How smoking affects the heart and blood vessels
Cigarette smoke is harmful; in addition to nicotine, it contains a number of chemicals. Among them is carbon monoxide (CO2). In the lungs, carbon monoxide instead of oxygen enters the blood, causing oxygen starvation of the body. Under the influence of CO2, the thickness (clotting) of blood increases, blood clots form, blood vessels lose their elasticity, and symptoms of VSD appear. When a blood clot breaks off, an acute circulatory disorder occurs - a stroke or myocardial infarction. 4 components of cigarette smoke:
- Nicotine.
- Arsenic.
- Formaldehyde.
- Carbon monoxide (carbon monoxide).
Nicotine causes vasospasm. During smoking, the blood vessels constrict and relax after a few minutes. Heavy smokers, especially those who smoke during VSD, often experience obliteration of the vessel, when it slams shut during a spasm and no longer opens. When obliteration of the vessels of the fingers or toes occurs, tissue death begins due to impaired circulation, which, without urgent amputation, ends in progressive gangrene.
This happened to the famous Soviet actor Pavel Borisovich Luspekayev, who was a heavy smoker. During the filming of the film “White Sun of the Desert,” he suffered from obliteration of blood vessels in his left leg, which was amputated under the groin due to delay. He finished the film while already disabled. Luspekayev did not quit smoking and soon the blood vessels in his right leg “slammed shut”. The actor did not allow the amputation to be carried out on time; he died in the ambulance on the way to the hospital. A smoker's heart rate is increased to 90 beats per minute. Due to this load, the heart and blood vessels quickly wear out. Signs of VSD begin to appear: hypertension, tachycardia, heart rate increases to 140-150 beats.
Breathing while smoking
There is an interesting, from a psychological point of view, explanation for why smoking relieves stress. A study was conducted that showed that even a few minutes before relief, a person calms down just by touching a cigarette.
Even inveterate neurotics peacefully close their eyes, feeling the smell of smoke, although just a minute ago they were ready to rush in rage at those around them.
Scientists associate this change in behavior and calmness with measured breathing, during which the smoker inhales nicotine. It is the ability to breathe rhythmically that relieves tension. Severe stress and smoking become interconnected, and the person seems to “exhale” the problem out of himself along with the smoke. This phenomenon is closely related to meditation, which is also based on proper breathing, but is much more peaceful and beneficial than smoking a cigar.
Is smoking a cause of VSD?
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is not a disease, but includes a number of symptoms of a physical and psycho-emotional state. Having started smoking, a person begins to notice signs of diseases that he had not seen before:
- Shortness of breath.
- Irritation.
- Cardiopalmus.
- Panic attacks.
- Coldness, tingling fingers.
These signals are signs of vegetative-vascular dystonia and the onset of serious diseases. Smoking with VSD contributes to the development of cardiovascular diseases.
How are nicotine and neurosis related?
“I can’t even sleep, I can’t even eat!” - says Baba Yaga in the film “Morozko”. With neurosis, most patients actually experience lack of appetite, insomnia, excessive irritability and tearfulness. Among the proven causes of a neurotic condition, the main contingent of which are women, smoking is not the least important.
You can not only actively smoke, but by being near a smoker and inhaling tobacco smoke, a person becomes a passive smoker. How does nicotine affect the nervous system?
In addition to the negative impact on the condition of blood vessels, the target organ for nicotine is the autonomous part of the nervous system, which controls the functioning of internal organs. A more appropriate functional name for nicotine is neurovascular toxin. In addition to nicotine, benzopyrene, carbon monoxide, radioactive elements and heavy metal compounds contained in cigarettes belong to the group of nerve toxins. By affecting the structure of blood vessels, nicotine leads to a decrease in the receptor sensitivity of blood vessels. In general, autonomic nervous control begins to suffer. People who start smoking expose their nervous system to decreased stamina and resilience.

Common emotional features of smoking and VSD
Against the background of smoking cessation, an exacerbation of VSD symptoms is possible. Over the course of several years, a number of chemical compounds entered the smoker’s body, which were artificial stimulants for the functioning of organs and systems of the body. During smoking withdrawal, the body is deprived of stimulants and tries to compensate for their lack, thereby worsening the person’s well-being.
Common emotional features of smoking withdrawal and VSD:
- Decreased attention.
- Difficulty sleeping.
- Depression.
- Irritability.
At the same time, the main obsessive thought is to light a cigarette. There is often a feeling of extreme hunger. This is how the body tries to return or compensate for nicotine and other stimulants.
According to statistics, the physical symptoms of VSD that appear after quitting smoking disappear within 7-10 days. Psycho-emotional signs of VSD take much longer to resolve.
Symptoms and treatment features of cardioneurosis
Have you been struggling with HYPERTENSION for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure hypertension by taking it every day...
Read more "
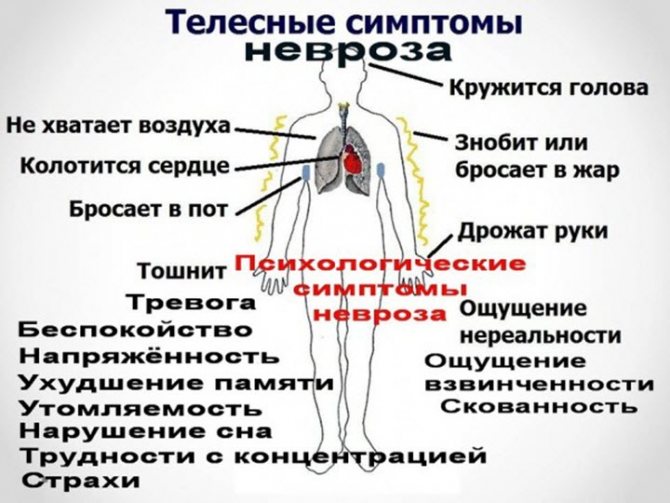
Cardioneurosis is a psychosomatic neurotic pathology characterized by painful sensations in the heart, arrhythmia and lack of air. The mechanism of development of the pathological condition lies in the disharmonious work of the hypothalamic centers and subcortical sections of the cerebral hemispheres. The problem can be considered as a separate syndrome included in the group of ailments of the neurotic complex.
Causes of the disease
The pathogenesis of cardioneurosis lies in disruption of the autonomic nervous system, as a result of which psychological discomfort increases, accompanied by the occurrence of nonspecific sensations. The main factor provoking the development of characteristic symptoms is stress as a form of accumulation of psycho-emotional stress. Research in the field of psychiatry has shown that among the stimulating factors of cardioneurosis there are not only negative psychological experiences, but also positive experiences, accompanied by a bright surge of feelings. People with neurological or mental disorders are most often affected by the disease; people experiencing severe emotional turmoil; older men and women with signs of dementia.

Cardioneurosis also occurs among people who do not have damage to the nervous system or heart. The cause of these conditions lies in a violation of mental activity of unknown etiology. Deviations from the norm, which contribute to an increase in anxiety and tension, cause a pathology of sensations, which are classified as psychosomatic manifestations of the disease. The following factors can provoke a characteristic symptom complex:
- a drastic change in lifestyle,
- non-compliance with the daily routine,
- unhealthy diet
- strong emotional shocks,
- the end of remission of diseases of the neurotic complex, etc.
Characteristic symptoms
The course of the disease is sudden: a wave of anxiety and fear covers the patient, against the background of which the signs of the disease are described as bright and intense. Patients primarily complain of compressive pain in the heart area, lack of air, increased heart rate, and arrhythmia. The fear of loss of consciousness increases, in some cases panic attacks are observed with an exacerbation of characteristic behavioral traits.
Let's consider the main symptoms of cardioneurosis:
- cold sweat;
- general asthenia (state of weakness, loss of ability to work);
- inability to concentrate;
- decreased blood pressure;
- suffocation;
- sleep disorders, insomnia;
- persistent psychological stress;
- heartache;
- change in heart rate.
Attacks of cardioneurosis can last from 15 minutes to several hours, during which the patient plunges into a state of fear for his life, clearly remembering his own feelings. The disease can manifest itself either daily, 2-3 times a day, or several times a year, when an exacerbation gradually passes into remission. Panic attacks and heart pain can occur every day for 9 months, until the acute form becomes latent. The disease often develops from adolescence, but sometimes the first symptoms appear in older people, when cardiac neurosis is a consequence of Alzheimer's disease.
Diagnostics
Cardioneurosis must be differentiated from a number of diseases of the cardiovascular system, for example, from myocarditis, rheumatism, and dystonia. Since this condition, having a characteristic picture, does not imply functional disorders of the heart, to make an appropriate diagnosis, you can resort to the following methods of identifying the disease:
- electrocardiogram,
- general blood and urine analysis,
- ECG,
- Treadmill test;
- Holter monitoring.
The diagnosis of cardioneurosis is made after consultation with a therapist, neurologist, psychiatrist and cardiologist.
Providing first aid during an attack
Considering that with an illness such as cardioneurosis, an attack can develop unexpectedly for the patient himself and his environment, the main task is to quickly remove a person from a state of active anxiety by following the following recommendations:
- the patient must be urgently taken out of the stuffy room into a well-ventilated room, try to calm him down in an even, confident voice;
- the second step is to sit or lay the person on a bed or sofa so that he is comfortable;
- then attempts are made to neutralize the psycho-emotional tension that has arisen: eliminate the irritating factor, stop the argument or quarrel, etc.;
- it is important to measure blood pressure and make sure there is no circulatory disorder;
- the patient needs to be offered a sedative: “Valocordin”, motherwort tincture, “Persen”, “Barboval”;
- If there is no positive dynamics in the patient’s condition, an ambulance must be urgently called. Massage, applying heating pads and other procedures during an attack are prohibited.
The main thing for those around you is to maintain your own calm. If you fuss, show excessive anxiety, constantly ask about your well-being, the feeling of anxiety will only intensify, and you will not be able to stop the attack on your own.

Treatment
Conventional medications used for the treatment of cardiac diseases are not suitable in the case of cardioneurosis; a special approach is required.
Why do you feed pharmacies if hypertension is afraid of the usual like fire...
Tabakov has revealed a unique remedy against hypertension! To reduce blood pressure while preserving blood vessels, add to…
Traditional methods
When visiting a doctor, the patient receives a prescription for medications designed to relieve the symptoms of the disease. There is no specific drug therapy in this case. Drugs for the treatment of cardioneurosis:
- sedatives (sedatives): “Motherwort Forte”, “Validol”, “Valerian extract”;
- antidepressants: Azafen, Sertraline, Fluoxetine;
- drugs to eliminate anxiety (used only as prescribed by a psychiatrist, as they are addictive and affect the speed of reactions): Diazepam, Teralen, Lorazepam, etc.;
- homeopathy: “Cardialgin” drops, “Passiflora” granules, “Aconite”.
To eliminate the root cause of the disease, a visit to a medical psychologist is scheduled, who, based on the interviews, examines the source of the problem and recommends additional methods to improve the condition:
- avoidance of worries and worries;
- frequent walks in the fresh air;
- regular exercise;
- rejection of bad habits;
- organizing the last meal no later than 3 hours before bedtime;
- normalization of the daily routine, healthy sleep;
- daily contrast shower;
- exclusion from the diet of foods that overstimulate the nervous system.

Traditional methods
Treatment of cardioneurosis allows the use of folk remedies with a calming and restorative effect. The choice of a specific prescription should be made after consulting a doctor in order to avoid negative reactions to the components of the product. The most effective means of alternative medicine are the following:
- herbal collection: mint (2 tbsp), hop cones (1 tbsp), valerian root (1 tbsp) and three-leaf watch (2 tbsp). The resulting mixture in the amount of one spoon is placed in a thermos and poured with boiling water (0.5 liters). After infusing for several hours, you can strain the composition and take 100 ml of it before meals in the morning and evening;
- hawthorn infusion. The flowers are poured with cold water (3 tablespoons per liter) and left overnight. In the morning, the composition is sent to the fire, boiled for 5 minutes and removed. After waiting for complete cooling under the lid, filter the infusion and take a glass daily in the morning on an empty stomach;
- honey and honey mixtures. Natural honey should be eaten in its pure form, 120 grams, divided into three doses. Before going to bed, it is recommended to drink warm milk with a dissolved spoon of beekeeping product;
- a collection of St. John's wort (5 parts), arnica (1 part) and yarrow (3 parts). Herbs with a sedative effect are mixed, a tablespoon of the resulting raw material is infused in cold water for several hours, and then boiled for 5 minutes over low heat. You need to consume 400 ml of the strained mixture throughout the day, drinking it in small sips.
Consequences and prognosis
A long-term lack of proper treatment for cardiac neurosis negatively affects the functioning of the entire cardiovascular system, causing the development of hypertension and ischemic diseases. Constantly recurring anxiety attacks significantly reduce the patient's quality of life, leading to tension, quarrels in the family and a general deterioration in the environment at home and at work. The consequences of the progression of the disease can be mental disorders.
The prognosis is favorable if you follow the doctor’s recommendations and provide psychological assistance. Patients manage not only to avoid recurrence of anxiety attacks, but also to completely get rid of the problem by working through its cause.
Preventive measures
You can reduce the likelihood of heart neurosis by following simple recommendations:
- it is advisable to avoid stressful and conflict situations; if you are in a depressive mood, you should contact a psychologist for timely treatment of the condition;
- sports activities should be regular, even at home;
- studying progressive relaxation techniques;
- proper diet with a complete supply of all useful components;
- it is important to organize communication with relatives, friends, and arrange meetings to receive positive emotions;
- Walks in the fresh air should be daily.
How to quit without harming yourself
To overcome the bad habit of smoking, you first need a psychological attitude. The thought “I quit smoking” should be categorical and categorical. You need to fuel this thought in every possible way, doing everything possible so that this mood does not pass. There are a number of nicotine-containing drugs that alleviate the symptoms of VSD when quitting smoking - lozenges, chewing gum, tablets, patches... If you have chronic diseases, vascular pathologies, vegetative-vascular dystonia or health complaints, you need to consult a doctor who will prescribe an examination and supportive therapy. It is strictly prohibited to take medications not prescribed by a doctor! What may help someone else may, at best, be a waste of money for you. There are drugs that are incompatible with each other.

Smoking. Negative consequences of smoking.
Is there a connection between smoking and neuroses? At first glance, these two pressing problems of medicine are quite far apart from each other, but upon closer, careful examination, a clear connection is revealed between them. Moreover, this connection cannot be called one-sided. In some cases, prolonged stress and neuroses lead to smoking, and sometimes, on the contrary, smoking becomes fertile ground for the emergence of neurosis. Cause and effect are closely intertwined.
Many heavy smokers explain and justify their addiction to tobacco by the desire to calm down and collect their thoughts in difficult times. Let us remember what a man does when he quarrels with his wife. You can get almost the same unambiguous answer to this question from fiction and films, even if they were created in different countries and under different social systems. An upset man lights a cigarette, and none of us has any doubt that it (the cigarette) is appropriate in this case.
Whether a cigarette relieves negative emotions, whether it promotes calm or not, is not entirely clear. However, it is clear that a cigarette smoked during a period of stress cannot prevent neurosis. Smoking in this case can be described as a neurotic obsession. After all, both a neurotic and a smoker, understanding the meaninglessness and burden of obsession, are not able to get rid of it on their own. A vicious circle arises. Neurotic anxiety forces you to take up a cigarette; smoking turns into obsession, which, in turn, leads to a neurotic breakdown. It would be wrong to say that this always happens. However, often a disease (neurosis) and an addiction (smoking) are closely intertwined.
Most smokers, when answering the question why they smoke, motivate it with pleasure and positive emotions associated with the smoking process. From what has been said, one could draw a conclusion that is surprising in its consequences: the more often you smoke, the more often you experience pleasure. Is this really what happens? It turns out that this is far from the case. Upon more detailed questioning of smokers, it turns out that out of the 20-25 cigarettes they smoke a day, only 3-4 give pleasure, while the rest are smoked automatically. A heavy smoker smokes even when he does not experience any pleasure from smoking. Instead of being the master of his habit, he turns into its slave. It is this “cigarette slavery” that is the cause of mental torment, endless thoughts on the topic “it’s time to quit smoking.” Ultimately, this forces a person to constantly worry about replenishing tobacco supplies, pushes him to search for “smoke” in any weather and time of day, thereby infringing on his freedom. Smoking turns into an obsessive neurotic ritual.
In modern conditions of widespread anti-nicotine propaganda, smoking becomes a source of constant intrapersonal conflict. On the one hand, there is a desire that has grown into the habit of smoking, and on the other, there is the awareness that smoking is harmful to health. This creates a conflict that leads to neurosis. From this perspective, it becomes clear why the number of people who want to give up this bad habit is increasing year by year. After all, by quitting smoking, they would also get rid of the disease - neurosis. According to domestic authors, currently 89.6% of smokers aged 20 to 59 years want to stop smoking.
So, most smokers know about the dangers of smoking for health, but, knowing this, they continue to smoke. The fact is that their knowledge is not of the nature of conviction. Gaining belief in something is more difficult than gaining knowledge. Beliefs require significant internal work, if not agony. A smoker treats knowledge about the dangers of smoking ironically.
A seemingly paradoxical situation arises. On the one hand, the smoker is not afraid to smoke and smokes, on the other hand, almost nine-tenths of this army want to stop smoking. Why is this happening? We are convinced that the answer to this phenomenon lies in the wrong orientation of people who want to get rid of their addiction. After all, most of them are convinced (just convinced, and do not have a stock of knowledge, as in the question of the dangers of smoking) that quitting smoking means a complete and irrevocable renunciation of this persistent habit. By the way, many doctors are guided by this. So it turns out that most smokers who turn to doctors to get rid of this habit actually don’t want to. It seems ideal to them to turn from a slave to the cigarette into its master, to break out of the captivity of tobacco smoke, to smoke only when they want, and not when they cannot live without it.
As for the cause-and-effect relationships of smoking with various diseases, today it would be more correct to consider smoking as a risk factor, and not as the cause of certain diseases. But no matter how smoking is viewed, no matter what opinions are expressed on this issue, even the most convinced smokers have to admit that this habit is harmful to health.
Probably, just as there is promiscuity and disease - drunkenness and alcoholism, there is also a bad habit of tobacco and painful addiction. Depending on how the smoker’s condition is assessed—in terms of illness or habit—various differentiated treatment methods should be used. In cases of illness, so-called aversion therapy is used, aimed at developing a conditioned reflex of aversion to smoking, which naturally implies a complete cessation of cigarettes. Against the habit of smoking excessively, the doctor and the smoker himself will not achieve the desired result with such treatment. This is due to the fact that the treatment will not eliminate the desire to smoke, but will only “scare” the smoker with unpleasant consequences. This creates significant internal tension, which can lead to relapse and relapse into smoking.
There is a proverb: “Hunting is worse than bondage.” In other words, the desire for reward is stronger than the desire to avoid punishment. If we take into account this time-tested folk wisdom, then it would probably be more advisable not to develop negative emotions or fear of smoking in the smoker, but to consolidate and strengthen the positive emotions that he will receive when overcoming his addiction. The role of the doctor in this case is limited to helping the patient understand the reasons for his addiction to smoking, in activating the patient’s will and desire to free himself from the oppressive “cigarette slavery”.
Whether you need to quit smoking or not, only you can decide for yourself. However, if according to the questionnaire you are in the first group, then we advise you to seek the help of doctors who will decide how to do this better.