Vascular genesis of the brain
Vascular genesis of the brain is a pathological condition that includes a whole complex of diseases associated with impaired blood supply to the brain.
Pathological changes in the vessels are accompanied by neurosis-like symptoms, but at the initial stage the clinical picture may be limited to only a headache. If the pathology is not detected in a timely manner, obstructed blood circulation in the cerebral arteries can provoke the development of severe complications.
Therefore, at the first signs of a vascular disorder, patients should consult a specialist to further determine the cause of the disease.
The first signs of vascular insufficiency
As a rule, the initial symptoms of vascular insufficiency of the brain appear after prolonged emotional and physical stress or prolonged exposure to a poorly ventilated room.
As the initial stage progresses, moments of increased excitability of the nervous system are observed
The first symptoms in patients are:
- dizziness;
- headache;
- heaviness and noise in the head;
- sleep disorder;
- increased fatigue.
At this stage, there are no significant neurological symptoms. The appearance of the first signs of cerebrovascular disease serves as the basis for a comprehensive diagnosis in order to exclude atherosclerosis, neurosis and dystonia.
Mental disorders
Mental disorders may have a vascular origin as a result of pathological changes in the circulatory system of the brain.
Therapeutic measures to eliminate mental symptoms will not bring the desired effect, since these disorders are a concomitant pathology.
Vascular diseases are manifested by increasing weakness as a result of insufficient supply of nutrients and oxygen to brain tissues
Pseudoneurasthenic syndrome is characterized by the following manifestations:
- Sleep disorder. Deterioration of venous outflow causes frequent headaches, as well as dizziness with a sudden change of position. At the same time, the process of falling asleep becomes difficult, and sleep is short. On average it is 4 hours. Chronic fatigue leads to a sharp deterioration in general condition.
- Increased sensitivity to irritating factors. Intolerance to loud sounds and bright light appears due to insufficient oxygen supply to the brain tissues.
- Frontal lobe eating disorder is manifested by functional changes in the processes of thinking, memory and planning. The patient lacks focus and consistency in activities.
Subsequently, the progression of pathologies of vascular origin leads to a change in a person’s personal qualities, and the most pronounced character traits appear. The asthenic syndrome, which is characterized by suspiciousness, increased anxiety, and uncertainty, is intensifying. As a rule, changes in personal qualities are associated with the localization of vascular changes in the brain.
Treatment of pathologies of vascular origin, in contrast to true mental disorders, responds well to conservative therapy.
Determining the nature of the headache
The nature of the headache depends on the nature of the circulatory disorder in the brain. Thus, a circulatory disorder in the arteries causes focal changes, and in the veins – general changes.
Detection of local violations, in contrast to general ones, is much easier
The type of vascular spasm influences the nature of the pain syndrome. An increase in cerebral vascular tone leads to an increase in pulse blood volume. This is the main cause of pulsating headaches, accompanied by specific tinnitus. As the pulsation amplitude decreases, the headache becomes dull and bursting.
Headache due to venous disorder develops against the background of excessive blood filling of the veins, which complicates its outflow. Patients experience a feeling of heaviness in the head, which can spread to the entire skull. A characteristic sign of this deficiency is increased pain in a horizontal position or during coughing, mainly in the morning.
Principles of treatment
In case of severe functional disorders of the brain, the patient is hospitalized until the neurological symptoms are eliminated. Therapeutic measures consist of eliminating increased intracranial pressure, manifestations of atherosclerosis and stroke.
Taking medications ensures restoration of normal blood flow
In the case of mechanical blockage of the lumen of blood vessels with fatty plaques, surgical treatment is indicated, aimed at removing the section of the obstructed vessel. The postoperative period includes low-lipid diet therapy, as well as therapeutic exercises.
Drug treatment consists of taking the following groups of drugs:
- Anticoagulants. Designed to thin the blood and prevent the formation of blood clots (Clexan, Curantil).
- Calcium channel blockers. Eliminate arterial spasm, restore microcirculation (Veropamil, Foridom).
- Antispasmodics. They eliminate vascular spasm, normalize blood flow, and reduce blood pressure (No-spa, Drotaverine hydrochloride).
- Nootropic drugs. They promote intercellular metabolism, the formation of a new vascular network, and also eliminate the manifestations of brain hypoxia (Cerobrolysin, Piracetam, Mexidol).
Diseases of vascular origin require constant monitoring and timely treatment, since they are characterized by rapid progression.
In most cases, impaired brain nutrition entails many negative consequences that require constant maintenance therapy.
To prevent repeated violations, it is necessary to eliminate bad habits, increase the body’s resistance to stress, and stop eating high-calorie foods.
Source: https://icvtormet.ru/prochee/sosudistyy-genez-golovnogo-mozga
Symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of organic personality disorder
Organic personality disorder is a pathology that doctors of all specialties encounter, but only a psychiatrist can provide full qualified assistance.
The relevance of diagnosis and treatment lies not only in increasing the number of elderly people, who more often develop this disease due to vascular disorders, but also in able-bodied citizens as a result of toxic factors, epilepsy and hormonal imbalances.
What kind of diagnosis is this
Understanding what kind of diagnosis this is is necessary in order to find the right approaches to treatment, rehabilitation and resolve expert issues related to work ability.
Common people may be confused between the definition of “organic personality disorder” and “organic asthenic disorder” or any other disease caused by a problem in the brain under the heading F06.
The key difference is the change in personality and behavior characteristic of the first and the lack of transformation of a person’s individuality for the second.
Etiology
The causes of mental disorder, that is, the etiology, are as follows:
- epilepsy and other pathologies affecting the brain (trauma, tumors);
- toxins;
- hormonal diseases;
- severe somatic diseases;
- vascular disorders.
Often, especially with age, factors can overlap one another.
Brain disorders (epilepsy and others)
The appearance of personality changes in connection with epilepsy is individual and primarily depends on the frequency of attacks. The more often seizures occur, the more damage occurs to the cerebral cortex. Accordingly, the more pronounced transformations will occur to a person. Tumor or traumatic brain injury, especially in the frontal lobe, also leads to organic disorder.
Exposure to toxins
Toxic effects on the brain include not only working with harmful substances, but also consuming alcohol or its surrogates, leading to liver cirrhosis and hepatic encephalopathy.
Drug abuse will leave an indelible mark on a person's personality.
Hormone exposure and endocrine disruption
Dishormonal pathologies leading to organic personality changes:
- diabetes mellitus (decompensation leading to encephalopathy);
- thyrotoxicosis;
- pathologies of the adrenal glands;
- diseases of the hypothalamic-pituitary system.
As a result of deteriorating hormonal levels, brain structures, including gray matter, suffer, which further leads to personality changes.
Somatic diseases
Common diseases that decompensate for worsening brain function at the level of cellular damage include:
- liver cirrhosis (hepatic encephalopathy);
- malignant tumors at the last stage;
- chronic renal failure in the terminal stage.
The development of brain pathology is similar to that which occurs under the influence of toxic substances coming from the outside.
Vascular origin
Organic personality disorder of vascular origin occurs when the cortex is damaged due to insufficient nutrition.
The reasons may be:
- cerebral infarctions (ischemic, hemorrhagic);
- discirculatory encephalopathy of the third degree.
Mixed genesis
Organic personality disorder of mixed origin occurs when any of the above-described diseases or brain injuries are combined. An example would be dyscirculatory encephalopathy in an epileptic or traumatic brain injury in a drug addict.
Behavioral symptoms, ICD codes
ICD-10 code for organic personality disorder F07.0. It is used for coding medical records.
Changes in the pattern of emotions and behavior, symptoms of thought disorder, and sexual dysfunction are key to identifying a personality disorder.
These symptoms last for at least six months and include at least three manifestations from the list:
1. A person is unable to carry out his usual daily work, achieve his goal, especially if he needs to do something for a long time.
2. Emotional transformations:
- lability, that is, instability of emotions, mood swings, loss of control;
- euphoric state, flat humor, inappropriate jokes;
- increased irritability, angry outbursts, aggressive behavior;
- lack of desire to do anything (apathy).
3. Neglect of social rules in pursuit of fulfilling one's needs, leading to antisocial behavior (theft, demonstration of sexual desires in public, gluttony, lack of personal hygiene).
4. Mental pathological symptoms:
- super-dimensional suspicion;
- fixation on one topic (religion, politics, medicine);
- categoricalness in judgment, criticizing any other point of view as absolutely wrong.
5. Changes in speech (its tempo, the appearance of intrusiveness, thoroughness, viscosity, increased detail).
6. Changes in the sexual sphere (change of sexual preference, disinhibition, lack of a sense of distance).
Emotionally labile disorder (asthenic)
Emotionally labile disorder in ICD-10 belongs to category F06 (F06.6) and is characterized by the absence of personal transformations. The main symptoms are:
- emotional instability (mood swings, tearfulness, weakness);
- weakness, fatigue, apathy;
- dizziness, headache, ringing or noise in the head.
All this occurs against the background of a disease directly or indirectly affecting the brain (dyscirculatory encephalopathy, hypertension, hormonal disorders, tumors, head injury). Symptoms subside when the causative disease is compensated.
With mild cognitive impairment
Organic disorder with mild cognitive impairment (F06.7) is manifested by:
- memory loss;
- reduced ability to learn new skills;
- problems with logical sequential thinking;
- difficulty speaking when choosing words or counting;
- poor concentration;
- severe fatigue when performing mental work.
Pathological symptoms must last for at least two weeks against the background of a disease leading to brain dysfunction.
Anxiety disorder
Organic anxiety disorder (F06.4) occurs as a result of brain damage and is characterized by increased anxiety as a leading symptom.
Dissociative disorder
Features of organic dissociative disorder (F06.5) are:
- loss of memory for recent events;
- disturbance of movements in the limbs;
- loss of sensitivity or, conversely, severe discomfort in the body.
Affective disorder
Organic mood disorders are associated (F06.3) with brain pathology without transformation of a person’s personality and are characterized by depressive symptoms, as well as, conversely, increased background or phase changes from a decrease in the emotional curve to euphoria.
Delusional schizophrenia-like disorder
Organic delusional disorder (F06.2) is characterized primarily by the presence of delusions, which may be constantly present or occur with varying frequency. Hallucinations are possible. To recognize and distinguish it from schizophrenia, it is necessary to examine a person to identify organic brain damage.
Catotonic state
Organic catatonic disorder (F06.1) is detected when:
- stupor, that is, freezing in one position without movement, speech, reactions to external influences;
- negativism, that is, resistance to changing body position;
- instead of stupor, agitation with chaotic movements is possible;
- the change of the above states is rapid.
Organic hallucinosis
The basis of the pathology coded F06.0 is the presence of hallucinations (visual, auditory) with unchanged consciousness. The person’s criticism is preserved, that is, he understands that the visions are not real, they scare him.
Treatment
Treatment of an organic disorder consists of the following elements:
1. Symptomatic therapy:
- mood stabilizers for emotional lability (carbamazepine, topiromate);
- anxiolytics for anxiety and irritability (benzodiazepines for no more than 1 month);
- antipsychotics for behavior correction and sedation;
- antidepressants for apathy and reduced emotional background (maprotiline, fluoxetine, sertraline, paroxetine, escitalopram).
2. Etiotropic therapy for an established cause of the disorder (vascular, nootropic, antiepileptic, hormonal and other drugs);
3.
Psychotherapy and psychocorrection.
Prognosis for elderly patients
In old age, the prognosis is unfavorable.
Cognitive decline occurs, leading to dementia. In the elderly, the manifestation of emotions and behavior, like in a child, occurs not only with whims, but also with failure to comply with requests and hygiene procedures. Contact and the possibility of leaving are difficult. This often leads to relatives sending such patients to nursing homes.
How to remove the diagnosis
In order to remove the diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo an examination by a medical advisory commission, and if you disagree with the doctors, contact a forensic psychiatric expert commission for an examination.
Is there any disability for this disease?
Whether a diagnosis of “organic personality disorder” gives a disability depends on maintaining the ability to care for oneself, navigate, communicate and control one’s behavior. The group is assigned according to the degree of impairment of these functions.
Non-organic personality disorders
This group of diseases reflects the pathological character of a person, his emotions and relationships with other people. The disorders are not associated with brain damage.
Conclusion
Personality disorders lead to changes in the quality of life of both the patient himself and his environment. To know how to help a person, you need to show him to a psychiatric specialist. Doctors will not only prescribe treatment in order to regulate behavior, but will also determine disability if the patient loses the ability to work and care for himself. Source
If you liked the article, please like and subscribe to the channel so as not to miss new material!
The information posted on the Zen channel is for informational purposes only. Be sure to consult a specialist.
Source: https://zen.yandex.ru/media/id/5c565b5022d89d00adadb245/5dfa43d9f73d9d00ae130d03
What is vascular genesis of the brain
Unfortunately, there are quite a lot of diseases caused by impaired blood circulation in the brain and they manifest themselves in extremely varied ways. The mildest of them are expressed only by headache and some neurosis-like disorders, and it happens that the disease is limited to only these symptoms. But in severe cases, treatment is necessary and very long-term.
Here it should be clarified: vascular genesis is an indication of the origin of the disease, and not the disease itself. When talking about brain diseases of vascular origin, we mean changes associated with circulatory disorders - in venules, arteries, veins, and so on.
These types of violations are divided into several main groups.
- Transient cerebral circulatory disorders - distinguish between general cerebral and focal. The first are characterized by headache, nausea, vomiting; focal ones are responsible for short-term disturbances in motor functions and sensitivity of certain parts of the body. The hallmark of this vascular disorder is reversibility . Treatment promises complete restoration of function.
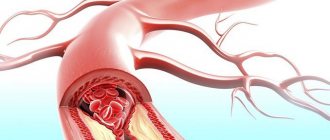
- Blockage of the arteries - narrowing of the working channel in any case leads to a deterioration in nutrition, which significantly affects the functionality of the served areas of the brain, and can cause changes of an ischemic nature. Here treatment may even include surgery.
- Rupture of a cerebral aneurysm, cerebral hemorrhage - in fact, a stroke of ischemic or hemorrhagic origin.
Symptoms of diseases
The most common signs of vascular disorders include the following:
- increased blood pressure, both constant and episodic, above 140 mm Hg. Art., in cases where it is not due to any other reasons;
- arrhythmia - changes in pulse are observed at rest, and very noticeable - from 60 to 90 beats per minute;
- dizziness, headaches - the nature of the latter depends on the nature of the disorder. Focal ones are more often associated with changes in arterial blood flow, general ones – with venous blood flow, but not necessarily;
- weakness in the arms and legs, which at first glance is unfounded;
- increased fatigue, impaired attention, impaired cognitive functions.
The symptoms are quite vague, of course, but in any case they do not indicate the vascular origin of the brain disease. The root causes can be very different.
Pseudoneurosthenic syndrome
Another characteristic sign of changes in blood circulation in the brain are mental disorders of vascular origin. Their symptoms coincide with the classical picture, but changes occur as a result of circulatory disorders.
Accordingly, treating only the mental component will not lead to the desired result: in this case, the disorder is a secondary disease.
- Very often, sleep disturbances occur against the background of a headache and a feeling of heaviness in the back of the head. As a rule, sleep is shallow, short - 3-4 hours, accompanied by natural weakness and a state of “being overwhelmed.” If the cause is poor venous blood flow, then physical activity brings your health back to normal much faster.
- Sensitivity to stimuli - sound, light, sometimes even dim light.
- Tearfulness, irritability, unstable attention. Moreover, the patient is clearly aware of the painfulness of the condition.
- It is difficult to remember new events and record them; chronological orientation is often disrupted: it is difficult to remember the date, day, or date the event.
- The search for small objects - glasses, keys, notepads - is associated with a refusal to perceive certain objects in the field of vision.
- With the further development of diseases of vascular origin, personality changes are possible - a kind of sharpening of the most striking character traits. At the same time, asthenic structures intensify - self-doubt, anxiety, suspiciousness. Gloomy dissatisfaction with others becomes almost constant. Personality changes are noticeably influenced by the nature of the vascular process: arterial hypertension, the location of focal lesions in the brain, and so on.
Unlike true mental disorders, treatment of vascular diseases is carried out mainly by medicinal methods and is quite successful.
We are trying to understand the results of MRI of the brain
We are trying to understand the results of MRI of the brain
- Doc
- 11-09-2015
- VSDshnik's Directory
About how many wonderful discoveries... MRI is preparing for us. Conclusion: lesions in the white matter.
What kind of bullshit is this and what does it threaten?
So, to begin with, let me remind you that I was prompted to do an MRI of the brain by bad symptoms that did not stop for three months.
I'll try to describe the symptoms:
Systemic, almost never-ending mild dizziness, almost imperceptible, but very unpleasant. Constant “fogginess” of perception of the surroundings, “stuckness” and lethargy in the head - I can’t describe it better. Sometimes “skidded” on turns, could “not fit” into the door frame , touch the corner of the table, etc.
Not often, but, as they say, I noticed. My ability to work has deteriorated quite noticeably - let me remind you that my main tool is a computer. It has become hard to work, that’s not the right word... Chronic fatigue - by the end of the day you can’t do anything at all, just drive away bad thoughts about your worthless health.
Problems with sleep – I began to wake up periodically early and could no longer fall asleep. In my case, early is 5 am, I usually slept until 6.30 – 7 am. I go to bed quite early, at 23:00, and someone will say that this is quite enough, but I know how much I need... I have become very sensitive to “lack of sleep”.
By the way, chronic early awakening is one of the main complaints to this day, but it has only gotten worse. But this will be a separate story... Periodic, but not frequent and not severe headaches.
Quite long-lasting (2-5 hours), mainly in the hemispheres and frontal region, there were no occipital pains.
With this “set” I decided to go for an MRI of the brain. Why go straight to an MRI without any referrals from a neurologist? Most likely, the fact that just before I developed these symptoms played a role was the fact that my ex-wife died of cancer. The story is a little different and quite long, I won’t tell it all, I’ll just say what concerns the topic of MRI.
So, as far as I know, her complaints were very similar to mine: no “wild” headaches, dizziness, unsteady gait, etc. As a result, based on the results of an MRI of the brain, she was diagnosed with a tumor (or metastasis to the brain, I can’t say for sure). So I decided that before seeing a neurologist, I had to “dot the I’s,” which is what I did.
It was scary - beyond words!
Now the results. The MRI conclusion (2007) states: MRI picture of a single lesion in the white matter of the brain - probably of vascular origin. Signs of moderate external hydrocephalus. For the general picture, here is a scan of the full text of the research result:
The doctor who wrote the conclusion did not find anything “military” in the study, did not see any tumors or neoplasms. Regarding the “Single lesion in the white matter,” he didn’t turn a blind eye, he said that most likely it was the result of a hypertensive crisis or even congenital, it couldn’t pose any particular threat and could hardly be the cause of my dizziness.
Later, while looking at the MRI results saved on DVD at home, I found this “black hole” in my head:
At the appointment with the neurologist, it was generally not possible to clarify the picture. I did not receive any specific comments about the single lesion, or about hydrocephalus, or even about the “black hole”. Everything is in general terms, like “nothing fatal.” General recommendations, etc. and so on.
Moreover, I visited two neurologists. They prescribed Cerebrolysin, vitamins and sedatives. They told me to periodically monitor him and do an MRI about once every two years to monitor his dynamics. They seem to have calmed down, but on the other hand, there are no concrete measures.
Doctors, of course, know better, but it’s alarming.
There were no changes, much less improvements in my condition. I took the prescribed courses - in vain. Over the years, I performed 4 more MRI studies of the brain. The picture remained almost unchanged. Here are excerpts from the MRI report (2012):
The wording “single” was somewhat annoying, i.e. in plural. The next visit to the neurologist calmed me down a little - I saw practically no reaction to the wording of the conclusion.
Here is the latest study, I present its results in full, because... I noticed (in my opinion) very bad dynamics. MRI GM 2013:
I highlighted with a yellow marker the point that made me worry. On the first MRIs, single lesions were 0.3 cm, but here the figure was already 0.4 cm.
Of course, I understand that I am getting older and my health is not getting better, but the picture was still depressing. Another appointment with a neurologist - again nothing.
The doctor explained the increase in lesions “most likely due to an error or different resolution capabilities of the devices.” Well, what to do is to believe... Moreover, it is more profitable than thinking about the bad.
Plus, a lipoma of the interhemispheric fissure appeared. Just some kind of kick-ass...
The last visit to the neurologist ended with another course of Cerebrolysin (now intravenously) and Mexidol intramuscularly. Plus 20 days of taking Tagista. Plus, the conversation again turned to antidepressants. But more on that later...
On my last visit, I asked the doctor a question about multiple sclerosis. The neurologist categorically denied the diagnosis of MS, but I will still tell you why I once again had an MRI and why I again saw a neurologist.
I think that many VSD sufferers have gone through similar torment and doubts, so in the next post we’ll talk a little about the symptoms of multiple sclerosis.
Source: https://xn--80acgb4aire.xn--p1ai/lib/25-head-mrt.html