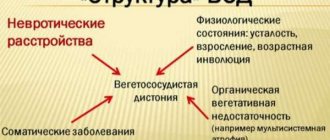
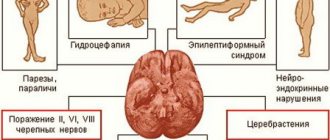
Vegetative-vascular dystonia in children is a malfunction of the body, which is expressed by a violation of the autonomic nervous system. Such a violation can be formed by a negative process, for example, severe overwork or some kind of illness.
The only and surest option for successful treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia, the symptoms and treatment of which we will consider later in the article, is to exclude the factor due to which it appeared. The main mistake in the treatment of this disease is treating symptoms without identifying the causes.
Causes of vegetative-vascular dystonia in children
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia (VSD) is a dysfunction of the vessels of the autonomic (peripheral) nervous system, leading to disruption of the functioning of almost all body systems, primarily the functioning of the heart and cardiovascular system
- Due to heartbeat disturbances, respiratory disorders, autonomic dysfunctions and vascular dystonia appear
- A person with VSD may have neurotic disorders, respiratory disorders, headaches, dizziness, sleep disturbances, and palpitations. He may experience hand tremors or internal tremors, cold hands and feet, swelling, joint pain, etc.
The cause of VSD in a child is usually complex.
Unfortunately, the diagnosis of vegetative-vascular dystonia is increasingly being made to children of all ages. However, the manifestation of VSD in children is somewhat different from in adults. The causes of VSD in children are:
- external environmental factors, rapid changes in the environment
- the presence of a large number of chemicals and objects around a person
- sharply increased consumption of various types of information
- increasing the complexity of the teaching load and the scope of the school curriculum
- a large number of stressful situations associated with lack of time
- genetic and hereditary factors
- factors of intrauterine development of a child
- organic pathologies of the child’s nervous system
- period of hormonal changes
- psychological characteristics of a child’s individual personality
- past infectious diseases
- allergies
- physical inactivity
- brain injury
- frequent psycho-emotional and physical fatigue
- other
Symptoms and diagnosis of vegetative-vascular dystonia
Signs of vegetative-vascular dystonia vary depending on the age of the child. Vegetative-vascular dystonia in infants is accompanied by the following symptoms:

bloating;- periodic regurgitation;
- constipation or loose stools;
- poor appetite, which results in slight weight gain;
- sleep disorders;
- frequent whims;
- skin rashes (diaper rash, allergic reactions, diathesis).
The symptoms of this pathology in children over two years of age practically do not differ from those of an infant, but they still have a tendency to catch colds. There is also a closed character, manifested in the form of unsociability with their peers. The following signs are also observed in preschool children:
- constant pain in the head;
- pre-fainting states;
- fainting;
- fast fatiguability;
- pale skin;
- hysterical fits;
- night terrors.
In addition, in medical practice there are clinical syndromes that arise from the pathology of vegetative-vascular dystonia.

Neurotic syndrome. It occurs within a couple of months or weeks from the onset of the disease, and begins to intensify over time. During the period of such a syndrome, sleep disturbances, hysterics, capricious mood, anxiety, and fear of something are observed.- Cardiac syndrome. It is expressed in cardiac dysfunction. Interruptions in the functioning of the heart may occur: bradycardia, arrhythmia, sinus tachycardia. Teenagers experience severe fatigue, dizziness, heart pain, restless sleep, and headaches.
- Respiratory syndrome. In this case, the child feels a lack of oxygen and shortness of breath in a calm or excited state.
- Thermoregulation disorder syndrome. It is characterized by a violation of the thermoregulation of the child's body. At first it may appear periodically, and over time it may become non-infectious and persistent. The temperature will remain at 37.5 °C, and all laboratory tests will be normal. At temperatures above 39 °C degrees, this period lasts no more than two days.
Vegetovascular dystonia is expressed by crises:
- Vagoinsular crisis. There is a drop in blood pressure, sweating all over the body, suffocation, and a headache in the form of a migraine.

Sympathoadrenal crisis. Tachycardia, headache develops, body chills are felt, the temperature rises, and frequent urination is observed.
If a child has any of the above symptoms, then it is necessary to undergo an examination by appropriate specialists. After preliminary diagnosis, special studies are prescribed to rule out a serious disease.
Depending on what symptoms are observed, and the appropriate treatment in this case will be prescribed. The diagnosis of vegetative-vascular dystonia in a child is made only when organic damage to organs is excluded. Then research procedures are prescribed:
- dopplerography;
- rheovasography;
- rheoencephalography.
Signs of vegetative-vascular dystonia in children
There is a certain set of signs of the child’s condition and behavior that should attract the attention of parents so that VSD does not go unnoticed. Among them:
- the child often looks tired or complains of being tired
- he does not want to play active games and prefers to be in a semi-somnambulistic state
- The child experiences frequent mood swings: he sometimes laughs loudly, sometimes gets upset, etc.
- the child begins to sleep poorly - either often has difficulty falling asleep, or is always sleepy
- the child may yawn frequently or have shortness of breath
- a low-grade fever may occur for no apparent reason
- The tips of the hands and feet may become cold

Lethargy, complaints of headache, cold hands and feet are possible signs of VSD in children.
IMPORTANT: Such symptoms are not necessarily characteristic of an individual case of VSD, they may be signs of other diseases, however, when observing them, parents should show the child to a doctor, first a pediatrician, then a neurologist
Types of pathology
Vegetative-vascular dystonia comes in several types, which differ in symptoms. The main classification of the disease is as follows:
- Hypertensive dystonia. With its development, autonomic dysfunction leads to increased blood pressure, which is accompanied by nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, trembling in the lower and upper extremities, headache, and tinnitus.
- Hypotonic dystonia. The occurrence of this type of VSD causes a decrease in blood pressure. This occurs due to disruption of the heart, blood vessels, and failure of blood circulation in the body. This type is characterized by the presence of arrhythmia, excessive fatigue, decreased performance, depression, and a feeling of coldness in the legs.
- Cardiac dystonia. In this case, signs of cardiac dysfunction predominate. The child experiences heart pain, abnormal sinus rhythm, and shortness of breath.
- Mixed dystonia. With this type of disease, symptoms of different types of VSD are observed. The patient does not have a constant decrease or increase in blood pressure, but there are changes in this indicator.
When conducting a diagnosis, the doctor must determine what type of autonomic dysfunction syndrome in children is present in this small patient. Further treatment tactics will depend on this.
Diagnosis of vegetative-vascular dystonia in children
- Doctors note the difficulty of identifying vegetative-vascular dystonia in children due to the fact that the child is in constant development, his body is not yet fully adapted to the environment, body systems, including the nervous, cardiovascular, and mental, are in the process of becoming
- But it is necessary to diagnose VSD in order to exclude other disorders of the body and identify which part of the child’s autonomic nervous system is disturbed
- Depending on the symptoms, history of the child’s life and development, medical testing and analysis, and taking into account other factors, the doctor diagnoses VSD
It can be difficult to identify VSD in a child.
Causes
The first manifestations of vegetative-vascular dystonia in a child may appear in the first year of life. The causes of dystonia in infants include disturbances in intrauterine development, difficult pregnancy, and negative external influences after birth.
The following signs of VSD appear at the age of 2-3 years. This period is difficult for a child psychologically, because... he begins to go to kindergarten and communicate with strangers without the support of his parents. The situation is aggravated by the fact that the body's defenses are reduced due to frequent infectious and colds in the first year of attending a preschool institution.
Often, signs of vascular dystonia in children appear at the age of 4-6 years, when they categorically refuse to go to kindergarten or developmental sections.
In children of primary school age (7-12 years old), VSD occurs against the background of intellectual and physical stress on a fragile psyche. The child begins to eat improperly, his sleep patterns are disrupted, and psychological pressure is observed from teachers and parents. Also, the causes of vegetative-vascular dystonia include problems communicating with peers and receiving a large amount of new information.
VSD of puberty (12-16 years) is caused by various reasons:
- hormonal changes in the body;
- psycho-emotional stress;
- overwork;
- bad habits;
- chronic diseases.
Important information: Why does a lump appear in the throat during VSD and how to relieve the spasm

In addition, VSD in adolescents during puberty can occur due to endocrine diseases, changes in place of residence, and temperamental characteristics.
How to treat vegetative-vascular dystonia in children?
This disease can be treated with both medication and non-drug methods, but, first of all, the child needs to change his daily routine. For this:
- Parents must ensure that the child sleeps enough time. For children under 1 year of age, the sleep norm is on average 14 hours a day, children under 5 years of age need to sleep 13 hours, a primary school child - 12 hours, a seven-year-old child should sleep at 10 - 11 o'clock, a ten-year-old child - 10 hours, and a teenager can sleep 9 hours
- You should put your child to bed at the same time as you should wake him up in the morning, even on weekends.
- Outdoor walks are required in any weather, at least 2 - 2.5 hours a day
- Compulsory physical education is shown, in sports sections, in the pool
- It is necessary to normalize nutrition. Particular attention should be paid to the intake of vitamins into the child’s body, preferably in the form of fresh juices, vegetables and fruits
- The child’s diet must, if possible, every day, contain meat or fish, as well as fermented milk products

Therefore, in order to avoid the occurrence of VSD and its treatment, adolescents urgently need to change their daily routine.
IMPORTANT: Sometimes psychotherapy, acupuncture, massage, and herbal medicine are used as a non-drug treatment for VSD in children.
- Among herbal remedies, hawthorn with its cardiotonic effect and motherwort extract, which calms the nervous system, are recommended
- You can also recommend taking taurine for a positive effect on the child’s nervous and cardiovascular systems.
- Medications for the treatment of VSD in children are prescribed on the recommendation of a doctor individually, taking into account the characteristics of the child
Prevention
Vegetative-vascular dystonia in little girls and boys causes unpleasant symptoms and often interferes with a full life. In this regard, it is necessary to engage in the prevention of this disease from an early age. Parents play an important role in this. A child should always feel care and love from loved ones.
If disagreements and conflicts arise in the family, you should not show them to your children. Children always react negatively to parents’ quarrels, which is fraught with the development of depression and stress, and these are common causes of vegetative-vascular dystonia. In addition, it is necessary to ensure that the child leads an active lifestyle, eats rationally, walks outside more, and does not overload.
During pregnancy, the expectant mother needs to be especially careful about her health. Carrying a child should not be combined with frequent stress, anxiety, smoking, drinking alcohol, or physical strain.
At the first signs of VSD, you should contact your pediatrician as soon as possible. At the first stage, it is much easier to get rid of the symptoms of the pathology without developing consequences that interfere with the normal functioning of the child.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia in a child under one year old
In infants, VSD can manifest itself due to the characteristics of intrauterine development and development during the perinatal period, the course of pregnancy in the mother, as well as external factors. All this can lead to minor dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system.

The baby has a tummy ache. It could be colic or VSD!
VSD in children under 1 year of age can be expressed by symptoms that are difficult to distinguish from the symptoms of other diseases. For example:
- baby has a tummy ache
- he has frequent regurgitation
- unstable chair
- shallow sleep with frequent awakenings
- weak appetite
VSD in babies can also manifest itself in allergic reactions to both mother’s milk and external food products. A symptom that will reveal the picture of VSD more clearly will help to rule out a problem with the baby’s stomach and intestines - a violation of thermoregulation and uneven breathing. The baby’s arms and legs may be cold in normal temperature conditions, which will already indicate a violation in the vegetative system.
Prevention of VSD: drugs
Both for the treatment of VSD in the initial stages of development and for the prevention of this condition, drugs from the following groups of pharmacological agents are most often prescribed:
- vasodilators;
- tranquilizing;
- sedatives;
- antidepressants;
- nootropics;
- normalizing blood circulation;
- normalizing blood pressure levels;
- sleeping pills and restorative drugs.
Prevention and treatment of VSD directly depend on subjective symptoms. That is, from those complaints that the patient himself voices to the treating doctor.
- If you have problems with sleep, Melatonin, Donormil, Afobazol, Atarax, Phenazepam, Phenibut will probably be prescribed.
- If the patient complains of severe anxiety, panic attacks and dizziness - Adaptol, Atarax, Sonapax.
- In case of pronounced heart problems - arrhythmia, tachycardia, etc. (after the doctor is convinced that there are no serious cardiac diagnoses), Betaserc, Valoserdin will be prescribed.
- With constant complaints of lack of vitality and bad mood, accompanied by palpitations and tearfulness, Fluoxetine, Zoloft, Paroxetine, Stimuloton will probably be prescribed.
Injectable nootropic peptides of the new generation - Cortexin and Cerebrolysin - have shown high effectiveness in improving cerebral circulation.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia in a 5-year-old child
Data indicate that fifteen or even more children out of a hundred have VSD, which means that one or another organ is functioning inadequately, with a violation of the mechanisms, or rather, it is malfunctioning in its work.
If a child is 5 years old and does not go to kindergarten, but is often sick, he may have VSD.
Parents should pay attention to:
- frequent colds in the child, perhaps their cause is not at all the situation in the kindergarten
- the so-called temperature “tail”, that is, when the disease that caused the temperature has already been cured, but the temperature of 37.1 – 37.2 persists for a long time
- enuresis
- frequent mood swings in a child
- lethargy and apathy
- reluctance to go to kindergarten for no reason
- the child’s breathing and heart rate, and the presence of shortness of breath
Accordingly, it is necessary to take the child to the doctor in order not only to establish a diagnosis, but also to exclude unwanted organic disorders in the child’s body.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia in a 7-year-old child
- 7 years is a very serious and responsible age in a child’s life. He is already a schoolboy, and is already responsible for his lessons and grades
- This is a lot of stress for the child’s nervous system, which is aggravated by the necessary daily routine, being at school, and restricting motor freedom.
- The child gets really tired and tense, which leads to a bad mood and organ failure
- During this period, parents should carefully look at the child, but not focus his attention on his mood and condition, but try to switch him, distract him with an interesting subject, take a walk with him
- It is also important to adhere to a daily routine and diet, as well as a study and walking routine, as mentioned above.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia in a 10-year-old child
VSD in ten-year-old children is associated with the main reasons that cause VSD in all children - inconsistency, imbalance between physical, mental, psychological and nervous stress, lack of oxygen, external factors, such as the family situation, etc.

Workload at school, lack of time for walks and rest are the causes of VSD in children aged 10 years.
As always with VSD, the child is advised to have a rational daily routine, psychological comfort, sufficient time in the air, and physical activity.
VSD in children: symptoms and treatment, causes at different ages
From this article you will learn the features of the course of vegetative-vascular dystonia in children, how this disease manifests itself in childhood (3–12 years). Effective conservative and traditional methods of treatment, prognosis for recovery, and preventive measures are described.
Author of the article: Alexandra Burguta, obstetrician-gynecologist, higher medical education in the specialty “General Medicine”.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is a pathological condition of the nervous system, which entails a disorder of other important organ systems: cardiovascular, endocrine, nervous, digestive. According to statistics, every 4th child aged 3 to 12 years is susceptible to this disease. But doctors are confident that in fact more than half of young schoolchildren suffer from symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia. The insidiousness of this pathology lies in the extremely complex clinical picture: the variety of seemingly unrelated symptoms significantly complicates the diagnosis of the disease.

Click on photo to enlarge
The danger of vegetative-vascular dystonia in childhood is the increased risk of developing severe complications:
- complex psychosomatic diseases (hypertension, ulcers, cholelithiasis, pancreatitis, obesity, cardiac dysfunction);
- psychological and physical disorientation of the child in society and space;
- periodic crises - a temporary exacerbation of symptoms (a sharp deterioration in the physical well-being and emotional state of a small patient).
This disease can be treated by a pediatrician, neurologist, or cardiologist.
From this article you will learn the features of the course of vegetative-vascular dystonia in children, how this disease manifests itself in childhood (3–12 years). Effective conservative and traditional methods of treatment, prognosis for recovery, and preventive measures are described.
Diagnostic measures. Which specialist should I contact?
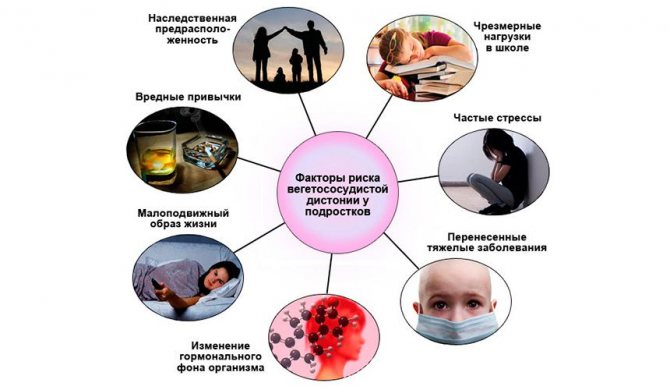
Risk factors for vegetative-vascular dystonia in adolescents
The first thing parents need to do when identifying any symptoms in their child is to consult a doctor, in this case a pediatrician. Based on the medical history, examination and assessment of the results of basic studies (electrocardiogram, general urine and blood tests), the specialist will refer the patient for further examinations to clarify the diagnosis of VSD and prescribe adequate treatment. The following doctors may be involved in the diagnosis and treatment of the disease:
- endocrinologist;
- neurologist;
- ophthalmologist;
- cardiologist;
- otolaryngologist;
- gastroenterologist;
- urologist;
- psychotherapist.
Comprehensive diagnosis of the disease may include the following methods:
- blood test for hormones;
- ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland;
- blood pressure monitoring;
- electrocardiogram;
- ultrasound examination of blood vessels located in the brain;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- vegetative tests.

Symptoms of VSD in children 7-12 years old
A complete diagnosis allows you to select the most appropriate treatment that will most effectively relieve the disease.
- massage;
- acupuncture;
- magnetic laser treatment;
- electrosleep;
- water procedures;
- electrophoresis;
- phytotherapy;
- aromatherapy.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia in a 16-year-old teenager
A special problem in the issue of VSD is teenagers, in whom, due to a discrepancy in the pace of physical and mental development, increased hormonal activity, VSD can be a frequent occurrence.
Adolescents are the main risk group for VSD. The problem is also aggravated because the school load can be very heavy, the teenager does not have enough time to complete all school assignments, and he may stay up late.

Hormonal changes in adolescents can cause VSD.
- Computers also play a negative role in this, taking up a lot of the child’s time and energy, distracting him from walks and an active lifestyle.
- The content of information consumed by a teenager on a computer also often has a negative impact on his fragile psyche - violence, shooting games, negative and stressful events happening in the world, the desire to meet imposed standards, etc.
- Also, problems with the autonomic nervous system in adolescents may be associated with difficulties in relationships with teachers and other adults, with peers and classmates. It is important to find the reason and try to tell the young man a way out of it