A cyst in the head is a benign tumor. It is formed after parasites, bacteria and viruses penetrate this area of the human body. A disease with a significant degree of danger, its treatment is associated with quantitative and qualitative indicators. Several tumors can form simultaneously in one area of the brain. Then only an urgent operation can save a person’s life.
A cyst in the head is a benign tumor.
What is a cyst in the brain?
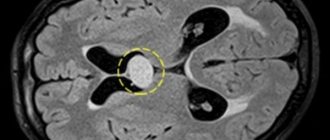
A cyst is a bubble with a liquid substance. The size of a subependymal cyst depends on lifestyle, concomitant diseases, and tumor type. It does not have a specific location. It can be congenital (a newborn is born with a fully formed pathology) and acquired.
A tumor is a bubble with a liquid substance.
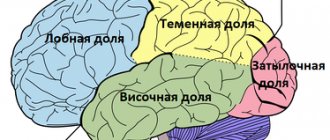
The tumor forms on the surface, affecting the membrane covering the hemispheres. This shell is very delicate and vulnerable, it is easily damaged. The cyst is usually discovered incidentally. A small bubble does not affect the body. A person is unaware of the existence of a problem for months and even years. Signs of multicystic brain disease (several tumors form at once) are much more common.
Classification
The arachnoid cyst, located in the temporal lobe on the left side, can be of two types. Pathology is classified depending on the reason for which it appeared. The primary nature is determined when the cyst is formed during intrauterine development .
For example, it can occur if the mother smoked, drank alcohol and took illegal medications during pregnancy. Also, the primary pathology may be due to a difficult birth, or trauma received during birth.
The secondary type appears due to various pathologies present in the body. For example, it can be caused by various viruses and infections that affect the brain. In a situation where it was the pathology that led to the appearance of the cyst, the neoplasm will be formed from scar tissue. If there is another reason for the occurrence, then the tumor consists of arachnoid material.
Doctors divide cysts into complex and simple . In the first case, the neoplasm is formed from several types of tissue. In a simple type of pathology, the tumor consists of cerebrospinal fluid. It is important to determine the specific type in order to make it easier to prescribe further treatment.
Kinds
During diagnosis, the following types of tumors are distinguished:
- Arachnoid. Located directly on the surface. This is a small bubble filled with liquid substance, stuck between the glued rows of the shell. The tumor forms after a blow to the head or hemorrhage. If the fluid pressure is greater than intracranial pressure, a feeling of discomfort appears.
- Cerebral. The bubble replaces dead brain tissue. The liquid fills the vacated space and penetrates deep into the tissue. The growth of the cyst is provoked by a lack of intracranial blood circulation. The pathology develops extremely quickly. Left untreated, it can lead to vision loss.
Arachnoid and cerebral tumors.
- Choroid plexus cyst of the brain. A harmless tumor that resolves on its own without outside intervention. The beginnings of a tumor are formed during the formation of the brain. It has virtually no effect on his health; it resolves before birth or a few months after it.
- Dermoid cyst on the head. Found in newborns.
The cause of the pineal tumor is echinococcosis and a disrupted process of melatonin excretion.
- Subarachnoid. Congenital formation. Accompanied by convulsions, pulsation inside the skull and gait disturbance.
- Colloid cyst of the brain.
- Retrocerebellar. Has signs and symptoms similar to cerebral.
- Pineal. The cause is echinococcosis and a disrupted process of melatonin excretion.
- Pineal. It occurs in the pineal gland and is a rare type of tumor. The gradually enlarging tumor provokes deterioration of vision and unsteadiness of movements. The tumor causes hydrocephalus and encephalitis.
- Liquor. The tumor forms between the adherent membranes; an increase in its size is accompanied by nausea, vomiting, changes in taste preferences, and convulsions. Some patients experience mental disorders. It is possible to detect a cyst only in an adult.
- Lacunar. Formed during age-related changes.
- Cyst of the intermediate velum of the brain.
- Porencephalic. The cause of formation is infection.
If a tumor is detected, it is recommended to undergo a full examination. Patients with a verge cyst are observed until the tumor resolves.
Treatment
Frozen cystic cavities without progression or cavities in the choroid plexuses do not require special treatment and are periodically observed. For dynamic formations, drug and surgical treatment is prescribed.
Drug treatment
Nootropic and immunomodulatory drugs are widely used.
Traditional therapy includes eliminating the cause of the pathology. Drugs may be prescribed to promote the resorption of tumor walls and adhesions. To restore blood circulation in the affected area, antihypertensive and antiplatelet drugs are prescribed. Nootropic and immunomodulatory drugs are widely used.
Surgical intervention
A radical treatment method in which the cystic capsule is completely removed from the brain.
- Shunting. A drainage tube is inserted into the cavity and the contents are evacuated. The walls fall down and become overgrown. During surgery, there is a high risk of infection of brain tissue.
- Endoscopy. A method of removing tumors through punctures. An instrument is inserted into the skull and the cyst is removed.
- Trepanation of the skull. Effective and long-lasting operation. Allows you to remove large tumors with a complicated course.
Newborns undergo similar operations in the pediatric neurosurgery department, but only if the size of the cyst threatens the development of the child.
Thanks to surgical treatment of cysts, patients avoid most of the negative consequences - mental disorders, headaches, loss of vision or hearing at an early age.
Causes
The likelihood of developing a scalp cyst in an adult depends on:
Receiving a head injury increases the risk of developing a tumor.
- fetal development;
- patient receiving head injuries;
- penetration of parasitic infections;
- drying of brain tissue;
- atherosclerosis;
- proper blood circulation.
The causes of tumor development are encephalitis and meningitis. Its gradual growth is based on:
- prolonged inflammation of the brain;
- increased blood pressure;
- concussion;
- disruption of blood flow;
- experienced a stroke;
- addition of other pathologies to the disease.
The likelihood of developing a tumor increases after a stroke.
If the pathology has developed in a newborn child, then the cause of this phenomenon is sought in:
- Birth trauma. The woman in labor should be provided with professional medical care. The risk of developing intracranial hemorrhage in a child who has passed through the birth canal in an incorrect position or has been injured due to the incompetence of obstetric staff is always very high. Even a minor blow can cause serious pathology.
- Infection of the fetus. The penetration of dangerous bacteria and viruses into the body negatively affects the health of the pregnant woman and the fetus. The consequences are difficult to predict.
Many people are at risk of developing an inflammatory process in the brain. Ideally, even if a person has not hit himself anywhere and has not suffered from anything serious, he is required to undergo an appropriate examination at least once every 5-10 years.
Clinical picture
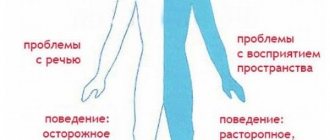
The course of this disease can remain asymptomatic for a long time. The presence and severity of neurological disorders depends on the size of the cyst and the degree of displacement of brain structures.
Manifestations may be as follows:
- Headache;
- Feeling of fullness or pressure in the head;
- Sensation of pulsation in the head;
- Noise in the ear with intact hearing;
- Hearing impairment (sensorineural hearing loss);
- Visual disturbances (double vision, spots before the eyes, etc.);
- Convulsive attacks;
- Swallowing disorders;
- Motor and coordination disorders.
The causes of cysts include bruises and hematomas, congenital disorders, parasitic infections, meningitis, dystrophic transformations, problems with blood circulation in the brain. It is impossible to perform an operation to remove a brain cyst without finding out the true cause of the disease. Even the slightest mistake in making a diagnosis will lead to further inflammation of the meninges and the emergence of new lesions.
Small cysts that are not accompanied by any symptoms are most often discovered during the diagnosis of other diseases. In some cases, they do not require surgical intervention, especially if they do not increase in size over a long period of time. It is enough to monitor your blood pressure, avoid hypothermia, avoid viral infections, and do not abuse smoking and alcoholic beverages.
Symptoms
The intensity of the tumor process and the activity of its manifestation are related to the size of the cyst. A growing tumor puts pressure on the brain and this leads to:
As the tumor grows, headaches appear.
- visual impairment;
- gradual hearing loss;
- headaches (using conventional painkillers is useless);
- insomnia;
- stiffness in movements;
- paralysis (the name of the paralyzed part of the body cannot be determined in advance, it all depends on which part of the brain is affected);
- overstrain of muscle tissue;
- convulsive syndromes;
- loss of consciousness;
- disorders of the nervous system.
The skin becomes less sensitive, the ears are noisy, and the temples are pulsating. Sometimes patients:
- be sick;
- vomits (after vomiting the condition only worsens).
Sometimes patients feel sick and vomit (after vomiting, the condition only worsens).
The limbs may make uncontrolled movements, causing the person to limp. There is a lot of pressure on the head and it is impossible to get rid of the pressure without special medications.
Having problems chewing and swallowing food.
The clinical picture of the disease depends on the location of the tumor. Thus, an intrasellar cyst compressing the cerebellum causes imbalance and affects gait (it becomes unsteady). The patient ceases to control his gestures, his handwriting changes beyond recognition. Compression of the areas of the brain responsible for movement and swallowing leads to problems with chewing and swallowing food and pronouncing certain words.
If the size of the cyst on the brain does not change (the size remains the same for a year or more), then this is a good sign. There is no need to treat such a tumor.
For prevention, the patient must visit a specialist several times a year and be examined.
Possible complications of cyst removal
The negative consequences that develop in a person during or after surgery are almost no different from the possible complications that could have occurred without the intervention. After all, if a cyst breaks through or puts a lot of pressure on the brain, then this provokes one or even several pathologies at once:
- microstroke or stroke;
- multiple sclerosis;
- neuroinfections;
- changes in human behavior due to a mental disorder;
- epilepsy;
- frequent headaches, migraines.
The same can happen after removal of the cyst. But the likelihood of this is much less. After all, preoperative diagnosis also involves calculating risks.
Diagnostics
An accurate diagnosis is established based on one or more of the presented studies:
Doppler ultrasound diagnostics.
- Doppler. The goal of diagnosis is to identify areas of the brain that are not receiving the amount of blood they need.
- ECG. Diagnostics of the cardiac region eliminates any risk from this side.
- Blood test for cholesterol and coagulation. A large amount of cholesterol and a high rate of blood clotting provoke vascular obstruction.
Measuring blood pressure is necessary to exclude the development of a cyst due to a stroke.
- Blood pressure measurement. Necessary to exclude the development of a cyst due to a stroke.
- Blood tests for autoimmune and infectious diseases. Diagnosis is made if arachnoiditis, neuroinfection, or multiple sclerosis is suspected.
Some studies (MRI, ECG) are performed repeatedly. This allows you to track the rate at which the tumor is increasing in size. During diagnosis, a cerebral pseudocyst is often also detected.
What's happened
A cyst is a special cavity that is filled with a liquid mass. This fold is made up of connective tissue containing nerves and blood vessels.
This formation is located in the upper part of the third cerebral ventricle. It usually occurs in utero, that is, a newborn is born with this pathology.
Treatment is usually not required, however, if there is expansion of the cistern velum intermedius, leading to strengthening of the formation, this can lead to constructive hydrocephalus.
Why is a brain cyst dangerous?
A brain cyst left without proper medical attention causes:
- paralysis of the limbs (a person has difficulty walking, driving a car, doing physical exercise, or doing anything around the house);
- deterioration of vision and hearing (negative changes occur gradually);
- hydrocephalus and cerebral hernia;
- porencephaly;
- encephalitis.
Deterioration of vision and hearing (negative changes occur gradually).
An overgrown cyst leads to disability and death of the patient.