There are many possible pathologies in the development of children. Fortunately, they are rare. But this, at the same time, reduces the chances of detection on time.
If a child of preschool age is not well versed in numbers, you should not expect him to outgrow it and everything has its time. Perhaps the cause of arithmetic errors is dyscalculia .
This term defines a disability that is characterized by a lack of ability to learn and understand arithmetic operations. The person does not know how to operate with figures and numbers.
How serious is the disorder? The editors of estet-portal.com suggest considering the causes, signs and options for correcting the pathology.
1. Where and when to look for the cause of dyscalculia 2. What symptoms indicate dyscalculia 3. Dyscalculia: how and when to diagnose 4. The essence of treatment and correction of dyscalculia 5. How parents can help overcome dyscalculia
Where and when to look for the cause of dyscalculia
If you suspect your child has abnormalities in their ability to count, do not rush to blame yourself.
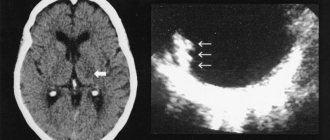
The main reason for the manifestation of the disease is insufficient development of the parietal lobe of the brain , which can appear as a result of:
● development of complications during pregnancy and childbirth (asphyxia, prolonged toxicosis, birth of a premature baby);
● the influence of genetic predisposition or hereditary disease;
● improper diet;
● receiving a head injury during the early development of a child;
● presence of a tumor in the brain ;
● transmission of neuroinfection. The development of the disorder is directly influenced by fear of arithmetic as a subject and possible punishment, and the child’s poor social environment (dysfunctional family).
Treatment of acalculia
Due to the compatibility of the symptoms of acalculia with other disorders of cognitive functions, it is often quite difficult to identify acalculia syndrome. It may simply not be noticed against the background of underlying cognitive dysfunction. However, detection of the described disorder is important work, since the system of corrective measures is determined by symptoms. In order to confirm the presence of a failure in computational operations and classify a person into a certain category, neuropsychological testing is carried out to determine counting disorders, speech defects, writing and reading disorders, and deviations in spatial orientation.
Acalculia can be corrected. However, for successful and complete elimination of symptoms, it is necessary, first of all, to treat the disease that provoked acalculia. The primary form of dysfunction requires a renewed understanding of the meaning of numbers and their bit structure. For such patients, in current medical practice, the visual method, the technique of operations with numbers and the perception of their digits are successfully applied to restore the lost function.
In order to overcome the disease in question, a neuropsychologist together with a speech therapist carry out labor-intensive and lengthy work. The therapist collaborates with other doctors, the patient himself, and also with the patient’s relatives. In the secondary form of the described disorder, other lost cognitive functions should be corrected in parallel. The following principles of successful therapy should be observed: complexity (combination of pedagogical influence with medical and psychological methods of correction), systematic approach (restoration of computational skills simultaneously with etiological therapy), continuity.
The success of correction of acalculia is determined by the time of initiation of adequate therapy, the prognosis of recovery is determined by the size of the damaged segment - early detection and timely implementation of therapeutic measures. In addition, the success and duration of therapy is determined by the age of the individual and the degree of speech disorders. The best dynamics are demonstrated by patients at an earlier age stage. Moreover, if the disease originated in childhood, then in the future there may be gross disturbances in the formation of speech.
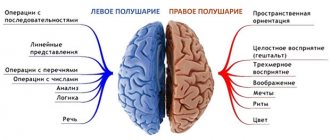
Characterized by violation of counting operations. Acalculia may be based on different mechanisms, the nature of which depends on the location of the lesion. Disturbances that occur with lesions of the occipito-parietal regions of the left hemisphere, or with bilateral lesions, belong to the so-called primary acalculia.
a) With lesions in the occipital region, the concept of number is disrupted, the optical image of the number disintegrates; numbers cease to be signs reflecting a known quantity. The numbers begin to mix up and become difficult to recognize, especially those that are similar in style (6 and 9). These disorders are optical-gnostic in nature and are similar to optical alexia (often they are combined).
b) Another type of acalculia is based on a violation of the representation and perception of the spatial arrangement of the digits that make up the place value. Multi-digit numbers are read as separate digits; numbers with the same digits, but arranged in a different sequence, are perceived as identical (187 and 781). It is especially difficult to recognize and evaluate the arrangement of elements in Roman numerals. Patients cannot determine the difference in numbers IV and VI, IX and XI, assessing them incorrectly or mixing them up. Similar errors occur when writing Roman numerals. Such manifestations of acalculia are based, according to A.R. Luria, on more general apraktoagnostic disorders characteristic of damage to the parietal lobe of the left hemisphere.
c) The third type of acalculia is associated with a violation of counting operations, which may be similar to the phenomena described above, but can occur when the meaning of simple numerical symbols is preserved. Patients lose the ability to perform simple arithmetic operations: addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and find it difficult to mentally count with single-digit numbers. Counting operations involving the transition through tens are especially grossly violated. The awareness of the size of multi-digit numbers in terms of the individual values included in it is also grossly impaired (for example, the number 178 is perceived as larger than 201); often the bit structure of the number completely disintegrates - the patient does not know where in the number they are
tens, hundreds, ones. The sequence of written counting in the vertical method of calculation (in a “column”) is forgotten; operations with fractions are inaccessible.
Primary acalculia, as a rule, is combined with semantic aphasia and other left-hemispheric parietal syndromes, part of the complex Gerstmann syndrome, resulting from damage to the angular gyrus of the parietal lobe of the left hemisphere.
Secondary acalculia can be detected in various forms of aphasia. The mechanism of these disorders is closely related to the mechanism of speech disorders. For example, disturbances in the nomination of numbers may be associated with general amnestic disorders in acoustic-mnestic aphasia, alienation to the value of the named number can be associated with a violation of the acoustic-gnostic link in sensory aphasia. Impaired counting operations in motor aphasia - with impairment of internal speech, inertia of brain processes, disautomatization (with lesions of the premotor parts of the speech zone).
Descriptions of acalculia are given in the works of N. Head (1926), A. R. Luria (1962, 1969), A. R. Luria, S. V. Tsvetkova (1966) and other authors.
3.3.8. Gerstmann syndrome
This syndrome includes finger agnosia, combined with “pure” agraphia, impaired orientation in the right and left, and often with counting disorders - acalculia. Gerstman regarded this combination as a separate special syndrome, which is based on unexpressed autotopagnosia. This syndrome is currently known as Gerstmann's syndrome (named after the author who described it). According to the author, in this syndrome the lesion is localized in the parieto-occipital region of the left hemisphere (angular and second occipital gyri of the left hemisphere in right-handed people).
3.3.9. Amusia
Impaired musical abilities. Observed in cases where jth abilities existed before the disease. Cases of amusia with local brain lesions in professional musicians are described, but impaired recognition or reproduction of well-known melodies can be detected
in patients who have not been specifically trained in music, but are able to sing correctly and recognize a familiar melody.
a) Sensory amusia
Characterized by impaired recognition of well-known melodies. Patients find it difficult to identify two short melodic passages presented in succession, mistake different melodies for the same and, conversely, find it difficult to compare two tones in pitch. Professional musicians cannot estimate the size of the interval between two musical tones, which leads to the impossibility of notating short melodies. Often sensory amusia is accompanied by a reading disorder - musical alexia.
Sensory amusia can act as an independent disorder or be combined with disorders of auditory gnosis - “pure” speech-auditory agnosia, in which the recognition of not only melody, but also other surrounding sounds and noises (voices of animals and birds, noise produced by the wind, the movement of a train) is impaired and so on.).
b) Motor amusia
Impaired ability to sing and play musical instruments. The melodies of familiar songs are reproduced inaccurately, there is distortion, the sequence of musical sounds and the melodic pattern are disrupted. In professional musicians, the reproduction of new, unfamiliar melodies, the repetition of a given musical tone, and the reproduction of the rhythmic pattern of a melody are impaired. Patients who could play musical instruments lose this opportunity. Not only do they find it difficult to play notes, but they often cannot reproduce well-learned pieces of music.
It should be said that the violation of musical abilities does not in any way affect the speech of patients, does not change its hyptonal-melodic and rhythmic structure. Motor amusia is detected only when singing. In patients with efferent motor aphasia in cases of severe disintegration of expressive speech (embolophasia), in most cases the correct reproduction of well-known melodies is preserved, and singing with words often promotes disinhibition of speech.
A description of sensory and motor amusia is contained in the publications of a number of authors: E. Feuchtwanger (1930), K. Kleist (1928), R. Brain (1963), I. M. Tonkonogogo (1973).
Amusia occurs more often with lesions of the right hemisphere. In sensory amusia, the lesion is located in the middle-middle parts of the temporal region, and in motor amusia, in the posterior parts of the second frontal gyrus.
Acalculia refers to diseases resulting from damage to certain areas of the cerebral cortex. A feature of the disease is impaired ability to perform computations, lack of understanding of the bit structure of numbers and arithmetic operations.
Patients often confuse visually similar numbers, for example, 416 and 614, and have difficulty counting. Depending on the type, the disease can act as a single symptom or be part of the structure of neuropsychological syndromes. The disease often develops due to traumatic brain injury.
What symptoms indicate dyscalculia?
You can spot a problem in your child yourself based on the following symptoms:
● inability to recognize the number of objects by external indicators when the child is asked to count them one by one;
● inability to correctly perceive the concepts of “more” and “less”;
● improper coordination of movements;
● difficulties in calculations;
● inability to calculate time abstractly;
● lack of understanding in solving simple arithmetic problems;
● inability to perform actions using logic and abstraction. The presence of even one, or even more so several symptoms in your child should alert you.
To recognize the pathology, it is best to visit a specialist in order to dispel all doubts and not confuse it with some other little-known pathology, for example, Tourette syndrome .
The causes of the development of dyscalculia are associated in the vast majority of cases with deformations in the brain, and the main symptoms are noticeable already in preschool age.
Types of disease
Depending on the manifestation, there are many types of acalculia.
Verbal
Characterized by difficulties in denoting mathematical terms, concepts and operations verbally. It is quite possible that the patient is fluent in arithmetic, but cannot express it.
Apraxic
A person is not able to independently determine the number of objects that are nearby.
Dyslexic
It manifests itself in the fact that the patient suffers defeats in attempts to read some arithmetic sign or symbol. It is believed that this type of disorder can be transmitted at the genetic level.
Graphic
In this case, the name speaks for itself; graphic acalculia deprives a person of the ability to display mathematical operations in writing. Such a person will not even be able to draw a basic geometric figure.
operating room
During the operational type of disorder, it will be almost impossible for the patient to perform arithmetic operations: add, subtract, divide and multiply. Perhaps this will manifest itself partially. For example, a person copes well with subtracting numbers, but cannot multiply them.
Primary
Scientists believe that the disease of primary acalculia has no connection with disorders of other mental functions. It appears due to damage to the left hemisphere of different areas of the cerebral cortex: frontal or parietal.
Frontal
Impaired functioning of the frontal lobes of the brain leads to loss of conscious activity in a person. Thus, the individual cannot perform precise mathematical operations.
Parietal
Occurs as a loss of spatial thinking. Accordingly, the patient cannot understand the concept of “numbers” and everything connected with them.
Secondary
It is part of a neuropsychiatric syndrome that already exists in the individual. It appears as a result of a lack of ability for purposeful mental functions. Secondary acalculia has several subspecies.
Optical
A variety that appears due to problems with vision receptors. The patient literally cannot distinguish one number from another.
Sensory
As a consequence of problems with the temporal areas of the cerebral cortex, sensory acalculia develops. Because of this, the patient loses the ability to count verbally.
Acoustic-mnemonic
If the prefrontal areas of the brain are affected, then an acoustic-mnemonic type of disorder may begin. It is expressed in the fact that the person cannot perceive any arithmetic terms or commands by ear.
Dyscalculia: how and when to diagnose
When can pathology be detected?
The first symptoms will be noticeable before the age of 6 years, because children begin to need to carry out basic calculations.
You can establish an accurate diagnosis if you seek help from a child psychologist or speech therapist. Diagnosis is made by examining the child and applying differential diagnostic methods.
The child is given the following test tasks to complete:
● count numbers from 10 to 20 (after all, counting to 10 can be normal even in the presence of pathology);
● name and classify different shapes according to color indicators;
● indicate numbers in ascending order and then in descending order;
● solve easy math problems.
Acalculia in children
The dysfunction in question is an acquired ailment, manifested in a failure to perform arithmetic operations.
The causes of acalculia in children are damage to brain structures. The ability to count is a fundamental skill, the absence of which significantly complicates life and interferes with obtaining an education and mastering a profession. The dominant place in the formation of counting processes belongs to the parieto-occipital zones and parietal segments of the cortex.
The causes of acalculia are due to damage to the listed brain areas, resulting in disruptions in spatial orientation and understanding of spatial relationships.
Luria determined that the majority of children suffering from the described defect are proficient in ordinal counting, correlating the number of objects, and can count, but they cannot understand the principle of place value or operate with generalized sets. The cardinal symptoms of this pathology are: a breakdown in the understanding of numbers, a disorder in understanding the bit structure of a number, and an understanding of the meaning of signs. Numeracy is the integration of several cognitive skills. An individual suffering from acalculia experiences great difficulties in four areas.
Acalculia syndrome and its manifestations are determined by the location of the abnormal focus. Thus, if the occipito-parietal segments are damaged or if there is a bilateral lesion, primary acalculia can be assumed. If the occipital segment is damaged, the visual image of the number disappears; for the patient it ceases to be a symbol reflecting a certain quantity. The individual recognizes the numbers, they are mixed into. This especially applies to numbers that are similar in style. If the temporal zones are damaged, failures in mental counting are observed, and in the prefrontal segments, purposeful activity is disrupted, the patient cannot plan counting actions and control their implementation.
Sometimes the dysfunction in question does not completely deprive the child of the ability to perform computational operations. Some young patients retain their addition skills, but subtraction becomes an impossible task for them. The described illness can often be accompanied by sensory aphasia. The degree of impairment in the work of arithmetic operations varies from absolute inability to calculate to errors in counting operations and when manipulating numbers.
The essence of therapy and correction of dyscalculia
Several specialists are involved in the treatment process to obtain the best result, including neurologists, speech therapists, etc. Therapy consists of organizing speech therapy and educational sessions.
Treatment is aimed at correcting the pathology and is carried out in compliance with the following rules:
● At first, classes are held individually, and then in groups where there are children with the same problems;
● classes are in the form of a game;
● the task of teachers is to develop the logic of calculation operations and teach them to understand them;
● classes are conducted aimed at expanding the child’s vocabulary and speech literacy;
● attention is paid to drug therapy, which is aimed at improving brain function and activating the child’s nervous system; other methods can be used to improve blood circulation in the brain .