Cerebral ischemia is a fairly serious disease in the field of perinatal neurology , which doctors are often forced to deal with. It is characterized by problems in supplying the brain with oxygen. Recently, ischemia has become increasingly common among infants, which is why attention has been paid to this problem from all corners of the world. Modern doctors distinguish only three degrees of ischemia:
- Easy. It is characterized by excessive activity or, on the contrary, depression of the newborn. This stage lasts only five days (maximum - a week), after which it sharply changes its character.
- Moderate severity, during which the baby exhibits prolonged agitation and severe convulsions.
- Severe, accompanied by seizures, delayed psychomotor development, and damage to the nervous system. At this stage, problems with the organs of touch, hearing, vision and smell are possible.
Unfortunately, to date, no unified treatment method or any effective therapy has been developed, which makes ischemia even more dangerous and worse in the eyes of mothers.
Causes of cerebral ischemia in newborns
As a rule, in adults and mature people, ischemia is acquired. It develops on the basis of thrombosis, increased blood viscosity, heart failure or vascular obstruction. In turn, in newborns, ischemia is most often caused by a lack of oxygen , which occurs during pregnancy, against the background of previous injuries. According to statistics, this is most often accompanied by:
- heart defect (most likely congenital);
- asphyxia;
- probable diseases of the mother of the newborn;
- age of the woman in labor (under twenty or over thirty-five years);
- injuries during childbirth;
- increased or decreased intracranial pressure;
- significant blood loss during childbirth;
Currently reading: Anti-dandruff shampoo
Most often, the risk of developing ischemia is increased by other factors, including the “negligent” attitude of service personnel to the work they perform.
Despite the fact that cerebral ischemia in newborns has quite diverse causes, the leading one was and remains oxygen starvation, leading to irreversible metabolic disorders of varying severity.
Cerebral ischemia in newborns
Causes of the disease
In all cases, cerebral ischemia in children is a consequence of oxygen deficiency. The main causes of hypoxia can be:
- serious health problems with the mother while carrying a child (cardiovascular, bronchopulmonary, genitourinary, infectious, endocrine diseases);
- the age of the woman giving birth is less than 18 or more than 35;
- non-compliance by a woman with a daily routine during pregnancy, smoking, alcoholism;
- pregnancy pathologies: severe toxicosis immediately before birth, oligohydramnios, multiple births, pathologies of the placenta and umbilical cord, premature (cerebral ischemia is very often diagnosed in premature babies) and late births;
- problematic childbirth: entanglement of the umbilical cord of the fetus, cesarean section, use of medications (stimulation, for example), birth trauma, prolonged, difficult, early labor, large fetus.
The main factor under the influence of which cerebral ischemia is diagnosed is a serious disruption of blood circulation between the placenta and the uterus. It entails necrosis of certain areas of the brain and hypoxia. Manifestations of the disease may be different in each individual case, so a thorough and detailed diagnosis is required.
Symptoms and diagnosis of coronary heart disease in children in Israel
Symptoms are similar to those of other cardiac pathologies. Manifestations of IHD usually manifest themselves after psycho-emotional or physical stress. Sometimes an acute attack of ischemia is preceded by palpitations, fatigue, shortness of breath and poor health.
The following symptoms are also observed:
- intense chest pain radiating to all parts of the body on the left side;
- excessive sweating;
- cold extremities and pallor;
- slow or rapid breathing;
- thready pulse;
- tachycardia;
- decrease in systolic and pulse pressure;
- enlarged liver and swelling of the arms and legs.
| Changes in cardiac activity in the asymptomatic form can only be detected using cardiac diagnostics. |
To choose the right tactics for treating coronary heart disease in children, Israeli doctors conduct a diagnostic course, which includes such procedures:
- Laboratory blood test will help determine disorders in lipid metabolism, ascertain inflammatory and necrotic signs.
- Electrocardiography (ECG) - examines electric fields, shows all the features of the heart muscle and diagnoses myocardial ischemia.
- Echocardiography - examines functional and morphological changes in the organ and valves.
- Stress test - determines the functional reserves of the heart muscle, detects the development of ischemia.
- Coronary angiography is a radiopaque, most reliable way to identify all the features of blockage of the coronary arteries. The technique is contraindicated in cases of decompensated diabetes mellitus, renal failure, mental disorders and exacerbations of chronic pathologies.
- Holter monitoring - carried out for 24 hours in normal life conditions, allows you to record hemodynamics. Excluded in case of inflammatory lesions of the skin.
- Radioisotope study (myocardial scintigraphy) - identifies ischemic foci and scars, assesses the condition of the myocardium and determines the level of occlusion. Scintigraphy with the introduction of isotopes helps to study the blood supply to the organ in great detail. It is not carried out in case of exacerbation of chronic ailments, allergies to drugs and sepsis.
- CT scanning is a non-invasive study for the presence of atherosclerotic plaques, assesses the degree of narrowing and patency of the arteries, and the condition of the valve apparatus. Contraindications: intolerance to iodine-containing contrast agents.
Medical examinations are carried out using ultra-modern equipment, which makes it possible to verify complex pathological processes as accurately as possible for the adequate development of a therapeutic program.
Symptoms of cerebral ischemia
Among the symptoms of childhood cerebral ischemia, the most striking and common are:
- increased excitability: the baby will constantly shudder, tremors of individual parts of the body will be observed, restless sleep, crying for no apparent reason;
- depression of the central nervous system: decreased muscle tone, low motor activity, weakened sucking and swallowing reflexes, facial asymmetry, strabismus;
- hydrocephalus: increased head size, increased intracranial pressure;
- coma: unconscious state, brain function to coordinate movements is absent;
- convulsions.
Thus, cerebral ischemia in a child manifests itself already in the first hours of his life. In the maternity hospital, they most often already assume that the baby has such a diagnosis, especially if pregnancy and childbirth were accompanied by pathologies and fetal hypoxia. However, all these signs can appear in newborns to varying degrees.
Prevention
To minimize the risk of developing cerebral ischemia in newborns, doctors recommend following preventive measures:
- During pregnancy, do not smoke and avoid the company of smokers.
- Do not drink drinks with alcohol.
- More is spent in the fresh air.
- Do not take medications without consulting a doctor.
- Don't wear tight clothes.
- During pregnancy, moderate physical activity is recommended to avoid weight gain for the mother in labor.
- During the examination, an ultrasound examination (scheduled) is performed.
- Take vitamins for the expectant mother.
- Try to maintain proper nutrition.
By following simple rules, you can avoid diseases such as cerebral ischemia in newborns. If you notice one of the signs of pathology in your baby’s behavior, be sure to contact your doctor with a complaint.
Types: 1, 2, 3 degrees
In medicine, there are three degrees of childhood cerebral ischemia.
- First degree
The mildest degree, which is characterized by depression or agitation of the child in the first week of life. Most often, the symptoms go away with a quick and timely response from doctors without serious consequences for the small organism.
- Second degree
If a newborn has seizures and other symptoms for more than a week, doctors diagnose a moderate degree of the disease. It, like the 1st degree, is curable with adequate therapy.
- Third degree
Babies suffering from grade 3 ischemia are placed in intensive care. Most often, this form of the disease leads to pathological, difficult-to-treat damage to the entire central nervous system. This manifests itself in ataxia, delayed psychomotor development, visual and hearing impairment, and focal seizures.
Depending on the degree of ischemia in newborns, complex treatment measures are carried out.
Preventive actions
To minimize the risk of the appearance and development of ischemic diseases in infants, the expectant mother must make every effort to ensure that the fetus receives sufficient oxygen. To do this, she needs to comply with a number of measures:
- take walks in the fresh air;
- get rid of alcohol and tobacco addiction;
- avoid stress;
- do not forget about adherence to the regime and a balanced diet;
- do not avoid moderate physical activity;
- control blood pressure;
- hemoglobin level control;
- maintaining normal body weight;
- beware of the occurrence of infectious diseases;
- undergo the necessary examinations in a timely manner;
- strictly follow the recommendations of your doctor.
Treatment of cerebral ischemia in children
In modern pediatrics, cerebral vascular ischemia in newborns is successfully treated with timely diagnosis and mild disease. The main goal of therapy is to restore blood circulation, timely resuscitation of damaged areas of the brain and save the rest. There are a few techniques:
- at first, only massage is prescribed, since medications for a small organism are stressful and the risk of multiple consequences;
- if massage does not help, medications are prescribed depending on individual indicators.
Cerebral ischemia in a newborn is a serious disease that can only be cured with timely and correct treatment. The consequences of pathology are determined by its severity.
Symptoms of the disease
Signs of pathology in infants are the following factors:
- The newborn has disturbances or lacks coordination of movements.
- The child is unconscious after birth.
- Constant whims of a child for no apparent reason.
- Sleep disturbance, the child is overexcited.
- Refusal to eat.
- Strabismus.
- Frequent and profuse regurgitation after every meal.
- Weak muscle tone.
- The skin is pale.
- Tremor of the limbs.
Signs of pathology make themselves felt immediately, from the moment the baby is born. These features are diagnosed in a baby immediately after birth. Depending on the severity of ischemia, additional symptoms may occur.
Consequences
The consequences of cerebral ischemia in children depend on the severity of the disease, the presence of concomitant pathologies, and the effectiveness of the therapy. After an intensive course of treatment, a rehabilitation period is needed, on which the prognosis will also depend. Among the most common consequences are:
- headache;
- sleep disorders;
- mental retardation;
- constant irritability;
- epilepsy;
- isolation;
- learning difficulties.
The problem of ischemia in newborns is quite relevant in modern pediatrics. In some cases, the disease becomes a cause of disability and results in the child’s inability to further social adaptation. Complex treatment of severe forms of ischemia and its consequences is a long and complex process that requires effort, patience and attention from doctors and parents.
source: www.vse-pro-detey.ru
Cerebral ischemia is a response to oxygen starvation due to narrowing of the lumen or blockage of the arteries of the brain. Increasingly, the disease manifests itself in children and accounts for about 85% of cases, and the reason for this is external and internal influences. Regardless of the nature of the onset of the disease, untimely treatment often leads to bad consequences.
Possible complications
As a rule, cerebral ischemia in a newborn of grade 1 (mild) has no residual effects. It is characterized by functional disorders of the central nervous system. This degree is not always diagnosed and such symptoms go away on their own within a week.
Hypoxia is much more difficult for premature babies, in whom even a mild degree can lead to negative consequences in the form of persistent neurological disorders: mental and physical development delays and cerebral palsy develop.
Grade 2 (moderate severity) has vivid symptoms and is characterized by more significant damage to the nervous tissue. For the most part, the changes are irreversible. Without medical help, pathological changes in the brain increase. But with timely diagnosis and adequate treatment, a favorable outcome is possible with minimal long-term consequences.
3rd degree (the most severe). Profound disorders of the central nervous system are not only irreversible, but also progressive. Hypoxia affects not only the brain, but also other organs. Multiple organ failure develops. The prognosis is unfavorable, more than half of children die. The surviving infant becomes disabled for the rest of his life.
In adults, cerebral ischemia has a progressive course, leading to the development of dementia and other psychosomatic disorders.
A lack of oxygen to the brain is called cerebral ischemia. It occurs in newborns. The pathological process is serious and provokes irreversible consequences.
Medicine can stop the disease, but it is impossible to get rid of complications. To prevent the disease, every parent should know about the causes of its occurrence.
How does ischemia manifest in young children?
Cerebral ischemia in a newborn is the result of hypoxia during pregnancy and childbirth. In perinatal neurology, this problem is difficult to solve, since there is still no sufficiently effective way to get rid of it. Ischemia can be suspected in an infant if:
- the child cries for no reason and shudders;
- the surface of the skin has a marbled tint;
- baby doesn't sleep well;
- he sucks weakly and swallows poorly;
- there is muscle weakness, the child is lethargic;
- the head is large and the fontanelle is enlarged;
- breathing is impaired, convulsions occur.
Diagnostics
Diagnostic methods will also be different.
If the fetus has signs of hypoxia, then most likely there will be signs of cerebral ischemia in the infant.
Therefore, prenatal observation of the mother is aimed at early detection of the child’s hypoxic state and taking measures to correct it:
- Ultrasound of the fetus. The biophysical profile of the fetus and signs of intrauterine growth retardation are determined.
- Dopplerography. Blood flow in the placenta and umbilical vessels is examined. Signs of increased fetal vascular resistance are revealed.
- Cardiotocography. The change in fetal heart rate in response to uterine contractions is assessed.
Newborn
If there are signs of intrauterine hypoxia and/or asphyxia during childbirth, the presence of cerebral ischemia is not questioned.
But sometimes the clinical picture is not completely clear, or a more detailed examination is required to determine the degree of cerebral depression.
Then additional research methods are used:
- Neurosonography (NSG). The method is quite simple to implement and informative. Detects the presence of structural changes in the substance of the brain, as well as edema and swelling of the brain. It is NOT a leading method as it often produces false results, both positive and negative.
- Dopplerography of cerebral circulation. Detects various cerebral circulation disorders. For example, an increase in blood flow due to dilated arteries, a decrease in its speed in some branches.
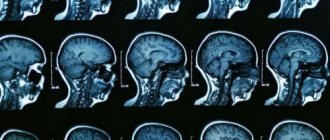
- CT, MRI. Detailed visualization of pathological changes.
- EEG. To determine the degree of neuronal damage, identify convulsive readiness of the brain, and select adequate anticonvulsant therapy.
- Analysis of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) according to indications.
- All laboratory tests: general clinical, biochemical blood parameters, coagulogram, blood electrolytes.
Degree of disease in newborns
There are three degrees of ischemia in children:
- Mild degree ( grade 1 ) - when the child is overly excited or depressed during the first 4-7 days of his life. Treatment is carried out in the maternity ward, after which the child is observed by a neurologist at home.
- With a moderate degree ( grade 2 ), the child experiences seizures and a number of neurological disorders occur. The child is being treated in hospital.
- Severe degree ( grade 3 ) of ischemia involves serious disorders in which the baby is admitted to the intensive care unit. After discharge, the baby will have a long rehabilitation period.
The first two degrees of brain disease are in rare cases considered to be a consequence of the development of neurological pathologies. And, if adequate therapy is carried out on time, the functional symptoms of the disease disappear completely. Severe ischemic dysfunction of the brain contributes to the development of abnormalities in the nervous system.
This leads to dysfunction of the central nervous system, as a result of which the child develops poorly, has seizures, and hears and sees worse.
If you are looking for a rehabilitation center for recovery, we recommend the rehabilitation center, where rehabilitation after neurological diseases is carried out using the most modern equipment.
What are the complications after cerebral ischemia
If treatment was carried out in a timely manner, there is a high probability that the baby will not have a single complication. However, as statistics show, only 20% of newborns are completely cured.
But don’t worry if it’s really stage I – complications are minimal:
- the baby may get tired faster;
- the child's memory deteriorates somewhat;
- there is a possibility of seizures.
Much more often, children who suffered from ischemia at an early age experience other consequences (the same 80% who could not recover completely):
- mentally abnormal;
- headache;
- mental retardation (mild to severe);
- sleep problems;
- epileptic seizures;
- difficulty concentrating.
Sometimes complications can reach the development of cerebral palsy, and of completely different degrees (the child may even become paralyzed). But since as the baby grows up (I’m not talking about adolescence, but about the period from a year onwards), nerve cells continue to divide, there is a high probability of a complete recovery.
Here you can watch a video about the treatment of encephalopathy (ischemia):
Therefore, dear parents, watch your little one as carefully as possible, because you are the support of your newborn baby. Give your child as much time as possible, protect him from frustration and give him a smile and hugs more often, because no matter what doctors say, mother’s love is the best medicine. This does not mean that you don’t have to listen to doctors!
I will say goodbye to you, but not for long, right? Subscribe to my blog updates and we will learn a lot more useful information! See you soon! Bye bye!
Currently reading:
Causes of ischemia in infants
Cerebral ischemia in infancy occurs as a result of a lack of oxygen that occurs during pregnancy or at birth. Provoking factors include:
- polyhydramnios diagnosed during pregnancy;
- mother's age under 20 years and after 35 years;
- premature or too late delivery;
- malnutrition of the placenta, too early abruption or presentation;
- multiple pregnancy;
- preeclampsia;
- pathological conditions of the cardiac and vascular systems;
- turbidity of amniotic fluid;
- illnesses of the mother while carrying a child.
Poor blood circulation between the uterus and placenta is the main factor in newborn hypoxia.
Moreover, it is the brain that is considered most dependent on the lack of oxygen. And in especially severe manifestations, death of individual cells or entire areas of the brain can occur.
Sometimes newborns are diagnosed with an arachnoid cyst of the brain. After reading the article, you will find out whether it is dangerous and how to treat it. Myoclonus is quite common in children. Most often they are harmless, but information about when to see a doctor is written in the section on neuralgia.
What is cerebral ischemia
It is believed that ischemia itself is a failure of blood supply in the body, in which tissues and the brain can “suffer” from a lack of oxygen.
This phenomenon often occurs in adults, but it manifests itself due to the fact that the arteries and blood vessels narrow (or become “clogged” with blood clots). Such a disease can “stick” to the fetus even during its development in the womb - usually due to insufficient blood flow from the mother to the unborn baby through the placenta.
Most often, it is the brain that is “infected,” because it “needs” oxygen the most. If the brain does not have enough oxygen (oxygen), the process of death of nerve cells may begin. It is important to try to eliminate such a pathology at the initial stage, because the lack of measures can lead to damage to the central nervous system (CNS), and at an advanced stage, to the death of the newborn.
What is noteworthy is that, unlike in an adult body, a disease noticed in a baby in the initial stages can be cured without consequences.
Main signs of the disease
Any abnormalities in a child may indicate neonatal ischemia. Signs of brain dysfunction in children are varied, and obvious developmental delays will certainly attract the attention of parents. In addition, a sudden change in behavior, loss of appetite, constant whims, frequent regurgitation and a reaction to changing weather should be a cause for concern. Symptoms of cerebral ischemia in a child include:
- an increase in the volume of the child’s head, as well as a large fontanel due to an increase in fluid in the brain, high intracranial pressure; the child is unconscious and lacks brain coordination functions;
- depression of the central nervous system, in which there is a deterioration in motor activity and muscle weakness, weakened sucking and swallowing reflexes, in rare cases, strabismus with asymmetrical facial proportions may develop;
- or vice versa, excessive excitability of the baby, characterized by low or high muscle tone, tremors of some parts of the body (chin, arms or legs), shuddering, increased reflexes, poor sleep, crying for no reason;
- twitching of the limbs and head, shuddering.
Symptoms of cerebral ischemia
Attentive parents may notice strange behavior in their newborn. Any suspicion should alert the mother (and we are not just talking about cerebral ischemia). If you see that your baby looks a little strange or his actions make you think, call your doctor.
Signs of brain damage (or encephalopathy, in medical terminology) can also manifest themselves in a newborn in different ways:
- the child has noticed an enlargement of the fontanelle and head (that is, hydrocephalus is present);
- the newborn has signs of tremor of the chin and other parts of the body (arms, legs, lips);
- the baby is too excitable, often cries and screams without reason, sleeps restlessly;
- the child’s face is somewhat asymmetrical;
- the baby behaves “inhibited”, has difficulty latching on to the mother’s breast, cannot feed normally, and has difficulty swallowing;
- strabismus is noticed behind the baby;
- the baby shudders for no good reason, the arms and legs are seized with convulsions (they can cause fainting - most often this is characteristic of stage II ischemia).
Sometimes the symptoms of cerebral ischemia occur as if they belong to a completely different disease.
Before treating your baby, you need to make a correct diagnosis.
Diagnosis of brain dysfunction in newborns
The main goal of diagnosis is to identify why the disease occurred. The main steps to establish a diagnosis include:
- physical examination: assessment of respiratory and cardiac functions, mandatory analysis of the child’s nervous status;
- duplex ultrasound examination of the arteries to analyze blood circulation in the vessels;
- angiography to detect disorders in the functioning of the brain: thrombosis, narrowing of the arteries, aneurysms;
- MR angiography and CT angiography;
- Additionally, ECG, ECHO-CG, X-ray, and blood tests are performed.
Types of diagnostics
Diagnosis of coronary heart disease is possible only with long-term fragmented Holter monitoring, as well as echocardiographic examination. If the disease is detected in a timely manner, the patient’s cardiac ischemia is treated according to standard regimens using laboratory and instrumental research methods.
Holter cardiac examination
After the cardiologist collects anamnesis, determines the patient’s complaints at the time of treatment, and conducts an external examination, the doctor prescribes the following diagnostic measures:
- clinical and biochemical blood test;
- ultrasound examination of the heart;
- vascular angiography.
Only with data from an in-depth examination of the patient can a cardiologist develop adequate therapeutic tactics.
Treatment of ischemia in newborns
Despite significant advances in the treatment of ischemia in newborns, there are still no effective means of eliminating the disease.
The main goal of treatment is to restore blood circulation to the blood vessels to ensure normal functioning of the damaged areas of the brain. In the mild stage of the disease, the treatment method is very simple and accessible to everyone - it is a regular massage without the use of any medications. In the case of more complex stages of the disease, therapy is selected according to individual characteristics and always according to the indications of a medical specialist. Usually, medications are prescribed to stimulate brain function, normalize the circulatory system, and medications to restore and strengthen the child’s body’s defenses. Folk remedies are widely used in the treatment of cerebral ischemia, and they must be combined with basic medications. Traditional methods can relieve the symptoms of the disease well, but only medications and surgery can eliminate the cause. Traditional methods of treatment are not used for newborn babies.
The main symptoms of convulsive syndrome in children are well described in this article. You will learn how to help your child during an attack and how to avoid it in the future. You can find out Dr. Komarovsky’s opinion on intracranial pressure in infants here. Is hand tremors dangerous in newborns, what causes them and how to prevent them
Treatment
Stroke in a teenager is treated comprehensively. Already at the prehospital stage, the patient is provided with assistance. It includes calling a medical team, resuscitation measures (if breathing and heartbeat stop) and pressure correction. Stroke therapy includes:
- Surgical intervention. It is required for the formation of hematomas, accumulation of blood in the ventricles, thrombosis and atherosclerosis. To improve blood flow, hematoma removal, drainage, stenting, decompression, thrombectomy (blood clot removal), endarterectomy, and angioplasty may be necessary. For hemorrhagic stroke, embolization, removal of malformations, and clipping are often performed.
- Use of medications. For ischemic stroke, antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants (Dipyridamole-FPO, Warfarin, Heparin), plasminogen activators, fibrinolytics (indicated for fresh blood clots), neuroprotectors (Vinpocetine, Pentoxifylline, Glycine, Piracetam, Cerebrolysin) are used. In case of cerebral edema, diuretics may be used. For seizures, low dosage Phenobarbital is prescribed. For stroke due to atherosclerosis, statins are used.
- Correction of respiratory failure.
For hemorrhagic stroke, many of the above medications are contraindicated. Treatment is aimed at stopping bleeding and resolving the hematoma. Hemostatic agents (Vikasol) and drugs that normalize blood pressure are prescribed. In severe cases, mechanical ventilation and tracheal intubation are performed. Colloidal solutions can be infused intravenously.
Possible consequences of the disease for newborns
The prognosis and consequences of ischemia depend entirely on the stage and severity of ischemia. In addition, existing pathologies and the correctness of treatment methods and rehabilitation methods are of great importance. Severe consequences cannot be ruled out, so treatment should be started as quickly as possible. Cerebral ischemia in newborns can cause:
- headaches;
- restless sleep and irritability;
- difficulties in communication and learning;
- mental retardation;
- in difficult cases - epilepsy.
Ischemia can even lead to death. You can avoid death if you seek medical help right away. Only a doctor will make an accurate diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment. The most important thing is that it is necessary to engage in prevention, preserving the health of the child for many years.
Classification of the disease
There is no clear division of forms of coronary heart disease in modern cardiology, which is due to the variety of manifestations of the pathology and, often, the simultaneous development of several of its forms in the patient.
Experts identify the following types of coronary heart disease:
- Sudden cardiac (coronary) death.
- Painless ischemia of the heart muscle.
- Angina pectoris.
- Myocardial infarction.
- Post-infarction cardiosclerosis.
Sudden cardiac (coronary) death is the most threatening form of the disease, characterized by causeless cardiac arrest, which occurs against a background of complete stability.
In this case, it is not possible to establish the obvious causes of the patient’s death; experts identify only the factors that provoked it.
These include:
- congestive heart failure;
- ischemic heart damage occurring against the background of ventricular arrhythmia;
- acute myocardial infarction;
- hypertensive crisis;
- disorders of lipid or carbohydrate metabolism;
- addictions, especially nicotine addiction;
- psycho-emotional and physical overload.
The danger of this pathological condition lies in the fact that predominantly cardiac arrest in an adult occurs as a result of sudden ventricular fibrillation in the patient in everyday life. Providing qualified medical care outside a medical institution is extremely difficult, so in most cases this form of heart pathology leads to death.
The development of silent ischemia of the heart muscle is predominantly asymptomatic, so the percentage of sudden deaths as a result of this pathology is also quite high. Without any clinical manifestations, the disease ultimately leads to the patient developing cardiac arrhythmias and chronic heart failure.
Angina pectoris
Angina pectoris (angina pectoris) is a disease characterized by the occurrence of attacks of pain behind the sternum, which radiate to the arm, shoulder and under the shoulder blade on the left. During an attack of angina, the patient feels an acute lack of air and disruptions in heart contractions, as a result of which he takes a forced position of the body.
A painful attack of angina may occur in the following situations:
- psycho-emotional stress;
- increased physical activity;
- moving quickly against a strong wind;
- binge eating.
Pain in the heart can either go away on its own or be relieved only after taking nitroglycerin or its derivatives. Over time, the disease progresses, attacks of chest pain occur for no reason when the patient is in a state of complete rest. If such situations arise, you must urgently contact a cardiologist for treatment.
Myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction is necrosis of a section of the heart muscle, which occurs as a result of acute heart failure caused by blockage of the lumen of the coronary artery by cholesterol plaque.
In this case, there are 2 forms of myocardial infarction:
- large-focal – arterial embolism, leading to necrosis of a significant area of the heart muscle;
- small-focal - partial blockage of the lumen of the artery.
A prolonged angina attack, psycho-emotional shock, and significant physical exertion can provoke a necrotizing process in the myocardium.
Mechanism of development of myocardial infarction
Post-infarction cardiosclerosis
Post-infarction cardiosclerosis develops as a complication of necrosis of the heart muscle and manifests itself in the replacement of damaged muscle fibers with scar tissue several months after the infarction. This pathological condition manifests itself in a weakening of the contractility of the heart and, as a consequence, disruption of blood circulation in the vascular bed.
When examining a patient, the doctor reveals not only signs of circulatory disorders, but also a significant increase in the size of the heart chambers and various heart rhythm disturbances. The patient complains of shortness of breath, increased heart rate, and swelling.
Post-infarction cardiosclerosis is chronic; drug therapy only helps to temporarily relieve the manifestations of heart failure.
Disease prevention
You should think about your health from early childhood. After all, the disease can be fatal. To avoid the development of ischemia, the following actions should be taken:
- do exercises regularly;
- walk a lot in the fresh air;
- eat right, try to stick to your diet;
- stop smoking and other unhealthy habits;
- avoid stress, have a positive attitude towards life.
These rules are very simple, and following them will protect anyone from dangerous diseases. In addition, a pregnant woman should regularly visit a gynecologist, treat all diseases in a timely manner, undergo routine ultrasounds, eat right, walk a lot in the fresh air and not be nervous. By following simple rules, you can give birth to a healthy baby. The video discusses one of the main causes of ischemia in newborns - fetal hypoxia during pregnancy:
source: gidmed.com
Cerebral ischemia in a newborn is a pathology that causes serious deviations in the health and development of the child. Even modern medicine does not have enough experience and knowledge to cope with this disease without any consequences. The treatment methods used can only reduce the progression of the disease and its consequences.
Cerebral ischemia in a newborn
Not everyone knows what it is: cerebral ischemia, and how this disease affects the condition of the newborn.
Pathology, as a rule, occurs during the prenatal development of a child, when the brain experiences oxygen starvation for various reasons. Blockage of cerebral arteries or narrowing of the lumen between them can occur under the influence of internal or external causes.
Cerebral ischemia is a response to oxygen starvation due to narrowing of the lumen or blockage of the arteries of the brain
If the blood circulation in the brain is impaired, the infant leads to damage to the central nervous system. This pathology is quite rare in children. If damage to the central nervous system occurs, the pathology is called “cerebral,” but in this situation the cause is heart pathology (ischemic stroke). When the circulatory system of the head suffers exclusively, the pathological process is called “ischemic encephalopathy.”
Attention! According to statistics, cerebral ischemia is observed mainly in premature infants.
Causes
In order to prevent ischemic changes in the brain or select the correct treatment system, it is necessary to identify the reasons why the disease occurred. Possible causes of illness developing in an infant include:
Cerebral ischemia in a newborn is the result of hypoxia during pregnancy and childbirth
- asphyxia or hypoxia that occurred during birth (poor labor, placental insufficiency or umbilical cord compression);
- disturbance of the respiratory process after childbirth (congenital heart disease or respiratory failure);
- low blood pressure after birth (severe bleeding or sepsis).
In each case, a different outcome of the pathological process is possible, but coronary disease is most often observed in newborns.
Provoking factors
The causes of stroke in children appear under the influence of various factors. Negative effects on the baby’s health can be caused by both internal and external factors.
- Mother's diseases:
- neurological diseases (for example, epilepsy);
- treated infertility;
- pathologies of the endocrine system (especially the thyroid gland).
- Course of pregnancy:
- eclampsia or preeclampsia;
- placental pathologies.
Severe ischemic brain dysfunction contributes to the development of nervous system abnormalities
- Deviations during childbirth:
- bleeding in the mother or fetus;
- premature birth;
- low weight of the newborn;
- high temperature in the child or mother;
- unplanned caesarean section.
Important! In most cases, brain damage is caused by a combination of two or more precipitating factors.
Thus, according to the observations of specialists, in 70% of sick newborns the cause was pathology during pregnancy, in 25% of children ischemia occurred at the time of birth, and in only 5% of babies the disease appeared after their birth.
Ischemia in newborns symptoms
Suspicion of cerebral ischemia can be caused by any abnormalities in infants. It is impossible to make a diagnosis based on the symptoms that appear. However, if your child exhibits suspicious signs, you should immediately contact a specialist. In addition, the pediatrician should also pay attention to violations. The simplest symptoms that should raise suspicion of problems in the health of a small child are: frequent whims, poor appetite, sudden changes in behavior, excessive regurgitation and others. Any abnormalities in a child may indicate ischemia in a newborn. Signs of cerebral ischemia:
- head sizes are larger than standard parameters;
- enlargement of the fontanel due to the influx of fluid into this area;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- disturbance of brain activity, which affects the patient’s consciousness.
Nervous system symptoms:
- CNS depression;
- muscle weakness;
- weakening of swallowing and sucking reflexes;
- possible strabismus and asymmetry of facial features.
Opposite signs of the central nervous system:
- excessive excitability;
- high muscle tone;
- tremor of the chin or limbs;
- sudden shuddering;
- sleep disturbance.
Depending on how severe the symptoms are, the baby may experience varying degrees of coronary artery disease.
Poor circulation between the uterus and placenta is the main factor in newborn hypoxia. Diagnosis
Symptoms are a reason to consult a doctor and undergo further diagnostic testing. Diagnostics is carried out using a whole range of studies:
- examination by a doctor to assess signs of the condition of the respiratory, cardiac and nervous systems;
- NSG - ultrasound examination of the brain to analyze the circulatory system;
- MRI and CT to identify pathological processes and the presence of excess fluid.
Additionally, ECHO-CG, ECG and X-ray are also prescribed. A blood test is required.
Important! Diagnostics allows us to identify the cause of the existing pathological process.
Ischemia degree 1 in newborns
Treatment of the disease and prognosis depend on the degree of pathology. A newborn may experience cerebral ischemia in one of the following degrees:
- the first one is easy;
- second – average;
- the third is heavy.
Each form of the disease involves specific symptoms.
Despite significant advances in the treatment of ischemia in newborns, there are still no effective means of eliminating the disease.
First
A mild degree of ischemic injury in a newborn has signs that can be noticed already in the first week after birth. With grade 1, the baby is overexcited or, conversely, depressed. The baby's sleep is too long (short), he can constantly be capricious, refuse the breast and roll up.
Second
The average severity of the pathological process has more intensely expressed symptoms. With degree 2 ischemia, the main symptom is convulsions for a long period. The baby also constantly has muscle tone and has symptoms of central nervous system damage.
Possible reasons for transient changes
It is worth noting that to find out the exact cause, you will have to run around to consultations with various specialists and a full examination. However, the appearance of transient ischemic attacks at a young age, especially against the background of (otherwise) full health, is an alarming symptom and you cannot put off going to the doctor.
Neurologist - first doctor
The first doctor a patient and his parents should knock on is a neurologist. He will examine the patient and ask about the smallest details of the unpleasant situation. The doctor will definitely ask about your exercise tolerance and clarify your family history - you will have to remember what serious diseases your relatives suffered from and why deceased family members died.
To exclude aneurysmal protrusion of the vascular wall, you will need to undergo an imaging study - always in the vascular mode, with contrast! Whether it will be a CT or MRI depends on the specific equipment of the clinic. However, it is worth considering that performing the study without vascular enhancement may be of little use. Meanwhile, aneurysm is the most common cause of TIA in young people. It is worth noting that some types of aneurysms are prone to rupture and then only a miracle can save the child. Some doctors call the vascular abnormality a “ticking bomb.”
An EEG (electroencephalogram) may be required to rule out epilepsy. Some forms of epilepsy are very similar to TIA - after all, not all epileptics classically fall to the floor in convulsions, foaming at the mouth; there are many forms of this disease.
Pediatrician is next in line
The pediatrician will conduct a detailed analysis of the clinical situation, draw up an examination plan, and, in accordance with the results, a treatment algorithm.
To exclude congenital blood diseases, a detailed coagulogram may be needed. TIA can be caused by local thrombosis, which resolves on its own due to the activation of the activity of the anticoagulant system. If before this time the child did not have a tendency to form blood clots, then it is necessary to exclude other factors contributing to this pathological process - perhaps the girl began taking oral contraceptives to correct ovarian function or prevent pregnancy and additionally goes to the solarium intensively. If there are recessive mutations in the genes responsible for blood clotting, these additional factors will trigger symptoms that would not appear in a completely healthy person. It is also necessary to carefully question the teenager about the use of dietary supplements, low-quality alcohol, psychoactive substances and drugs.
Another, no less important reason may be the development of a tumor formation. On the one hand, its cells release procoagulant substances, that is, they promote thrombosis. On the other hand, even a small formation can compress nearby centers and cause corresponding symptoms. The typical debilitating headache may not yet exist. The diagnosis is excluded or confirmed according to CT or MRI data.
An important test will be a blood test for homocysteine. Hyperhomocysteinemia can cause an increase in blood pressure, as well as thrombosis - there are known clinical cases of TIA due to an increase in this amino acid.
Familial forms of hypercholesterolemia can cause early forms of atherosclerosis. If unfavorable lipid profile indicators are detected in the blood (extreme increase in total cholesterol and its harmful fraction), the teenager needs to verify the diagnosis using a test for lipoprotein “a”.
If associated risk factors are identified, the pediatrician may recommend a fundus examination by an ophthalmologist.
The cardiologist will rule out remaining causes
A cardiac doctor will examine the child and listen to heart sounds and murmurs above the blood vessels. He may need a cardiogram of the child, an ultrasound examination of the heart and blood vessels of the neck (ECHO-CG and ultrasound DG MAG, respectively). At the appointment, possible defects of the interchamber septa, arrhythmias, and congenital anomalies of the neck vessels (S- and C-shaped vascular bends), which can contribute to abnormal blood flow with the formation of blood clots in the presence of unfavorable causes, will be excluded.
Identifying the cause of unpleasant conditions may require a certain amount of time from the child and parents, however, in the event of transient ischemic attacks, it is better to be examined as much as possible so as not to miss the opportunity to be completely cured on time and prevent the development of a fatal scenario.
List of consequences caused by the disease
The consequences of cerebral ischemia in newborns can be completely different, based on the severity of the disease.
A mild degree of ischemic disease occurs without causing negative consequences; the development of babies occurs similarly to healthy children. Even if treatment of the disease was started in a timely manner, patients may subsequently experience disturbances in sleep and attention, headaches, epileptic seizures may appear, and mental development may occur with some deviations.
The consequences after the 3rd degree of the disease are directly dependent on in which part of the brain the damaged areas are localized and the area of dead tissue. These may be problems with the functioning of the musculoskeletal system, sometimes the patient remains completely paralyzed. In the future, his condition may improve, since nerve cells have a wonderful feature - they are able to recover.
Possible complications in ischemic disease can be predicted based on how severe the oxygen deprivation was, what area of the brain was affected, and how timely professional medical care was provided.
First degree
The first degree of the disease, as a rule, ends favorably for babies. Their development follows the same pattern as that of their peers. Only in rare cases is the appearance of excessive activity and malnutrition observed.
Second degree of disease
May lead to the following complications:
- From 10 to 20% of patients subsequently experience a slight increase in blood pressure and frequent regurgitation;
- From 30 to 50% of patients have some disturbances in their mental development.
Third degree
Complications arising after the third degree of ischemia:
- Up to 50% of cases of the disease end in death within the first days or a little later, when the cause of death is a severe form of pneumonia or another infectious disease;
- Up to 80% of children suffer complications that are irreversible. The child may develop dementia or become autistic;
- In 10% of children, mental development occurs with minor deviations from the norm;
- In 10% of cases, the disease occurs without any negative consequences for the child.
All types of cerebral ischemia in infants should be treated in a hospital setting under the constant supervision of doctors. Based on the results of the examination, the doctor chooses one of the most suitable methods of treating the disease.
02/17/2015 Newborns Ischemia occurs due to the fact that in one or another organ there are disturbances in the blood supply, and, accordingly, in oxygen supply, because in this case there may not be enough of it. Subsequently, two directions of the disease can be distinguished: ischemia and hypoxia. With hypoxia, the cells of a certain organ or the body cannot receive oxygen at all or, for some reason, use it. With ischemia, there is not enough oxygen due to blockages in the vessels.
There are no cases when ischemia occurs just like that. There must be good reasons for the occurrence of this disease, and they can be:
- the formation of a blood clot that completely or partially closes the vessel. If the vessel is completely closed and cannot transport blood to the organ, then the organ dies.
- if there is a fracture of the tubular bones and a small amount of fat gets into the blood. Thus, the blood begins to transport gas bubbles to the brain. As a rule, such symptoms can occur during decompression sickness and then we can talk about the presence of cerebral ischemia. Air bubbles can also enter the bloodstream when an empty syringe is administered intravenously or due to injury or lung damage.
- The results of the life of parasites have entered the blood, which can also clog blood vessels.
- If a person suffers from atherosclerosis, then atherosclerotic plaques may begin to form in the vessels, which will cover some part of the vessel and significantly reduce the lumen.
- blood vessels are compressed. This situation may arise due to the presence of a tumor or for another similar reason.
Basic principles of pathology treatment
Unfortunately, there are no treatment methods that can restore brain tissue cells damaged by oxygen starvation. However, there are techniques that allow you to normalize the supply of oxygen in the blood in the required quantity and help the body resume functionality after a lack of it.
Resuscitation methods for acute hypoxia
If within 1-2 minutes after birth the child does not begin to breathe on his own, the following resuscitation methods are used:
- Carrying out intubation and starting mechanical ventilation (artificial pulmonary ventilation) - with minor hypoxia, the baby can be transferred to the mother within 2-4 minutes after intubation. If necessary, the newborn is placed in the intensive care unit.
- Anticonvulsant therapy – stops convulsive manifestations and eliminates further damage to brain tissue.
- Maintaining the activity of the cardiovascular system.
- Hypothermia technique - in recent years, research has been conducted, according to which lowering the baby’s body temperature by 3-4 degrees can prevent the development of necrosis of brain cells during hypoxia. The technique has been used in clinics in our country since 2010 and gives good results.
It is impossible to restore dead brain cells, but it is possible to stop the development of hypoxia and ensure the maintenance of the most important functions of the body until the child recovers.
Clinical manifestations and diagnostic principles
Experts distinguish three stages of the disease in children: mild, moderate and severe. Each of them has its own symptoms.
Mild or first degree ischemia
The disease is characterized by mild damage to brain tissue and develops as a result of mild hypoxia or asphyxia experienced during childbirth.
The main symptoms of grade 1 cerebral ischemia in newborns are as follows:
- the presence of disturbances in the tone of the muscular system;
- increased motor activity, appearing with trembling of the chin and limbs;
- enhanced reflexes;
- restlessness - shallow sleep, unreasonable crying, sudden movements.
In prematurely born children, grade 1 ischemia is manifested by a syndrome of depression of the central nervous system, the signs of which are lethargy, low muscle tone, weakening of unconditioned reflexes (grasping, swallowing and sucking).
With a mild degree of pathology, clinical manifestations disappear within 5-7 days. In the vast majority of cases, they do not need to be treated.
Changes in laboratory and clinical research
A blood test can detect a decrease in oxygen levels (hypoxemia) and an increase in carbon dioxide (hypercarbia), and acidosis is also observed - a shift in the reaction to the acidic side. All instrumental studies were without pathological abnormalities.
Second degree of ischemia
The main causative factors are fetal hypoxia in the prenatal period, moderate asphyxia during childbirth, the presence of RDS or congenital pathologies such as heart disease, pneumonia.
Ischemia of the 2nd degree is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Syndrome of depression or excitation of the central nervous system - in some cases, their alternation is observed.
- Convulsions are single, short-term clonic in full-term infants, and frequent tonic or atypical in premature infants. Such convulsive manifestations include apnea, rowing movements with the arms and pedaling with the legs, and causeless shuddering.
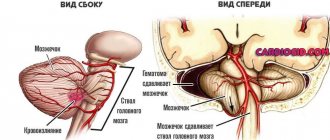
- Increased intracranial pressure - it can lead to the development of hydrocephalus, characterized by an increase in the size of the head and opening of the sutures of the skull.
- The presence of vegetative-visceral disorders - marbled skin, dermographism, gastrointestinal dysfunction, consisting of frequent constipation, diarrhea, flatulence, increased regurgitation.
- Loss of consciousness or lightheadedness caused by changes in blood pressure.