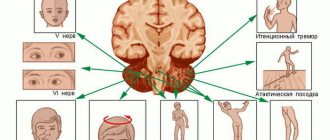
Pathological processes of the central nervous system are represented by ischemic, degenerative, inflammatory, neoplastic and other disorders.
Deviations are usually dangerous. This is due to the limited space inside the skull. And on the other hand, the incredible “gluttony” of nerve tissue. They are one of the main consumers of oxygen and nutrients for their functioning.
Fainting is an acute, short-term disturbance of cerebral circulation that leads to a sudden loss of consciousness. Unlike a stroke, an eating disorder occurs spontaneously and suddenly, lasting a matter of seconds. Therefore, no pronounced degenerative processes are observed, everything remains relatively normal. But the symptoms are clearly visible.
In general, fainting is not a disease. This is just a sign of some deviation from the norm. However, ICD-10 has a separate code for syncope - R55.
The disorder occurs as a result of acute ischemia, and what it may be associated with must be carefully clarified during diagnosis. Neurologists work with patients. The rest of the doctors are on an as-needed basis, if the clinical situation allows it.
The essence and mechanisms of development of the condition
The pathology is based on a group of factors. Possible points include:
Inflammation
Acute processes in which spontaneous degeneration of the brain substance occurs. In themselves, such diseases are very dangerous, since they involve all tissues of cerebral structures without exception. Accordingly, if nothing is done, acute dysfunction will develop.
No one can say for sure how this might end. At a minimum - neurological deficit, disorders of higher central nervous system activity.
As for fainting, it develops as a response to insufficient nutrition of brain tissue. This occurs with meningitis and encephalitis.
Acute mental overload
Stress leads to vasoconstriction of cerebral structures. Loss of consciousness in this case has nothing to do with an epileptic seizure, but it is quite difficult to distinguish between these pathological processes.
In diseases of the central nervous system, the electrical activity of the brain increases. This does not happen here, because the disorder occurs relatively easily and resolves itself without problems.
Orthostatic pressure surge
Simply put, a drop in blood pressure with a sudden change in body position in space. If you stand up quickly, the blood will flow to the lower part of the body and move away from the brain.
This will lead to darkening of the eyes, other symptoms and, ultimately, to fainting.
No recovery is required as such. Most often, the problem is encountered by patients with hypertension who take special medications.
There are other categories of sufferers (read more about orthostatic hypotension here). What to do depends on the specific clinical case.
Traumatic brain injuries
They end with a disruption of normal nutrition, or even the structure of the central nervous system. The condition itself is very dangerous. It is not known what the situation is until a diagnosis is made.
Therefore, such patients are required to be checked under the supervision of a neurologist and undergo an urgent tomography.
Diseases of vascular origin
Ischemic processes. For example, encephalopathy, stroke, transient attack.
Attention:
There can be many options, all of them are potentially dangerous and even lethal.
These are not disorders that you can calmly turn a blind eye to. The reason why a person faints is an acute violation of the trophism of cerebral structures.
Heart problems
They lead to approximately the same results. Normally, the myocardium pumps large volumes of blood. If it is not active enough, the amount of fluid tissue supplied to the brain is sharply reduced. This is the main factor in the development of transient loss of consciousness (fainting). Or even something more serious and dangerous.
The picture is very approximate. In reality, everything is much more complicated. It is worth noting that representatives of the female part of humanity are most prone to developing fainting. To be even more precise - young girls in puberty.
This is due to the characteristics of the central nervous system. It is still being formed, is not strong enough and does not tolerate loads well. Also with the characteristics of a stormy hormonal background.
Substances are constantly in motion until everything returns to normal, and the likelihood of syncope remains.
Statistics show that fainting occurs in almost half of the world's population. At least once in a lifetime. Further, everything depends on the characteristics and inclinations of the individual person’s body.
The second peak in the development of the pathological process occurs at the age of 50 years and older. The likelihood of a violation increases several times. You need to carefully monitor your health.
Fainting woman
Gentle ladies and young ladies of past centuries considered it good form to escape from all everyday difficulties and delicate situations with the help of a banal fainting spell. This passage was facilitated by tight corsets, squeezing the ribs and making breathing difficult, dietary restrictions leading to anemia, and a mobile psyche, loosened by reading French novels. Nekrasov's and Leskov's characters of peasant and bourgeois origin suffered from fainting much less frequently, and did not experience hysterical loss of consciousness at all.
Pathological causes
Syncope develops in a variety of cases. Let's try to understand the issue in more detail.
Atherosclerosis
A disorder in which blood flow is disrupted. The culprit may be either a sharp narrowing or blockage of the arteries with cholesterol plaques.
Both options are equally dangerous and require high-quality treatment under the supervision of a cardiologist or endocrinologist. Depends on the origin of the problem.
Symptoms of the pathological process relate to the functioning of the brain.
For example, the following symptoms arise:
- Headache.
- Movement coordination disorders.
- Weakness.
- Drowsiness.
- Exercise intolerance.
- Dyspnea.
- Focal neurological problems.
- Dizziness.
And this is not a complete list.
Be that as it may, syncope (fainting) develops as a result of impaired cerebral blood flow, insufficient nutrition and cellular respiration of central nervous system tissues.
This is dangerous because the pathological process, the primary condition, provokes ischemia. Possible stroke. It is necessary to undergo treatment. Which one exactly?
Drugs are prescribed to normalize the condition of blood vessels. Statins, fibrates to remove abnormal deposits. It also makes sense to take vitamins and medications to relax the arteries.
The prognosis for fainting is quite positive. As for atherosclerosis, if treated on time, the disorder will go away. But it can come back, the main thing is to correct the original deviation.
For example, hormonal imbalance or lipid metabolism disorder. All processes are interconnected and follow from one another.
Stroke
Acute disturbance of cerebral blood flow. Leads to rapid death of nerve tissue. In what volumes depends on the degree of disorder and the size of the pathological focus.
In any case, it is very dangerous. Not only does the person run the risk of death, he will certainly face neurological deficits. This can be either weakness in one half of the body or complete paralysis, dementia, irreparable loss of vision and hearing. There are a lot of options.
Symptoms of the disorder are nonspecific, including:
- Fainting: Since the brain does not receive enough nutrients and oxygen, it goes into starvation mode with loss of consciousness.
- Weakness.
- Drowsiness.
- Nausea.
- Vomit. Up to several times.
- Feeling of the skull bursting from the inside. A very strong feeling.
- Headache.
- Disorder of normal orientation in space.
- Focal signs: loss or deterioration of vision, hearing, tactility, and other higher nervous functions.
A stroke may be accompanied by paralysis, paresis, speech perception disorders, loss of the ability to speak, and other symptoms. They are all equally dangerous. Without treatment, the patient will most likely die.
Therapy takes place in a neurological hospital. Most cities have special departments for patients with acute disorders of cerebral blood flow.
It is necessary to use cerebrovascular drugs, nootropics, diuretics, and medications to correct blood pressure. The issue is resolved as quickly as possible.
At best, there are several tens of minutes of non-first aid (read more about the algorithm for providing it here). Then irreversible processes in the brain will begin.
As for the treatment itself, you need up to a month of therapy plus almost a year or even more of rehabilitation measures. The stages of rehabilitation after a stroke are described here.
Heart attack
Acute disturbance of coronary blood flow. In many ways, the condition is very similar to a stroke, but the cause of development is completely different.
Let's start with the basics: normally, the heart pumps a certain volume of blood per minute. It is difficult to give specific numbers; it all depends on the size of the person.
But this amount is quite enough to provide the muscles, the heart itself and, of course, the brain, which consumes a lot of resources.
As soon as the organ stops working normally, the myocardium contracts weaker. This means that blood volumes are falling. Accordingly, body tissues receive less than they should. Nerve cells are very voracious; they are the first to suffer.
Objectively, the cause of loss of consciousness is a violation of cerebral blood flow as a result of a decrease in myocardial contractility. It is worth noting that the same thing happens with various forms of arrhythmias and other heart pathologies. Right down to the vices.
A heart attack needs to be treated urgently; it is a very dangerous condition. A cardiologist is involved in the case.
Several types of drugs are prescribed: diuretics, cardioprotectors, drugs to lower blood pressure or, conversely, increase it. Depends on the indicators. Other medications as needed.
Mortality ranges from 10 to 70%, so you can’t relax. Fainting due to a heart attack is usually isolated. But often, after an acute condition, heart failure develops.
This is chronic weakness of the myocardium, its inability to provide tissues with sufficient nutrition. Syncope may then become recurrent and frequent.
Stress
Not really a disease, more of a feature. It occurs against a background of excessive work, nervous tension and other problems.
Younger patients are especially prone to developing the condition. From 12 to 18 years old, give or take. This is due to weakness of the central nervous system (although the nervous system of an adult woman is more stable than that of a man).
Repeated stress conditions increase the likelihood of a pathological process. Excessive stress is characterized by a short-term loss of consciousness, which is caused by a sharp drop in blood pressure and cerebral blood flow for several seconds.
As such, such a violation does not pose any danger. Although it looks quite menacing.
In any case, it would be a good idea to conduct a thorough diagnosis. Anything can be disguised as stress: from problems with blood vessels to brain tumors.
Hormonal disorders
Chronic changes in the level of specific substances. And very different: the adrenal cortex, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, pancreas, all of them can lead to syncope.
The cause of fainting is a violation of the regulation of vascular tone in an indirect way, because they narrow and less blood flows in than it could.
Recovery is carried out by endocrinology specialists. The goal is to return hormonal levels to normal.
Substitutes are appointed. If there is an excess of substances, use other special medications, depending on the case.
The forecasts are favorable. But, if the cause is not found out, the disorder may persist indefinitely.
The situation with women's problems is more complicated. Changes in the concentration of sex hormones are usually associated with dysfunction of the reproductive system.
We need to find the cause, eliminate it, and only then will the hormonal levels be restored. Additional help from a gynecologist is required.
Inflammatory processes in the brain
There are several types of disorder. A classic of the genre is meningitis. Tick-borne encephalitis is less common, although this is also possible.
As for the causes, they are mainly focal. Nearby affected areas increase the likelihood of developing a pathological process. For example, a sore throat, ears. Up to carious teeth.
With encephalitis, everything is simpler; its carriers are often ixodid ticks. Although there are other types of damage, including toxic and even allergic.
That is why it is so important to conduct a full diagnosis and find out what caused the pathological process.
Treatment is provided by neurologists and infectious disease specialists. Antibiotics, anti-inflammatory, and steroid drugs are prescribed. Also anti-viral drugs, immunomodulators and other medications as appropriate.
During the course of the infection, a person faints because tissue destruction of cerebral structures is observed. Syncope itself does not need to be treated. Correction of the underlying pathological process is required.
Anatomical features
We are talking about both a variant of the physiological norm and congenital defects. For example, insufficiently developed large vessels (hypoplasia of the left vertebral artery), disorders of brain formation.
They are quite difficult to treat. All that remains is to fight the symptoms and adhere to the rules of prevention.
For example, cerebrovascular drugs, nootropics are prescribed to optimize energy expenditure, diuretics that reduce intracranial pressure. A neurologist solves the problem. It is also possible for a specialized surgeon to participate.
Traumatic brain injuries
From a simple concussion to the formation of a hematoma, rupture of the substance of cerebral structures. All such violations are potentially dangerous.
Pathological processes are accompanied by severe disorders of consciousness, nausea, vomiting, weakness and other signs of neurological deficit. Both general and focal. Depends on the location of the damage.
A semi-fainting state with a central nervous system injury indicates increasing symptoms of ischemia; rapid loss of consciousness and even coma are possible. Until MRI results prove that the condition is relatively mild, it is preventively considered severe. Doctors act accordingly.
Diuretic drugs, nootropics, and cerebrovascular drugs are prescribed. Antiplatelet agents as agents against excessive blood clotting. Surgeries are performed as needed to restore the anatomical integrity of blood vessels and tissues of cerebral structures.
Tumors
Neoplastic formations of the central nervous system. There are a variety of types: from a banal pituitary adenoma or meningioma to malignant glioma.
All of them are potentially dangerous because the space in the cranium is limited. Read more about the types of brain tumors in this article.
Quite large formations, more than a few centimeters, lead to fainting. Although there are exceptions, you need to look at where the structure is localized.
It is important to treat tumors promptly, especially if they are large or tend to grow rapidly.
Surgical correction is prescribed. The neoplasia is removed and then, depending on its characteristics, irradiated. Chemotherapy drugs are also administered. However, many types of formations are insensitive to them.
Classification of fainting
Depending on the main conditions of occurrence, all fainting is divided into three large groups.
- Reflex ones develop against the background of pain, severe fear, emotional stress, after coughing, sneezing, urination, when swallowing, defecation, against the background of pain in the internal organs, and during physical exertion.
- Syncope associated with orthostatic loads can occur with diabetes mellitus, amyloidosis, taking antihypertensive drugs, Parkinson's disease, a decrease in circulating blood volume, and blood retention in the veins.
- Cardiogenic are associated with diseases of the heart and blood vessels.
Natural factors
There are also so-called non-pathological causes of the disorder. Here are just some possible examples:
- Physical overload. Because the brain simply doesn't have enough nutrition, blood pressure drops.
- Change of weather. Within the framework of autonomic dysfunction and VSD as such. Adaptation to new conditions. Climatic, temporal, geographical and so on. The effect of atmospheric pressure on arterial pressure is described in detail here.
- Hungry fainting is the result of insufficient blood glucose levels and poor nutrition of cerebral structures.
- Disturbances in the trophism of the central nervous system are the main factor in the development of the problem. But the sources can be very different.
Symptoms of fainting
The loss of consciousness is immediately preceded by a period of precursors:
- nausea, lightheadedness
- sour taste in mouth
- dizziness, flickering spots before the eyes, darkness in the eyes
- increased sweating
- hand trembling
- pallor of the skin and mucous membranes
- noise in ears.
Then a sudden loss of consciousness develops, during which the person may fall and hit himself.
- During the period of fainting, the muscles are relaxed and the body is motionless.
- The pupils are dilated and do not respond to light, the pulse is rare and superficial, breathing is slow, and blood pressure is reduced.
- During deep fainting, involuntary urination and muscle cramps may develop.
First aid
Sudden loss of consciousness is the result of the influence of an inflammatory, degenerative, ischemic or other factor; treatment approaches will vary. But the initial activities are almost always the same.
The procedure for providing first aid in case of fainting is as follows:
- Call an ambulance.
- Move the patient to a safe location.
- Provide an influx of oxygen and fresh air.
- Moisten your chest and forehead with cool water.
- Turn your head to the side. Vomiting is possible, this is necessary so that the person does not choke.
- Give ammonia. But not under your nose, since ammonia can damage your respiratory tract. To avoid burns, the bottle is placed 10-15 cm from the face and the volatile substance is distributed towards the patient with light waving movements.
If a person faints, breathing and cardiac activity must be constantly monitored. When required, perform a cardiac massage.
Next, you need to bring the person to the ambulance. If he came to his senses, it would still be a good idea to see the doctors. It is important to find out the cause of the disorder.
Treatment
The main goal of treatment for bettolepsy is always aimed at treating the underlying disease that caused the development of cough syncope. An action plan is drawn up individually after all necessary examinations have been carried out.
During and after an attack of coughing syncope, symptomatic therapy is carried out, aimed at alleviating the patient’s condition. It may involve the use of the following means:
- ammonia;
- oxygen therapy;
- improving bronchial patency and antitussives;
- cardiotonic drugs;
- vasoconstrictors: Ephedrine, Mezaton;
- administration of Atropine sulfate (for bradycardia).
Cough fainting often frightens the patient and those around him. Their appearance should always be a reason to consult a doctor and conduct a comprehensive examination and treatment of the underlying disease that triggered the development of bettolepsy.
Be careful about your health and don’t put off visiting a specialist! Even a fall that accompanies loss of consciousness can cause serious injuries, and in some diseases, coughing fainting causes structural damage to brain tissue and irreversible complications. Remember this and be healthy!
Calm! Only peace...
The first thing you should do if someone faints somewhere near you is to say to yourself: “Calm down! Calm down! It’s okay, it’s just an everyday matter...” In fact, most often it is better for a woman who has lost consciousness simply not to bother her. Consciousness will return when normal blood supply to the brain is restored, and you simply cannot influence this blood supply in any way (unless, of course, you don’t have a great resuscitator with a resuscitation kit on hand). To restore adequate cerebral blood flow, a horizontal position of the body is required (vascular tone is sharply reduced and if we raise the head or body, the blood will simply flow into the lower extremities and, of course, there will be no talk of any normal blood supply). Therefore, the patient must be immediately placed on her back (in mild cases, you can simply sit her with her back supported on the back of a chair or armchair). Please note that nothing is placed under the head! The head must be at least level with the body.
There is no need to try to find the pulse; due to low pressure and loss of vascular tone, the pulse wave is very weak and you may simply not feel it. In such cases, doctors determine the pulse in the neck, on the carotid artery (if you think you know where the carotid artery is located, you can try to find the pulse there).
It is necessary to ensure good access to oxygen (often this alone leads to the cessation of fainting) - unfasten the collar, if a lot of onlookers are crowded around the fallen person - make way. You can sprinkle cold water on your face or bring ammonia to your nose with a cotton swab soaked in alcohol. Do not try to pour half a bottle of ammonia on the patient or wipe his temples with it - this is an ammonia solution, and it does not restore cerebral circulation, but stimulates the respiratory center through the nerve endings in the nasopharynx - the person takes a reflexive breath and a large portion of oxygen enters the body with inhalation. You can, while continuing to hold the cotton wool with ammonia to your nose, cover your mouth with your palm for a couple of seconds - all the inhaled air will go through the nose, and the ammonia vapor will enter the nasal cavity. You can, at worst, just click on the tip of your nose - a painful stimulus can also sometimes stimulate the restoration of consciousness. The main thing, I remind you once again, is not to get lost and not to panic. And everything will be alright.
Fainting
Fainting
characterized by an asthenic state, loss of postural tone, inability to stand up and loss of consciousness. It begins with malaise, blurred vision, noise in the head or intense sweating. It can come very quickly, without any precursors. The skin becomes pale in color and the pulse is weak. Complete loss of consciousness can be prevented by taking a horizontal position. At the same time, the blood supply to the brain improves. Then the pulse normalizes, the skin acquires a healthy color, and consciousness becomes clearer.
Main syndromes of clouded consciousness
Several syndromes of clouded consciousness have been identified - amentia, stupor, delirium, oneiroid, twilight stupor.
Stun
– a pathological condition characterized by the fact that a person seems to be in a dream, has difficulty answering standard and simple questions, gives unclear answers, becomes inactive, often silent and indifferent. But he does not exhibit hallucinations, as well as affective disorders or delusional states.
Oneiric obscuration
- dream-like, delusional-fantastic cloudiness. Fantastic dreams grow in a person’s head, which can be partially combined with the surrounding environment, then the patient can react to people nearby. A person with this type of clouding of consciousness usually has a frozen expression on his face; he may be silent, inactive, and practically motionless. The gaze alternates between amazement or delight, detachment or fear.
Delirium or delirious confusion
is distinguished by many psychological abnormalities. These can be fantastic illusions, vivid hallucinations, visual memories. A person in such a state can actively move, run somewhere, rush, defend. His facial expression is constantly changing.
The doctor can identify not only visual, but also auditory hallucinations, plus olfactory or tactile ones. Patients with delirium may have “lucid” periods of consciousness. Delirious delirium is manifested by muttering and uncoordinated monotonous actions. After this kind of clouding of consciousness disappears, a person may not remember it.
Sudden loss of consciousness
– this pathology can manifest itself in almost every person. The inability to think clearly sometimes occurs as a result of a severe head injury, after a blow, when the blood supply to the brain is disrupted, after hypoxia, severe emotional shock, sharp fluctuations in blood sugar levels, or at high temperatures.
Sudden loss of consciousness is caused by drugs and alcohol, some sedatives and psychotropic medications. Sudden clouding of consciousness is manifested by disorientation, hallucinations of all kinds, spontaneous personality changes, excessive agitation, irritability or apathy, difficulty expressing thoughts clearly, memory lapses or unpredictable behavior.
Twilight haze
consciousness arises abruptly, sometimes lasts minutes or hours and also suddenly disappears. After which the patient usually falls asleep. Pathology is expressed by disorientation, but with the preservation of familiar actions, so it may go unnoticed by outsiders. Often, a disorder of this kind is acute, accompanied by motor and speech agitation, fears, rage, and hallucinations.
A person can be aggressive and even pose a danger to others. After the twilight haze, he does not remember anything, as if he was awakened from sleep. This condition often accompanies traumatic psychoses and epilepsy, while delirium and other forms of confusion occur against the background of infectious diseases and intoxication, schizophrenia and vascular psychoses.
This is a side effect of your medications
Some medications, such as painkillers and some anti-anxiety medications, can cause dizziness, Dr. Burrow-Peña says, possibly due to a direct effect on the brain or by slowing the heartbeat, which can lead to these symptoms. "Patients sometimes complain of unexplained dizziness," says Dr. Phillips, "and it turns out that this is one of the rare side effects of their medications."
There is also a small chance that you are allergic to the medicine you are taking. In rare cases, patients experience an anaphylactic reaction to the drug and, as a result, dizziness and even fainting. “In this case, the reaction is caused by the immune system causing the blood vessels to constrict.”