Horner's syndrome (or oculosympathetic syndrome) is a pathology of the autonomic nervous system caused by a violation of the sympathetic innervation and accompanied by damage to the oculomotor nerve, which is responsible for the movements of the eyeball, the reaction of the pupils to light and the raising of the eyelid.
The disease itself is not dangerous. But if it indicates a serious pathology, it requires careful diagnosis and adequate treatment.
Etiology and pathogenesis
Diseases manifested by Horner's syndrome:
- Oncological diseases: malignant and benign tumors of the lungs, brain, thyroid gland, neuroblastoma, neurofibroma, lymphoma, metastases;
- Vascular pathology: dilation of the veins of the neck, limited intraluminal dilatation of the aortic vessel, insufficiency of the vertebrobasilar artery, underdevelopment of the internal carotid artery;
- Blunt or surgical neck trauma, traumatic brain injury;
- Inflammatory diseases: otitis media, mediastenitis, inflammation of the upper ribs and cervicothoracic spine, severe osteoarthritis of the neck with bone spines,
- Systemic diseases: neurofibromatosis, demyelinating disease of the central nervous system, pathologically rapid fatigue of striated muscles;
- Endocrinopathies: diffuse toxic goiter;
- Diseases of the nervous system: blockade of the nerve plexuses of the neck, meningitis, arachnoiditis, encephalitis, inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, formation of cavities in the spinal cord, blockage of the cavernous sinus by a thrombus, severe and painful headaches;
- Intoxication of various origins: alcoholic, medicinal, food.
Horner's syndrome in neurology is characterized by total damage to neurons going along the optic canal to the eyes from the medulla oblongata. Pathological innervation of the eye muscles is caused by a violation of impulse transmission along nerve fibers. Horner's syndrome affects the nerve centers responsible for heart function, pupil size, sweat production, blood pressure and adaptive functions that allow the body to adapt to changes in the environment.

Causes of pathology in children:
- The congenital type is caused by a violation of embryogenesis. It accounts for 50% of all cases of Horner's syndrome in children. Its causes are usually: birth trauma, nasopharyngeal neoplasms, central nervous system tumors, intrauterine infection.
- There are known cases of a relationship between congenital Horner's syndrome and varicella-zoster virus and cytomegalovirus infection. These microbes have a tropism for nervous tissue, which contributes to the appearance after birth of characteristic signs of oculosympathetic syndrome.
- The acquired form in infants is a consequence of the use of special obstetric devices: rotation of the fetus, difficult birth of the shoulder, application of obstetric forceps during obstetrics, vacuum extraction of the fetus.
- The eye muscles can completely lose their contractile ability if the sympathetic innervation is disrupted, provoked by surgery on the baby’s chest to correct a congenital heart defect. This is an iatrogenic variant of the pathology, in which the nerve pathways and ganglia are affected, which is manifested by a characteristic symptom complex.
Horner's syndrome
Horner's syndrome is a complex of symptomatic manifestations that occurs due to damage to the nervous system.
Characteristic signs are ophthalmological disorders, failure of sweating, and vascular tone.
Visually it is impossible not to notice the presence of pathology. Treatment is carried out using plastic surgery and physiological therapy.
Causes
The main reasons for the development of this syndrome:
- the presence of benign or malignant tumors that affect the respiratory organs, brain, thyroid gland;
- dysfunction of blood vessels - varicose veins, pathological structure of the carotid artery;
- traumatic brain injuries and neck injuries (may occur during surgery);
- inflammatory diseases – otitis media, sinusitis;
- presence of systematic diseases;
- goiter, pathologies of the endocrine system;
- diseases of the nervous system;
- any type of intoxication.
Horner's disease has a neurological etiology. Accompanied by complete damage to the neurons that lead to the optic nerve. Pathological lesions lead to disruption of the transmission of impulses to nerve fibers. In addition, this syndrome leads to heart damage, impaired sweating function, and increased blood pressure. It is difficult for a person to adapt to the environment.
The etiology of the syndrome can be determined only after examination by several specialized doctors. Initially, the reasons that led to such consequences should be eliminated. Then the doctor prescribes therapy to eliminate the symptoms of this pathology.
Risk group
The risk group includes patients who suffer from thyroid diseases. Any violations, especially if not treated in a timely manner, can cause the development of such a syndrome. There is a potential danger for people who abuse alcohol and drugs.
Patients of different age groups are at risk of encountering this disease. Pathology in rare cases can be inherited. The risk can only be reduced by timely and correct treatment of various diseases.
In children, visual organs develop with age. Therefore, they are more susceptible to the development of ophthalmic diseases. In order to reduce the risk, you should visit an ophthalmologist 1-2 times a year.
Symptoms
To determine the presence of such a syndrome, a visual examination is sufficient. In most cases, the lesion occurs unilaterally. The severity of the manifestations often leads to the development of complexes about the patient’s appearance.
Characteristic symptoms:
- ptosis of the upper or lower eyelid;
- impaired visual acuity;
- narrowing and asymmetry of the pupils;
- impaired photoreaction;
- the pupils slowly adapt to changes in lighting;
- lack of eye reaction to the use of medications;
- hardening of the eyeball;
- decreased or complete absence of sweating on one side of the face;
- red color of the affected eye;
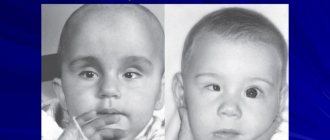
- difference in eye color in pediatric patients;
- chaotic placement of color pigments;
- dry eye syndrome;
- the affected part of the face sags;
- doubling of objects before the eyes.
The disease is accompanied by characteristic signs that will help diagnose the presence of this pathology. Even the presence of 1-2 symptoms may indicate the presence of this syndrome. Therefore, if there are suspicions, you should consult a doctor. Timely diagnosis will help avoid the development of complications and severe forms.
Doctors share another form - this is an incomplete syndrome. In this case, characteristic symptoms are completely absent. This leads to the danger of this pathology.
Only an experienced ophthalmologist can diagnose this type of syndrome. It is difficult to cure any form of this syndrome. Initially, the doctor must determine the cause of its development, and then prescribe treatment.
Efficiency is observed when using minimal electrical currents.
Complications
This pathology can be accompanied by various complications. Especially in the absence of therapy. Against this background, inflammatory processes often develop, which lead to such diseases as keratitis, blepharitis, conjunctivitis. To eliminate them, ophthalmic drops and ointments are used. In severe cases, antibiotics may be necessary.
The presence of this syndrome leads to dysfunction of the lacrimal gland. Often its dysfunction and the development of xerophthalmia may appear. There is a constant risk of infection.
Particularly serious complications are the formation of phlegmon and orbital abscess. Mostly they arise due to improper treatment or its complete absence. Most patients experience the development of secondary hemaralopia.
Standard therapy does not have the desired result.
Untimely treatment of any disease leads to the development of a chronic form and negative consequences. The presence of one pathology can lead to damage to other organs. The risk of such events can only be reduced with proper treatment. Also, special attention should be paid to a healthy lifestyle and disease prevention.
Poor vision significantly worsens the quality of life and makes it impossible to see the world as it is.
Not to mention the progression of pathologies and complete blindness.
MNTK "Eye Microsurgery" published an article on non-surgical restoration of vision up to 90%, this became possible thanks to...
Read more Was this article helpful?
Rate the material on a five-point scale!
( 1 5.00
Source: https://proglazki.ru/bolezni/sindrom-gornera/
Types of Horner's syndrome
Depending on the origin, Horner's syndrome has the following types:
- Primary – it is also called idiopathic. The disease occurs without connection with abnormal processes and is an independent pathology.
- Secondary – occurs as a result of various pathologies. So, the cause of the problems may be a stroke.
With the development of Horner's syndrome, disturbances are observed at the level of different neurons:
- damage to the first neuron - occurs as a result of transverse dissection of the spinal cord;
- damage to the second neuron – associated with a tumor formation that compresses the sympathetic nerve pathway;
- pathology of the third neuron is caused by damage to motor fibers.
The main cause of the pathology is considered to be a disruption in the functioning of a certain part of the sympathetic nervous system. According to statistics, the area of the brain that takes part in the functioning of the visual channels usually suffers.
In this case, the following categories of causes of Horner's syndrome are conventionally distinguished:
- congenital disorders of sympathetic fragments of the nervous system;
- disorders resulting from other pathologies;
- anomalies associated with medical procedures or treatment protocols for a disease.
Sometimes the disease is congenital. It is caused by the development of pathologies that arise during the formation of the embryo or is a complication of childbirth.
The main causes of Horner's syndrome in a newborn child include the following:
- application of forceps during childbirth;
- late birth;
- vacuum extraction of the fetus;
- congenital chickenpox;
- difficulties at birth of the shoulder;
- traumatic injuries and formations in the nasopharynx;
- hereditary predisposition;
- cytomegalovirus.
Most often, the syndrome is associated with pathologies that provoke its appearance. Usually its occurrence is caused by diseases of the central nervous system.
However, other violations also cause problems:
- inflammation of the nervous system;
- traumatic brain injuries of varying degrees of complexity;
- aortic aneurysm;
- disorders of the endocrine system associated with the thyroid gland;
- traumatic injuries of the cervical spine;
- otitis;
- cluster headaches;
- malignant tumors in the brain;
- chronic alcohol intoxication;
- stroke;
- inflammation of the trigeminal nerve.
Also, the appearance of the syndrome can be caused by medical procedures. So, the cause of the problems is surgical intervention, which is required according to the treatment protocol. It is usually caused by surgery on the brain or upper spine. In this case, the nature of the syndrome is iatrogenic.
Symptoms of Horner's syndrome
The development of the disease usually affects only one part of the face.
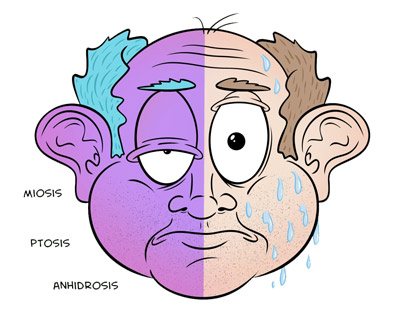
Symptoms of Horner's syndrome are the following:
- drooping eyelid;
- reduction in pupil size;
- decreased sweating on the affected side;
- anisocoria - more pronounced in dim lighting, since a narrow pupil dilates less than a wide one;
- moderate ptosis.
The eye appears to be set deep into the orbit. In this case, endophthalmos is slightly expressed. The clinical picture is aggravated by narrowing of the palpebral fissure. With this diagnosis, there is a sharp disturbance in the secretion of tears. Sometimes the eye feels wet.
Persistent miosis leads to deterioration of dark adaptation. People with this diagnosis report worsening vision at dusk. At the same time, visual acuity is maintained. As the disorder develops in children, the iris on the affected side acquires a lighter shade.
Diagnosis of Horner's syndrome
It is not difficult to identify this violation. The diagnosis can be made by examining the patient. It is more difficult to determine the disease that provoked the syndrome. Therefore, after examining the patient and studying the medical history and clinical picture, he is prescribed laboratory tests and instrumental procedures.
The main diagnostic tests for Horner syndrome include the following:
- General urine and blood tests, biochemistry.
These studies at the initial stage of diagnosis help determine the nature of the disease - inflammatory or oncological. - X-ray of the chest organs.
This procedure helps eliminate abnormal processes in the chest. It also helps to eliminate degenerative processes in the spine. - Magnetic resonance and computed tomography.
These are modern imaging methods that help exclude the tumor nature of the syndrome. - Examination by an ophthalmologist.
It must be accompanied by ophthalmoscopy. The doctor also measures intraocular pressure. - Injection of special drops containing cocaine into the affected eye.
This technique helps identify Horner's syndrome. In a normal state, the introduction of such drops provokes pupil dilation. If a person has such a diagnosis, pupil dilation does not occur. - Paredrin test.
The procedure helps to carry out topical diagnostics. It allows you to detect lesions of a specific anatomical structure. The anomaly is associated with damage to one of the three neurons that include the sympathetic fibers of the lateral horns. If the third neuron is not involved in the abnormality, injection of paredrin into the affected eye provokes pupil constriction. If the third neuron is damaged, the pupil does not constrict.
The syndrome does not cause death. However, in combination with other complex pathologies, it can cause dangerous complications.
Most often, the pathology manifests itself in a mild form and does not cause discomfort. Active therapy is necessary as the disease progresses. The choice of treatment for Horner's syndrome depends on the severity of the disease.
With a simple course of the disease, it is enough to carefully choose the means depending on the patient’s medical history. It is strictly forbidden to prescribe medications yourself.
If eliminating the provoking factor does not lead to positive results, it is worth using narrow-profile methods that affect the nervous system. Neurostimulation can be used if necessary.
It works with the affected muscle tissues, applying a weak current voltage to them. The manipulation must be carried out by a highly qualified specialist. When performing the procedure, there is a risk of severe pain.
With an aggressive course of the disease, there may be a need to use plastic surgery methods. The specificity of the pathology often leads to damage to parts of the face and distortion of the localization of the eyeball. In such a situation, there is a need for a serious change in the patient’s appearance.
Often, in case of pathology, a special massage is prescribed. It activates the functions of those parts of the sympathetic nervous system in which abnormalities have been identified.
If the causes of the pathology cannot be eliminated, it may have an unfavorable prognosis. If the provoking factor is hormonal imbalance, the use of hormonal drugs helps eliminate all symptoms of the disease.
Horner's syndrome in cats and dogs
Pathology can occur not only in humans, but also in animals. As a result, owners are often forced to consult a veterinarian-ophthalmologist with complaints about changes that occur in their pets' eyes. The appearance of a bulge in the third eyelid or the occurrence of hyperemia indicate symptoms of conjunctivitis or other inflammation.
Horner's syndrome in dogs and cats manifests itself in the form of a recessed eyeball. This disease is characterized by a small pupil, a raised third eyelid and drooping upper eyelid. In this case, the behavior of the animal practically does not change. He does not experience pain or discomfort.
There is a breed tendency to develop the syndrome. 90% of cases occur in Golden Retrievers. Second place goes to the cocker spaniel.
Pathology occurs when a certain part of the sympathetic nervous system is damaged. The brain or spinal cord may be damaged. However, most often the damage is localized along the sympathetic nerve. This may occur in the chest, in the neck area, behind the middle ear, or under the front leg.
Provoking factors for the development of Horner's syndrome in animals include the following:
- damage in the cervical area - it can be caused by bites of other animals or surgical intervention;
- otitis media;
- neoplasms – the cause of the problem is lymphosarcoma;
- disturbances in the functioning of the vestibular apparatus;
- damage to the brachial plexus and traumatic injuries in this area;
- retrobulbar damage.
Hormonal imbalance can also lead to Horner's syndrome. The provoking factors of the disease are hyperadrenocorticism and hypothyroidism.
To identify the presence of the syndrome in a dog or cat, you should pay attention to the characteristic manifestations. It is of no small importance to identify the site of damage to the sympathetic nervous system. To do this, phenylephrine is injected into both eyes.
Rapid dilation of the affected eye and slow dilation of the healthy eye indicate pathology along the nerve directed from the cranial cervical ganglion to the eye. If the nerve from the brain along the thoracic trunk is affected, the pupil dilates within 1 hour. The same reaction is observed in a healthy pupil.
When neurons are damaged from the thoracic trunk to the cranial cervical ganglion, pupil dilation occurs within 45 minutes. In the postganglionic region this occurs within 20 minutes.
To cope with the disease, you need to clearly establish the causes of the disease. All lesions are divided into 2 categories - postganglionic and preganglionic. In the second case, the animal's behavior is easier to control.
For the postganglionic form of the disease, phenylephrine drops are prescribed. Relief is achieved after 1.5-2 months. The preganglionic type of the disease requires a more thorough examination. In this case, radiography of the spine and tomography are performed.
Complications of Horner's syndrome
With complications of Horner's syndrome, various inflammations may appear in the anterior segment of the eye. These include blepharitis, keratitis, conjunctivitis. A change in the topography of the eyeball in relation to the lacrimal gland provokes its dysfunction. This causes xerophthalmia.
When the eye retracts into the orbit, infection can occur. In difficult situations, there is a possibility of phlegmon appearing. Subperiosteal orbital abscess may also occur. In most cases, secondary hemeralopia occurs. It cannot be cured using standard methods.
Prevention of Horner's syndrome
There is no specific prevention for Horner's syndrome. Nonspecific methods boil down to timely detection and treatment of pathologies of the ENT organs and thyroid gland. Correction of hormonal levels is of no small importance. If there are space-occupying formations in the orbit, the person should be registered with an ophthalmologist.
Horner's syndrome is a serious pathology that can lead to negative health consequences. To cope with the disorder, you need to consult a doctor in a timely manner and follow his recommendations.
Source: https://oftalmologiya.info/zabolevaniya-glaz/220-sindrom-gornera.html
Symptoms
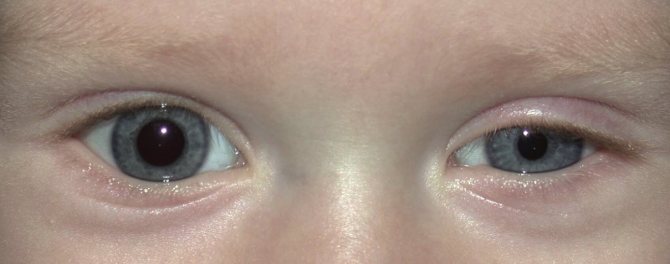
The main symptoms of the disease can be seen with the naked eye. Most often they are determined on one side of the face.
- Ptosis of the upper eyelid and “inverted ptosis” of the lower eyelid reduce the size of the palpebral fissure.
- Difficult visibility, blurred vision.
- Constriction of the pupil.
- Anisocoria – different pupil diameters.
- Decreased photoreaction of the pupil.
- Slow adaptation of the pupil to varying degrees of illumination.
- Lack of pupillary response to various medications.
- Recession and flattening of the eyeball.
- Decreased sweat production on one side of the face or its complete absence.
- Dilatation of conjunctival vessels, red color of the eye.
- Different colors of the iris in children.
- Uneven distribution of color pigment across the iris.
- Hypoproduction of tears on the affected side.
- Increased accommodation or its paralysis.
- Dry eye syndrome.
- Haggard appearance of the face from the affected side.
- Diplopia is double vision.
Horner's syndrome is manifested by specific clinical signs, by which it is easy to determine the presence of this pathology in a person. The presence of at least two symptoms from the list above indicates this disease.
There is a separate form of the disease - incomplete Horner's syndrome, characterized by the absence of typical symptoms. Only a highly qualified ophthalmologist can diagnose this disease.
See also[edit | edit code]
Anisocoria Petit syndrome - reverse Horner syndrome
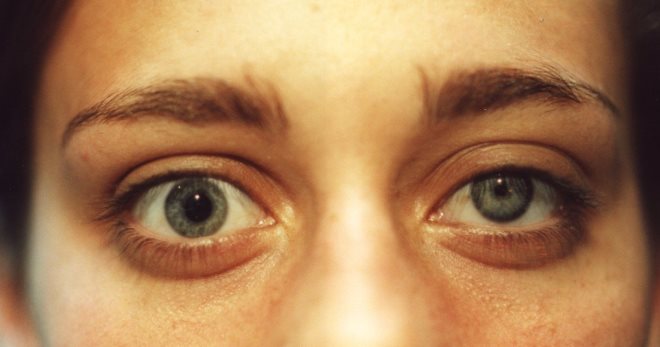
Horner's syndrome is a complex symptom complex associated with damage to the human sympathetic nervous system. The disease leads to disruption of the visual apparatus and vascular system. In some cases, the appearance of the syndrome may be a sign of malignant lung tumors or neck lesions.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of Horner's syndrome begins with a direct visual examination of the patient. The doctor studies the obvious symptoms of the pathology and collects a detailed medical history. Physical examination consists of palpation of the supraclavicular lymph nodes and thyroid gland.

Then they move on to specific diagnostic techniques that will accurately identify the disease.
- Ophthalmologists instill mydriatics into the eyes - “Midrimax”, “Irifrin”, “Cyclomed”. Under the influence of these solutions, the pupil dilates in healthy people. If this does not happen, then there is a pathology in the body. The specialist compares the reaction of the pupils and determines the condition of the patient’s nervous structures.
- Determining the adaptive ability of the eye to changes in light intensity is another test that confirms the presence of Horner's syndrome. In patients, adaptation of the pupil to varying degrees of illumination is slow.
- Study of the nature of ptosis and its differentiation with inflammation of the oculomotor nerve. Horner's syndrome is characterized by moderate or mild, barely noticeable drooping of the upper eyelid and constriction of the pupil. When the cranial nerves that ensure adequate functioning of the visual analyzer are damaged, ptosis is pronounced and the pupil is greatly dilated.
- CT and MRI of various areas of the human body can reveal the root cause of the syndrome.
- X-ray examination is carried out to detect tumors and determine their location.
- Ultrasound of the vessels of the head and neck.
- General blood analysis.
- Lymph node biopsy and carotid artery angiography are auxiliary methods for diagnosing the syndrome.
The final diagnosis of pathology is made by ophthalmologists and neurologists after a joint examination of the patient.
Treatment
The idiopathic form of the syndrome goes away on its own, without treatment. There is currently no specific therapy for the acquired form of the disease. The symptoms of the pathology noticeably weaken after the elimination of the underlying disease that provoked the development of the syndrome.

The main methods of treating pathology:
- Neurostimulation is the most effective treatment for Horner's syndrome. Electrodes are attached to the skin, through which electrical impulses are sent to the affected muscles and stimulate them. At the same time, blood supply improves and muscle innervation is partially restored. Even weak muscle fibers become prepared for regular exercise. This painful procedure improves metabolism and tones the eye muscles.
- Plastic surgery provides correction of discomfort areas and cosmetic imperfections. Professional surgeons restore the correct shape of the palpebral fissure, eyelids and return the patient to a healthy appearance.
- Kinesiotherapy is a special complex treatment that activates the nerves and muscles of the affected eye. It includes breathing exercises, physical therapy, outdoor games, and massage. These methods allow you to stimulate the affected areas through physical contact.
- Eyelid massage is carried out carefully with a cotton swab soaked in an antiseptic or soaked in tetracycline ointment, albucid. Using light, stroking movements with slight pressure and patting, begin the massage at the inner corner of the eye and end at the outer corner.
- There are exercises that increase the tone of the eye muscles. They are carried out with only the eyes without turning the head. Patients are advised to look up and then sharply down; to the left and then sharply to the right; move your gaze diagonally; look at the phalanx of the finger approaching the nose; roll your eyes in different directions; fix your gaze on a distant object and then on a near object; abruptly close and open your eyes. Such daily exercises, performed for three months, will help strengthen the eye muscles and increase their tone.
Traditional treatment of Horner's syndrome is carried out with the consent of the attending physician. For this, aromatic oils and lifting masks are used. The egg-sesame mask is applied in a thin layer to the sore eyelid for 20 minutes. A paste of raw potatoes is applied to the eyelid, left for half an hour and washed off with warm water.
Horner's syndrome in itself does not threaten the patient's life, but only causes cosmetic defects. Often it is a manifestation of serious diseases of the body. To avoid the development of dangerous complications, it is necessary to consult a doctor as soon as possible. Even minor discomfort in the eyes cannot be ignored. Consultation with an ophthalmologist and neurologist, a comprehensive examination and course therapy will prevent further progression of the pathology.
Preventive measures
It should be noted that the disease, with the exception of cases of congenital pathology, is predominantly acquired. Therefore, there is no universal remedy or preventive drugs for it. As is the case with all muscle-related ailments, you can use homemade masks to strengthen the affected areas, but you should definitely get a doctor’s advice on the use of certain components to avoid a possible worsening of the condition.
Horner's syndrome requires complex diagnostic measures to identify, carefully study the history and determine the degree of disruption of parts of the nervous system, since its manifestation and progressive course may indicate the presence of problems of a more serious nature. And in the presence of diseases that provoked it, it can lead to complications that pose a serious threat to the body. Therefore, at the first suspicion and appearance of the described symptoms of Horner's syndrome, you should immediately consult a doctor and undergo all the necessary examinations, taking into account all possible diseases in your history and hereditary factors.