Primary point pain
Primary punctate cephalgia is rarely a sign of the disease; more often a headache is caused by the influence of external factors.
© shutterstock
Causes
Each person has his own reasons why his head will hurt. Point pain can occur under the influence of :
- changes in atmospheric pressure;
- heavy eye strain;
- overwork.
When a headache occurs in one place due to external causes, people can foresee in advance the moments when a point pain will appear.
Symptoms
People describe the sensation that occurs when primary point pain appears as:
- “injected with a sharp icicle”;
- “missed a current discharge”;
- “an unbearable painful pulsation appeared.”
The duration of the attack is 1-10 seconds, but it hurts so much that afterwards the person feels weakened.
The pain always appears in one place and, unlike migraines or other types of cephalgia, has no warning signs.
Common localizations of point pain are:
- forehead;
- whiskey;
- eye area;
- near the ears.
Usually only one point on the head hurts, less often – several.
Treatment
Despite the fact that the headache is caused by external causes and the resulting symptoms are not dangerous to health, the appearance of pain affects the quality of life. For treatment, people are prescribed to drink in short courses :
- Indomethacin;
- Ibuprofen.
If these drugs and their analogues are ineffective, Melatonin is prescribed, which affects neurohumoral regulation.
Who to contact
Single point pain does not require medical attention. If point pain appears frequently in the head, then you need to visit a neurologist or therapist.
Headache at one point: causes, diagnosis and treatment methods
Headaches vary in intensity and nature. Most often, this condition does not cause people to worry about their health - after all, everyone gets migraines from time to time. Everyone has had this condition at least once in their life. However, migraine does not bring any significant health consequences.
The majority of the population thinks so. This is a mistake - some headache symptoms should alert the patient and cause a visit to a neurologist. Diagnostics is necessary to exclude the appearance of neoplasms. Point pain in the head in one place is a serious symptom that cannot be ignored.
Types of migraine and their causes
Migraine is a neurological disease. We talk about it if the patient complains of recurring headaches. They can be different in nature and intensity. Migraine can be either an independent illness or a symptom of a disease.
In order to find out what disease caused the development of migraine, many diagnostic studies should be carried out. These are CT, MRI, checking the condition of the cervical spine, assessing the functioning of blood vessels, etc.
If your head hurts in one point, this is also one of the manifestations of migraine.
Neurology identifies the following types of migraine:
- Classic (with aura). This type of migraine is characterized not only by a severe headache in the temples or forehead, but also by a so-called aura. It seems to the patient that he sees flickering on the left and right, but when he shifts his gaze, it turns out that there is nothing there. This effect is called “visual aura,” and all patients suffering from classic migraine are familiar with it.
- Regular migraine without aura usually occurs in people aged twenty years and older. The cause of this condition is often osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, pathologies of the cardiovascular system, and mental disorders. A typical migraine is not characterized by pinpoint pain in the head. It is encircling in nature. often the back of the head, the forehead, and the temples hurt at the same time. Or the temple on one side and the back of the head. The top of the head almost never hurts during a regular migraine.
- Ophthalmoplegic migraine is a condition in which the muscles of the visual organs cease to function completely or partially. As a result of this, double vision, ptosis or mydriasis are observed in the developing pain syndrome. This diagnosis is quite rare, and it is treated not only by a neurologist, but also by an ophthalmologist. If the patient notes that pain on the right side of the head (in rare cases, on the left) or in the forehead is accompanied by visual impairment, he may have ophthalmoplegic migraine.
- The retinal form of the disease is accompanied by the appearance of “blind” spots. The patient suffers from the appearance of black areas in the field of vision. This process is accompanied by shooting pain in the back of the head. in some cases, the pain may not be sharp, but aching. For an accurate diagnosis and effective treatment, the patient will have to undergo an MRI of the brain and an electroencephalogram. In some cases, diagnosis may require checking the condition of blood vessels.
- Complicated migraine is characterized not only by headache, but also by visual, auditory, and vestibular disorders. In some cases, an attack of this disease can provoke loss of consciousness. If the condition is complicated by seizures, the patient may have an epileptic seizure. To identify the exact cause of the disease, you should undergo an electroencephalogram and a number of other studies.
Point headache
A piercing headache that suddenly appears at one point is an extremely dangerous syndrome. This condition, depending on the frequency of occurrence and intensity of the sensation, may indicate the following diagnoses:
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- neoplasms of a benign or malignant nature;
- intracranial pressure;
- surges in blood pressure (hypertension or essential hypertension);
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.
These are the main reasons why a headache occurs at one point. The more often discomfort and pain occur, the more likely it is that the patient is dealing with a serious illness.
Feelings experienced by the patient
Before consulting a neurologist, the patient should listen to himself so that during the appointment he can describe as accurately as possible exactly how his head hurts at one point. Feelings may be as follows:
- Sharp and sudden pain, reminiscent of a puncture with a sharp needle.
- Localization of the problem: headache in one point - on the top of the head, in the back of the head or in another place.
- The vision becomes dark when an attack occurs, or perhaps the patient lost consciousness during an exacerbation of a migraine.
- During an attack, the patient observes any shadows, flickering on the left or right, darkening of some areas in the field of vision.
It will also be necessary to clarify how long the attacks last - a few seconds or minutes? The more detailed the patient describes the symptoms to the neurologist, the easier it will be to draw up a clinical picture for prescribing appropriate treatment.
Cluster headache: symptoms
A rarer and more complex manifestation of point headache is cluster cephalgia. Doctors also call it cluster, histamine or Horton’s, depending on the location and nature of the pain. It manifests itself in the following symptoms:
- pain in the temporal artery during the next attack;
- discomfort and pain only on one side (not always), in the temple area;
- cephalalgia can develop at night - and often the patient is forced to wake up from the intensity of the painful sensations;
- the duration of the attack varies - most often it is five to six minutes, but in rare cases it can last for hours before taking the anesthetic;
- swelling of the nasopharynx and lacrimation;
- constriction of the pupils.
A harbinger of serious illness
Cluster cephalgia, in which the patient constantly experiences pinpoint throbbing pain in the right side of the head, may indicate the development of the following diseases and conditions:
- brain tumors of various origins;
- withdrawal state;
- aneurysms;
- hematomas due to traumatic brain injuries and concussions;
- poisoning with certain drugs;
- taking vasodilators (for example, nitroglycerin) or histamine.
Therapy for cluster headaches
Drug treatment may be prescribed by a neurologist after receiving the research results. For an accurate diagnosis, it is often necessary to undergo an MRI of the brain and electroencephalography. If the exact cause of beam cephalgia is not known, until the exact diagnosis is determined, the pain can be relieved with the following medications:
- “Ketorol” is a powerful prescription pain reliever that relieves even the most severe pain ten to fifteen minutes after administration.
- "Moment". The active ingredient of the drug is ibuprofen. It is a fast-acting, effective anti-inflammatory and analgesic medicine. Sold at any pharmacy without a prescription.
- “Citramon” is the most popular and cheapest analgesic, which also contains caffeine. Gives vigor and has a stimulating effect.
With a sharp point pain in the head, most people prefer to take a tablet of a potent analgesic. This approach is questionable: the attack of pain will return, and more than once.
Stopping it every time with pills is wrong.
It is better to undergo a full diagnosis once, find out the cause of the pain and take a course of medications that will eliminate the cause of the disease and prevent recurrence of pain.
Which doctor treats migraines?
In order to permanently get rid of attacks of cluster cephalgia or point migraine, to find out why the back of the head hurts, you should undergo a full examination. By influencing the source of the problem, long-term remission can be achieved.
You can make an appointment with a paid neurologist. But then all the research will be paid.
As a result, the total amount that the patient will have to spend to find out the cause of the pain will be at least twenty thousand rubles (you will need to pay for an MRI of the brain, an electroencephalogram, and a decoding of the result).
You can go a different route and not spend a penny on diagnostics. But this will take more time.
The patient must take his medical insurance card and go to the district clinic, where he will be given a coupon for an appointment with a local physician. He, in turn, will issue a coupon for a consultation with a neurologist.
Already there, after all the complaints have been stated, further treatment will be prescribed and a referral for the necessary research will be issued.
The relationship and difference between point pain and regular migraine
Point cephalalgia is often a component of other types of headaches:
- “Tension pain” is a concept in neurology that arose a long time ago and is still relevant today. It occurs in both men and women due to severe nervous and physical fatigue. It is expressed not only in point cephalgia, but also in the fact that the forehead and back of the head hurt (the localization and nature of the pain changes on average once an hour). At the same time, the patient feels nausea, dizziness, and may lose consciousness. A good night's sleep is often enough to stop these symptoms. If the patient is unable to fall asleep on his own, he should resort to taking a sleeping pill.
- Histamine pain. In 40% of cases it is associated with pain of a primary nature. One type of migraine can act as a harbinger of another and change the patient’s condition. For example, the condition begins as a migraine with aura, and after an hour it develops into an ophthalmoplegic form.
- Cranialgia is a condition that occurs when the trigeminal nerve becomes inflamed. This is a common reason why the back and top of the head hurt. Cranialgia is characterized by lumbago in the form of short-term impulses. Most often, this condition does not require any special treatment and goes away after the inflammatory process of the trigeminal nerve stops.
Advice from neurologists: how to avoid the development of cluster and point pain
A list of simple recommendations that will help prevent the development of migraines of any etiology and diseases that provoke them:
- You need to sleep at least eight hours every night. no matter what problems the patient may be experiencing, no matter what stress he may be experiencing, a good night’s sleep should be a must.
- Good nutrition is the basis of a healthy nervous system. Under no circumstances should you adhere to strict diets and starve yourself - even if the consequences do not appear immediately, they will come over time (the nervous system exhausted by fasting does not forgive such an attitude).
- A sufficient amount of amino acids, vitamins and microelements in the diet.
- The correct reaction to stress is to remain calm in any situation, so that later you don’t think about why your head hurts (the back of your head, the top of your head or your forehead).
- Moderate physical education - do not exhaust yourself with exercises, do not provoke overwork.
Source: https://FB.ru/article/390662/bolit-golova-v-odnoy-tochke-prichinyi-diagnostika-i-metodyi-lecheniya
Histamine (cluster) point headache
The appearance of this type of point pain in the head is more often observed in men.
© shutterstock
Causes
Relatively harmless phenomena such as exposure to cold, bright light or sharp sounds can provoke the development of pain.
But more often the causes of headaches are associated with the development of brain pathologies:
- tumors;
- aneurysms;
- intracranial hematomas.
Point pain may appear after alcohol abuse or while taking certain medications.
Symptoms
A distinctive sign of histamine headache is the long duration of the attack (up to an hour) and the appearance of several painful points on one side of the head.
In addition to pain, a person experiences:
- nasal congestion;
- lacrimation;
- redness of the eye and constriction of the pupil;
- nausea;
- dizziness.
The attack is so severe that after the pain is eliminated, the person needs time to recover.
Treatment
Therapy depends on the cause of histamine pain. If pinpoint pain in the head is caused by an aneurysm, tumor or hematoma, then treat the underlying pathology.
To alleviate the condition that has arisen, it is prescribed:
- analgesics;
- oxygen therapy;
- hormonal agents;
- nootropics.
People with histamine cephalgia are prohibited from taking medications with a vasodilating effect and are recommended to completely abstain from drinking alcohol.
If a hematoma or tumor causes compression of brain structures, then surgery is performed.
Who treats
In case of prolonged point pain, it is recommended to begin the examination by contacting a neurologist, and if you have a headache after a traumatic brain injury, consult a traumatologist.
Headache in one point (left, right): causes, treatment
Almost every person has experienced attacks of cephalalgia (headache).
Pressing, squeezing, boring pain that encircles the entire head speaks of many diseases. Rarely does anyone attach special importance to it if there are no other symptoms. A painkiller tablet eliminates the unpleasant syndrome, and it is forgotten for a long time.
What to do when you have a headache in one spot and you can clearly point to the sore spot?
What are the signs
Specific symptoms of pinpoint pain include:
- It occurs unexpectedly, resembling a needle prick.
- Lasts 1-10 seconds and returns several times a day.
- The sensations are so piercing that they force a person to freeze in one place or wake up from sleep if the attack happened at night.
- It appears strictly in a certain area, but is sometimes capable of wandering.
- Any part of the head can suffer: temples, eye area, ears, frontal lobe.
It has been proven that point pain is not differentiated from symptoms of pathologies of internal organs and is considered primary. This condition can be triggered by bright light, freezing, stress, anxiety, and sudden movements.
In exceptional cases, pain may be accompanied by vomiting, dizziness, lacrimation, and the appearance of spots before the eyes.
Doctors include cephalalgia caused by injuries, bruises, vascular pathologies, and brain tumors as secondary pain.
Pain in the head at one point is not common. According to statistics, no more than 3% of people over 45 experience such sensations. Patients describe it differently.
For some it has the character of a pulsating burning sensation, for others it feels like a flash of light, for others it feels like an icy prick.
Among the causes that provoke wandering point pain are: periodic ophthalmodynia (pain in the eyes), histamine, tension cephalalgia, pain caused by neuritis and migraine.
Periodic ophthalmodynia
Primary ophthalmodynia is localized in the vertex, temporal, orbital region and can manifest itself in several places simultaneously. The exact causes and physical pathologies causing the attacks have not yet been found. A possible factor in its appearance includes vasoconstriction due to constant tension in the muscles of the neck and head. In this case, the brain cells do not receive oxygen in full.
Cephalgia occurs spontaneously and lasts 1-3 seconds without other symptoms, both before and after the attack. The injections are felt where the head hurts during migraine attacks.
Histamine (cluster) cephalalgia
Occurs in 1.5% of the population. An intense headache at one point can bother a person for several months in a row, affecting the area of the temples and eye sockets. The attack lasts from a minute to 3 hours. Pain at night can wake a person. Main features:
- Nasal congestion with mucus discharge.
- Tearing of the eye on the side where the headache hurts.
- Nausea, dizziness.
- Excruciating pain syndrome, after which the patient needs time to recover.
This type of pain can be provoked by strong noise, cold, or bright light. Men are susceptible to cluster pain (about 90% of cases). The causes of such pain may be:
- Brain tumors.
- Aneurysms.
- Hematomas.
- Alcohol intoxication.
- Taking certain medications.
To accurately establish the diagnosis, doctors refer the patient for histamine testing. 0.01 mg of histamine is injected intravenously and wait 3 minutes. If the head does not hurt, then another 0.03 mg is administered. The result will be positive if typical unilateral cephalgia appears.
Tension cephalgia
When a person has a headache in one place, tension pain can be suspected. It occurs due to strong experiences, head injuries, bruises and lasts from 30 minutes to several days, intensifying in the evening. Characteristic features:
- Starts on one side of the skull.
- Manifests itself in the frontal, cervical, and temporal zones.
- The patient feels as if the head is being squeezed all around.
- It can “shoot” in the shoulders, chest, and neck.
- Body muscle tension increases.
Tension pain is similar to a migraine, but with it a person does not react sharply to external stimuli: cold, noise, bright lighting, sunlight. Pain syndrome occurs due to lack of sleep, overwork, and stress.
Neuritis
Inflammation that destroys the structure of the nerves is called neuritis. The disease occurs when:
- Infectious and viral diseases.
- Alcohol abuse.
- Diabetes mellitus.
- Cancerous neoplasms.
- Weakened immunity.
This is a serious disorder that can impair visual acuity, hearing, and intelligibility of speech. Neuritis is always accompanied by point pain in the head. Usually it stings in the head on the side where the inflammation is localized.
Migraine
Migraine is a neurological disorder with unbearable pulsating attacks concentrated in one area of the skull. Women suffer most from migraines. Pain can be caused by:
- Insomnia.
- Sudden change in weather or climatic conditions.
- Taking contraceptives.
- Overvoltage.
- Poor nutrition.
- Drinking alcohol.
You can understand that a headache at one point is caused by a migraine by the pronounced symptoms:
- Headache in one area.
- The painful sensation gradually increases.
- The face turns red.
- On the eve of an attack, the patient may experience circles, zigzags, and dots before the eyes.
- The pain syndrome is felt in the temporal and frontal parts on one side.
- With sudden movement, light, noise, the pain intensifies.
- Nausea or vomiting may occur.
- General weakness and tingling in the limbs appear.
This is a chronic disease transmitted through the female line. Attacks, both mild and severe, can be repeated daily.
Treatment methods
When you have an unbearable headache at one point, doctors advise taking Indomethacin, Melatonin (or Gabapentin). Indomethacin eliminates pain in the head in 65% of patients, relieving muscle inflammation. Melatonin, which regulates the circadian rhythm of hormones, has a beneficial effect on brain function, strengthens sleep, improves memory and concentration.
Important! Prescribing the drug to yourself is strictly prohibited. Only a specialist can determine the course of treatment and dosage. Both drugs have many side effects and contraindications.
Treatment of periodic ophthalmodynia
Typically, primary stabbing pain is not treated, since episodic attacks quickly pass without affecting the patient’s well-being and activity. If the pain recurs frequently, take painkillers to relieve tension. In such cases, the patient needs to undergo an examination in order to find out the cause of the regular occurrence of pain.
Treatment of histamine and tension pain
Acute attacks of histamine cephalgia are relieved by intravenous administration of dihydroergotamines and triptans, which reduce arterial tone and tonic peripheral vessels. A lidocaine solution is dripped into the nasal passage. Oxygen masks and antihistamines have a calming effect.
Tension point pain in the head is treated with antidepressants, since the main cause of its occurrence is stress, anxiety and anxiety. Experts advise patients to take Paracetamol to relieve inflammation, and to do gymnastics, developing the muscles of the neck, chest and shoulders. If therapy does not have a positive effect, muscle relaxants are prescribed.
During an attack, a cold compress is applied to the head to relieve pain. The patient needs to remove allergenic foods (citrus fruits, condensed milk, smoked meats, honey, peanuts) from his diet.
Treatment of cephalalgia with neuritis
You can escape from this type of cephalgia by curing the disease that provokes it. Neuritis is treated:
- Glucocorticoids (Metypred, Decortin).
- Diuretics (hypothiazide, torasemide).
- Vasodilator drugs.
- Vitamin therapy.
- Courses UHF, Ural Federal District.
- Massage, exercise therapy.
Treatment of migraine The stabbing pain in the head goes away if the patient gets enough sleep and rest. Painkillers do not always relieve headaches. They are often taken when the attack is in full swing, and the effect of the drug comes later. Doctors advise to relieve pain syndromes with Papazol, Sedalgin, Nurofen. When prescribing medications, the frequency and severity of attacks are taken into account. A warming bath or hot shower, ventilating the room, maintaining peace, comfort and silence, and rubbing essential oils into the temples help well. An excellent way to eliminate migraines is acupressure, which you can do yourself. For pain in the forehead, gently massage the point above the bridge of the nose for 5-10 seconds. Temporal pain is relieved by simultaneously pressing on 3 points.
- The first is located above the outer edge of the eyebrow.
- The second one is from the top at the base of the ear.
- The third is in the middle of the scalp.
All of them are deep and when pressed accurately, a slight feeling of pain is felt.
Prevention
The appearance of pain in one point of the head is associated with an emotional and mental state. In order to avoid another attack or significantly weaken it, it is recommended:
- Play sports, yoga.
- Sleep at least 7 hours a day.
- Eliminate preservatives and yeast from the diet, which have a vasoconstrictor effect.
- Quit alcohol and smoking.
If a point on your head constantly hurts, you feel discomfort and pronounced discomfort, you should consult a doctor. He will refer you for diagnostics to find out the true cause of the disorder.
Source: https://BolitGolova.info/golovnaya-bol/bol-v-golove-v-odnoy-tochke.html
Migraine
A neurological disease characterized by the appearance of point pain in the head. Emotionally labile women suffer more often; the disease is less often detected in men.
© shutterstock
Causes
Pain in the head is provoked in one place by a local spasm of cerebral vessels. Vascular spasm and the appearance of point pain can be caused by :
- climate change;
- changes in atmospheric pressure;
- poor nutrition;
- smoking;
- alcohol;
- taking contraceptives;
- overwork;
- stress;
- sleep disorder
The trigger for headaches can be a reaction to a sudden bright light or sound.
Symptoms
In most patients, before the onset of point pain associated with the development of migraine, precursors (aura) appear.
There are several types of auras:
- Dots appear before the eyes, which gradually increase in size, turning into circles or zigzag lines.
- “Blind” spots appear and the person cannot read or does not see all the contours of the object. Sometimes spot blindness is so severe that patients see almost nothing.
- Sensitivity is impaired and numbness or goose bumps appear on one side of the body.
- A movement disorder may also occur. This is usually a mild decrease in muscle strength, but there may be short-term unilateral paralysis and paresis.
The duration of the aura is from several hours to a day.
Tension cephalgia
In its manifestations, tension point pain is similar to migraine, but occurs for other reasons and, unlike migraine, has no warning signs.
© shutterstock
Causes
Provokes the appearance of point pain:
- head bruises;
- concussions;
- nervous tension;
- frequent stress;
- chronic lack of sleep;
- overwork.
The main distinguishing feature is that tension point pain in the head never appears due to sharp sounds, bright light or due to the influence of weather conditions.
Symptoms
Point pain appears on one side of the head: right or left and is severe. The duration of the attack ranges from half an hour to several days. Head pain worsens in the evening.
The localized point pain will most often be on the back of the head, but can spread to the temples, forehead and upper part of the neck.
As the attack progresses, the pain spreads to another part of the skull and people complain that the pain “squeezes” the head around the circumference. Painful discomfort increases with movement and muscle tension.
Additionally, the patient may experience pain radiating to the shoulder, collarbone or neck.
Treatment
To relieve point pain and prevent attacks, the following is prescribed:
- Indomethacin and Ibuprofen;
- Melatonin;
- nootropics;
- painkillers.
If the cause is stress or overwork, then taking sedatives and sedatives is indicated.
In addition to medication treatment, patients are advised to get adequate rest and avoid stress.
Who will help
If tension point pain appears after a head injury, then a traumatologist will help. In other cases, it is recommended to visit a therapist or neurologist.
Treatment
During acute point pain in migraines, medications are prescribed to eliminate vascular spasm:
- Papaverine;
- NO-SHPA;
- Platyfillin.
To strengthen blood vessels, vitamin therapy is prescribed.
Who to contact
If the cause of the headache is migraine, then a neurologist will help.
Prevention of throbbing pain on the left side of the head: what should be done?
Prevention of throbbing pain on the left side of the head
Those people who lead a healthy lifestyle, do not abuse alcohol and tobacco, are less at risk of being caught off guard by a throbbing headache. Here's what else you need to do to prevent throbbing pain on the left side of your head:
- Morning or evening exercises
- Balanced diet
- Good rest
- Well-designed daily routine
All this will help you win in the fight against the disease. Don’t forget about regular medical diagnostics, which will help identify the presence of diseases in the early stages.
Worth knowing: If the pulsation in the back of the head or on the left side of the head does not go away, and the intensity of the pain increases and increases, you should immediately seek help from a specialist, even if you are taking painkillers.
After conducting the necessary examination, the doctor will be able to determine the source of discomfort. After all, throbbing pain is often the cause of serious illnesses that, without the intervention of a specialist, are difficult to treat and can lead to unpleasant consequences. Good luck!
Neuralgia of the facial nerve
Damage to the superior branch of the trigeminal nerve may be accompanied by the appearance of pinpoint pain on the forehead or in the eye area.
© shutterstock
Causes
Causes irritation of the facial nerve:
- hypothermia;
- herpes;
- spasm of small vessels on the forehead;
- compression of the nerve root by a growing tumor.
Sometimes the cause of point pain caused by irritation of nerve endings is a disorder of cerebral blood flow or the formation of cholesterol plaques in the cerebral vessels.
Symptoms
With neuralgia, headaches can be unbearable, or they can manifest themselves moderately. Point pain is concentrated in the area of the eyes and forehead and appears in short attacks.
The nature of the pain can be aching or burning. Pain increases when pressing on the forehead or exposure to cold.
Headache on one side - bilateral nerve damage is rare.
Treatment
To eliminate pain, patients are prescribed:
- NSAIDs;
- painkillers;
- ointments with anti-inflammatory action.
© shutterstock
In addition to relieving the combat syndrome, therapy is carried out to eliminate the provoking factor.
If the cause of pain in the head is the formation of atherosclerotic plaques, then the patient is prescribed statins and a diet with low cholesterol is selected.
In case of disturbances of cerebral blood flow, drugs are prescribed to improve blood circulation and eliminate vascular spasms.
Antiviral therapy is indicated for herpes.
Who to contact
A neurologist treats neuralgia, and for herpes, additional consultation with an infectious disease specialist will be required.
Sometimes there are mixed causes of pain in the head, when the appearance of neuralgia provokes an attack of migraine or histamine cephalgia.
First aid for pain
Regardless of the location, nature and cause, you should not endure unpleasant sensations. The examination takes time, but help is often needed here and now . In order to relieve obsessive pain in the left hemisphere, you can use tips to alleviate the situation:

At the first warning signs, you should take a painkiller tablet. Preference is given to antispasmodics - Ibuprofen, Nurofen, Spazmalgon, but analgesics that perform similar functions are also suitable. These include Baralgin and Ketorol.- A cold or hot compress will make the pain less severe.
- Washing and sweet tea or coffee will help get rid of dizziness and nausea. But if you have hypertension, you should avoid strong drinks: they increase blood pressure.
- Sometimes just getting out into the fresh air is enough.
- If the cause is osteochondrosis, you can relieve discomfort with breathing exercises, massage of the back, neck and head.
- A hot shower or warm bath will calm your nerves and relieve emotional stress at the end of the day. Healthy sleep also helps reduce migraine attacks.
- Aromatherapy, if not abused, can work real miracles. A few drops of essential oil of lemon balm, lavender, citrus, pine or mint in an aroma lamp, bath or a special pendant will lift your spirits and relieve your condition.
- In rare cases, when the cause of the illness is eye strain, you can try to get rid of the attack with a special relaxing exercise - palming.
Less common causes of pinpoint headaches
They can provoke the occurrence of point pain:
- Inflammation of the eye socket. In this case, the head hurts and the painful point is localized under the eyeball or near the eye.
- The head may hurt at one point due to the inflammatory process in the lower jaw joint. The pain is localized at the temples and behind the ears.
- Pinching of the occipital nerve due to osteochondrosis. In this case, pain appears in the lower back of the head and at the temples.
- Microstroke and TIA. In addition to point pain, confusion and unilateral motor activity disorder appear.
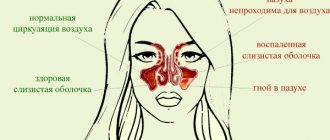
- ENT diseases. Points on the head often hurt due to sinusitis, otitis and frontal sinusitis. Additionally, fever and purulent discharge from the nose or ear appear.
- Psychogenic factor. When people are nervous or stressed, the spots on their heads begin to ache. In this case, pain manifestations do not have a clear localization.
- Furuncle or carbuncle. If you have a headache on the upper left in one place or a similar symptom appears on the right, then the cause may be a boil, invisible under the hair.
- Tumors. Tumors do not necessarily appear on the head; tumors that cause irritation of the nerve roots can be localized in the neck or in the brain.
Pain in the head in one place can occur for relatively harmless reasons (boil or psychogenic factor), or it can be a harbinger of dangerous pathologies.
Do you always need to see a doctor?
Treatment of point headaches is not required when there was a one-time short-term combat attack due to overwork, nervous tension or exposure to travel. If there are no other signs of deterioration in health, then a visit to the clinic is not necessary.
An examination is necessary in the following cases:
- point pain appears several times during the month;
- a painful attack lasts half an hour or longer;
- additionally there is weakness in the limbs, sensory disturbance and/or confusion;
- visual impairment is noted;
- In addition to point headaches, fever appeared.
Point pain in the head is rarely “harmless” - the syndrome almost always indicates the development of neurological abnormalities, less often – diseases of other organs. To prevent the development of life-threatening complications, it is recommended to undergo an examination if painful spots appear on the head.