Causes of pituitary adenoma
The development of the disease is influenced by head injuries, as well as infections affecting the nervous system: polio, meningitis, encephalitis, brucellosis, tuberculosis with damage to the nervous system, syphilis. Tumor predisposition sometimes develops in utero due to toxic or radiation exposure to the fetus during pregnancy. Autoimmune diseases of the thyroid gland with a decrease in its function (hypothyroidism) can also lead to neoplasms. People with underdevelopment of the internal sex glands (hypogonadism), congenital or acquired, are also considered at risk.
"Important! It is worth remembering that there is a hereditary predisposition to pituitary adenoma.”
The danger of pituitary adenoma of the brain, what is it?
Pituitary adenoma of the brain is not a fatal disease, with the exception of the development of malignant tumors. When the adenoma grows into neighboring organs, the prognosis becomes unfavorable.
In addition to the degeneration of a benign adenoma into a malignant tumor, another danger may arise for the patient. Pathology can cause disruption of the endocrine system, which leads to dysfunction of other organs and systems.
The patient's condition worsens as the tumor progresses and begins to worsen when hormonal imbalances cause irreversible changes in internal organs. To prevent this, patients with even the smallest pituitary adenoma of the brain need to be constantly examined by their attending physician.
Types of neoplasms
Depending on the size, there are micro (up to 1 cm in diameter), macro (more than 1 cm) and giant adenoma (4-5 cm or more). In addition, medicine classifies tumors by location. For example, if an adenoma grows upward, doctors call it suprasellar, downward - infrasellar. There are also cases of tumor growth backwards, i.e. towards the back of the head (retrosellar) and the location inside the so-called sella turcica of the bone (endosellar).
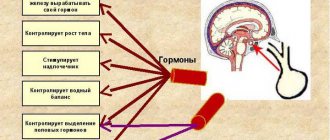
An important feature is the endocrine nature of the tumor. A hormonally inactive adenoma is a tumor in cells that do not produce hormones. If the tumor produces hormones, it is called hormonally active, or secreting.
Hormonally active pituitary adenoma affects the functioning of organs and systems. For example, if the production of the hormone prolactin is disrupted, the tumor of the pituitary gland is called “prolactinoma.” If there are problems with adrenocorticotropin (ACTH), Cushing's disease may occur, with somatotropin, or growth hormone, kromegaly (in this case, the adenoma is called “somatropinoma”). A more rare case is thyrotropinoma, or adenoma with impaired production of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). It leads to increased thyroid function (hyperthyroidism). There are also corticotropinoma and gonadotropic tumor.
If misdiagnosed, a hormone-secreting adenoma can cause visual impairment and neurological disorders.
Types of pituitary adenomas
Pituitary adenoma is divided into types, depending on the location of the tumor in relation to the location of the gland and the sella turcica.
Types of adenomas:
- Endosellar pituitary adenoma is located inside a bone pocket.
- Endoinfrasellar pituitary adenoma is a tumor located downstream of the pituitary gland.
- Endosuprasellar pituitary adenoma - growth of the tumor is directed upward.
- Endolaterosellar pituitary adenoma - the tumor is shifted to the left or right side.
- Mixed pituitary adenoma is located diagonally in any direction.
Depending on which direction the adenoma is shifted, compression of certain areas of the surrounding tissue occurs. This determines how the clinical symptoms of a pituitary tumor manifest.
Manifestations and diagnosis of the disease
The symptoms of this disease are related to the type of adenoma the patient has. There are ophthalmo-neurological manifestations and endocrine-metabolic ones. The first include:
- visual disturbances, double vision;
- headache, often in the temples or forehead, for which painkillers are not effective;
- decreased vision, even to the point of blindness.
As the tumor grows, it compresses nearby tissues. With large adenomas, vision decreases more due to compression of the optic nerves by the tumor. Already with a tumor of 1-2 cm in diameter, atrophy of the optic nerves and complete loss of vision can occur.
Endocrine metabolic symptoms vary depending on which hormone malfunctions due to tumor development. The most common type of prolactinoma is prolactinoma, in which women's menstrual cycle is disrupted, body hair begins to grow in a male pattern, body weight increases, infertility develops, and sexual activity decreases. In men, the symptoms are usually less pronounced, but enlarged mammary glands, a drop in libido, and impotence are observed.
Corticotropinoma, in which the balance of adrenocorticotropic hormone is disturbed, is dangerous because more often than other adenomas it becomes malignant and metastasizes. Its manifestations are associated with Cushing's disease:
- purple stretch marks on the stomach and thighs;
- obesity;
- spots (pigmentation) on the skin;
- baldness in men and body hair growth in women;
- mental disorders are possible.
Somatotropic adenoma is associated with growth hormone. In pediatric patients, it causes gigantism, and in adults, acromegaly (a growth disorder in which the feet and hands appear enlarged compared to the proportions of the rest of the body). This pathology can be accompanied by diabetes and obesity. With gigantism, on the contrary, growth is high, and the functions of internal organs, which do not have time to increase with the body, are disrupted. Both forms can be accompanied by thyroid diseases.
Thyrotropinoma, directly related to the functioning of the thyroid gland, manifests itself with symptoms of hyperthyroidism and thyrotoxicosis. The patient's hands are shaking, he is emotionally unstable to the point of tearfulness, cannot tolerate hot weather, is losing a lot of weight, and has tachycardia.
Gonadotropinoma is an adenoma with the production of sex hormones. Its main manifestations are associated with decreased sexual function, but decreased vision and headaches are also noticeable.
With any type of large tumor, fatigue, weakness, suppressed libido, impaired sense of smell and signs of thyroid dysfunction are observed. This causes compression of the pituitary body, disrupting the production of all hormones.
Forecast
Adenoma is a benign formation, but in the process of growth, the process of its malignancy is not excluded. In general, the prognosis for pituitary adenoma is quite favorable, in contrast to other types of brain tumors. But a lot depends on its character and size. For example, with small corticotropins, complete recovery is observed in 85% of cases, and with prolactinomas - only in 25-30%.
Relapses do not occur often, in approximately 10-12% of cases. They require repeated treatment. The greatest risk of recurrent disease is observed in patients whose adenoma size was more than 2 cm.
Treatment methods
To treat pituitary adenoma, radiation therapy or surgery are used. However, treatment without surgery is also possible.
Surgery is not prescribed if its risk exceeds the location of the adenoma inside the brain for the patient. Then conservative therapy comes to the rescue. It is carried out only after a complete endocrinological examination. The essence of treatment is the selection of hormonal replacement drugs. If the production of hormones is too high, then medications are used to suppress their excess production.
"Important! With conservative therapy, it is necessary to monitor possible side effects."
Diagnostics
When signs characteristic of a pituitary adenoma appear, the patient usually turns to an ophthalmologist or neurologist. Doctors perform a physical examination and evaluate the patient's vision. In addition, a number of tests are prescribed:
- General blood and urine tests;
- Tests for hormone levels.
If the examination results indicate a suspicion of pituitary adenoma, the patient must undergo a neuroimaging procedure for the tumor. The following can help with this:
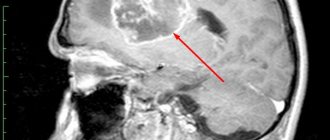
- Radiography. She is able to display in the image the deformation of the sella turcica, which occurs due to the growth of the adenoma;
- CT and MRI. These are the most accurate methods that can not only confirm the presence of a tumor, but also determine its location. Unfortunately, in 25% of cases, tumors that are too small are not visualized;
- Angiography. Allows you to assess the condition of the brain vessels and determine their pathology. This method is not always suitable.
CT is one of the most accurate methods that can determine the location of the adenoma.
Once the tumor is diagnosed, the doctor selects appropriate treatment therapy, which may include surgical removal of the pituitary adenoma.
Indications for surgery
Surgical intervention is prescribed if the tumor is hormonal in nature, producing a dangerous amount of hormones for the body. You cannot do without it even if medication methods are ineffective.
The operation is indicated in case of compression of tissues or nerves adjacent to the adenoma, especially the optic nerves: this threatens the person with loss of vision. If the optic nerves are not affected, minimally invasive surgical techniques may be used.
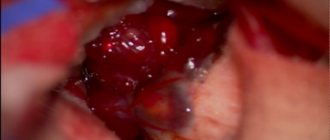
Surgical intervention is performed in three ways:
- transcranial (classical);
- transnasal (through the nose);
- radiosurgery.
The endonasal transsphenoidal method is minimally invasive. No incisions are made during this operation; the tumor is removed through the nasal passage. A probe with miniature instruments is inserted into it. The progress of the operation is monitored through the monitor. For microadenoma, this method provides 90% effectiveness.
The newest gentle method is radiosurgery, in which the tumor is removed using a radioknife (cyberknife). Before the operation, the patient undergoes a series of MRIs of the brain, the results of which are used to create a 3D model of his brain and the tumor in it. Then, using a special device, the adenoma is targeted with gamma radiation.
When choosing a surgical method, the location of the tumor plays a role. Thus, gentle surgical methods are indicated when the adenoma is located within the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone. They are used for tumor sizes less than 30 mm, to remove remnants of tumor tissue after open surgery, after irradiation, etc.
Surgery that opens the skull is called a craniotomy. It is practically unavoidable if the adenoma extends beyond the sella turcica of the bone, has secondary nodes or grows asymmetrically, all of which are reasons for open surgery. In such cases, a situation that threatens the patient’s life cannot be ruled out. There are emergency cases (for example, hemorrhage) when a person can only be saved with emergency surgery.
"Important! The decision on the method of treatment and method of operation is made by qualified doctors, based on the overall clinical picture.”
The patient's condition after surgery
With the development of pituitary adenoma, surgical treatment in many cases is the only option. The operation prevents vision loss due to damage to the optic nerve, neurological disorders due to compression of adjacent brain tissue, and the consequences of hormonal stimulation of the gonads, thyroid, and adrenal glands. However, complications in the postoperative period often occur. They require timely identification and treatment.
Degree of operational risk
The deterioration of the general condition of patients is associated with anesthesia and the surgical intervention itself. The risk of surgery increases in older patients. In this group of patients, the following often occurs:
- sudden changes in blood pressure levels - transition from vascular collapse to hypertensive crisis;
- inadequate response to medications, lack of results;
- heart rate disturbances (tachycardia, bradycardia, arrhythmia);
- development of cardiomyopathy and heart failure;
- blockage of the deep veins of the extremities, detachment of a blood clot with pulmonary embolism;
- postoperative pneumonia;
- stress ulcers of the stomach and intestines with massive bleeding.
Therefore, before removing the adenoma, the surgeon and anesthesiologist determine the degree of risk of removing the adenoma and correct cardiac dysfunction. After surgery, such patients are advised to monitor ECG and ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
We recommend reading the article about the symptoms and treatment of hypothyroidism. From it you will learn about the causes and symptoms of hypothyroidism in men and women, as well as about the diagnosis, treatment of the disease and prevention.
Find out more about diagnosing thyroid diseases here.
Reaction of neighboring structures
General cerebral complications include:
- cerebral edema;
- transient disorders of cerebral circulation;
- intracerebral and subarachnoid hematomas;
- ischemic stroke.
When stopping bleeding from a branch of the carotid artery, its blockage, narrowing or formation of a false aneurysm, and blood loss when flowing through the nasal passages are possible.
Disorders of the adrenal glands and hypothalamus
Insufficient formation of catecholamines (adrenaline, norepinephrine and dopamine) due to removal of an adenoma is a fairly common complication. It may be associated with damage to the pituitary gland during surgery, as well as previous compression of the brain tissue that produces adrenocorticotropic hormone. This condition reduces the patient's ability to withstand the stress of surgery.
When there is swelling of the brain in the hypothalamus region, hematoma or bleeding in this area, or compression of the arteries of the circle of Willis, a hypothalamic crisis occurs. Its main manifestations:
- high body temperature or its uncontrolled decrease;
- delirium, hallucinations, sudden agitation;
- pathological drowsiness with transition to a coma;
- heart rhythm disturbances - the heart rate per minute can increase to 200 beats at normal or low body temperature, and at high it can be even more;
- increased breathing;
- change in blood acidity.
Severe cardiovascular and pulmonary insufficiency leads to death.
Liquororrhea and meningitis
The discharge of clear or pinkish fluid from the nasal passages (cerebrospinal fluid rhinorrhea) appears after tumor removal due to bone defects through which the surgical approach passes. It may appear in the first days or even after a few years. Postoperative meningitis (inflammation of the choroids of the brain) occurs when the surgical field becomes infected; their risk increases with prolonged interventions.
Consequences of surgery and complications
Any operation is a heavy burden on the body. The operation to remove an adenoma is a complex neurosurgical procedure. It is produced by very qualified doctors. The slightest mistake can lead to disaster. However, even if performed according to all the rules of modern medicine, it can greatly affect the functioning of the pituitary gland. One of the possible serious complications is dysfunction of the adrenal cortex. Complications can occur within 36 hours after surgery. If measures are not taken in time, adrenal insufficiency can develop within a month.
A complication of the operation may be poor circulation in the pituitary gland. As a consequence of the intervention, there are known cases of suppression of the function of the thyroid gland, gonads, and associated libido disorders.
In case of medical errors during surgery, additional consequences are possible: injury to the optic and other nerves, cerebral circulation disorders, hemorrhages, liquorrhea (cerebrospinal fluid leakage through the nose, death is not excluded). If infection occurs, it can lead to meningitis or encephalitis.
"Important! There is a higher risk of complications with craniotomy. Radiosurgery is the safest.”
Consequences
With a small size of the adenoma and its timely treatment, the patient can hope for the restoration of impaired functions: visual or endocrine. But if, when the formation is diagnosed, it is already large in size, it is likely that there will be consequences for the body. In this case, the patient may be granted disability.
Complications during treatment can occur mainly with open surgery, as there is a risk of bleeding and infection. Other methods involve fewer side effects.
Forecast and consequences
The patient’s chances of recovery after surgery are quite high: according to statistics, 85% of patients are cured. This mainly depends on the size of the tumor, the possibility of its removal, and its endocrine nature (whether the adenoma produces hormones). The overall picture emerges after a comprehensive examination. Doctors evaluate the results of the operation, the condition of the organs of vision, thyroid and other glands. If the visual impairment was minor and lasted less than 1 year, there is a chance of complete recovery. In more advanced cases, doctors try to at least maintain the level of vision that remains. This once again suggests that at the first signs of illness you should not postpone a visit to the doctor.
Patient prognosis
The prognosis is influenced by the size of the tumor and how timely therapy was started. If a pituitary adenoma was detected at an early stage, then, according to statistics, about 85% of patients recover completely after its removal. Difficulties can arise only with vision - it is restored only after a short course of the disease. If the pathology has been observed for more than a year, then it will not be possible to completely return to its former visual acuity due to compression of the optic nerves.
Complications after removal of a pituitary tumor
The incidence of complications after surgery is related to the size of the tumor, the degree of its functional activity (hormone formation), and spread. Patients in whom the disease is detected at a late stage endure removal the most difficultly.
Their adenoma grows significantly over a long period of time and compresses the surrounding tissues, intensively produces hormones, and penetrates into neighboring structures.
In such cases, the volume of surgery increases, which can cause damage to nearby and distant brain structures. In this group, the likelihood of complications and adverse outcomes is higher.
Lost my sense of smell
Loss of smell can be caused by damage to the olfactory receptors in the nasal cavity during endonasal tumor removal. This condition is considered temporary; recovery usually occurs as the mucous membrane heals over the course of a month.
A more serious situation arises if low sensitivity to odors is part of the pituitary hormonal deficiency syndrome - panhypopituitarism. It occurs due to compression of the remaining parts of the organ by the growing adenoma.
Also, such a pathology can be a reaction to radiation therapy, which is needed when large tumors are incompletely removed. In such patients, the period of normalization of smell is longer. Its success depends on hormone replacement therapy.
Diabetes insipidus
When the secretion of the hormone vasopressin by the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland is impaired, patients develop a condition called diabetes insipidus. With this disease, there is constant thirst, and the volume of urine produced can reach 5-20 liters per day. The patient cannot go without fluid for more than 30 minutes.
Due to the location of the pituitary gland, this complication is more common with endonasal tumor removal. To treat it, a synthetic analogue of vasopressin is available in the form of drops or nasal spray.
Headache
Headache is considered one of the signs of an enlarging pituitary adenoma. After a successful operation, this symptom gradually disappears. The speed of this process largely depends on the initial size of the tumor and the state of cerebral circulation in general.
It was found that during the first month, a significant reduction in headaches was observed in less than half of those operated on. Most patients require 3 to 5 months. If pain persists, additional examination should be carried out.
Headache is considered one of the signs of an enlarging pituitary adenoma