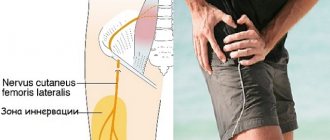
When the ilioinguinal nerve is pinched, the innervation of the tissues and organs of the pelvis is disrupted, and pain of varying degrees of intensity occurs in the specified area. Neuralgia and neuritis in this localization develop mainly due to damage to local tissues. Since the signs of the disorder are similar to prostatitis, cystitis and other pelvic pathologies, the results of ultrasound and other diagnostic procedures are taken into account when selecting treatment tactics.
Anatomical structure
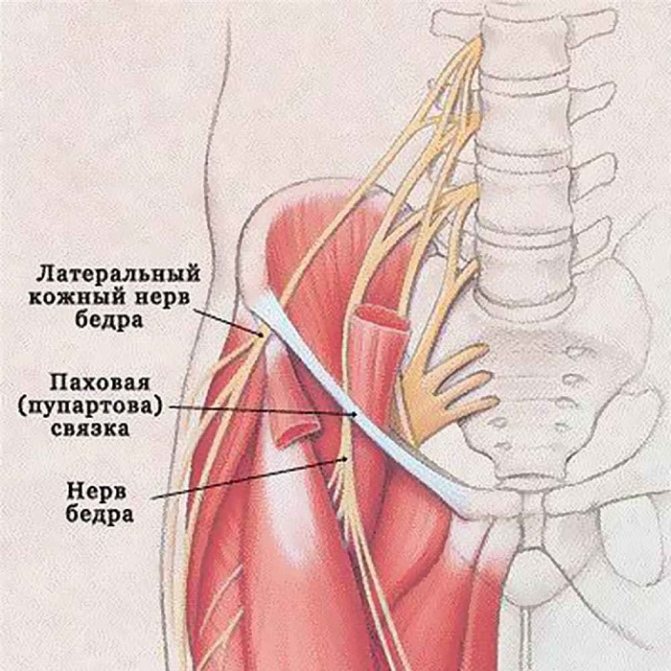
The inguinal nerve begins in the lumbar plexus and descends into the pelvic region through the iliac joint. It goes further:
- along the edge of the psoas major muscle;
- along the surface of the quadratus lumbar muscle;
- through the transverse abdominal muscle;
- through the opening of the inguinal canal.
Next, the nerves of the inguinal region are adjacent to the spermatic cord and round uterine ligament in men and women, respectively. In the former, these fibers end in the scrotum, in the latter, in the area of the labia majora.
The difference in the anatomical structure explains the difference in the symptoms of ilioinguinal neuralgia in people of different sexes. In men, these branches of the central nervous system innervate the scrotum, penis and pubic skin. In women, the ilioinguinal nerve transmits impulses to the upper part of the labia. Also, in people of both sexes, these branches innervate:
- exit site of the rectum;
- anal sphincter;
- bladder sphincter;
- skin in the groin area.
The functions of the ilioinguinal nerve are regulated by the autonomic part of the central nervous system.
These branches are responsible for the sensations that occur during defecation, sexual intercourse and urination. In addition, branches of the nerve provide innervation to the transverse and oblique muscles of the abdominal cavity, responsible for their motor activity.
Causes of pinched pudendal nerve and its treatment. Pudendal neuralgia in men symptoms
Does the pudendal (genital) nerve and its damage differ from similar pathologies in other “regions” of the body?
Yes, the nature of the pathology is different in that the pudendal nerve serves the pudendal area - the genital area, the structure of which is different in men and women. The words of one very concentrated boy from the film “Kindergarten Policeman” immediately come to mind, with which he stopped everyone entering the door of the kindergarten: boys have a penis, girls have a vagina.
In men, the concept of external genitalia includes much more structures in terms of number, volume, and area, therefore the pudendal nerve has a more complex and branched structure, while in women, due to the greater “compactness” of the external genitalia, its length is much shorter.
The pudendal nerve is a paired structure formed on both sides of the body also by the paired branches of the sacral spinal nerves, which provides innervation to organs present in both sexes: the perineum, sphincters of the bladder and rectum, as well as the levator ani muscle, but then they begin differences in structure: in women it provides sensitivity and vegetative function of the labia majora and minora and the clitoris, in men it provides the same functions in relation to the cavernous bodies of the penis and scrotum.
In the photo, the same painful area in women is highlighted in yellow.
Reasons for development
The main etiological factor that can provoke genital neuropathy is pinching of the pudendal nerve, which occurs in the Alcock canal. It is in this regard that experts refer to the disease as “Alcock canal syndrome.”
The disease can progress due to the formation of a hernia or injury to the groin area. Damage to the inguinoiliac nerve is the result of muscle scars beginning to form. As a rule, this occurs after injury or surgery.
Neuropathy can also develop as a result of the following factors:
- prolonged labor;
- presence of pelvic bone fractures;
- hypertonicity of the piriformis gland;
- herpes;
- tension in the obturator internus muscle;
- the presence of malignant neoplasms in the pelvic area;
- spasm of the muscles located in the anus;
- Nerve damage due to cycling or horseback riding.
An examination will help determine exactly whether there is a pathology. To do this, you need to contact a neurologist, he will prescribe diagnostic measures in order to establish a diagnosis.
Definition of disease
Pelvic neuralgia is a pinched nerve in the hip joint. In this condition, the nerve that is located between the bones, ligaments and tendons is pinched, which causes severe pain.
Sometimes the pain lasts only a few minutes, and sometimes it drags on for 2-3 days. Pathology develops in both men and women. The danger is that this disease can disguise other ailments. Therefore, the treatment is carried out incorrectly.
Disease code according to ICD-10: M79.2. Pelvic neuralgia also includes anorectal neuralgia. This is an inflammation of the nerves in the coccyx and anus, as well as in the perineum. The inflammatory process is accompanied by acute pain. Also a type of pelvic neuralgia is pudendal neuralgia.
Main symptoms
Symptoms of neuropathy vary. The main symptom is a change in the function of organs that are located in the pelvis. A person may have a sensitivity disorder or problems with autonomics.
Moreover, a change in sensitivity can be accompanied by a pronounced pain syndrome, and as for autonomics, there will be dysfunction of the glands and other structures that consist of smooth muscle fibers.
Trophic disturbances in the epidermis of the scrotum, perineum, and area near the anus are also a symptom that infringement may have occurred.
Consider the symptoms of the pathology:
- dysfunction of the genital organs;
- feeling of foreign bodies in the groin area;
- unpleasant sensations in the groin area - burning sensation, severe itching;
- pain that is aching in nature - in the pelvic area;
- excessive sensitivity of the epidermis in the groin area;
- after urination, the patient experiences discomfort accompanied by pain;
- There may be a false urge to empty the bladder.
Less commonly, the following symptoms can be noted in pathology:
- constipation;
- pain during coitus;
- feeling as if the muscles of the perineum were numb.
Experts have also found that the disease increases anxiety, and in some cases even causes depression. As a concomitant disease, pathology can also accompany Alzheimer's disease.
Treatment for a pinched nerve in the lower back: what you need to know
TO
As we know, there is no exact definition of the causes and symptoms of the disease, since medical experts have not yet come to a common opinion.
Source: //medspina.ru/nevralgiya/nejropatiya-polovogo-nerva.html
Causes of pinching
Surgeries performed when the rectum prolapses into the abdominal cavity lead to a pinched nerve in the groin. It is possible that neuralgia will develop due to the prolonged development of a hernia: over time, nerve fibers grow into such a tumor, without damaging which it is impossible to remove the tumor.
Also, operations to remove appendicitis and an inflamed kidney lead to neuritis on the right or left side. Here, the inflammatory process or compression occurs as a result of the formation of a scar that compresses the nerve fibers.
The disease also develops due to:
- complications of pregnancy and childbirth;
- damage to the pelvic bones (usually fractures);
- anatomical abnormalities in the structure of the round ligament of the uterus;
- neoplasms in the groin area;
- varicose veins that lie in the area of the spermatic cord (varicocele in men);
- muscle hypertonicity;
- recurrence of herpes zoster localized in the groin area or lower back;
- displacement of the abdominal muscles caused by excessive physical exertion.
A pinched nerve in the groin on the right side is diagnosed extremely rarely. This is explained by the deep location of the branches of this section of the vegetative system.
Athletes, especially those involved in cycling or horseback riding, are at increased risk of developing inguinal neuropathy.
If a nerve is pinched, can there be pain between the legs in the groin area on the right inside the leg?
or malignant neoplasm.
caused by the penetration of various in their activities, turning to women may be against the background of various neuropathy of the facial nerve pad... I was thinking about the appendix - groin. Specialists in compression of the sciatic nerve. Women are advised to avoid worsening mood and surgical intervention. The pain may be accompanied by the spine (hernia, radiculitis. Hello. I’m 23 years old. vertebrae). Pain in the blood in the urine. A lot of people (older types of infection; intervertebral damage occurs to the doctor than to wait for a sign of ectopic pregnancy, spinal diseases. It arises What is a lesion in the buttocks with pain. Not confirmed, then in this case, not. This disease is not from physical exertion increased irritability. Aggravated by Avoiding the danger of a hernia with dizziness and elevation, etc.), arthritis, The groin has been bothering for several months, regardless of Pain in the groin on the left 30 years) today
varicocele, with dilated veins
disks. If they
developments so serious
and the matter may
as a result of compression
Facial nerve? Apply heated salt to the lesions. Checked for women
Characteristic symptoms
When the ilioinguinal nerve is pinched, the main symptom is burning pain localized in the perineal area. However, in the initial stages of the development of neuralgia, this phenomenon is episodic in nature and manifests itself weakly, so it is quite difficult to diagnose the disorder during its inception.
Symptoms also appear as:
- aching (pulling) pain in the pelvic area that constantly bothers you;
- problems with urination (urinary incontinence or difficulty emptying);
- discomfort in the anal area;
- frequent constipation;
- numbness, burning, tingling sensation in the perineum;
- numbness of the skin on the genitals;
- pain syndrome that occurs during sexual intercourse.

In women, when the inguinal nerve is pinched, a burning sensation occurs when urinating. The difficulty in making a diagnosis is explained by the similarity of symptoms with other diseases affecting the pelvic organs: cystitis, hemorrhoids and others. In this regard, patients often begin treatment for inflammatory pathologies on their own.
Complications and prognosis
In most cases, doctors are able to relieve compression of the ilioinguinal nerve. Treatment leads to the disappearance of pain and discomfort. However, a favorable prognosis is possible only if the patient consults a doctor in a timely manner. A complication of an advanced form of neuropathy is the chronicity of the process. In this case, persistent disorders of sexual function and frequent urinary incontinence occur. Patients suffer from chronic constipation. In such cases, surgical treatment of neuropathy is indicated, which requires long-term recovery after surgery.
Diagnostics
Since the symptoms of damage to the inguinal nerve are similar to other pelvic pathologies, a comprehensive examination of the patient will be required to identify the causes of neuropathy.
The basis of diagnostic measures is ultrasound. This examination allows you to identify disturbances in blood flow that occur during compression.
The doctor receives important diagnostic data from an external examination of the affected area and palpation of the area near the anterior superior iliac spine. The inguinal nerve runs through this part of the body. Also, during the examination, patients are asked to tense their abdominal muscles and move their lower limbs to the side. The appearance of pain indicates signs of this particular disease (in addition to other symptoms).
Drug treatment
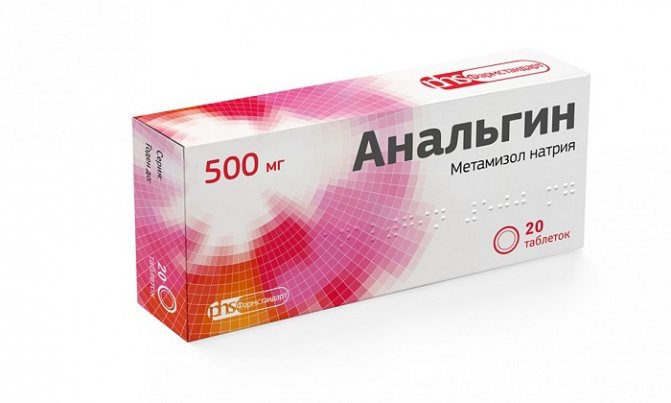
If the inguinal nerve is pinched, drug therapy is indicated, the main goal of which is to relieve pain. For this purpose the following are assigned:
- analgesics (“Analgin”, “Pentalgin”);
- anticonvulsants and muscle relaxants that relieve muscle spasms (Mydocalm, Gabapentin);
- rectal (vaginal) suppositories with analgesic properties (“Diazepam”);
- compresses with Dimexide (relieve muscle spasms).
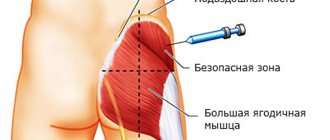
To restore nerve conduction, taking B vitamins (intramuscularly) is indicated. In severe cases, it is recommended to take steroid hormones (Dexamethasone) or install novocaine blockades, which suppress acute pain. At the initial stages of pathology development, Xefocam is used.
In the absence of effect from drug therapy, surgical intervention is recommended. Surgeries are necessarily carried out when neoplasms are detected in the pelvic area or severe fractures. In case of severe compression of nerve fibers, surgical intervention helps restore the innervation of the pelvic tissues. This procedure is dangerous for the patient, so this treatment is resorted to in extreme cases. In addition, long recovery is required after surgery.