In most cases, a stroke and its consequences are quite serious for the patient. The process of rehabilitation after an attack takes a long period of time, regardless of age. Pathology therapy is carried out under the supervision of specialists in various fields. Not all patients are able to return to a normal lifestyle.
Main types of pathology
A stroke is nothing more than a pathology that develops in the spinal cord or brain. Depending on the nature of the progression of the disease, several types of the disease are distinguished:
- ischemic pathology – formed as a result of narrowing, blockage of blood vessels, preventing normal blood circulation;
- hemorrhagic disease - thinning of the walls of the arteries with subsequent rupture and hemorrhage;
- subarachnoid pathology - appears as a result of traumatic brain injury.
Stroke is a pathological condition in which a general cerebral or focal neurological deficiency lasts for about a day or more; this period is defined as a transient cerebral circulatory disorder, which is why a stroke is dangerous. If the patient's neurological and brain function recovers within a few weeks, the attack is considered minor.
Chances of recovery
A stroke in old people always has serious consequences, and rehabilitation is difficult. The chances of active rehabilitation after a year are very low.
This is due to the following reasons:
- Radical treatment of ischemic stroke, such as dissolving a blood clot with drugs (thrombolysis) or removing blood clots from vessels with a special thin catheter, is not always possible. Due to age, there are a large number of contraindications. Older men and women simply do not have the capacity to endure such severe interventions. It is known that the absence of radical treatment worsens the prognosis.
- Restoration of lost functions occurs due to the development of alternative pathways of blood supply to the brain (collateral blood flow). In elderly people, all vessels have severe atherosclerotic damage. This significantly reduces recovery potential and leads to lifelong consequences.
- A large number of concomitant diseases - heart failure, problems with the lungs, kidneys, and gastrointestinal tract. A stroke is a strong stress for the body, since the brain plays a leading and coordinating role in it. In older men and women, exacerbations of other diseases often occur after a stroke, which negatively affects the prognosis.
- Infectious complications. Paralysis and paresis lead to immobility and constant stay in bed. A long-term sedentary lifestyle in elderly people leads to congestive pneumonia and bedsores. They form on the body in places of constant long-term pressure. For example, the sacrum when lying in bed on your back. In older patients, bedsores quickly become deep and can fester. All these circumstances worsen the post-stroke prognosis.
- The need to reduce dosages of drugs due to their poorer tolerability in older people and the significant risk of side effects after use.
- The likelihood of recurrent strokes within a year in older patients is much higher, even with active post-stroke prevention.
- Major stroke in older men and women is often accompanied by loss of consciousness and coma. Full restoration of consciousness after a long coma is a very difficult task for old people. Naturally, this factor also worsens the post-stroke prognosis.
Stroke in middle-aged patients
Ischemic pathology has similar causes for male and female patients - atherosclerosis and prolonged hypertension.
Among the factors of the disease, which has a hereditary predisposition, there are:
- In women - rheumatic pathology of the heart muscle in combination with obstruction of the cerebral middle vessel by emboli of various types.
- In men - occlusion of the neck arteries of a traumatic nature (damage followed by narrowing of the carotid basilar artery).
Hemorrhagic disease has similar factors for both sexes - hypertension, vascular and arteriovenous aneurysms.
The main causes of the disease are of hereditary origin:
- in female patients – hypertension;
- in men - vascular aneurysm, subarachnoid hemorrhage, post-traumatic gradual dissection of the vascular network.
In women during pregnancy, hemorrhagic pathologies are much more common than among men. The features of the process and consequences of cerebral stroke up to a certain age are different.
During ischemic attacks, a dangerous illness often develops in the presence of normal consciousness against the background of a neurological deficiency. Severe pathologies among female patients occur as a type of cerebral embolism of a cardiogenic nature, in men - thrombosis of the main arteries, as well as atherosclerosis.
Types of Palotogia
According to the mechanism of occurrence, there are two types of strokes:
- Ischemic – based on thrombosis of cerebral vessels.
- Hemorrhagic - the cause is rupture of the arteries and bleeding into the brain tissue.
In people over 70 years of age, ischemic strokes are much more common. Here's why this happens:
- Systemic vascular atherosclerosis. As mentioned above, in men and women after 80–90 years of age, on the inner wall of blood vessels there is a significant amount of cholesterol deposits - atherosclerotic plaques. At this age, they reach large sizes and can completely block the lumen of blood vessels or provoke thrombosis. This leads to ischemic stroke and death of brain cells - neurons.
- Frequent atrial fibrillation after 82–85 years. Blood clots in the heart cavity, formed due to arrhythmia, travel through the bloodstream to the brain. Vascular occlusion leads to ischemic embolic damage. Such blood clots in this situation are called emboli.
Atherosclerotic narrowing of cerebral vessels causes frequent micro-strokes. Doctors call them transient ischemic attacks (TIAs). These are temporary, reversible circulatory disorders.
TIA is a common occurrence among older men and women.
Main symptoms:
- Weakness, numbness, or paralysis of the muscles of the face, arm, or leg on one side.
- Slurred speech or difficulty understanding others.
- Blindness in one or both eyes, loss of visual fields.
- Dizziness or loss of body balance in space.
Signs may appear for 1–2 minutes, after which they disappear. Older people often do not pay attention to such short-term symptoms. However, all TIAs require neurological examination and treatment. Over the age of 82 years, mini-strokes significantly worsen the prognosis and increase the risk of a major stroke within a year.
Stroke in old age
At 65-79 years of age, attacks are most common among male patients, after 80 - among women.
The main causes of the pathology:
- the first category of patients (men) – cholesterol plaques, arterial hypertension.
- the second group (women) – ischemic disease, carotid vascular stenosis, wandering arrhythmia, cardiovascular disorders.
Features of the course of stroke and further consequences are practically independent of gender. The disease usually occurs against the background of neurological disorders with an increased risk of disability. What is associated with the presence of severe conditions before the attack. After 65 years, the risk of relapse increases several times than at a young age.
Repeated stroke
One of the most serious consequences is the tendency to have another stroke. The second and subsequent attacks determine the prognosis, because it is even more difficult to recover from them. How long the life expectancy will be depends on the effectiveness of preventing a second attack within a month of the first. The statistics are as follows:
- in the first year the pathology recurs in 5-20%;
- in the first three years, recurrent stroke occurs in 40%.
Relapse is more often observed in old age, with untimely hospitalization, poor care, and stress. The disease also recurs in people with serious chronic diseases - diabetes, hypertension and others. In the long-term stage, the attack may occur again if the patient continues to smoke, forgets to take medications for thrombosis, to lower cholesterol and blood pressure.
Main risk groups
It is possible to reduce the likelihood of an attack if the patient does not forget about the provoking factors. Among the circumstances that can cause a stroke are the following reasons:
- age after 50 years – adequate sleep, nutrition;
- gender – male;
- hypertension – it is recommended to keep records;
- chronic pathologies of the heart muscle - timely diagnosis, surgical intervention;
- transient effects of ischemic origin - pre-infarction state;
- work – constant nervous tension, excessive physical exertion;
- heavy smokers – negatively affects blood pressure;
- cholesterol, obesity, and diabetes;
- heredity - the presence of pathology in close relatives.
Possible risk factors include urgent hospitalization, which in most cases is delayed, the lack of necessary equipment and a full rehabilitation period. Brain stroke and its consequences require special monitoring by the attending physician.
Features of treatment in the elderly group
Treatment of stroke in old age is very different from the tactics that are offered to people under 60-65 years of age. This is due to the physiological characteristics of the body, its susceptibility to side effects - coma occurs more often, and consequences arise after taking potent medications.
To increase the chances of a favorable outcome, it is necessary to treat stroke in older people in a hospital. If the patient undergoes a full course of treatment and subsequent rehabilitation, his life will be much easier. Even after a coma or in a state of unconscious sleep, a person will receive the necessary help , and subsequently will be able to recover faster from the blow suffered.
The prescription of drugs and methods of physiotherapy occurs after the patient has been removed from a serious condition.
First aid for stroke
First aid for a stroke in an elderly person partially determines whether the prognosis for him will be good after treatment. An immediate reaction will help prevent dangerous consequences:
- the patient should be placed so that the legs are 25-30 degrees below the head;
- if possible, you need to take into account pressure and pulse indicators, measuring them immediately after ensuring rest;
- if the patient has lost consciousness during an attack, he must be positioned correctly, but should not be moved to the bed;
- when the ambulance arrives, you need to describe all the symptoms and the person’s previous condition, and also show the medications that he took.
If signs of a stroke occur in an elderly person, ammonia should not be used to recover from fainting . Doctors also prohibit holding limbs if convulsions occur. No drugs that can get stuck when swallowed should be given to the patient.
Features of choosing medications for treatment
The goal of treating stroke in the elderly is to reduce the consequences of the condition, accelerate regeneration processes and reduce blood clots in blood vessels. Drugs are the main method of therapy. They are prescribed by a doctor, and most are available only by prescription:
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors . A group of drugs is aimed at reducing blood pressure by reducing vascular tone and stopping the synthesis of ACE. The group of medications is quite extensive, and the patient cannot independently choose from the list. Unlike most other drugs, ACE inhibitors do not affect cholesterol and also have no effect on atherosclerosis.
- Class 2 receptor blockers . They last longer than representatives of the first group, steadily reduce blood pressure and have a minimum of side effects. In most cases, they are prescribed as medications for chronic hypertension.
- Diuretics . If a person has suffered a stroke in old age, he may be prescribed these drugs to lower blood pressure. They are prescribed when the first groups of drugs are contraindicated for various reasons.
- Beta blockers . Necessary for dilation of peripheral blood vessels. They lower blood pressure, help fight arrhythmia, and cannot be used together with MAO inhibitors.
- Calcium antagonists . The drugs are used to treat stroke in old age, when there is additionally angina pectoris and other heart rhythm disorders. Often prescribed together with ACE inhibitors.
- Adrenergic receptor blockers . Used to reduce blood pressure and have a mild effect. Unlike most other drugs, they can be used for renal failure and diabetes.
The main symptoms of this condition
To prevent pathology and its possible consequences, you need to know how to promptly identify the first signs of a stroke and seek medical help. There is every reason to assume the presence of hemorrhage if the patient suddenly feels:
- problems with constructing phrases and forming thoughts.
- weakness, tremors in the limbs, especially if they are present on only one side.
- problems with balance and coordination of movements.
- sudden loss of clarity of vision.
- vomiting, severe feeling of nausea, headache.
- spots and blurry circles appeared.
- There is paralysis of the muscle tissues of the face, and there are cramps.
If a patient has similar symptoms, in order to prevent serious complications after a stroke, it is necessary to urgently call an ambulance, since it is very important to carry out all resuscitation procedures within 3 hours after the hemorrhage.
Patients with pathologies of the vascular-cardiac system are afraid of an acute condition that the pathology can cause:
- stupor, lack of normal consciousness;
- changing the rhythm, as well as the frequency and depth of breathing, up to a complete stop;
- tachycardia, decreased general pressure, “failure” of the heart is quite possible;
- sudden emptying.
All these disorders indicate the presence of hemorrhage, which can cause serious consequences of ischemic stroke in men, since a pathological attack is quite a severe blow to the body.
Rehabilitation measures
It is impossible to give a favorable prognosis after a stroke in elderly patients even if all recommendations are followed. However, you can significantly reduce the risk of a recurrent attack by changing your lifestyle for the next year allocated for rehabilitation:
- For elderly patients, proper nutrition is of particular importance: cereals, whole grain bread, vegetables and fruits. Even if there is no appetite, you still need to eat food, since the body needs support during the recovery period.
- Often, older patients experience complete or partial paralysis of the body. An anti-decubitus mattress will help prevent the development of skin infections. The patient needs to regularly change body position.
- Swelling of the legs develops gradually. To prevent it, diuretics are prescribed.
- Treatment of concomitant diseases is necessary.
Modern medicine believes that taking maintenance medications for older patients helps reduce the rate of ischemic attack and expand the “therapeutic window” (the period immediately after hemorrhage).
Constant use of such medications should be under medical supervision.
Thus, stroke is especially dangerous for older patients. The main consequence of an attack can be partial or complete paralysis of the body, leading to the inability of the patient to self-care. Visual and auditory dysfunctions are also common.
The patient’s psyche may change, he becomes whiny or, conversely, aggressive. The main goal of treatment and recovery after a stroke is to prevent another attack, which often ends in the death of the patient.
Violation of vital functions
The lack of normal physiological and neural activity is associated with loss of conductivity of brain tissue - sensory neurons. It is through them that a person coordinates movements, speaks, and thinks adequately. The same factor prevents the patient from recovering from an attack.
Neurons die due to lack of transport of necessary nutrition to the brain. The development of pathology provokes the destruction of blood vessels.
Violation of coordinating functions
The lack of normal blood circulation in the parts of the central nervous structure responsible for coordinating various movements as a result of a sudden stroke can cause ataxia. This is most often observed in brainstem pathology and is explained by the fact that the main centers from which the signal to the nerve endings are located are located in this area of the brain.
Such violations can have varying degrees of severity. If there is a favorable prognosis, malfunctions in the vestibular apparatus disappear within several days after an acute attack. In more severe situations, dizziness and loss of coordination while moving can persist for months.
Swallowing and speech disorders
The main consequence of hemorrhage is disruption of blood circulation in the cerebral middle artery. In this process, the main hemisphere is most often involved, that is, in right-handed people, similar changes are formed when the left side is damaged.
Depending on the type of pathological process, motor or sensory aphasia may develop. In the latter case, the patient does not perceive what others say to him, while he himself utters unrelated words. The patient reads, but does not understand what is written. With a motor disorder, a person understands speech, but cannot write or speak.
The consequences of a primary stroke in women can be eliminated in almost all cases, while with a recurrent syndrome the prognosis is not so rosy.
Decreased vision clarity
Pathology of the visual system can be of a different nature. The degree of the syndrome depends on the size of the lesion and the location of the hemorrhage. Basically, the disorder manifests itself in the form of loss of vision (hemianopia). In this case, only half or one quarter of the image is present, which is called square hemianopia.
Deviations associated with the psyche and memory
Frontal pathology is formed when there is a change in the main part of the brain artery. The syndrome is characterized by decreased self-control, selfishness, and severe irritability. The patient is no longer interested in the people around him, he becomes somewhat inhibited, and there are practically no emotions. But intellectual abilities and memory do not always suffer.
The psychopathological sign characteristic of hemorrhage on the right side, in which the cerebral middle vessel is involved, on the contrary, is accompanied by loss of personality, orientation, decreased intelligence and constant forgetfulness.
Apoplectic pathology attacks the patient’s cognitive system – memory. The patient does not remember his name and does not recognize people close to him. Memory may be lost partially or completely.
Paralysis of limbs after hemorrhage
Frequent complications of stroke are disorders of the motor system of varying degrees of damage. Often, disorders make themselves felt in the form of paralysis (loss of motor function) and paresis (partial inability to move).
When hemorrhages are present:
- Monoplegia is immobilization of one of the limbs.
- Hemiplegia is a lesion of the upper and lower extremities located on one side of the human body.
- Paraplegia is the immobilization of two legs or arms at once.
With synkinesis, the injured limb does not act on its own, but when the healthy leg or arm is raised, the injured part performs a similar movement. Peripheral pathology is characterized by the lack of function that allows you to move the limbs in the affected part of the body. With central paresis, synkinesis is present - joint movement of the limbs.
Along with paresis, there is a speech disorder or difficulty pronouncing sentences, words, as well as a lack of understanding of speech errors.
Other consequences of hemorrhage
Stroke can be the main cause of various pathological processes:
- impaired sense of smell, hearing, loss of motor skills while maintaining strength and other ailments that need to be treated;
- decreased sensitivity after hemorrhage, and it can be of a different nature, mainly the inability to perceive pain, cold and heat.
The consequences of a stroke can make themselves felt, like the first symptoms of the disease - at its very beginning and persist for quite a long time in the absence of active rehabilitation. The severity of the changes that occur and their duration depend on the degree of damage and the nature of the attack.
Rehabilitation of the elderly
Rehabilitation after a stroke is a long and complex process, consisting of medications, physiotherapeutic procedures and means of preventing relapses. The basis of rehabilitation is a special diet:
- it is necessary to minimize sugar and salt in the diet;
- reduce the consumption of animal fats (pork, lamb, butter, fatty dairy products);
- eat crushed food that does not cause chewing difficulties;
- introduce lean soups, vegetable oils, cereals, fruits and vegetables into the diet;
- prepare food by boiling, baking or steaming food.
After a stroke, older people are advised to exercise on exercise machines - first in a hospital setting, and then at home.
When practicing PNF therapy, the patient performs simple exercises aimed at restoring the ability to move. These drugs also improve motor functions and prevent the development of serious complications, including paralysis and muscle dystrophy. Additionally, other methods are prescribed:
- soft tissue manual therapy – all muscles and the musculoskeletal system are worked on, stretching improves;
- Vojta therapy – areas of the patient’s body are subjected to targeted pressure, which causes rolling over and crawling reflexes in almost completely paralyzed patients. The process triggers the activity of motor muscles and reflexes;
- The Castillo Morales method is a set of exercises to restore breathing, swallowing functions and speech. The specialist influences the patient, additionally psychological therapy is carried out;
- Kinesio taping is a technique that uses special elastic patches. They are glued to the skin, as a result of which the joints receive support and strengthening. Additionally, the patches improve lymph outflow and restore microcirculation;
- Mulligan concept is an innovative technique for restoring the musculoskeletal system in older people after a stroke. Aims at the patient learning to perform movements day after day, even if they cause pain;
- Bobath therapy is a special technique for elderly people over 75 years of age, aimed at restoring blood circulation and the functioning of all organs.
These techniques cannot be performed at home. Typically, older patients are treated after a stroke in a rehabilitation center. Additionally, standard physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed: magnetic stimulation of the brain to restore speech, transcranial stimulation to improve vascular function.
Fact! Laser therapy is useful for improving the body's sensitivity to medications.
Good results are obtained by acupuncture, which restores a whole range of body functions: the condition of tissues improves, muscle activity is normalized, reflexes are formed, and motor functions are restored.
Stroke is one of the most dangerous vascular diseases, because it is an acute disturbance of blood circulation in the brain. The consequences of a hemorrhagic stroke are especially severe; with this pathology, a person can quickly die or become paralyzed.
How to determine the affected part of the brain
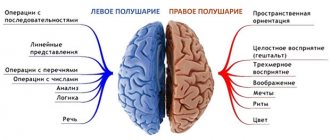
The right-sided type of ischemic stroke is expressed in paralysis of the left side of the body. Speech disturbances may also appear. If the left side is damaged, then problems are observed with the right half of the body. Paralysis is not all the consequences. With a left-sided stroke, a serious impairment of speech and the ability to perceive what others say is noticeable.
Trunk stroke most often leads to death, since this is where the centers that regulate the cardiac and respiratory systems are located. The main signs of such a lesion are nausea, vomiting, loss of spatial orientation, and inability to coordinate one’s movements.
The cerebellar type also causes problems with coordination and dizziness. In this case, a coma is possible, from which only a part of patients manage to get out.
Extensive brain damage manifests itself in the rapid development of all possible symptoms, ranging from headaches to loss of consciousness.