (27) kubantemos (33) Gambibiomboth (32) Granda (31) kodsre (37 ) BogyPageexage (45) pooplenex (37) PlelfHone (41) yerannccus (33) Borisperoff (34) intadiaadvand (40) VemeMorry (33) immimeTut ( 38 ) quibelikise ( 35) EnemetteVog ( ADrottDype (32) stroypra (43) lekafleurs (32) Brixacier (44) LoffsmuTs (33) Atmorpomi (45) Pibmeebra (44) amefengeaph (37) intuimetathic (43) YiogSpibiow (43) FookeTaperode (36) Cherryadd (45) Anthalsx (33) heevoisleds (35) AbetibeToBtut (33 ) AGarrugges (45) Nalena (35) Effinearcer (45) Nogjuraevargo (44) dalleyholve (43) enlalaenugs (34) Nilokoki (44) Affiddicync (33) GrooloToilt (44) Lexarrole ) oreseeRof (38) Denterrondosy (44) CKScupercuro (45) Dessendslup (43) Veseamuffmupe (38) ZoorAddepeJen (32) RinsKisee (44) DanielWex (39) Donnellabut (35) CliftonCeni ( Irremycle (36 Victormn ) rereFiereop (39) Anthonykib (34) bukowka (32 ) Namelili (32) Whiciedia (43) offivess (37) Anthonykt (35) Georgetat (43) JavierDype (34) Natali_ (31) FemSwerne (42) Stuartret (40) vera40987 (33) RonniePuby (34) Drodymn (42) Rartgaila (38) rabotaiv (32) Tyronekr (44) Michealcaf (35) Jeffreybef (40) CakHoalualbib (40) Ivannis85pom (32) MarcusMes (44) alieneJUG (42) Mr.PRTCSa (42) SylviaEt (37) ritulik84 (36) ARefAnync (39) AACAXIANOP (35) PaymndypeBymn (39) ArailsMal (36) VoneAnnenue (43) Georgezep (34) Clementkt (41) Plutoulfece (37) BoobsterKons ( Zweqwist (32) TerrellSr (41) WilliamGach (33) Ekaterina 87 ( 33) Willm#gnick[WgSgJjWg,2,4] (41) TiffanyGato (45) baguito (38) JacksonSi (45) lauarda (36) nikusssa (28) ussrMIGAS (43) LorenzosMa (37) Octavionada (40) Keraalato (40 ) Odolinka (32) Matthewsend (39) Emanuelsof (35) MarvinNow (41) Danielhem (40) ArthurCami (36) Nati-bio (38) DsveroCem (44) Richardwix (35) Carltonkib (43) Alenkanend (33) Biqzerti (44 ) Williamamen (45) Georgemar (45) ArthurLom (36) LavadaRop (43) Malcolmwak (44) StroivGew (36) AssdrmapKr (41) Thomasfaws (38) Antoninalab ( GopokgeDor 38) Lindiyacok (41) Wikdlazed (41) TirioneRog (41) AnfisaZorovaya (35) Deqwuhas (32) nadenilab2015 (36) AngalllKn (45) binapDota (45) Robertsnut (40) alisssa81 (39) Nohemizof (37) Kateinqf (44) TltSniper (43) Alexwore (44) udaamPat (35 ) werCak (43) CharlesCem (35) VUBarrentineflip (40) AenVot (42) Charliejuts (44) Maxgamemabs (44) Mkdqjxqz ( hkurkiPt (40 Francesbigh (35) Kqizjdbr (37) Maroldusen (36) Vera1988nika (32) Zorita (39) Natali 34 (38) LiuP (24) Furanurne (33) [show all]
Forum statistics
1644480 Messages in 24913 Topics from 272154 Users. Last user: rebenokby200904 Last message: “Re: quot: be...” ( 03:09:2020, 12:20 ) Latest messages on the forum. [Detailed statistics]
Online users
Currently online on the site: 605 Guests and 6 Users. Maximum online today: 637 . All-time maximum: 21257 (08/14/2020 at 11:50).
Epiphyseal dysostosis
Epiphyseal dysostosis (dystrophic dwarfism) is a congenital disease characterized by metaepiphyseal chondrodysplasia with changes in the tubular bones, spine and growth retardation. In patients from birth, shortened limbs (mainly due to the hips and shoulders), clubfoot, and clubhandedness are detected. Characteristic signs also include scoliotic deformity of the spine and chest, looseness in the joints up to subluxations and dislocations, flexion contractures, mainly in the knee and hip joints with pronounced bilateral clubfoot. Patients have an unsteady “duck” gait and have difficulty walking on crutches. By the age of 1.5-2 years, bilateral hip dislocation forms. There is pronounced atrophy of the muscles of the limbs and trunk. X-rays of the joints reveal severe multiple or even total damage to the epiphyses: they are flattened and expanded. In addition, there is an expansion of the bone metaphyses and deformation of the vertebral bodies in the anteroposterior direction.
Make a choice in favor of professional medicine!