For many people, the word “stroke” or “cerebral infarction” is associated with vivid symptoms and severe, often irreversible, consequences. However, there are also disturbances in the flow of blood in the brain that do not result in paralysis or speech impairment, symptoms characteristic of a stroke. Such circulatory disorders include lacunar infarction. But it should be noted that even an asymptomatic stroke can be insidious and lead to serious consequences.

Lacunar cerebral infarction: what is it?
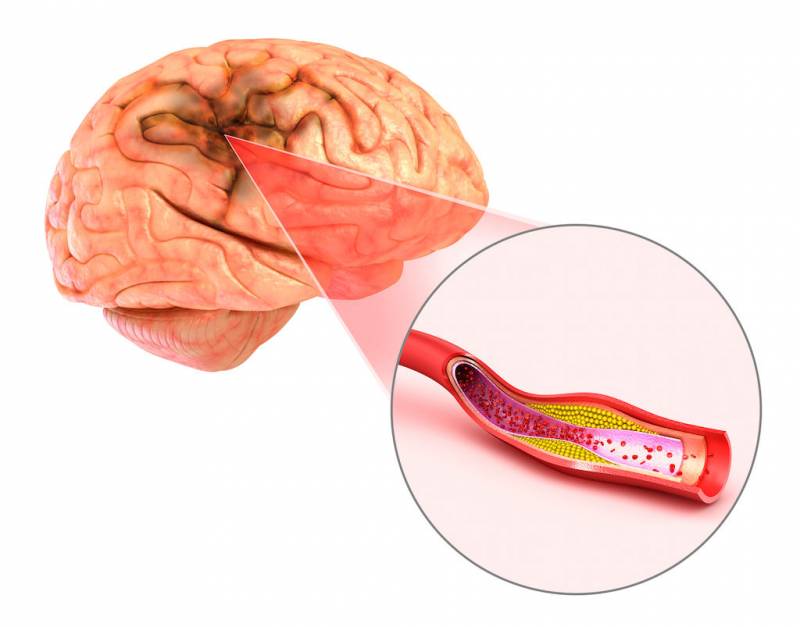
This is one of the types of stroke, that is, an acute circulatory disorder in the brain, which is characterized by the presence of small foci of death of brain tissue (necrosis), located deep in the tissues of the cerebral hemispheres or the brain stem. This size of necrosis is determined by the small diameter of the vessels, blocked by a thrombus or embolus (in an ischemic stroke) or damaged by a rupture of a thinned wall (in a hemorrhagic stroke). Most often, it is lacunar ischemic infarction that occurs, rather than hemorrhagic.
Since the diameter of the damaged vessels is insignificant, changes in the brain are often discovered by chance, during examination for other diseases. If the area of necrosis has a small diameter, then even modern magnetic resonance imaging is unable to visualize it. Necrosis larger than 20 mm is extremely rare and is called giant necrosis.
Classification
This cerebrovascular accident is divided depending on the vessels in which blood supply to the brain the catastrophe occurred. There are two vascular beds: carotid and vertebrobasilar. Thus, there are two types of cerebral infarction:
- lacunar infarction in the area of basal structures - occurs when blood flow in the vertebrobasilar region is disrupted;
- infarction in the cerebral hemispheres - appears when the carotid circulation is impaired.
How to recognize pathology
The symptoms of lacunar cerebral infarction are mild or the attack is asymptomatic. Manifestations of lacunar syndrome are divided into general and local.
General manifestations
These symptoms occur regardless of the location where the lacunar lesion is localized:
- unilateral hemiparesis (patients complain of impaired facial expressions, decreased strength in the arm or leg);
- the appearance of areas with reduced skin sensitivity (usually on the face, leg or arm, less often sensitivity on the torso);
- loss of coordination (one side of the body is less responsive: the gait becomes unsteady, the hand on the affected side makes it difficult to lift familiar objects or perform precise actions);
- difficulty speaking (decreased mobility of facial muscles and partial numbness of the tongue makes articulation difficult; the patient speaks as if he has “porridge in his mouth”).
A distinctive feature of the attack is that the intellect, consciousness or vision is never affected. If lacunar infarction recurs repeatedly and no treatment is given, then persistent dementia gradually develops.
Local signs
Signs of lacunar ischemic stroke depend on the location of the ischemic focus:
- Lacunar stroke in the thalamus . Minor damage to the thalamus or brain stem is accompanied by decreased sensitivity. If the motor nerve bundle is affected, then additional signs of hemiparesis appear. There may be no other symptoms.
- Lacunar stroke in the territory of the right MCA . Weakness and isolated hemianesthesia appear on the left side. If the middle artery of the brain is damaged, dysarthria on the left may occur. The patient will complain that the arm or leg “does not obey”, that it is difficult to walk and perform precise movements.
- Lacunar stroke in the LSMA basin . Symptoms are similar to those of PSMA, but signs of motor and sensory impairment will appear on the right side.
- Lacunar ischemia in the basal ganglia . The gray matter located among the white structures of the brain is called the basal nucleus and is responsible for sleep, heat exchange, congenital and acquired reflexes. An infarction in the area of the basal structures causes insomnia, impaired thermoregulation (chilliness or increased sweating), pathological reflexes may occur (grasping, involuntary obsessive movements, etc.).
- Single lacunar lesion of the right frontal lobe . Most often, the formation of a lacuna is asymptomatic. Sometimes, when this area is damaged, the patient experiences decreased self-criticism, increased talkativeness, and difficulty motivating himself when performing certain actions.
Main reasons
The reasons for the development of strokes, including lacunar strokes, are very individual. A pathology that causes lacunar cerebral infarction in one person may never cause such problems in another. However, you need to know that the risk factors for stroke listed below require consultation with a doctor in order to correct them and prevent the development of severe consequences. The main causes of lacunar infarction include:

What is it, features of the condition
Lacunar cerebral infarct (LACI) is a disorder characterized by motor and sensory disturbances.
Occurs due to thrombosis or embolism of small cerebral arteries. Thrombosis occurs due to vascular atherosclerosis. An embolism is usually caused by the formation of a blood clot elsewhere in the vascular system (often in atrial fibrillation) and its penetration into the cerebral vessels. Lacunar cerebral infarction most often affects the mobility of various parts of the body, but early treatment (up to 3-6 hours after the onset of the attack) significantly increases the chances of completely curing the neurological consequences.
Features of lacunar cerebral infarction (stroke):
- possibility of unnoticeable manifestation - can only be detected on MRI;
- after the attack is completed, a cavity (lacuna) is formed;
- neurological manifestations are mild or transient (transient hemiparesis, hemihypesthesia, dysarthria, ataxia).
Lacunar ischemic stroke of the brain was described in 1965 as a manifestation of hypertensive encephalopathy.
With the development of this type of pathology, the cerebral cortex does not suffer in patients. Gaps are localized:
- in the white matter, the main ganglia, the internal capsule and the optic thalamus;
- in the cerebellum and pons.
Unlike other types of stroke, with the development of the lacunar form, disturbances are observed not in the basilar artery, but in the capillaries, the size of which is only a few tens of microns. They are located inside the brain, and their function is to ensure blood flow in this organ.
The following is typical for damage to perforating arteries:
- if damaged, it is almost impossible to replace them with auxiliary vessels;
- pathological foci are local, the size of the damage is maximum 2 cm;
- microaneurysms may form, which will cause hemorrhage;
- There are no cholesterol plaques in these vessels.
General clinical manifestations
As noted above, lacunar infarction is often asymptomatic, without causing any inconvenience to the victim. But in the presence of larger foci of necrosis, erased symptoms may develop, which tend to gradually increase as the size of the damaged brain tissue increases.
All types of lacunar stroke are characterized by the following features:
Clinical manifestations depending on location
In addition to the size of the damage, symptoms also depend on in which blood supply to the brain the circulatory disturbance occurred: carotid or vertebrobasilar.
So, if there is a blockage of a vessel in the carotid basin, a slow increase in focal symptoms over several hours or even days will be characteristic: mild weakness in the muscles of the limbs, face, which is replaced by stronger ones (paresis), impaired sensitivity of the skin. Such changes usually occur in isolation, that is, only on one arm or leg, or only on the face. They are also prone to rapid recovery; after about six months, sensitivity and motor functions completely return to normal.
If changes occur in the vertebrobasilar region, the patient experiences dizziness, headache, nausea, and rarely vomiting. The development of paresis and sensory impairment is not typical.
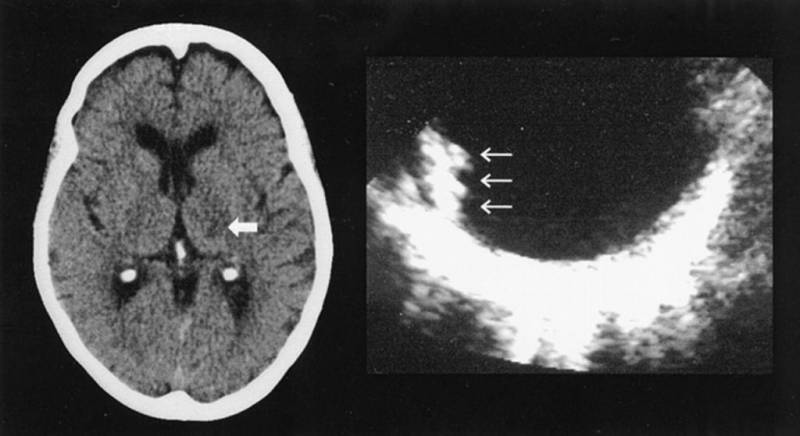
Diagnostics
It is quite difficult to determine the focus of a lacunar infarction in the brain, given its small size and the frequent absence or insignificance of symptoms, which force the patient to see a doctor. Therefore, such a lesion is visualized only when its size is more than 15 mm. This often occurs spontaneously during examination for other diseases.
The main methods of brain imaging for any stroke, including lacunar:

Consequences of the disease
Since lacunar stroke is characterized by its, in most cases, asymptomatic course, its diagnosis, and therefore timely treatment, is often difficult, which leads to the development of complications. Among the main consequences of lacunar cerebral infarction, there are both those that occur in the short term after the heart attack (the first six months) and more distant consequences.
In the first six months, progression of vascular disorders may occur with the development of more severe strokes and repeated lacunar strokes.
Among the more long-term consequences that develop several years after an episode of lacunar stroke, the most common are vascular dementia, that is, dementia, and mental health problems. This is manifested by sudden mood swings, changes in behavior, up to the complete impossibility of self-care.
The main outcome of lacunar infarction, which does not pose a danger, is the formation of a brain cyst. This is a round cavity filled with liquid. It is its visualization on MRI that confirms a lacunar stroke suffered in the past.
Symptoms and diagnosis
The clinical picture of lacunar cerebral infarction is typical of mild or transient symptoms.
Although 2/3 of lacunar infarctions occur without warning signs, warning signals are present in approximately 1/3 of cases. The following symptoms are typical for lacunar infarction:
- loss of muscle strength or sudden onset of awkward movements of a body part, especially unilaterally (on the face, upper or lower limb);
- numbness or other unusual sensations in some parts of the body, especially if it is on one side;
- bilateral or unilateral complete or partial loss of vision;
- inability to speak or understand speech;
- loss of balance, uncertainty when walking, unexpected fall;
- any other sudden temporary deterioration in health (dizziness, headache, difficulty swallowing, sudden memory loss);
- unusually severe, sudden headache;
- unexplained disturbance of consciousness, convulsions.
Later the disorder may manifest itself as psychological changes, mainly:
- slowing down of mental processes;
- decreased memory, especially in relation to fresh impressions (old memories are retained in memory);
- loss of interests;
- apathy;
- depression.
Principles of treatment
Treatment of lacunar infarction is carried out in the department of neurological diseases. Not only treatment of cerebrovascular accidents should be carried out directly, but also therapy of the risk factors that led to its development, restoration of nervous tissue, prevention of relapses of lacunar stroke and prevention of the development of long-term consequences and complications.
Research, statistics
Frequency of strokes, incl. lacunar, in our country is 2 times higher than in other countries of Western Europe. It is the third leading cause of death in the world. In 85% of cases, the disorder is caused by blockage of blood vessels and interruption of the supply of oxygenated blood to a certain part of the brain.
In 90% of cases, stroke occurs in people over 45 years of age, mainly in men. But in women the condition is more dramatic. This is often associated with the hormonal burden of women (childbirth, menopause, hormonal therapy, contraception) and a higher incidence in older age groups.
Determining the cause of the increased incidence in our country is not easy. A number of studies show a connection with an unhealthy lifestyle, lack of physical activity, type of diet, and a large number of smokers. But to some extent, unfavorable statistics are also associated with underestimation of risk factors leading to stroke.
Therapy for circulatory disorders
Treatment of lacunar stroke itself depends on its type. In case of ischemia, that is, blockage by a blood clot, antiplatelet agents (prevent platelet aggregation and the formation of a blood clot) and anticoagulants (prevent the formation of clotting factors - proteins that thicken the blood) are used. The main antiplatelet agent is acetylsalicylic acid, the anticoagulant is heparin, warfarin.
For hemorrhagic stroke, therapy is aimed at stopping bleeding into the brain parenchyma from a ruptured vessel. For this purpose, a fibrinolysis inhibitor is used - alpha-aminocaproic acid.
Sometimes, if significant arterial stenosis (more than 80%) and a large area of necrosis is detected, neurosurgical intervention is indicated. But surgery is very rare in patients with lacunar infarction.

Therapy
With early initiation of specific treatment, lacunar cerebral infarction has a favorable prognosis relative to other types of stroke. Therefore, at the slightest suspicion, it is extremely important to send the patient for a neurological examination as soon as possible.
Direct therapy is prescribed according to the diagnosis. The cause (etiology), clinical data, and time of occurrence of the disorder are taken into account. Treatment of the acute stage should meet two main goals:
- protection of brain tissue cells by reducing ischemic penumbra;
- increased blood flow at the site of the stroke.
Mostly, treatment consists of taking the following medications:
- acetylsalicylic acid is the most important antithrombotic drug that reduces platelet aggregation (Anopyrin, Aspirin);
- pentoxifylline, which improves blood properties by reducing the adhesion of leukocytes to the mucous membrane of blood vessels (Agapurin Retard);
- medications with calcium channel blockers (Nimotop);
- nootropics that improve deficient metabolism (Enerbol, Encephabol);
- Heparin, which prevents the formation of blood clots and embolization.
The use of vasoactive substances in the acute stage is problematic. Oxyphylline has a beneficial effect, which can be explained by a decrease in hyperemia, the absence of tissue pressure and the formation of cerebral edema in the immediate vicinity of ischemic deposits when taken, and not by the widely described versatile pharmacological effects of this drug.
Treatment of the disease is carried out in a hospital. Correction of arterial hypertension is a prerequisite, otherwise there will be no positive results.
The patient must:
- get enough sleep;
- avoid stressful situations, do not be nervous;
- quit smoking;
- follow a diet, table No. 10 is recommended, fatty, spicy, sweet, salty, caffeinated and alcoholic drinks should be excluded from the menu; fermented milk products, chicken, vegetables and unsweetened fruits should prevail in the diet.
All therapeutic measures are divided into basic and specific.
Basic treatment is as follows:
- taking medications to eliminate hypertension;
- if the patient has a disorder of carbohydrate metabolism, angiitis, atherosclerosis, then you need to take medications that help keep the disease under control;
- control of blood clotting, if necessary, taking medications that reduce it;
- prevention of cerebral edema, for this purpose diuretics are prescribed;
- taking sedative medications;
- prescribing anticonvulsants according to indications.
Specific therapy includes the following:
- Thrombolytic therapy is carried out within 6 hours after the attack, fibrinolysin is injected drip into a vein;
- prescribe medications that prevent the formation of blood clots (drugs based on acetylsalicylic acid, for example, Thrombo ACC, CardiASK, Cardiomagnyl, antithrombotic agents);
- taking medications that improve cerebral circulation, such as Mexidol, Piracetam, Omaron;
- prescribing drugs that prevent damage to brain neurons, for example, Cerebrolysin.
If treatment is carried out correctly and in a timely manner, clinical manifestations disappear after 3-6 months.
If the disease is not treated or the treatment regimen is not followed, then recovery after a stroke does not occur; on the contrary, everything develops again. If it is repeated very often, then the patient experiences mental disorders:
- memory problems are noted, the person forgets the names and faces of family members and friends;
- the patient becomes nervous and tearful;
- a person does not orient himself in space and time, he “relives” his youth again.
Eliminating Risk Factors
Since in almost 100% of cases the development of lacunar stroke is accompanied by an increase in blood pressure, it is necessary to carry out drug therapy to reduce it. However, it should be remembered that the decrease in pressure should be gradual and not very significant. In hospitals, magnesia is most often used for these purposes; it is also possible to use ACE inhibitors (Captopril, Enalapril), diuretics (Furosemide), calcium channel blockers (Nifedipine, Verapamil).
To prevent recurrent ischemic strokes if the patient has high cholesterol levels in the blood, drugs are used to reduce it. The most effective is the group of statins (“Atorvastatin”, “Lovastatin”). It is worth noting that to achieve the effect, you must also adhere to a diet and take medications systematically.
If the patient has diseases of the cardiovascular system, a consultation with a cardiologist is necessary, who will select the necessary medications. For example, in case of arrhythmia, in addition to the use of antiarrhythmic drugs, it is also necessary to take anticoagulants to prevent recurrent thrombosis and embolism.
Prevention
Prevention of the development of lacunar stroke consists of following a number of rules. Need to:
- regularly devote time to physical activity, spend time in the fresh air;
- undergo auto-training, do yoga therapy;
- give up nicotine and alcoholic beverages;
- normalize body weight;
- exclude from the menu foods that provoke the development of atherosclerosis, limit the consumption of salt and fast food;
- take pills to normalize blood pressure and monitor it constantly;
- if there was a myocardial infarction, then you need to undergo a full course of rehabilitation;
- if the doctor prescribes, take medications that prevent the formation of blood clots, and constantly monitor the prothrombin index during treatment;
- At the first signs of a stroke, immediately visit a doctor and follow all his recommendations, otherwise the consequences of a lacunar stroke will be very severe.
Relatives of the patient and medical staff should show special sensitivity to those who have suffered a lacunar stroke, since the favorable outcome of the disease largely depends on their friendly attitude.
Preparations for the restoration of nervous tissue
To shorten the recovery period after a lacunar stroke and ensure complete restoration of the nervous system, medications such as:
Forecast
The prognosis for the development of lacunar stroke with timely diagnosis is favorable, characterized by rapid and complete recovery. However, recurrent strokes and the presence of multiple lesions reduce the chances of full recovery.
There is evidence that 10 years after a lacunar stroke, only 30% of patients remain alive, many of whom show signs of vascular dementia.
Many are also interested in the question: is it possible to work with lacunar cerebral infarction? During treatment and the rehabilitation period, it is worth avoiding increased mental and physical stress, as this can lead to a recurrence of a heart attack or the development of further adverse consequences (dementia, mental disorders).
We can conclude that such a seemingly insignificant pathology as lacunar stroke can lead to irreversible consequences in the absence of timely diagnosis and treatment. Therefore, this pathology should receive special attention from neurologists and radiation diagnosticians, and a person who feels the symptoms listed above should not delay, but immediately seek qualified help. After all, our health is in our hands!
Symptoms of lacunar stroke
Unlike other varieties, lacunar cerebral infarction is not accompanied by acute disruption of vital functions, since cortical structures do not participate in the pathological process. And in most patients the disease is diagnosed in an advanced form, the pathological process is asymptomatic or the signs are poorly expressed. Symptoms usually increase gradually and depend on the location of the cavity and the degree of impact on the subcortical center.
Ischemic lacunar stroke is manifested by the following symptoms:
- arterial hypertension, which is present in this form of heart attack;
- general cerebral signs in the form of nausea, vomiting, dizziness do not appear, as do fainting conditions;
- neurological symptoms manifest themselves at night and in the morning. In the evening, a person begins to experience headaches, and in the morning he wakes up with signs of a stroke;
- all impaired brain functions and disorders are restored over time, but partial neurological deficits may remain;
- Angiography results are inconclusive, but CT and MRI can identify lesions with a diameter of at least 1.5 cm, which become noticeable a week after the attack. If the heart attack is small, then studies will not show anything.
Complexes of symptoms are combined into syndromes, of which there are about 20 clinical syndromes in medicine that accompany the development of lacunar stroke. Lacunar syndromes are distinguished:
- isolated motor type. The formation of pathology in the posterior thigh of the internal capsule is manifested and characterized. There is paralysis of that side of the body where pathological reactions do not occur and there are no symptoms;
- isolated sensitive type. It is in second place in prevalence and occurs in 20% of patients. A special feature is a violation of all types of sensitivity; symptoms occur in the head, limbs and torso. Over time, sensitivity returns;
- atactic hemiparesis. Occurs in 12% of cases and is characterized by muscle weakness of the limbs, pyramidal disorders and ataxia;
- upper limb clumsiness and dysarthria. In the process of pathology, lacunae form in the layers of nervous tissue. Speech function is impaired, awkwardness occurs when moving and paralysis of the head or parts of the body occurs. This type is diagnosed in 6% of all cases.
In addition to the symptoms inherent in each of the syndromes, with lacunar ischemic stroke there are symptoms:
- muscle cramps and tension;
- uncontrolled urination and bowel movements;
- clumsy hand syndrome, joint numbness;
- unsteady walking with small steps;
- Parkinson's syndrome.
The clinical picture appears immediately a few hours after a heart attack, and so on for several days. Before the onset of an attack, patients experience repeated hypertensive crises or frequent attacks of transient ischemia. People report headaches in the evenings and uncontrollable increases in blood pressure. After detecting changes, you need to consult a doctor who can identify the symptoms of a stroke and make the correct diagnosis.