Strokes, or acute cerebrovascular accidents (ACVA), are in second place in the total number of deaths. More often they die only from myocardial infarction. A major stroke affects large areas of the brain and has serious consequences - lifelong disability or death of the patient. The situation is aggravated by frequent relapses of the disease - a second blow occurs in 40 percent of those who have recovered from the disease.
The most common prerequisites for the disease are long-term hypertension and atherosclerosis.
Classification of major strokes
Massive strokes occur when, for various reasons, a large area (or several areas) of the brain is left without blood supply. The viability of bloodless lesions does not last long, after which they die.
Main types of acute brain disorders
Extensive ischemic stroke, or cerebral infarction. This is the most common form, developing in 80% of cases. Occurs as a result of narrowing, thrombosis or embolism of one of the largest arteries supplying a certain area of the brain.
Extensive hemorrhagic stroke, or intracranial hemorrhage. The most dangerous category of brain disorders, the mortality rate of which reaches 82%.
At the site of the rupture of the vessel, a hematoma (blood clot) forms, compressing the brain. Mechanical effects on tissue trigger a number of pathological processes: cessation of the outflow of venous blood, the development of intracranial high pressure and subsequent cerebral edema.
Cerebellar stroke (cerebellar stroke): causes, symptoms, recovery, prognosis
Cerebellar stroke is less common than other forms of cerebrovascular pathology, but represents a significant problem due to insufficient knowledge and diagnostic difficulties. The proximity of the brain stem and vital nerve centers makes this localization of strokes very dangerous and requires quick, qualified help.
Acute circulatory disorders in the cerebellum are infarctions (necrosis) or hemorrhages, which have similar development mechanisms to other forms of intracerebral strokes, so the risk factors and main causes will be the same. The pathology occurs in middle-aged and elderly people, and is more often found among men.
Cerebellar infarction accounts for about 1.5% of all intracerebral necrosis, while hemorrhages account for a tenth of all hematomas. Among strokes of cerebellar localization, approximately three-quarters of them are infarctions. The mortality rate is high and in other cases exceeds 30%.
Causes of cerebellar stroke and its types
The cerebellum, as one of the parts of the brain, needs good blood flow, which is provided by the vertebral arteries and their branches. The functions of this part of the nervous system are reduced to coordination of movements, ensuring fine motor skills, balance, the ability to write and correct orientation in space.
In the cerebellum it is possible:
- Heart attack (necrosis);
- Hemorrhage (hematoma formation).
Disruption of blood flow through the vessels of the cerebellum leads to either their blockage, which happens much more often, or rupture, in which case the result will be a hematoma. The peculiarities of the latter are not considered to be the saturation of nervous tissue with blood, but an increase in the volume of convolutions that push apart the cerebellar parenchyma. However, one should not think that such a development of events is less dangerous than brain hematomas that destroy an entire area. It must be remembered that even if some neurons are preserved, an increase in the volume of tissue in the posterior cranial fossa can lead to death due to compression of the brain stem. Often it is this mechanism that becomes decisive in the prognosis and outcome of the disease.
types of strokes
Ischemic stroke of the cerebellum, or infarction, occurs due to thrombosis or embolism of the vessels supplying the organ. Embolism is most common in patients suffering from cardiac pathology. Thus, there is a high risk of blockage of the cerebellar arteries by thromboembolism during atrial fibrillation, recent or acute myocardial infarction. Intracardiac thrombi with arterial blood flow enter the brain vessels and cause their blockage.
Thrombosis of the cerebellar arteries is most often associated with atherosclerosis, when there is a proliferation of fatty deposits with a high probability of plaque rupture. With arterial hypertension during a crisis, so-called fibrinoid necrosis of the arterial walls is possible, which is also fraught with thrombosis.
Hemorrhage into the cerebellum, although less common than a heart attack, causes more problems due to tissue displacement and compression of surrounding structures by excess blood. Typically, hematomas occur due to arterial hypertension, when, against the background of high pressure numbers, the vessel “bursts” and blood rushes into the cerebellar parenchyma.
Other causes include arteriovenous malformations and aneurysms that form during fetal development and remain undetected for a long time because they are asymptomatic. There have been cases of cerebellar stroke in younger patients associated with dissection of a portion of the vertebral artery.
The main risk factors for cerebellar strokes have been identified:
- Diabetes;
- Arterial hypertension;
- Lipid disorders;
- Old age and male gender;
- Physical inactivity, obesity, metabolic disorders;
- Congenital pathology of vascular walls;
- Vasculitis;
- Pathology of hemostasis;
- Heart diseases with a high risk of thrombosis (heart attack, endocarditis, prosthetic valve).
How does a cerebellar stroke manifest?
Manifestations of a cerebellar stroke depend on its scale, so the clinic distinguishes:
- Major stroke;
- Isolated in the area of a specific artery.
Isolated cerebellar stroke
An isolated stroke of the cerebellar hemisphere, when the blood supply from the posterior inferior cerebellar artery is affected, is manifested by a complex of vestibular disorders, the most common of which is dizziness. In addition, patients experience pain in the occipital region, complain of nausea and gait disturbances, and speech suffers.
Heart attacks in the area of the anterior inferior cerebellar artery are also accompanied by disorders of coordination and gait, fine motor skills, and speech, but hearing impairment appears among the symptoms. With damage to the right hemisphere of the cerebellum, hearing is impaired on the right, with left-sided localization - on the left.
If the superior cerebellar artery is affected, then the symptoms will be dominated by coordination disorders, the patient has difficulty maintaining balance and performing precise targeted movements, the gait changes, dizziness and nausea bother him, and difficulties arise in pronouncing sounds and words.
When the focus of damage to the nervous tissue is large, the vivid symptoms of coordination and motor disorders immediately prompt the doctor to think about a cerebellar stroke, but it happens that the patient is only bothered by dizziness, and then the diagnosis includes labyrinthitis or other diseases of the vestibular apparatus of the inner ear, which means the correct treatment will not be started on time. With very small lesions, there may be no clinical necrosis at all, since the functions of the organ are quickly restored, but about a quarter of cases of extensive heart attacks are preceded by transient changes or “small” strokes.
Characteristic signs
Some symptoms may appear weeks or even months before illness.
A person should be alert to the following phenomena:
- Unreasonable headaches of unclear localization, severe dizziness;
- Darkening in the eyes after standing up suddenly;
- Episodic memory loss;
- Sudden disorientation in space.
Symptoms of a stroke are divided into two categories:
- General cerebral - intense headache, nausea, imbalance, dizziness, agitation or stupor.
- Focal - paralysis, weakening of muscles (paresis), blindness in one eye, difficulty speaking, inability to make targeted movements.
With a massive stroke, oculomotor disorders are often observed: different pupil sizes, lack of their reaction to light, atypical movements of the eyeballs, strabismus. Severe tension in the extensor muscles may also occur.
If a brain stroke is suspected, a simple test is performed: the person is asked to smile or bare his teeth, raise his hands up and say something.
If a stroke has occurred, the following disorders are noticeable:
- The corners of the mouth are twisted, the tongue is turned, half of the mouth sags. The eyelid does not droop on one side. This is associated with paralysis of the facial muscles.
- When you raise your arms, one of them spontaneously lowers. A person cannot shake the other person's hand.
- Speech is unintelligible and pronunciation is difficult.
The presence of these signs means that the death of brain cells has begun. The faster a person is taken to hospital, the greater the likelihood of recovery.
Features of left-sided and right-sided stroke
Each hemisphere of the brain has its own functions. The left controls speech and logical thinking. Its cells analyze new information. The right hemisphere is responsible for the emotional component - feelings, experiences, creative processes, perception of the environment. In other words, it synthesizes processed information.
Stroke of the left hemisphere is slightly more common - in 57% of cases. It should be mentioned here that left-sided hemorrhage (or ischemia) leads to paralysis of the right side of the body, and right-sided hemorrhage leads to paralysis of the left side.
Damage to the left hemisphere also causes the following deviations:
- Unintelligible pronunciation, misunderstanding of speech addressed to the patient;
- Loss of speech memory;
- Articulation impairment;
- Inability to write, read, talk. Limiting communication leads to the patient withdrawing and losing interest in life.
Speech disturbances are a clear symptom of acute stroke, which is why patients quickly turn to doctors. Early treatment significantly improves the prognosis.
If an extensive stroke of the brain affects the right side, the signs will be as follows:
- Paralysis of the legs, arms, facial muscles on the left side of the body;
- Distortion of perception of one's own body. It seems to the patient that he has many limbs, or that numb arms and legs do not belong to him;
- Memory impairment, up to its complete loss;
- Difficulty understanding someone else's speech;
- Loss of orientation in space. The patient dresses incorrectly, cannot adequately assess the speed of movement, the size of the object and the distance to it;
- Depression, lethargy, complete indifference to the outside world.
Patients who have experienced a right hemisphere stroke often change their attitude towards life. Chronic depression and pronounced mental passivity occur.
Complications and consequences of brain stroke
Why is a stroke dangerous? Since the brain coordinates all functions of the body, disruption of its functioning threatens the patient’s life. After a stroke, a person may develop the following complications:
Coma
Due to damage to the brain, all signals are inhibited in its cortex and subcortex. The patient falls into an unconscious state, his breathing and cardiac activity are depressed, and his reflexes are impaired. Coma can occur quickly and begin with a sudden loss of consciousness, interruptions in the heart and breathing. The second scenario is gradual immersion. The patient experiences and increases in pulse changes over the course of several hours, feels a general malaise, experiences frequent yawning, loses coordination of movements, becomes numb in the body and paralyzes the limbs. Breathing becomes shallow, consciousness “floats away”.
A coma can last from several hours to 2-3 weeks, but every day you stay in it worsens the prognosis for the patient. The prognosis also depends on the degree of coma observed in a person.
Brain swelling
It comes in two types:
- Impaired outflow of blood and intercellular-interstitial fluids due to damage to capillaries. Blood and fluids cannot enter the vessels and are forced to accumulate in the intercellular space.
- Cytotoxic edema is swelling of brain cells due to lack of ATP and oxygen. A deficiency leads to disruption of the membrane pumps, and excess sodium ions penetrate into the cell, which provoke the accumulation of water.
- Cerebral edema after a stroke is diagnosed based on the results of examination and observation, computed tomography and lumbar puncture. Symptoms of a dangerous condition may include: signs of increased intracranial pressure (vomiting, nausea, headache), convulsions with psychomotor agitation. In severe cases, when the edema progresses, paralysis and coma occur, the pupils stop responding to light, and respiratory function and cardiac activity are impaired.
Paralysis
A brain stroke can lead to paralysis - it happens when the motor center is affected. Most often, ischemia or hemorrhage of the left hemisphere and paralysis of the right side of the body are observed. The degree of motor impairment is determined by the location of the lesion and its area.
Aphasia
Aphasia is a complex of speech and writing disorders. Depending on which part of the brain is affected, aphasia can result in slow and slurred speech, an inability to understand other people's words, and difficulty writing and remembering.
Loss of coordination
Impaired muscle tone and coordination of movements leads to the fact that a person cannot move independently. The spasm prevents the patient from performing any actions, as the patient is forced to overcome the resistance of his muscles. Paresis occurs due to the weakening of nerve motor impulses. Another type of disorder is apraxia of walking, in which a person performs elements of steps, but is not able to control the process of walking and walk purposefully.
Repeated stroke
The second and subsequent episodes of cerebrovascular accident aggravate the health of the patient who has not yet recovered from the first episode. Some diseases (thrombosis, atherosclerosis, diabetes, hypertension, vascular structural abnormalities) increase the likelihood of a recurrent stroke. The risk of recurrence increases when patients have a frivolous attitude: having barely coped with the first stroke, they stop visiting the doctor, return to bad habits, and refuse treatment for concomitant diseases.
Risk factors
Most stroke patients have ischemic disorders in the brain caused by stenosis (narrowing) of the supply vessels.
The situation is worsened by the following reasons:
- Smoking and alcohol abuse;
- Arterial hypertension;
- Diabetes;
- History of micro-strokes;
- Asymptomatic carotid stenosis;
- Inactive lifestyle;
- Overweight;
- Uncontrolled use of certain drugs, in particular oral contraceptives. If a woman also smokes and suffers from hypertension, the risk of a brain stroke increases many times;
- High levels of cholesterol in the blood;
- Negative attitude in life, stress and nervous stress, especially for patients who have already suffered one stroke.
Each of these factors can cause insufficient blood supply to the brain, but their combination greatly increases the risk of a major stroke.
Diagnostics
The following algorithm is used to make a diagnosis:
- Patient interview. The doctor finds out the exact time of onset of the disease, the rate of development of symptoms, and identifies risk factors - previous vascular diseases, smoking, atherosclerosis, hypertension.
- Assessment of the functions of various body systems. Neurological disorders are determined using special scoring tables.
- Laboratory tests: general urine test and blood tests - clinical, biochemical, coagulogram.
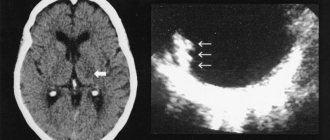
- Instrumental diagnostics - computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging of the brain.
It is important to distinguish a stroke from other pathologies with similar symptoms: abscesses and brain tumors, subdural hematoma, epileptic seizure. To do this, differential diagnosis is carried out using tomographic methods and electroencephalography.
Diagnosis of stroke
For proper treatment, doctors must determine the location and size of the affected area of the brain. They must also rule out other possible causes of neurological symptoms, such as a brain tumor or a reaction to certain medications. When diagnosing a stroke, the following methods are used:
• Physical examination. The doctor must examine the patient, check blood pressure and heart function, and assess the neurological status.
• Blood tests. Blood tests will give doctors important information such as blood clotting time, glucose levels, presence of infection, and more.
• Computed tomography (CT). Obtaining a clear image of the brain is necessary to assess which part of it is damaged and how severely it is damaged. The doctor may inject a contrast agent into the vessels and perform a CT angiography to obtain a detailed image of all the vessels in the brain.
• Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). MRI uses powerful magnets to produce detailed images of the brain. An MRI can see some things that are not visible on a CT scan. In this case, a contrast agent can also be used to better see the blood vessels - a method called MR angiography.
• Ultrasound examination of the carotid artery. Ultrasound shows the presence of fatty deposits on the walls of the artery and the flow of blood through the vessels.
• Cerebral angiography. In this procedure, the doctor inserts a thin catheter through a small incision into a distant vessel (such as the thigh). Then, along the vascular bed, it reaches the cerebral arteries and injects dye into them. This substance highlights blood vessels on an x-ray.
• Echocardiogram. Echocardiography uses sound waves to create a detailed image of a patient's heart. Echocardiography helps to find the source of blood clots in the heart. The doctor may perform a transesophageal echocardiogram, in which a tube with a small device is inserted into the patient's esophagus. Because the esophagus is close to the heart, this method provides a clear picture.
Stroke treatment
A patient with stroke is sent to the intensive care unit or to a neurological hospital.
If intensive treatment began in the first 3-6 hours after identifying a brain disorder (the so-called “therapeutic window”), then there is a chance of full recovery of health. The treatment tactics for different types of strokes are different because they have different goals.
Therapy for hemorrhagic form
First of all, specialists find out whether neurosurgical intervention is required. Indications for surgery:
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage;
- Continued bleeding;
- Aneurysm rupture;
- Large accumulation of blood in the cranial cavity.
If such pathologies are not diagnosed, drug treatment is carried out. It is aimed at maintaining breathing, heart rate, water-salt balance, preventing cerebral edema and renal failure. Hemostatic drugs, antioxidants, anticonvulsants, and vitamin K are prescribed.
Treatment of ischemic stroke
The first thing doctors focus their efforts on is restoring impaired blood flow. For this, surgical intervention or conservative therapy (medication) is used. If possible, preference is given to the second option.
After the patient has been brought out of a serious condition, emergency thrombolysis is prescribed - intravenous administration of drugs that dissolve blood clots. Next, anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents are used to thin the blood and maintain it in this state for a long time. To improve blood flow and metabolism in damaged neurons, Ceraxon, Piracetam, Trental are prescribed.
Taking medications helps restore lost brain functions. At the same time, rehabilitation measures are carried out - massage, physical therapy, gymnastics, physiotherapeutic procedures.
Rehabilitation measures
Activities in the rehabilitation program after a stroke include:
- Prevention of complications.
Complications include changes in muscle tone and joint damage. To prevent them, exercise therapy, paraffin wraps, placement in splints, and bandages are used.
- Restoration of movements with the help of exercise therapy, physiotherapy, massage.
Physical therapy begins in the hospital, when the doctor performs passive exercises, moving the patient’s body. After this, the person is shown simple exercises that he must do in bed under the supervision of medical staff, and then he is allowed to gradually sit up, stand up and walk.
- Restoring self-care skills.
Training in independent walking, nutrition, hygiene, dressing and undressing.
- Rehabilitation of speech and communication skills.
A speech pathologist-defectologist teaches the patient to speak and listen, read and write.
- Psychological adaptation to changes in life.
Since a brain stroke often leads to the fact that a person is forced to give up his favorite job or hobby, cannot speak clearly, becomes absent-minded, and experiences pain - this has a bad effect on the psychological state. The patient becomes irritable, depressed, and avoids contact with family and friends. A psychologist can help here, who should work not only with the stroke survivor, but also with his family. Relatives are also upset by the changes that have taken place, worry about their loved one and see that he has become different. Both sides need to learn to live in new conditions and accept them.
Recovery after a stroke is somewhat similar to the development of a child - a person learns again to speak, walk, eat, dress and undress, and communicate with others. For training to be successful, the patient needs to be praised and encouraged - just like a mother does with her baby. You cannot scold, let alone laugh at, changes in speech, gait, forgetfulness or untidiness - remember that the patient is very vulnerable psychologically, and with your comments you risk causing serious psychological trauma.
Source: MedAboutMe.ru
Consequences
Some patients recover after stroke and return to normal life, sometimes with restrictions in work activity.
For others, recovery is slow, and the following disorders are possible:
- Paresis and paralysis;
- Speech defects (aphasia);
- Partial or complete blindness;
- Swelling of the legs;
- Unsteadiness when moving, poor coordination of movements;
- Epilepsy attacks;
- Acquired dementia associated with neuronal death;
- Inability to perform daily activities and self-care.
Recovery
After a major stroke, the patient faces long, often lifelong rehabilitation. Neurological deficits caused by brain cell death cannot be restored. However, the body adapts to life at the expense of neurons that remain unharmed. This is possible if both the patient himself and his relatives are actively interested in independent recovery.
Some stages of rehabilitation are carried out in a hospital or sanatorium, but daily care falls on the shoulders of loved ones. It is recommended to seek help from speech therapists, massage therapists, chiropractors, and specialists in the field of acupuncture.
During the adaptation period, the patient undergoes the following procedures:
- Exposure to low frequency magnetic field;
- Electrophoresis;
- Electrical stimulation with alternating sinusoidal current;
- Ozocerite therapy.
The consequences of a major stroke are treated with medications:
- Instenon, Tanakan, Lipamide - for ischemic damage;
- Gliatilin, Delecit, Actovegin - for hemorrhagic stroke;
- Sirdalud, Menovazin - to restore muscle tone;
- Trittico, Neurol, Coaxil - for depressive states;
- Piracetam, Nootropil - for memory impairment.
Great importance is attached to physical therapy. From the very first days after stroke, motor functions of the limbs should be restored. Exercise therapy also solves problems such as decreased muscle tone, improved blood microcirculation, and prevention of joint contracture.
The more severe the stroke, the more difficult adaptation is . Therefore, rehabilitation procedures must be carried out every day. This will help restore vital functions and reduce the risk of another stroke attack.
Despite the severity of the condition and obvious prognosis, one must not give up. The resources of the brain have not been studied enough, and it is quite possible that persistent exercise will lead to lasting improvements in health.
By ischemic stroke (IS), doctors usually mean a focal disorder of cerebral circulation with disruption of some of its functions and damage to organ tissue. This happens due to a partial or complete cessation of blood flow there. As research in recent years has shown, ischemic stroke is the most common cause of premature human death.
In the 21st century, there is a persistent trend of rejuvenation of ischemic stroke - if earlier, people over sixty years old faced this problem, now IS is a typical case in 50 and even 40 year olds. In thirty percent of cases, a patient who has experienced an ischemic stroke of the brain fully recovers and leads a normal life. Unfortunately, most often the individual consequences of AI significantly affect the quality of life and are manifested by a variety of negative conditions, from speech impairment to partial or even complete paralysis. The prognosis of the possible consequences of cerebrovascular accident depends on the location of the problem, the affected area and the effectiveness/timeliness of treatment.
After myocardial infarction: consequences, rehabilitation and complications
Have you been struggling with HYPERTENSION for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure hypertension by taking it every day...
Read more "
The heart muscle or myocardium takes on the consequences of obstruction of the coronary arteries, which causes necrosis of its tissues or infarction. To avoid consequences and complications after a myocardial infarction, rehabilitation must be carried out in compliance with certain rules.
To fully restore all parameters of cardiac activity, the patient, under the supervision of a doctor, undergoes rehabilitation after myocardial infarction, which consists of diet, therapeutic exercises, medication correction, psychological adaptation and moderate exercise.
A cured myocardial infarction necessarily requires rehabilitation, as it prevents possible attacks and reduces the risk of deterioration in the functioning of the heart muscle.
Consequences of a heart attack
At the site of tissue necrosis, the resulting scar should restore contractile function, and if this process does not go well enough, the symptoms of the consequences of myocardial infarction may look like:
- resumption of angina;
- atherosclerosis of the abdominal or thoracic aorta;
- expansion to the left of the border of the heart;
- muffled first heart sound;
- increased blood pressure;
- pathological scar on ECG.
Undesirable consequences can occur at different times, which is why complications of myocardial infarction are distinguished as early and late. The entire post-infarction period is conventionally divided into two: immediate, up to six months, and long-term, after six months.
Complications
The consequences of myocardial infarction can take forms that complicate the patient’s life and even threaten him with death. Early complications of myocardial infarction include manifestations in the form of:
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- disturbances in the conduction of cardiac impulses;
- acute aneurysm;
- acute forms of heart failure (heart rupture; cardiac asthma or pulmonary edema; arrhythmogenic and cardiogenic shock);
- post-infarction angina;
- pericarditis;
- parietal thromboendocarditis.
Later complications after myocardial infarction include post-infarction cardiosclerosis, expressed in deviations in the scarring process, which are manifested in disturbances in heart rhythms, conduction and contractility of the heart muscle. Complications of acute myocardial infarction in a later period include mental abnormalities in the patient’s condition: uncritical behavior, euphoria, complication of marital relationships.
Disruption of the tissue scarring process can cause a serious complication of myocardial infarction - cardiac arrest.
Types of rehabilitation
Usually rehabilitation lasts quite a long time. The patient’s recovery proceeds simultaneously in the following directions:
- physical rehabilitation for myocardial infarction (returning performance and achieving normal functioning of the cardiovascular system);
- psychological rehabilitation (victory over the fear of another heart attack);
- social rehabilitation (the patient either returns to work after 4 months, or after a heart attack he is given a disability group).
To improve life after myocardial infarction, rehabilitation is carried out in a sanatorium, if the patient does not have general contraindications or from the cardiovascular system.
Diet
Numerous dissertations and abstracts have been written on the complications of myocardial infarction. And all of them emphasize the need to adhere to a certain diet, especially during the period of treatment and rehabilitation after a major myocardial infarction.
Immediately after the disease is detected, the use of salt is excluded from the patient’s diet. He is prescribed a diet of vegetable soups, low-fat dairy products, liquid cereals and carrot juice.
Later, the diet after myocardial infarction prescribes completely abandoning or not abusing spicy seasonings, fatty foods (meat, lard, fish, poultry), strong coffee and tea, pickles and smoked meats, sweets, alcohol, and flour products.
Why do you feed pharmacies if hypertension is afraid of the usual like fire...
Tabakov has revealed a unique remedy against hypertension! To reduce blood pressure while preserving blood vessels, add to…
Nutrition after myocardial infarction is intended to create the most favorable conditions for strengthening the heart muscle and enhanced disposal of harmful metabolic products.
The list of what you can eat after a heart attack is quite extensive:
- a minimum of fats in the form of vegetable oils: sunflower, olive, soybean, cottonseed, saffron;
- lean boiled meat: beef, chicken, pork, rabbit, turkey, game;
- boiled or baked after boiling, lean white fish (cod, flounder) or fatty fish (herring, sardines, mackerel, salmon, tuna);
- low-fat dairy products (milk, cottage cheese, cheese, kefir);
- vegetables: frozen and fresh, boiled, fresh or baked (potatoes are recommended to be eaten with their jacket);
- fresh fruits, unsweetened canned or dried fruits;
- walnuts;
- bread made from coarse flour, peeled, grain, rye, yeast-free, crackers (dried at home in the oven), oatmeal cookies;
- unground cereals for porridges, puddings and cereals;
- weak coffee and tea, unsweetened drinks, mineral water, unsweetened fruit juices, beer with low alcohol content;
- vegetable, dairy, cereal soups, beetroot soup, cabbage soup;
- protein omelet from 1 egg per day;
- seasonings in the form of lemon, yogurt;
- spices and herbs in reasonable quantities.
You should eat food in small portions without overloading the digestive tract every 3-4 hours.
Prevention of complications and relapses
Life after myocardial infarction is subject to certain rules, among which the main ones are maintaining blood pressure within 140/90 and controlling weight (and, if necessary, reducing it). Also extremely important are defeating bad habits, following a diet, moderate physical activity and regularly taking prescribed medications.
Many people are interested in the question of the possibility of having sex after a heart attack. It is not contraindicated for those who have already returned to their pre-infarction level of activity, but it should be remembered that sex is accompanied by significant physical activity. Therefore, you should have on hand nitroglycerin or other nitro-containing drugs that are incompatible with potency enhancing drugs, which makes Viagra and other stimulants prohibited.
If the basic rules of rehabilitation are followed, a heart attack can be completely cured without unpleasant consequences or complications.
Causes of stroke
The direct cause of ischemic stroke is disturbances in the passage of blood in the vessels, caused by their blockage with blood clots, cholesterol plaques, emboli or spasm. Atherosclerotic processes occurring in the body significantly increase the risk of developing IS: people who have previously suffered transient ischemic attacks or suffer from arterial hypertension face the above-mentioned problem five times more often than others.
Additional risk factors are a number of pathological conditions and chronic diseases, in particular: high blood viscosity, endocarditis, congenital malformations of the cardiovascular system, aortic aneurysms, heart failure, hematological diseases, physical inactivity, diabetes mellitus, atrial fibrillation, lipid metabolism disorders, and also alcohol abuse and active smoking.
Stroke left and right side
Focal disturbances of blood supply and symptoms of stroke depend on the location of the lesion - on the left or right hemisphere of the brain. Let us recall that the left hemisphere in humans is primarily responsible for speech and logic, while feelings, emotions, perception of the surrounding world and creativity depend on the right.
As practice shows, in 60 percent of cases the patient is diagnosed with a right hemisphere ischemic stroke. The main consequences of this problem can be considered violations of speech and its understanding, right-sided paralysis, the ability to read, write and articulation completely or partially disappears.
In the case of a right-sided lesion, the patient may not immediately feel problems; only in some cases does paralysis of the left side of the body occur. Most often, perception is disrupted, mental passivity appears, and memory loss appears. A patient with an ischemic stroke of the right hemisphere of the brain may not be able to orient himself in space and dress independently.
Signs of a stroke and how to recover quickly after it - doctor’s advice
“I felt slightly dizzy,” “I swayed, I could barely stand on my feet, but then everything went away,” “my vision became fuzzy, blurry...” Such complaints may appear several days or hours before the stroke.
But not all people listen to themselves and pay attention to these seemingly insignificant symptoms. But they are the ones who can save you from an impending vascular disaster.
If part of the face is numb, an arm and leg on one side have lost sensation, or speech has been impaired, then an ambulance should be called immediately. The sooner the patient is in the hospital and receives adequate treatment, the better the prognosis will be, the less the body will suffer.
This was discussed during the FACTS direct line. Lyudmila Dubinina, head of the neurology department of Kyiv City Clinical Hospital No. 6, answered readers’ questions.
“The ratio of “good” and “bad” cholesterol is determined by a blood test.”
*— Hello, Lyudmila Vitalievna. This is Elena from Kyiv. I am 60 years old. When I get nervous, my blood pressure can jump to 200. And then it gradually returns to normal. I'm afraid of a stroke: my grandmother and mother died from it. True, at an advanced age. Do I need to get examined somehow?
- Certainly. You should have done this a long time ago, because a predisposition to stroke really exists. You could have inherited from your relatives a tendency to atherosclerosis and arterial hypertension. Apparently, this is what happened. If there are pressure surges, you must take medications for hypertension. Were they prescribed to you?
- No. I just lower the pressure if it goes up.
- It is not right. Regardless of whether you are nervous or not, your blood pressure should be kept normal. Ideally it should be 120/80. But not higher than 140/90.
It is during the “leap” that blood vessels, which become less elastic with age, can rupture and blood will flood an area of the brain. This is a hemorrhagic stroke.
And if the vessel is narrowed due to a cholesterol plaque or a blood clot, then the blood flow is disrupted, and at some point the person risks an ischemic stroke: no blood flows to the area of the brain, and the cells die.
— What tests do I need to take?
— First of all, a lipid profile is a blood test that allows you to determine the ratio of “good” and “bad” cholesterol. By the way, after 40 years everyone should do this analysis annually. If cholesterol levels are high, the doctor will prescribe an ultrasound of the blood vessels of the head and neck - Doppler scanning.
You need to know whether, for example, a cholesterol plaque has formed in the carotid artery, how much the lumen of the vessel is reduced, and whether a stroke can occur. In a word, is there atherosclerosis?
With this disease, any blood vessels can be damaged - the heart (which threatens myocardial infarction), legs (intermittent claudication occurs, and the risk of limb amputation increases). You also need to know your blood sugar level and blood viscosity (it is determined by a coagulogram).
To prevent serious complications, you need to consult a neurologist or cardiologist and follow their recommendations.
*- "DATA"? This is Sergey from Kyiv. I have a question: is it possible to lower cholesterol without drugs, just through diet? Tests showed that my level was slightly higher than normal...
For those who have even slightly elevated cholesterol, following a diet is very important. Vegetable fats, vegetables and fruits should prevail in it (especially now, in the summer-autumn period, when there are a lot of salads and healthy herbs).
It is better to prepare dishes from lean meats - poultry, beef, and do not overuse pork and lamb.
Sea fish is preferable - it contains polyunsaturated fatty acids, which help fight bad cholesterol, are good for the brain and improve immunity.
But it's not just diet that matters. A sedentary lifestyle has a bad effect on the condition of blood vessels. But after work, many sit down with a plate of food in front of the TV and, having eaten enough, go to bed. Why can't this be done? Metabolic processes slow down, blood viscosity increases, and its microcirculation worsens.
You need to walk, swim, lead an active lifestyle. If you smoke, it is better to quit this habit. Because of it, the blood vessels become brittle. Believe me, you can do without cigarettes. Almost all stroke patients, even very heavy smokers, quit smoking. But it is already difficult for them to return to a normal quality of life.
— What if all this doesn’t help lower cholesterol?
— The doctor will determine whether cholesterol-lowering drugs (statins) should be prescribed. Don't be afraid to take them: they have minimal side effects. The risk of having a stroke is a much more dangerous situation.
How to keep blood vessels in good condition
- Monitor your cholesterol and blood sugar levels.
- Follow a diet and do not gain excess weight.
- Lead an active lifestyle: walk, swim, ride a bike.
- If a diagnosis of arterial hypertension has been established, constantly take medications that keep the blood pressure normal (not higher than 140/90 millimeters of mercury).
“If a red spot appears on the eyeball, this is a dangerous symptom”
*— Hello, this is Nikolai Emelyanovich from Cherkassy. During an ultrasound, a small cholesterol plaque was discovered in my carotid artery. What to do?
“It is important to stop its growth and prevent it from blocking the vessel, so that it does not lead to a stroke.
- It's real?
- Yes. But you will have to take care of your health: follow a diet to reduce cholesterol levels, and, if necessary, take medications (statins). Check blood viscosity. Normally, platelets and other blood cells should repel each other, not stick together, to prevent a blood clot from forming, which could break off and block one of the brain vessels if pressure increases.
You need to control your blood pressure, drink enough fluids and move actively - then your blood circulation will be normal. To prevent the blood from thickening, your doctor may prescribe anticoagulants or antiplatelet drugs—blood thinners. The simplest one is aspirin. In small doses, it will not provoke peptic ulcers, but its use has been proven to be important for the prevention of stroke and heart attack.
*- Good afternoon. I'm calling from Kharkov, Anna Fedorovna. My husband recently suffered a heart attack. Is he at risk of having a stroke?
“Unfortunately, the likelihood of a stroke is higher among those who have already had a heart attack. And vice versa. These diseases are most often associated with atherosclerosis. Only with a heart attack does ischemia occur in the tissues of the heart, and with a stroke - in the brain.
The main thing in your case is to ensure that your husband constantly takes the medications prescribed to him. You should not stop taking antihypertensive drugs or blood thinners for a day.
More than once we have encountered a situation: a person has run out of pills, he has taken a break for two or three days (most often this concerns warfarin) - and the ambulance brings to us a patient with a recurrent stroke.
- And sometimes I have a hemorrhage in my eye - a bright spot appears. Is it dangerous?
“Such a symptom should never be ignored. Most often, hemorrhage under the conjunctiva occurs during pressure surges. You need to undergo an examination - check your blood vessels, take tests.
But first, start a diary today, in which you write down your blood pressure numbers in the morning and evening. By the way, indicators can change throughout the day - you move, worry, do some work.
You should not measure your blood pressure too often, so as not to cause increased anxiety. And under no circumstances should you prescribe medications to yourself based on the “it helped a neighbor” principle.
*- Hello. Valentina Grigorievna, Vasilkov. Tell me, do you prescribe herbal medications for blood pressure? Otherwise I don’t want to take “chemistry”.
— I prescribe herbal-based sedatives: they help reduce the doses of antihypertensive drugs in emotional, stressed people and in women during menopause. But in other situations I prescribe them with caution.
Here's an example: Some patients become overly excitable after a stroke. And relatives ask: is it possible to give them tincture of valerian or motherwort? I answer: “No way!” They depress the nervous system, and we need to make it work.
We need antidepressants that have a different mechanism of action.
We measure pressure correctly
- Relax and sit quietly for about ten minutes.
- Measure the pressure three times.
- Write down the minimum indicators in your diary.
- The procedure should be carried out daily in the morning and evening so that the doctor can select antihypertensive drugs.
“The feeling of being “drunk without wine” may be a signal: a stroke is coming”
*- Hello. Leonid from Kherson, 43 years old, is worried. A friend suggests going to the gym to get pumped up. But I'm somehow afraid. Maybe get examined first?
- Of course, you need to visit a doctor. If we were talking about regular charging, there are no contraindications. And training, fitness classes, “pulling iron” require a serious approach. When overloaded, the pressure can go off scale. More than once young people were brought to us straight from the gym. It turned out to be a hypertensive crisis or a stroke.
One day, a young man had a stroke during sex. Perhaps he also took stimulants. And the body could not withstand the overload - emotional and physical. So one must exercise moderation and caution in everything. Dacha labor “feats” are also dangerous - people work in the garden with their heads down.
As a result, they often become our patients.
*- "DATA"? Evgeny Petrovich, Kyiv. Tell me, are there any warning signs of a stroke?
- Yes. For example, a few days before the disaster, a slight lack of coordination of movements may appear. The person notes that he has not drunk alcohol, but feels as if he is a little drunk. Attributes this symptom to fatigue or bad weather.
Slight dizziness, slight numbness of the extremities, temporary visual impairment, transient speech impairment, and sometimes memory impairment - the events happened for about two hours, and then the memory returned. This is how the body gives alarm signals.
But if they increase - the face is distorted, the corner of the mouth is drooping, speech is impaired, an arm and leg are paralyzed on one side - an ambulance must be called immediately. These are clear symptoms of a stroke.
By the way, after a video about stroke began to be shown in schools in Germany, the number of timely ambulance calls regarding this disease increased by 70 (!) percent. Even children were able to recognize dangerous symptoms in their grandparents.
— How are strokes treated today?
— First of all, we find out what kind of stroke a person has - ischemic or hemorrhagic. These are two different diseases, and the treatment should be prescribed completely differently.
But, according to statistics, ischemic strokes account for almost 85 percent. First of all, we do a computed tomography (CT) scan. If the pictures show that there is no hematoma, we assume that the cause of the stroke is a blood clot.
During the first four and a half hours it can be dissolved - thrombolysis can be performed.
- But a very expensive drug is used to dissolve the blood clot...
— There is a government program under which thrombolysis is provided free of charge. The effect is very high.
This year we performed it on four patients, and all of them left the hospital on their feet, meaning the brain cells were saved.
But such drugs have many contraindications: for example, recent surgery, poor blood clotting, taking anticoagulants, and others. And I would like to emphasize once again: for the procedure to be effective, the time factor is important.
*- Good afternoon! This is Alina Viktorovna, Kyiv. Dad had a stroke. He was saved, but his arm and leg do not work, and his speech is slow. He refuses to do exercises...
- Be persistent. The rehabilitator will show you the necessary exercises. Almost all patients experience depression after a stroke. But the attention of relatives and the desire to help do wonders. Encourage your father to talk - ask about something, demand an answer.
Sometimes you have to learn letters using the children's alphabet and force them to write with a marker. It is very good for fine motor skills to assemble figures from Lego parts. “Mirror therapy” is effective. The method appeared five years ago, and we are using it.
A mirror is placed in front of the patient, and he does exercises with his healthy arm or leg. At this time, the brain perceives the mirror image and “sees” how the affected limb works. As a result, it really starts to work. Read books, newspapers to dad, do crossword puzzles with him.
The main thing is not to lose hope. The first months are the most effective for rehabilitation. But it is important to continue training over the next few years.
Signs of a stroke
- Distortion and numbness of the face, the corner of the mouth has drooped.
- Speech impairment.
- Numbness of the arms and legs on one side.
*Photo by Sergei TUSHINSKY, “FACTS”
Read us in the Telegram channel, and
Source: https://fakty.ua/280709-priznaki-insulta-i-kak-bystree-posle-nego-vosstanovitsya—sovety-vracha
Symptoms of ischemic stroke
Many people mistakenly believe that with an ischemic stroke, acute pain must manifest itself - this syndrome is far from being the main one in the specifics of the problem, and most patients do not feel it at all. Unfortunately, failure to seek qualified help in a timely manner only aggravates the problem, and the risks of irreversible physiological processes increase many times over.
The first harbingers of an ischemic stroke can be considered repeated dizziness with darkening of the eyes, short-term disturbances in the functioning of the speech apparatus, as well as severe weakness in the limbs or one side of the body, up to temporary numbness. They appear most often in the morning or at night. It should be taken into account that with the embolic type of problem, there are no precursors at all - an attack and stroke in this situation is formed during the day, after strong excitement, physical stress, etc. In addition, regardless of the type of ischemic stroke, a person feels nausea, there is a strong gag reflex, double vision, it is impossible to smile, stick out the tongue completely, and even raise both arms up. The patient feels as if stunned, disorientation in space is accompanied by short-term convulsions.
Periods of stroke: description and principles of assistance
Acute cerebrovascular accident (ACVA), or stroke, is an extremely dangerous emergency condition for human life and health. As a result of local damage to parts of the brain, blood flow is disrupted in a specific area of the organ.
This leads to the failure of a number of physiological processes and inhibition of important body functions. If you know how to act during different periods of a stroke, the development of most negative consequences can be prevented.
The lack of timely or adequate assistance in a third of cases leads to the death of the victim or causes disability.
First aid for ischemic stroke
Unfortunately, ischemic cerebral stroke does not choose the place and time - it can catch a person anywhere. Before the ambulance or emergency help arrives, it is necessary to provide him with all possible assistance - in the vast majority of cases, the patient cannot do anything on his own.
- Immediately lay the person horizontally, placing pillows under their head, shoulders and shoulder blades. The head itself is raised at an angle of at least thirty degrees to the level of the horizontal surface.
- If you are indoors, open the windows and provide fresh air. Do not keep the patient in the sun, take him into the shade.
- Unfasten your collar, remove belts and other restrictive clothing. Free your neck from any constricting accessories.
- Remove all foreign objects from the oral cavity - chewing gum, dentures, etc.
- Measure your blood pressure and report it to the arriving medical team later.
- If the patient is unconscious, turn your head to the side so that mucus and saliva do not flow into the airways. If a person starts vomiting, carefully turn him on his side and after the process is completed, clean the oral cavity.
- Cover the patient with a blanket, apply dry cold to the head, preferably choosing the part opposite to the paralysis of the side of the body/limbs.
- Periodically rub the paralyzed part of the body, massaging it.
- Constantly monitor the person’s condition and if there are signs of clinical death, immediately begin artificial ventilation of the lungs and chest compressions.
- Never give the person pills, water, food, etc. Wait for a qualified medical team to arrive.
Periods of stroke - critical days in case of cerebrovascular accident
Among the huge number of neurological diseases, stroke is the most important problem.
Hemorrhage in the brain leads to disruption of intracranial circulation, neuronal necrosis and disruption of vital body functions.
Only 10% of patients return to a normal, full life; the rest adapt to life with lost abilities. Some patients have to relearn how to speak, walk and perform basic everyday activities.
The vast experience and high professionalism of neurologists, physiotherapists, neurosurgeons, psychologists, and speech therapists at the Yusupov Hospital allow us to achieve the highest results. Patients who were abandoned by doctors in other medical institutions successfully undergo rehabilitation at the Yusupov Hospital and begin an active life.
A stroke is a brain pathology that develops as a result of destruction or blockage of the blood vessels that supply the brain. Blood stops flowing to the neurons and they die.
Stroke is divided into two types – ischemic and hemorrhagic. The first type is also called cerebral infarction. It develops due to poor blood flow to brain cells when neurons begin to die.
Hemorrhagic stroke develops due to hemorrhage in the brain when a vessel ruptures. In this case, even capillary bleeding is enough for the development of severe disorders.
In any case, be it an ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, they develop in a matter of minutes and the patient requires immediate hospitalization. Timely medical assistance often saves the lives of patients at the Yusupov Hospital.
Periods of ischemic stroke
In ischemic stroke, a number of processes are observed that together lead to the death of neurons. Cell destruction occurs against the background of cerebral edema. At the same time, the brain increases in volume and intracranial pressure increases.
Due to cell swelling, displacement of the temporal lobe is observed, as well as infringement of the midbrain.
Compression of the medulla oblongata may also occur due to wedging of the cerebellar tonsils into the foramen magnum. This process quite often leads to death. Therefore, early hospitalization of the patient is extremely important.
When the first signs of an ischemic stroke appear, medical assistance should be provided within the first three hours, otherwise the prognosis is disappointing.
There are several periods of ischemic stroke:
- acute;
- spicy;
- early recovery period of stroke;
- late recovery;
- stage of residual effects.
Rules for providing assistance before the doctor arrives
Many do not have even the slightest idea how to help a person who complains of a feeling of severe nausea, repeated vomiting, headaches, especially if all this is accompanied by a loss of coordination in space.
However, despite all this, a person needs emergency care at the pre-hospital stage, and it must be provided before the doctors arrive. The patient needs urgent help so that later he does not have to “disentangle” the consequences of serious complications.
Remember, if you at least follow the list of basic actions given below, you can safely eliminate the possibility of aspiration from food masses:
- Ensure the proper position of the patient's head - make sure it is 30 cm from a flat surface. This can be done as easily as possible - just put a fabric roll under your neck.
- If an attack of vomiting occurs, you should immediately lay your head to the side so that the person does not choke on the vomit. As soon as the attack of vomiting ends, the oral cavity should be thoroughly cleaned, and dentures should be removed (if possible).
- Remove from your neck all third-party objects that could pinch it (chains, ties, etc.).
If a hypertensive attack develops in a person immediately after eating, and there is reason to believe that there is hemorrhage in the tissue of the brain, there is a high probability of a gag reflex, which is likely to lead to the development of aspiration - the entry of food masses into the respiratory tract.
The main task of those people who are near the patient will be to cleanse the oral cavity of ingested food and constantly monitor the waste of consumed food, which should continue until the arrival of the emergency medical team.
Another important point is that a person usually begins to feel sick before a sharp rise in blood pressure. Moreover, this feeling may not stop for a long period of time.
If this kind of symptomatology occurs, it is definitely necessary to measure the blood pressure level and, if necessary, take rapid-acting antihypertensive drugs (captopress, magnesium sulfate solution 25%, nifedipine).
In this way, it is possible to prevent the development of a cardiovascular accident.
It would be useful to administer 2 ml of metoclopramide (Cerucal) solution even before the arrival of the emergency medical team. Please note that this drug best relieves the feeling of nausea and calms an attack of vomiting - such effectiveness is achieved by its central action.
You may feel sick all the time - this indicates (most likely) a pathology of a psycho-emotional nature, and not an approaching CVD catastrophe.
The most acute period of ischemic stroke
In the first three hours, it is possible to restore blood flow and eliminate or reduce neuronal death through the use of thrombolytics. It is also possible to administer drugs into the stroke area itself, which helps prevent the development of complications.
Then doctors take measures to restore pressure, carry out rehydration, dehydration and oxygen therapy.
During the most acute period of a stroke (from 4 to 5 hours after the attack), the patient should be under the close supervision of a doctor in a hospital setting.
Diagnosis of the disease
Basic methods for diagnosing ischemic stroke:
- History taking, neurological examination, physical examination of the patient. Identification of concomitant diseases that are important and influence the development of ischemic stroke.
- Laboratory tests - biochemical blood test, lipid spectrum, coagulogram.
- Blood pressure measurement.
- ECG.
- MRI or CT scan of the brain allows you to determine the location of the lesion, its size, and how long ago it formed. If necessary, CT angiography is performed to identify the exact location of vessel occlusion.
It is necessary to differentiate ischemic stroke from other brain diseases with similar clinical signs, the most common of which include tumor, infectious lesion of the membranes, epilepsy, hemorrhage.
Early recovery period of stroke
The early recovery period is considered to be the period from 2 to 6 months after a stroke. At this stage, complex treatment is carried out:
- the patient takes medications according to an individual treatment regimen;
- in case of speech impairment, a speech therapist works with the patient;
- various manipulations are prescribed to restore sensitivity of the limbs and other parts of the body (massages, baths, acupuncture and others);
- physical therapy – the method helps strengthen ligaments and muscles.
Clinical picture
One of the earliest clinically significant symptoms in stroke is dyspepsia, in particular nausea and vomiting.
The duration of severe ailments can be up to several hours, gradually increasing and complicated by a feeling of numbness in the left or right half of the body, significant cognitive impairment or total fainting.
All this once again confirms the fact that damage to the center responsible for the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is associated with disruption of the activity of other vital centers for the regulation of autonomic functions.
It is also necessary to consider this option if vomiting does not subside even after the start of professional treatment. It is in this case that the risk of obstruction of the respiratory tract by vomit increases many times over.
In order to prevent the development of these events as quickly as possible, the doctor prescribes the immediate introduction of a nasogastric tube.
Thanks to this, it will be possible to remove the contents of the stomach and prevent aspiration syndrome.
Against the background of a complicated hypertensive crisis, the most dangerous brain disorders manifest themselves - a paroxysmal headache appears or increases many times over, and it is often one-sided.
A characteristic symptom is repeated vomiting without prior nausea, after which the patient loses consciousness, his complexion becomes bluish or red, and hoarse breathing appears.
After this, the development of a convulsive seizure with a pronounced predominance of clonic unilateral seizures is likely.
Nausea and vomiting after a stroke indicate that the medulla oblongata is affected.
This once again indicates the fact that the pathology in question (more correctly, a symptom) is extremely unfavorable in prognostic terms, since damage to this part of the brain will also affect the work of other centers of unconditioned reflex regulation, in particular, cardiovascular activity, respiration and thermoregulation . Even if we take into account purely digestion, those patients whose stroke caused nausea and vomiting will most likely have impaired swallowing and chewing function.
The most unpleasant thing is that these disorders will remain for a long time, and even if everything is done correctly at the rehabilitation stage, it is not a fact that the signs of dyspeptic syndrome will disappear along with other manifestations of neurological deficiency.
Period of residual effects of stroke
The time from one to two years after a stroke is considered the residual period. At this stage, it is important to follow all doctor’s instructions and take measures to prevent a recurrent stroke.
Rehabilitation specialists and neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital create a treatment and rehabilitation program individually for each patient, which allows achieving high results in recovery after a stroke. You can make an appointment by phone.
Author
Svetlana Vladimirovna Shcherbakova
Anesthesiologist-resuscitator, cardiologist
Nutrition
The diet implies restrictions on the consumption of salt and sugar, fatty foods, flour foods, smoked meats, pickled and canned vegetables, eggs, ketchup and mayonnaise.
Doctors advise adding more vegetables and fruits rich in fiber to your diet, eating soups prepared according to vegetarian recipes, and fermented milk products.
Meals must be fractional, consumed in small portions five times every day. In this case, the diet after a stroke involves a volume of fluid not exceeding one liter.
But do not forget that all actions taken must be discussed with your doctor. Only a specialist can help a patient recover faster and recover from a serious illness.
Development mechanism
Our brain contains two main areas responsible for vomiting. The first of them is located in the medulla oblongata, called the vomiting center.
Naturally, when this area is affected, a person experiences nausea and the contents of the stomach pour out.
Stimulation of the vomiting center is possible in other forms of stroke due to the presence of connections between its neurons and other parts of the brain.
The second zone is located on the two fourth ventricles of the brain. It consists of receptors that detect fluctuations in the concentration of various substances in the blood and cerebrospinal fluid.
Exceeding threshold values, the receptors are excited and transmit a signal to the vomiting center. A person develops nausea and vomiting, due to which the body is cleansed of harmful substances.
A similar mechanism occurs during apoplexy: the death of neurons is accompanied by the accumulation of toxic metabolic products.
What to do if nausea and vomiting occur?
If cognitive impairment along with nausea did not manifest itself in a person for long, i.e. less than a day, which means it was a transient attack. The good news is that this disease cannot cause a stroke.
The negative side of transient attacks is their neurological nature. They are difficult to correct even with the help of medications. If you suspect you have this disease, consult your doctor. He will help you develop an effective treatment plan.
If you have been experiencing nausea, dizziness and vomiting for several weeks, you may have suffered a mini-stroke. The problem with this disease is that 90% of patients do not pay attention to it.
It is well tolerated on the legs, so it is very easy to confuse it with seasonal illness or exacerbation of anemia. But the risk of a full-blown stroke remains high, so such patients are referred for examination.
If cognitive impairment increases, as does nausea and vomiting, then you have a person suffering from a stroke. In such a situation, you should take the following actions:
- call an ambulance to send a team;
- put the person on a bed, sofa or table in a comfortable position;
- remove tight clothing and various jewelry;
- give aspirin;
- measure blood pressure readings.
Ideally, you should take a taxi or your own car to quickly get to the clinic. In case of cerebral circulatory disorders, the speed of surgical procedures comes first. The faster they are carried out, the more parts of the brain can be kept in a normal state.
Source: https://MedLazaret.ru/kardio/rvota-posle-insulta.html
Treatment of ischemic cerebral stroke
Treatment of AI is a very long, complex process and often does not guarantee a good result - too many factors affect the patient’s further quality of life. As practice shows, timely treatment and qualified treatment gives a positive effect in half of the patients who apply.
After delivering the patient to a hospital or hospital, he undergoes an MRI or computed tomography, based on the results of which the type of stroke, the current state of the body is determined, and a further treatment plan is formed. In some cases, in the absence of contraindications, a lumbar puncture is performed.
The essence of treatment is mandatory immediate basic therapy and a differential scheme taking into account the pathogenicity of the problem.
- Sanitation of the respiratory system, in some cases - tracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation.
- Antiarrhythmic therapy with antianginal drugs, in particular heparin, Cavinton.
- Normalization of the pumping function of the myocardium - cardiac glycosides and antioxidants.
- Control of homeostasis and all types of balance (water-salt, acid-base, etc.) using droppers with saline solution.
- Neuroprotection - thiocetam, ceraxon, actovegin.
- Symptomatic therapy with psychotropics and anticonvulsants, use of analgesics and muscle relaxants if necessary.
- Proper nutrition - dietary table or, in the absence of the ability to swallow independently, intravenous administration of vitamins, glucose, tube administration of liquid mixtures.
- Control of defecation, urination, hygiene of mucous membranes, eyes and skin, fight against bedsores.
- If there are complications, their specific therapy, as well as the use of other complex techniques developed by a council of doctors taking into account the current condition of the patient.
Bedsores
This is a complication that occurs in bedridden patients at any time after a stroke, if due to paralysis the person cannot move, as a result of which pressure is applied to certain areas of the body for a long time. As a result of compression of the vessels, local blood circulation is disrupted, which causes the patient to experience tissue necrosis and develop bedsores. The main places where they appear:
- heels;
- elbows;
- sacral region;
- buttocks;
- shoulder blade area;
- back of the head
Recovery after a stroke
The recovery process after an ischemic stroke takes a long period of time. The most important stage here is the first three months, because it is then that motor functions are restored in 50 percent of surviving patients. If significant progress was not achieved during this period, then most likely the process of destruction and dysfunction has become irreversible. The more severe the patient’s problem, the less likely he is to make a full recovery.
A neurological hospital usually offers a number of comprehensive measures to restore the functions of the affected body - these are a variety of massages, classes with a speech therapist, occupational therapist, kinesiotherapist, neurophysiologist, physiotherapist, the use of innovative methods, in particular cold treatment, etc., as well as complex drug therapy.
Rehabilitation at home
After hospital and inpatient recovery, another important stage of the patient’s recovery begins - his rehabilitation at home. Its exact timing cannot be determined, since it depends not only on the effectiveness of the treatment, but also on the individual characteristics of the human body. Typically, basic activities need to be carried out over one to two years. The basis of recovery is systematic gymnastics, exercises and medications prescribed by the attending physician.
Impact loads are absolutely contraindicated, the emphasis is on reducing tension and muscle tone, improving microcirculation, preventing contact, protecting the skin and tissues from bedsores and resuming fine movements. Before performing any physical therapy, it is necessary to warm up the muscles and tissues - massage and a heating pad help best in this context. The following procedures should be carried out regularly, 3-4 times a day, several approaches with increasing amplitude/number of times after consultation with the physiotherapist.
Bed rest
In this case, simple extension and flexion of the feet, knees, elbows, hands, fingers, as well as rotational movements of them, would be appropriate. While lying down, you can use a splint - it helps restore the function of the arm and hand.
Smooth raising of the arms above the head and clasping the shins over the ankle with the hands are effective. Also, rotational exercises for the eyeballs and fixing the gaze on objects in order to develop accommodation spasms will not be amiss.
Seated position
If the patient’s condition allows exercises to be performed in a sitting position, then this significantly expands the range of possible rehabilitation measures. Sitting on the edge of the bed, lower and raise your legs, arching your back, and alternately press your knees to your chest, holding your breath at the peak. In addition, you can bring your shoulder blades together and tilt your head back and follow other specialist recommendations.
Exercises while standing
- Raising your arms above your head and lowering them to your knees with inhalation and exhalation.
- Using an expander with arms moving away from the body.
- Alternately tilt the body in different directions.
- Squats with connected feet.
- Lifting a matchbox from the floor and fixing it on the table.
- Other necessary activities.
Let us note once again that restorative procedures are prescribed exclusively by the attending physician; try not to self-medicate and introduce new exercises without approval that may harm the patient.
Memory and speech
Restoration of motor activity should be combined with exercises aimed at the functional development of affected speech and memory. With the first, a number of exercises are usually recommended:
- Curling your lips into a tube.
- Pushing the tongue forward.
- Licking the edges of the lips and biting them with the lower/upper jaws.
- Baring teeth.
Recovering memory is more difficult. Here, comprehensive training of the brain’s ability to memorize will be effective, from repeating numbers, words, paragraphs of books to using board and logic games. In addition, the doctor usually prescribes nootropics that improve physical brain activity - Lucetam, Fezam, Noofen.
Periods of stroke: its critical moments, rehabilitation, further prognosis
A stroke is a circulatory disorder in the brain that is caused by blockage of a blood vessel or, conversely, its rupture. This acute process is dangerous to human health and can lead to death if the victim is not provided with medical and timely assistance.
Types of stroke and their critical moments
In medicine, there are 2 types of stroke and the third is mixed, and it has signs of both the first and the second. The danger of this circulatory disorder is that it is irreversible, because we are talking about the vessels of the brain. The possibility of recovery is influenced by the patient’s age, the presence of additional health problems, and lifestyle.
Depending on the type of disorder, different periods of stroke are distinguished. The assistance provided at one time or another influences further recovery. Hemorrhagic stroke is more difficult to treat. Regardless of the stage, the violation carries great danger and consequences.
Hemorrhagic stroke
A hemorrhagic stroke is characterized by the rupture of a blood vessel or vessels, which causes blood to leak into the brain. Depending on the location of the rupture, this type of stroke is divided into several types: parenchymal, ventricular, subarachnoid, subdural, epidural, and mixed.
Regardless of which variety is identified, in 40% of cases it will lead to death if help is not provided. The most dangerous periods of hemorrhagic stroke are the first day on which the clinical picture begins to appear and two weeks after that. At least 85% of deaths occur during this period.
Useful information The most dangerous days for this type of violation are the first, seventh to tenth, fourteenth and twenty-first. On these days, a relapse may occur. After a month, this risk decreases significantly.
Hemorrhagic stroke occurs much less frequently than ischemic stroke, but despite this, it carries great danger and consequences.
Ischemic stroke
This is the most common type of circulatory disorder in the human brain, which is characterized by blockage of blood vessels. As a result, oxygen starvation occurs and neurons die. Blockage of the lumen of a vessel occurs due to a blood clot, an atherosclerotic plaque.
This condition is characterized by a process in which one unpleasant symptom is replaced by another. But the faster it is completed, the fewer neurons that are responsible for many body functions will be affected.
The most acute period of ischemic stroke includes the first day, when there was a pronounced clinical picture. Afterwards, the third, seventh, tenth are considered dangerous days. But even though these days will pass without complications, the possibility of relapse cannot be ruled out. A recurrent stroke is possible even a year after the first.
Despite the high prevalence of this type of disorder, it is extremely difficult to get rid of the consequences. This will take years of rehabilitation.
Periods of stroke
A stroke has more or less dangerous periods. But this applies only to the ischemic variety. The presented cerebral blood supply disorder is divided into 5 main stages:
- acute;
- spicy;
- early recovery;
- late recovery;
- residual phenomena.
Each of the presented periods has its own characteristics of manifestation. Depending on it, a set of actions is selected that is aimed at improving the patient’s condition.
In order to know how to ease the well-being of the victim, it is worth familiarizing yourself with each period of a stroke separately.
The most acute period
The presented period lasts on average 4 or 5 hours. It begins with the first sign of a stroke. The first three hours in medicine are called the “therapeutic window.”
This means that it is during this period that it is necessary to provide medical care to the patient. If this does not happen, complications of varying severity will occur.
The more time has passed since the onset of the disorder, the worse they will be, even death.
In order not to miss this most acute period of ischemic stroke, it is worth knowing how it manifests itself. There are simple and clear tests that can be used to check for the presence of a disorder:
- a person cannot smile normally; when asked to do so, he gets a crooked smile, in which one of the corners of the mouth is lowered. This indicates that one part of the face is paralyzed;
- the patient cannot say anything. This happens if the part of the brain responsible for speech has been damaged. This can also occur when there is a failure in thinking;
- when asked to raise both arms, the victim cannot do this, since one of the limbs “does not listen” to him;
- a protruding tongue turned to one side also indicates a stroke;
- a person cannot walk exactly in a straight line due to lack of coordination;
- If the patient is conscious, you can ask him to write a message. This method can be used if no other signs are noted. If a disturbance occurs in the brain, instead of a coherent message there will be an incoherent set of letters, and the person himself will not understand this.
Acute period
The acute period of ischemic stroke occurs two days after the first period. It has time restrictions and is 14-20 days. All this time, the victim has been in a medical facility for treatment. Therapy includes taking medications. If we are talking about a complex form of the disorder, the period of stay in the hospital is extended to a month.
The therapeutic approach during this period is aimed at:
- elimination of tissue edema, inflammation processes, and also to improve blood supply to the brain;
- normalization of the cardiovascular system, maintaining it and blood pressure;
- elimination of negative symptoms that accompany the post-stroke condition;
- preventive work aimed at eliminating relapse.
After the presented measures have been carried out, specialists move on to restoring the body and its functions that were lost due to impaired blood circulation in the brain. The next stage after acute is called subacute and lasts 2-2.5 months.
Early recovery period
The early recovery stage begins 3-6 months after the onset of the first signs. The recovery period that was previously established is adjusted if necessary. Drug therapy is also ongoing.
In order to fully eliminate the consequences of the most acute period of ischemic stroke, it is necessary to use an integrated approach to treatment. Its main stages include:
- taking the necessary medications, if indicated;
- going to massage, acupuncture, and other procedures that help restore the functionality of the body;
- conducting classes with a speech therapist to eliminate speech defects;
- exercises on simulators with equipment. To restore muscle strength and coordination.
Efficiency is determined by the systematic implementation of the presented procedures. Ignoring these treatment options will inevitably lead to disability.
Late recovery period
This period lasts from six months to a year. If the patient has been exercising, then by this time he will already have significant improvements. If he carried out everything according to plan, then after a year the person has the opportunity to move independently and take care of himself.
During this period, speech and fine motor skills of the hands are restored. Unfortunately, those nerve fibers that were damaged during the stroke will not recover, but those that surround them adapt and help to live a new life. They take over the functions of dead neurons. For this reason, you should not stop doing exercise therapy and socially adapt to your new life.
Period of long-term consequences
This period is no longer limited in time, but begins a year after the attack. This stage is characterized by the fact that the work being carried out is aimed at consolidating the results that were obtained earlier.
Here, increased attention is directed to preventive work that will reduce the likelihood of relapse. The patient must adhere to a diet, undergo regular examinations and undergo treatment at a sanatorium at least once a year.
Despite the work done, it is almost impossible to achieve one hundred percent recovery. This happens only 10% of the time. But this does not mean that you should not take care of yourself. Since this will allow a person to do many things independently, including self-care, performing simple actions without family, friends and staff.
In addition, during this period it is worth seeking help from a psychotherapist who will help improve psychological health, which has also suffered.
Recovery time and prognosis
It is difficult to say exactly how long it will take to recover from the most acute period of an ischemic stroke. This process is influenced by the type of stroke suffered, the age of the victim, as well as the size of the affected area of the brain and the characteristics of therapy.
This is also influenced by the patient’s mood for the result. Often after a stroke, patients become depressed, and this complicates the treatment process. Since in this case not only physical health suffers, but also the human psyche.
Useful information You can make any predictions only after treatment and the start of rehabilitation.
It is impossible to predict how this or that person will behave, so everything depends on the effectiveness of the work done, the mood of the patient and the relatives who will care for him.
A stroke unsettles both the victim and those around him.
But in order to be able to return to your previous life, it is worthwhile to engage in rehabilitation and, even after achieving the effect, not to abandon restorative measures.
Source: https://nervy-expert.ru/insult/vidy-insulta/periody-insulta/
Stroke Prevention
- Change your lifestyle, give up alcohol and smoking.
- Monitor and treat hypertension, as it causes ischemic stroke in 80 percent of cases.
- Measure your blood pressure regularly - if the window is above 140/90 mm Hg. Art. - this is a reason to immediately consult a doctor.
- Avoid foods rich in cholesterol.
- Go on a diet if you are overweight.
- Do regular moderate physical activity.
- Avoid constant stress.
- Be sure to treat cardiovascular diseases and see a doctor if you have diabetes.
Video
Life is great with Elena Malysheva! Stroke
Elena Malysheva in the program “Live Healthy!” Recovering from a stroke
The consequences of a stroke can be reversible or irreversible. The consequences of a stroke and whether a person can survive directly depend on what percentage of the affected area of the brain occupies. The speed of therapeutic intervention, correct diagnosis and timely treatment also influence the consequences of a stroke.
Period of residual effects of stroke
The time from one to two years after a stroke is considered the residual period. At this stage, it is important to follow all doctor’s instructions and take measures to prevent a recurrent stroke.
Rehabilitation specialists and neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital create a treatment and rehabilitation program individually for each patient, which allows achieving high results in recovery after a stroke. You can make an appointment by phone.
Source: yusupovs.com
Consequences of stroke depending on its type
Extensive stroke is divided into ischemic and hemorrhagic. Extensive stroke consequences and consequences of hemorrhagic and ischemic stroke are similar. The difference is in the speed and severity of their development.
Ischemic stroke is characterized by a disruption of the blood supply to parts of the brain due to blockage of an artery by atherosclerotic plaque. Ischemic stroke has a more favorable prognosis for the patient's recovery. The consequences of an ischemic stroke are usually manifested by impaired motor activity, muscle weakness, loss of control of motor activity, problems with coordination, difficulties in concentration and perception, speech disorders, loss of sensation, and epilepsy.
Hemorrhagic stroke is a consequence of a ruptured vessel, resulting in bleeding in the brain. As a result, cerebral edema occurs and an acute inflammatory process develops, which leads to brain necrosis and death. Very often it happens due to high blood pressure, at a critical level.
Hemorrhagic stroke is very dangerous, difficult to treat, characterized by high mortality; with extensive brain damage, coma and death can occur. The consequences of a hemorrhagic stroke are usually disappointing: a person can become disabled, remain blind, deaf, insensitive to pain and heat, smells and speech addressed to him for the rest of his life. A person is not able to care for himself - he cannot eat, and he cannot control bowel movements and urination. The general condition of the patient is lethargy.
With a major stroke, it is important for the patient’s condition how quickly he receives help. The consequences depend on the degree of brain damage. With a major stroke, the left side of the body can be paralyzed, memory and thought processes can be affected, and reactions can slow down. The facial muscles will be affected – the patient’s facial expressions will be skewed and distorted. On the mental side – apathy, a feeling of detachment and hopelessness. Persistent paresis occurs, sensitivity suffers, and eye movements may be impaired.
When a patient with a massive stroke is taken to the hospital, his relatives are worried about the questions: what is the diagnosis of “major stroke”, what are the consequences, the chances of survival, the possibility of restoring the patient’s condition?
It all depends on the age of the patient - the elderly condition aggravates the diagnosis, the severity of the lesion, the strength of the body, and gender. During the first days after a stroke, approximately 25% of patients who have suffered a major stroke die. When vital parts of the brain are damaged by an extensive stroke, 95% of patients die immediately, and the remaining 5% fall into a coma. Recovery from a major stroke without consequences is possible in only 5% of patients. Unfortunately, they are not immune from a second stroke; within a year after the first attack, it occurs in 25%, and in 40% after 5 years. Being older increases your chance of having another stroke.
The consequences of a stroke are divided by type:
- Motor: paralysis of the limbs, paresis, increased muscle tone, paralysis of part of the body - left or right side, problems with swallowing;
- Disorders of the vestibular apparatus: impaired coordination, orientation, balance, dizziness;
- Visual impairment: blindness - partial or complete, impaired eye movement, strabismus, visual agnosia, double “picture” in the eyes;
- Hearing impairment: the occurrence of hallucinations, hearing loss or reduction, auditory agnosia;
- Loss of smell, loss of pain, disturbances of tactile sensitivity, or, on the contrary, the appearance of hypersensitivity;
- Cognitive: decreased and impaired attention, decreased intelligence (dementia), logic, memory impairment or loss (amnesia), information perception, speech problems;
- Mental: anxiety, aggressiveness, instability of the psyche and emotional background, depression, apathy.
The consequences of a stroke in old age very often lead to dementia, because the destroyed brain cells are replaced by connective tissue.
Features of life after a stroke
Post-stroke depression is detected in 40-70% of patients. Emotional disorders are associated with social maladjustment. Statistics show that the combination of depression and neurological deficits worsens survival prognosis. The negative impact of emotional disorders is due to a decrease in the motivation of the patient, who does not actively participate in rehabilitation activities and does not show interest in the success of treatment.
Depression develops as a result of the loss of the usual routine of life, a reduction in the range of interests, and a lack of faith in the success of therapy and recovery. The development of post-stroke depression correlates with the progression of disability. A partially or completely paralyzed person already in the first days after a stroke shows signs of psycho-emotional disorders.
The behavior of people after a stroke can be called inadequate and unpredictable. For example, the joy of meeting relatives in such patients is instantly replaced by irritation. Aggression gives way to apathy when the patient does not want to make volitional and physical efforts to recover. If a person is paralyzed, he experiences sensations such as fear of the future, a feeling of uselessness, and inferiority.
What is happening around us seems like a terrible dream that will never end. At such moments, psychological support from loved ones is important. Participation and understanding on the part of relatives, combined with psychotherapy sessions, will help overcome difficulties and restore faith in recovery. In the books “Life after a stroke” (S. Kuznetsov), “Paralysis. The path to recovery" (M. Leontyev), "Rehabilitation after a stroke" (E. Belyanskaya, M. Krasnova), "Stroke: before and after" (K. Rodionov) describe practical ways to overcome the consequences of a stroke.
Whether it is possible to work after a stroke depends on the degree of functional recovery. The decision is made individually. In clinical practice, there are cases when a person returns to work after experiencing several episodes of stroke.
Stroke, consequences, possibility of recovery
Increased blood pressure after a stroke indicates the active activity of the heart, which works in an increased mode, trying to eliminate the consequences of a stroke - a violation of the blood supply. As a rule, it does not have much effect on the course of further development of the disease. In some cases, it can cause swelling of the brain and the occurrence of encephalopathy, which can cause a recurrence of the stroke.
An increase in temperature after a stroke is a fairly common symptom that does not bode well. Sweating begins to increase, the temperature does not drop. The appearance of such a symptom indicates a poor prognosis in the future and contributes to the development of the risk of death by 30%.
The soporous state manifests itself in the patient’s lack of self-control and the occurrence of lethargy. This symptom manifests itself especially often in patients suffering from hemorrhagic stroke - it occurs in 20% of cases. After some time, cramps may appear. In patients with ischemic stroke, they occur in 3% of cases, in patients with hemorrhagic stroke in 8%.
Pain in the head – this symptom occurs in 65% of patients. It appears more often in young women.
Paralysis – leads to loss of motor activity. It is often accompanied by blindness and deafness.
Memory loss is the most common symptom of strokes. Manifests itself in the form of amnesia, hypermnesia, paramnesia, hypomnesia.
Speech dysfunction is a symptom of a left-sided stroke. It can be either full or partial. It manifests itself in incoherent speech, impaired pronunciation of sounds, and incorrect coordination of phrases and sentences.
Impaired motor skills are manifested by weakness of the hand muscles - the patient is not able to make precise movements with his fingers - fasten a button, take a spoon in his hand. In the future it can be eliminated with special exercises.
Symptoms of a coma in a patient are lack of response to stimuli, loss of consciousness, spontaneous bowel movements or urination. In this case, the swallowing reflex may be preserved, which is very important for the patient’s nutrition.
Convulsions, loss of consciousness, a sharp decrease in blood pressure, temperature - these manifestations also mean a stroke, symptoms and consequences of coma. Unfortunately, in most cases, coma can be fatal. The critical threshold for coma is 60 minutes.
Early recovery period of stroke
The early recovery period is considered to be the period from 2 to 6 months after a stroke. At this stage, complex treatment is carried out:
- the patient takes medications according to an individual treatment regimen;
- in case of speech impairment, a speech therapist works with the patient;
- various manipulations are prescribed to restore sensitivity of the limbs and other parts of the body (massages, baths, acupuncture and others);
- physical therapy – the method helps strengthen ligaments and muscles.
Left side stroke consequences
It is generally accepted that left-hemisphere disorders are more amenable to recovery than right-sided ones, but the patient’s relatives are concerned about the question they ask the doctor: left-sided stroke, consequences, how long do they live? Approximately 1/4 of patients do not reach the age of 65 years. Of those who have had a stroke, only 20% remain fully able to work. However, there are cases of recovery from a stroke, with minimal consequences for the person.
If the left hemisphere is affected, this is expressed in such consequences as:
- Paralysis, impaired sensitivity on the right side of the body, paresis;
- Visual impairment – right eye;
- Impaired memory, speech;
- Impaired perception - the patient does not understand what is being said to him;
- The consequence of a violation of the thought process, logic and intelligence;
- Consequences of mental disorders.